Whats Behind Your Knee A Brief Anatomy Lesson
The back of the knee is a complicated area. There are several critical structures back there. From a functional perspective, we have many muscles, such as the hamstring and calf muscles. The hamstrings start at the pelvis, cross the back of the knee, and attach to your tibia or shin bone. The calf muscles start on the back of your thigh bone or femur, cross the knee and form the achilles tendon, which attaches to your heel.
Behind our knee, we have critical structures such as the popliteal artery and the nerves to the leg. The nerves are the peroneal nerve and the tibial nerve. The peroneal nerve is a troublemaker sometimes. It doesnt cause pain in the back of your knee but can cause pain elsewhere. We discuss the peroneal nerve elsewhere on this page.
Most people think their knee joint is in the front. But the back of our knee goes further back than we think. The attachment of both the medial and lateral meniscus is in the back of the knee. These meniscus attachment points are called roots. Root tears can be a cause of severe knee pain which may start in the back of your knee. We cover root tears of the meniscus in this post.
There is cartilage on the bones in the back of the knee. Osteoarthritis can start back there, so the first sign of osteoarthritis could be pain in the back of your knee.
Below we are going to cover some of the more common causes of pain behind your knee.
Knee Pain Caused By Larger Muscle Groups
As we travel further down the kinetic chain, we now have to address some of the larger anatomical systems in place. That is, the muscle groups that are directly linked to the knee itself in this case, the calves and hamstrings.
Your calf muscles make up the back portion of your lower leg, while the hamstrings are the large muscles in the back of your thighs. Because both of these muscle groups sort of sandwich your knee joint, theres a high likelihood that injury or deficiencies within these tissues can lead to subsequent pain behind your knee.
Lets dig into some of the most common diagnoses!
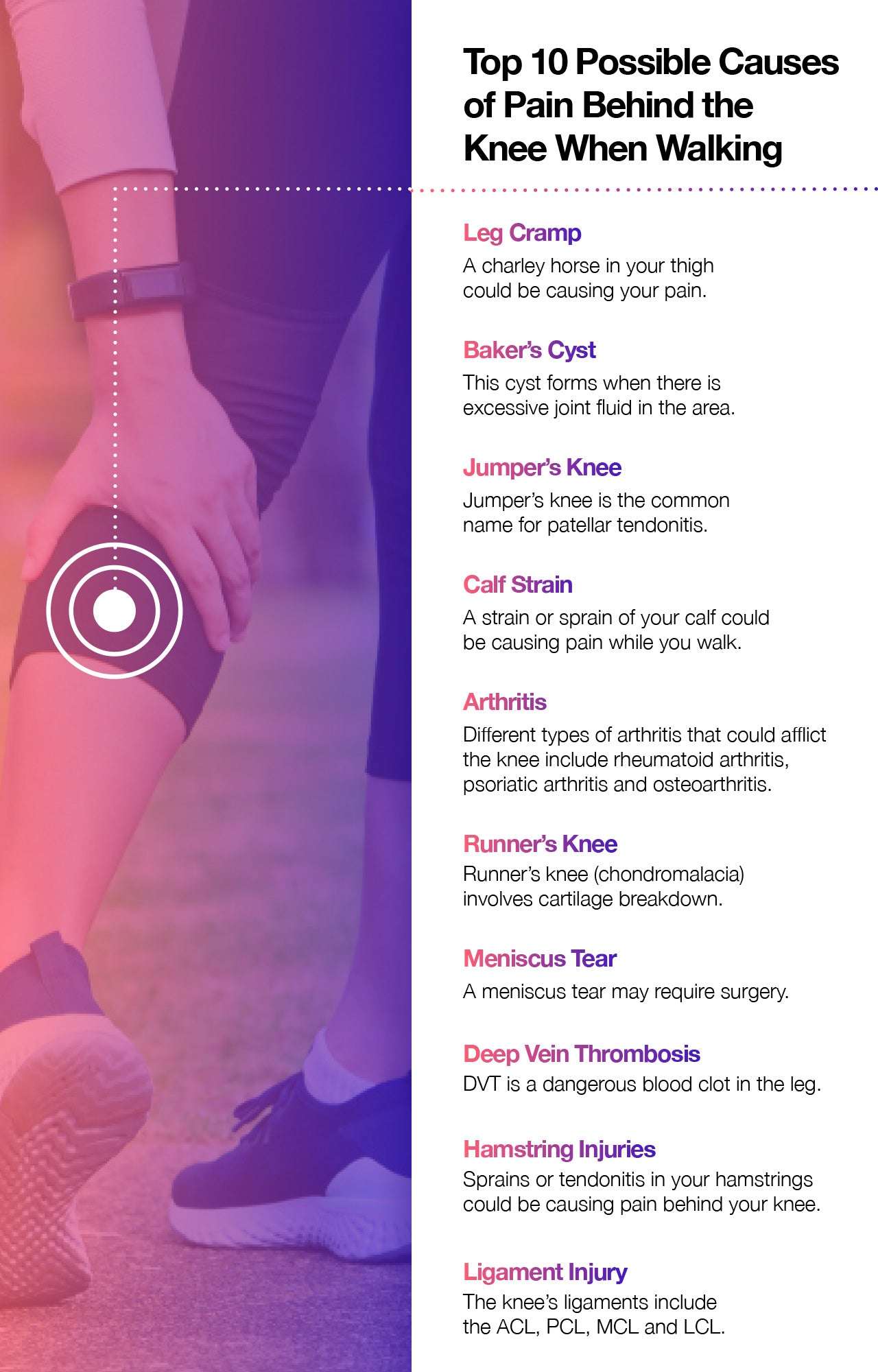
Pain Behind The Knee In Runners
Overuse syndromes are prevalent in runners. Most runners are going to experience an overuse injury during their running careers. The most common cause of pain behind the knee in runners is due to a hamstring strain. Hamstring strains that occur around the knee tend not to be as painful or as chronic as those that occur up higher in the buttock region.
Runners should consider shortening their stride and increasing their cadence, as well as avoiding hills for a few weeks. In most cases, this approach should enable a painful hamstring to settle down.
A less common cause of pain in the back of the knee in a runner is bursitis that occurs where a few tendons cross over and therefore rub against each other. The pain is usually associated with a grinding or snapping sensation as you squat down. The grinding sensation is due to the hamstring tendons being irritated from rubbing against each other.
Some believe the location of this friction might be due to one of your calf muscles rubbing along one of the hamstring muscles in the back of the knee. This has also occurred in some patients after a hamstring ACL reconstruction. Surgical treatment is rarely necessary for this situation.
In runners, the pain in the back of the knee will usually subside with a change in their running style and workout schedule. Physical therapy may be useful, as well.
Read Also: Inversion Table Knees
Can Knee Pain Come Back After Treatment
Frequently, knee pain will occur for a short period of time and then resolve. Sometimes it can return a few weeks or months later. For chronic knee pain, it is important to get it evaluated to avoid further damage to cartilage, bones, or ligaments. Prognosis depends on the underlying causes of the pain.
With modern surgical techniques, its possible to relieve many of the knee pain syndromes and return to an active lifestyle.
Recommended Reading: Roller Knee Walker
What Can I Do At Home
There are a bunch of things you can do at home, including:
- Modifying your activities. Temporarily changing certain movements that hurt your knee will help it heal.
- Practicing low-impact activities that arent painful. Examples would be walking, swimming, or biking.
- Wearing a knee sleeve. It provides compression and warmth that can help reduce the pain. Although, the type of knee sleeve you need will depend on whats causing your knee pain.
- Using anti-inflammatories or icing only if necessary. They help make the pain more manageable but they might also impair tissue healing.
If your pain and/or swelling worsens over time, or if it limits you in your daily activities, please go to your doctor or physical therapist.
Recommended Reading: Inversion Table Benefits For Knees
A Popping Sensation Behind The Knee Or Pain And Stiffness At The Side Of The Knee
May be the result of a torn meniscus, particularly the posterior horn of the meniscus. This can often occur due to an impact or twisting sports injury, and is more likely as one gets older and the meniscus becomes worn. Pain might not be evident until some time after the injury occurred. RICE may temporarily alleviate the symptoms, but the tear will often require a surgical procedure.
Causes And Symptoms Of Knee Instability
When you feel your knee is giving out, meaning that the knee suddenly feels unstable, it is usually due to a ligament injury. A ligament is a short, tough band of tissue that connects two bones. In the knee, there are four major ligaments and several minor ones.
If your knee suddenly gives out, it is often the result of a tear in one of three of these major ligaments. This article explores what it feels like to have your knee give out, which ligaments are commonly involved, and some of the treatments used to correct the injury.
Also Check: Dcf Compression Knee Sleeve
Don’t Miss: Knees Crack When Doing Squats
Brief Anatomy Of The Knee
The knee is a vulnerable joint that bears a great deal of stress from everyday activities, such as lifting and kneeling, and from high-impact activities, such as jogging and aerobics.
The knee is formed by the following parts:
-
Tibia. This is the shin bone or larger bone of the lower leg.
-
Femur. This is the thighbone or upper leg bone.
-
Patella. This is the kneecap.
Each bone end is covered with a layer of cartilage that absorbs shock and protects the knee. Basically, the knee is 2 long leg bones held together by muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
There are 2 groups of muscles involved in the knee, including the quadriceps muscles , which straighten the legs, and the hamstring muscles , which bend the leg at the knee.
Tendons are tough cords of tissue that connect muscles to bones. Ligaments are elastic bands of tissue that connect bone to bone. Some ligaments on the knee provide stability and protection of the joints, while other ligaments limit forward and backward movement of the tibia .
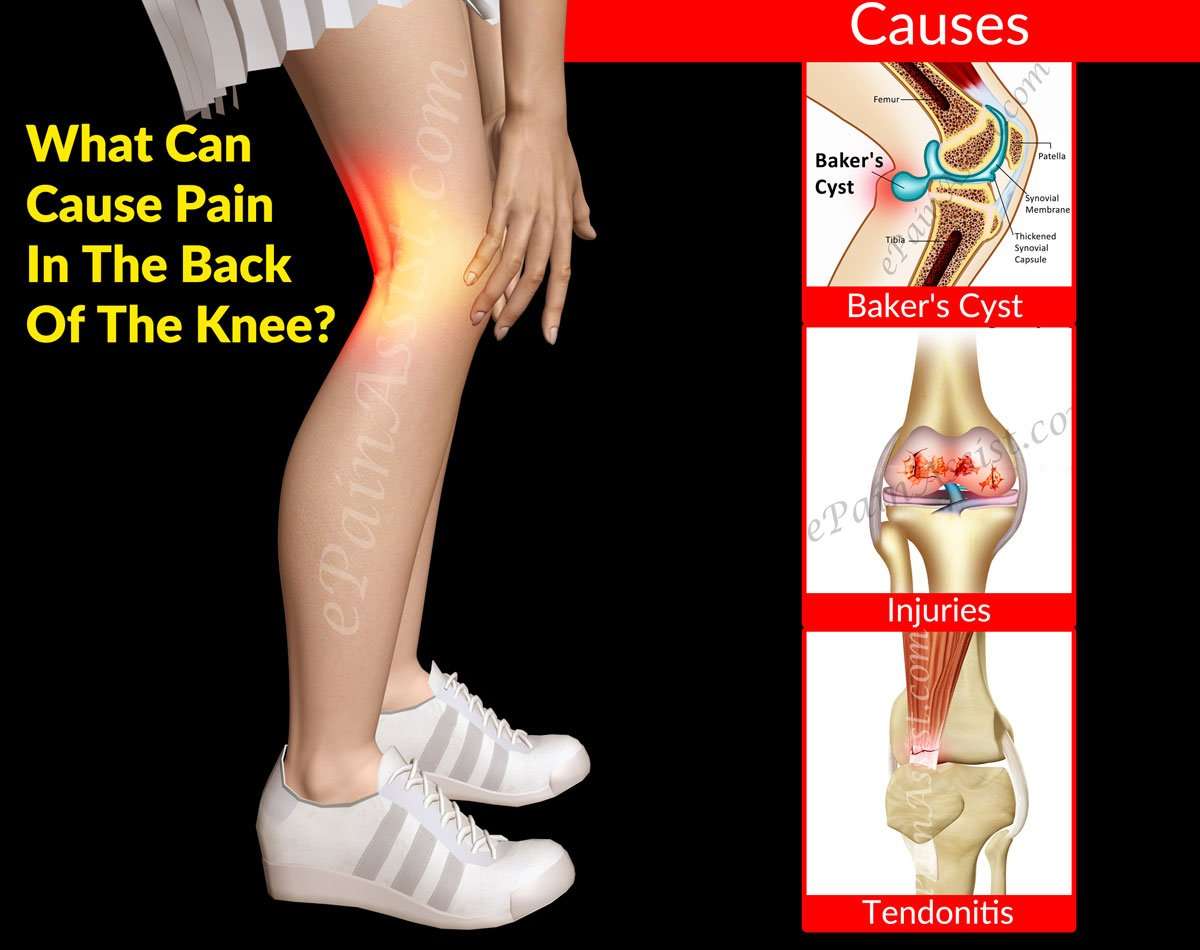
Types Of Pain Behind The Knee
There are a number of health conditions that may result in pain behind your knee. Two common conditions that cause it are a:
- posterior cruciate ligament injury
- popliteal cyst, also called Bakers cyst
A posterior cruciate ligament injury can happen if you overstretch or tear this ligament, which runs across your knee from your thigh to your shin bone. It often results from a heavy blow to the front of your knee while its bent. This can happen if you hit your knee on the dashboard during a car accident, or over-straighten your leg and bend your knee backwards. Doctors call this hyperextension.
A cyst is a collection of fluid or material inside a thin layer of tissue. A popliteal cyst is a cyst in the shallow pit at the back of your knee. Its often linked to other conditions that affect the knee, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or cartilage injuries. If you injure your knee, it can cause a collection of fluid to develop within your knee. Sometimes you can feel this in the depression at the back of your knee.
Osteoarthritis of the knee is another common cause of knee pain. The smooth, shiny cartilage that lines your knee joint becomes worn and rough. This causes pain and damages your knee over time. It mostly affects people over 50. The older you are, the more likely you are to get it.
Read Also: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Outpatient Surgery
Diagnosis Of Pain Behind The Knee
Your doctor will examine your knee and take a history, asking about:
- the type of pain you have, when it started and whether it comes and goes
- how active you are
- any activity, accident or injury that could have caused it
If you have signs of a popliteal cyst, your doctor may suggest an ultrasound scan. If they suspect a posterior cruciate ligament injury, they may suggest an X-ray or a magnetic resonance imaging scan.
Recommended Reading: How To Whiten Knees And Elbows
Anatomy Of The Posterior Knee
Okay, before we get ahead of ourselves, lets first review the anatomy for the back of the knee.
Lets start by looking at the large muscle anatomy of the posterior knee. In the image above, you can visualize the two heads of the calf muscle and the multiple muscles that make up the hamstrings.
Another feature of the posterior knee is the gap behind the knee, where theres a distinct lack of soft tissue this is known as the popliteal fossa. In the deeper muscle layer of the posterior knee, youll find the popliteus and plantaris muscles.
Deeper still, youll find the posterior capsule of the knee joint and some important nerves that run along the back of the knee.
Alright! With that brief overview of the anatomy of the back of the knee, we can explore some of the most common diagnoses for posterior knee pain.
Also Check: Does Aflac Cover Hysterectomy
More About Piriformis Syndrome Injections
Generally, a piriformis syndrome injection reduces pain from the piriformis muscle. Injecting the piriformis muscle helps to reduce pain and help with rehab. Usually, we inject a combination of local anesthetic and low-dose cortisone. Also, injections for piriformis syndrome should be done under ultrasound guidance to make them more accurate and effective.
Piriformis syndrome injections are done after the consultation and only take 15-20 minutes.
How Do You Relieve Pain In The Back Of Your Knee
- Apply ice packs for 20 minutes three to four times a day
- Elevate your affected leg using pillows to the same height or slightly higher than the level of your knee
- Rest your leg and try to keep any weight off it you can use crutches or canes to help keep weight off your affected knee
- Take over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs eg for aspirin, ibuprofen or naproxen
- Wear elastic compression bandages make sure they are not on too tight as this can further damage your knee and leg
Read Also: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Knee Surgery
But Dont All Meniscal Tears Need Surgery
Actually no. If we perform MRI scans in people with no knee pain, a significant number will have a meniscal tear. And a surgeon would not recommend surgery in these cases. So, the presence of a tear on the scan should not be the reason to have surgery.
In general, evidence would support physiotherapy. In a recent study, people with a partial meniscal tear either had surgery or physiotherapy. At 3 months and 2 years, there was no difference between groups either in knee pain or function. Also, there is some evidence that having keyhole surgery increases your chance of having a knee replacement by 30%.
Moreover, a recent review collecting all high-level evidence for meniscal surgery suggests that key-hole surgery provides a small benefit compared to physiotherapy. However, the benefit only occurs in those people with no underlying arthritis. Generally, you should avoid surgery if you have co-existing knee arthritis. Removing part of the meniscus in knee arthritis may accelerate the wear and tear and lead to earlier knee replacement.
So best to stay away from keyhole surgery if you can.
However, there are some cases that need surgery. Some of these cases include:
- Persistent pain that does not settle within 24 weeks of exercise therapy
- Gross swelling of the knee limiting the range of motion
- Mechanical symptoms such as the feeling of instability, giving way or locking
Your Knee Feels Unstable Or You Felt A Pop
Most ACL tears and patella dislocations occur from a twisting, non-contact injury. A typical story is that you were turning or twisting hard, and you felt a pop. As I mentioned earlier, most patella dislocations will reduce or go back into their usual place on their own. But if your patella remains dislocated the knee will look strange.
If you felt or heard a loud pop as you twisted or turned to avoid another player, then you may have torn your ACL. Other causes of popping include a patella or kneecap dislocation. If you felt or heard a loud pop in your knee, then there is a strong chance that you have a severe knee injury. Most ACL injuries and patella dislocations are non-contact injuries. A running back turning to head upfield. A striker moving laterally to avoid the defense. These are familiar stories when we see high school and college athletes who have torn their ACL.
This post dives further into the immediate management of suspected ACL injuries.
Don’t Miss: Bleach Dark Knees
Torn Anterior Cruciate Ligament
You hear a pop and can’t move after you suddenly change direction — often while playing soccer, football, or basketball. You may have torn your ACL, which connects the femur and the tibia and prevents the tibia from moving too far forward. Your knee will hurt and swell and feel unstable.
You can tear or strain any of the tissues that hold your knee together: Ligaments connect bones to each other tendons connect muscle to bone. Irritated tendons from using them too much? That’s tendinitis.
Why Would A Teenager Have Knee Pain
Knee pain isnt a condition that only happens to older people. Despite being young, your teenager can develop knee pain too.
Knee pain in teens is a common result of overuse, but also results from specific knee injuries and medical conditions that affect the knee. Knee pain can also be temporary and not related to an injury, but rather a change in your teens level of activity or sport.
Because of the many different reasons for knee pain, if your teen complains of pain, its wise to get it checked. Never think that knee pain in your teen is simply growing pains. This is not a typical cause of knee pain in a teenager.
You May Like: Cellulite Above Knees
Don’t Miss: Cellulite Above Knees
Can You Prevent Knee Problems
Not all knee problems are avoidable, but you can lessen your chance of problems by participating in regular strength training. To protect your knees, it’s important to have a very strong core and strong legs, says Dr. Rebecca Breslow, an instructor in orthopedic surgery at Harvard Medical School. Make an effort to perform strength training at least twice a week. In addition, work on increasing joint flexibility, which can also help you head off an injury.
Symptoms Of Pain Behind The Knee
Since several conditions can cause pain behind the knee, the symptoms can vary. The most common symptoms include:
Varying types of pain
The pain can be sharp, dull, or burning. It may come on suddenly or gradually. It may be constant, or it may occur when you put weight on the leg or when you bend the knee. This information can help a doctor diagnose your knee problem.
Swelling or stiffness
The knee may look swollen or misshapen. You may be unable to bend the knee, or your knee may pop, lock up, or collapse when you put weight on it. These symptoms usually indicate that you have sustained an injury, but there are other possibilities as well.
Redness or warmth
Under certain circumstances, the back of your knee could feel hot to the touch, or redness could be visible. You might also have a fever. These symptoms would point to a different cause than if you only have pain.
Don’t Miss: Does Tommie Copper Knee Sleeve Work
Knee Pain Caused By Nerve Aggravation
This is an incredibly common cause for pain in the back of your knee. As an official diagnosis, it refers to aggravation or compression of the sciatic nerve .
Most often, sciatica is caused by compression of the nerve roots in either your lower back or from soft tissue in the buttocks. People often describe the sensation as a pain that travels or shoots down their limbs, commonly hitting that tender spot behind the knee.
Sciatica is typically diagnosed in your 50s, though its possible for it to start as early as your 20s or 30s. Research estimates that, on average, you can have up to a 40% chance of experiencing sciatica at some point in your life.
Luckily, though, since its a common diagnosis that afflicts a wide population, theres plenty of research surrounding methods for alleviating that radiating pain.
The most effective solution is to seek physical therapy. Your treatment will likely focus on improving movement patterns that is, working on your movement during activities that compress or load the lower back. Depending on your general lifestyle habits, this could include anything from stretching to core strengthening, or lifting education and manual manipulation of the tissues.