Cyst Of Internal Knee Joint Meniscus
The cyst of the inner meniscus of the knee joint is less common than the cyst of the outer meniscus, for the reason that the lateral meniscus is more susceptible to strain. The meniscus cyst does not have the property to connect with the capsule of the joint and protrudes front or back relative to the inner lateral ligament, less often protrudes through the ligament thickness. The main and dominant symptom of the knee cyst of the inner meniscus is pain that appears when the joint is stressed and disappears at rest. When palpation is marked soreness, a dense swelling of a size of several mm to 3 or more cm. If for a long period of time there is no treatment for the knee cyst of the inner meniscus, this leads to bone tissue degeneration and, accordingly, to the development of deforming arthrosis. The most effective and popular method of treatment of the internal meniscus cyst is its removal by endoscopic arthroscopy, which is less traumatic for the joint and has a small risk of complications.
, , ,
Ganglion Cysts Can Disappear
Around 30 to 50 per cent of ganglion cysts disappear by themselves without the need for medical treatment. However, it is always best to consult your doctor to make sure the lump isnt a symptom of some other disease. If your ganglion cyst is painful, or if it interferes with your mobility or causes sensations of numbness or pins and needles, see your doctor.
Ganglion Knee Cyst Information
Knee Cyst is a fluid-filled synovial fluid swelling that causes a lump around the knee area. The Ganglion Knee Cyst can cause tightness and restricted movement hence it can be painful when you bend or extend your knee. Knee Cysts are difficult to treat because they are mostly connected to the knee joint. Although its 90% synovial fluid like all ganglia the location makes it hard to diagnosis and remove. Knee cysts symptoms are swelling, discomfort and very painful around the knee. Determining the location is extremely important in planning surgery because it may lead to a recurrence *National Library of Medicine.
Therefore this condition is due to a problem that affects the knee joint, such as arthritis or a cartilage injury. The best procedure is to have the cyst examined before seeking a remedy. Treating the underlying cause can often alleviate the problem. Very often a knee cyst doesnt cause any long-term damage, it can be very painful and fluid can then leek down the calf and lead to a bruise around the ankle.
We must consider the facts that there is a 40% chance of recurrence rate. G-Relief caps functions differently. It is called the I.B.V.S System They utilize the persons blood flow to dissolve the roots of the ganglia and have it dispursted into your body. If you want to dissolve your knee cyst naturally it will take time but it will not return with the G-Releaf Caps. What is long enough
Recommended Reading: What Not To Do After Knee Replacement Surgery
My Grandfather Stated That Hitting The Ganglion With A Bible Would Make The Condition Go Away
To some extent your grandfather is correct, in that often the ganglion can be burst, resulting in the ganglion sac leaking into the soft tissue surrounding it and preventing a new ganglion forming. We would not recommend such a traumatic technique of treating a ganglion but certainly rupture of the ganglion can be successful. This is usually best done using ultrasound guidance for aspiration or surgically.
Symptoms Of A Meniscal Cyst
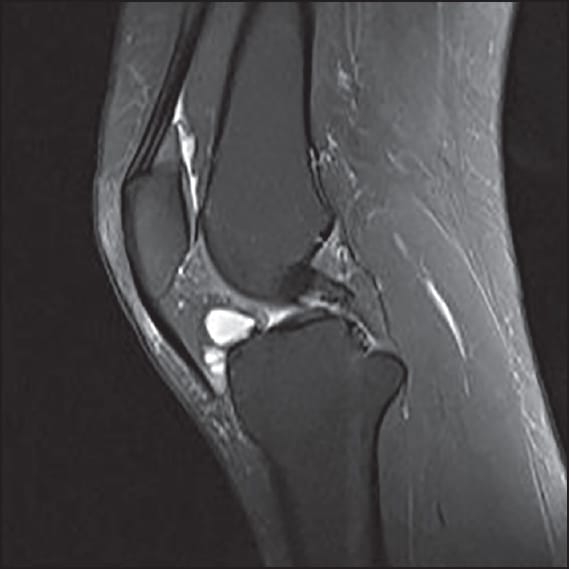
Meniscal cysts do not always cause symptoms. When they do, the most common are:
- Pain in the knee when standing
- Tenderness directly along the joint
- A bump or lump at the cyst site, usually near the outside of the knee
- A bump that becomes more visible as the knee straightens, though the bump itself may be painless
- A bump that changes size
- Swelling or locking of the knee joint
Read Also: Whats Best For Aching Knees
Read Also: What Mm Knee Sleeve Should I Get
Degenerative Or Subarticular Cysts
Geodes are not true cysts, since they do not have an epithelial lining . They are usually associated with osteoarthritis and most of the times they are multiple, small cystic lesions located in both opposing sides of weight-bearing regions of the knee joint . Common osteoarthritic changes such as osteophyte formation, absence of overlying cartilage, joint space narrowing and presence of marked surrounding bone oedema are common accompanying diagnostic clues in MR diagnosis . These features are usually adequate to differentiate geodes from other cystic lesions that can be encountered in the same anatomic area of the bone, such as insertional and ganglion cyst, intraosseous abscess, giant cell tumour, chondroblastoma and chondrosarcoma .
Fig. 12
Subarticular cyst . The sagittal fat saturated proton density weighted image shows a cystic lesion in the subarticular surface of the lateral tibial condyle at the proximal tibiofibular joint. Note chondral defects of the tibial-femoral articular surfaces
Ganglion Cyst Around The Knee
Ganglion cyst of the cruciates can cause knee pain and interfere with flexion and extension of the knee. The patient may complain of pain and tightness in the knee, especially with flexion of the knee. These cysts can be seen clearly on an MRI. It is a benign, subcondylar, radiolucent lesion without degenerative arthritis. The most common locations are:
· Epiphysis of long bones
· Femoral head
· Carpal bones
· Acetabulum
Ganglion cysts are typically seen on x-rays as a well demarcated, solitary radiolucent lesion with sclerotic margins and no communication with the joint can be seen. An MRI will show the solitary, uni, or multiocular lesion, which has a sclerotic rim and the bone scan is usually not hot. This cyst can compress the common peroneal nerve. Treatment usually consists of a decompression of the cyst and the nerve. A fusion of the proximal tibiofibular joint may be considered, especially if the cyst reoccurs after the excision.
You May Like: Should I Wrap My Knee If It Hurts
Causes Of A Knee Cyst
With hyperproduction of the synovial fluid, it accumulates in the posterior part of the knee. The accumulation of synovial fluid in turn generates many diseases of the knee joint. The knee cyst usually appears due to these diseases. The most common cause may be rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis. Less commonly, the knee cyst arises from damage to cartilage tissue, excessive physical exertion, and traumatic injuries. The liquid that has accumulated, begins to press strongly on the nerve endings, which leads to painful sensations in the knee and restriction of movements. Sometimes the reasons for the appearance of the knee cyst remain unknown. In children, this disease is not observed often, mostly people of the older generation are exposed to it. To determine the exact cause of the knee cyst, the doctor prescribes an MRI or an ultrasound of the knee joint, and less often punctures the cyst to examine the contents. To date, the knee cyst occurs in 17% of all cases of knee disease.
How Are Ganglion Cysts Treated
Ganglia cyst treatments include:
- Anti-inflammatory medication may minimize swelling, easing mild levels of discomfort.
- Splints or braces offer support and stop you from moving the affected area, reducing swelling and pain.
- Aspiration is a procedure where your provider uses a needle to remove fluid from the cyst. Providers usually do aspiration in their office. You may feel better right away. Because this treatment only removes the fluid and not the entire cyst, your symptoms may return.
Dont Miss: How To Sleep After Total Knee Replacement
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Dark Knees
Citation Doi & Article Data
- Cysts around the knee joint
There is broad differential for cyst-like lesions around the knee.
Differential diagnosis
- fibular collateral ligament-biceps femoris bursa/fibular collateral ligament)-biceps femoris bursitis
Dont Miss: Whats Wrong With My Knee
Paramentic Cyst Of The Knee Joint
The paramental cyst of the knee joint is a meniscus cyst that has spread to the caapsular region and ligaments. Tumor formation reaches a large size and does not disappear when the knee is unbent. It is easy to palpate and diagnosis is not difficult. Paramentic knee cyst refers to the third degree of cystic degeneration of the meniscus and is a complex form, the treatment of which requires surgical intervention. In most cases, complex treatment, surgical intervention and subsequent physiotherapy gives a positive result and the functions of the knee joint in patients are almost completely restored, which helps a person return to a healthy and full life without restrictions. But do not forget that the paramenisk cyst of the knee joint is often a neglected form of the ordinary knee cyst, so a timely visit to the doctor, diagnosis and treatment of the disease at an early stage will avoid surgical intervention.
Dont Miss: How To Relieve Knee Pain From Standing All Day
You May Like: What Causes Pain In Both Knees
Meniscal Cysts Vs Bakers Cysts
Meniscal cysts are similar to popliteal or Bakers cysts. Bakers cysts, however, are located in the back of the knee joint.
Bakers cysts are seen with many types of knee joint problems that lead to fluid accumulation. They can occur with meniscus tears, but also with arthritis, ligament injuries, and other problems that cause knee swelling.
Ganglion Cyst Causes And Risk Factors
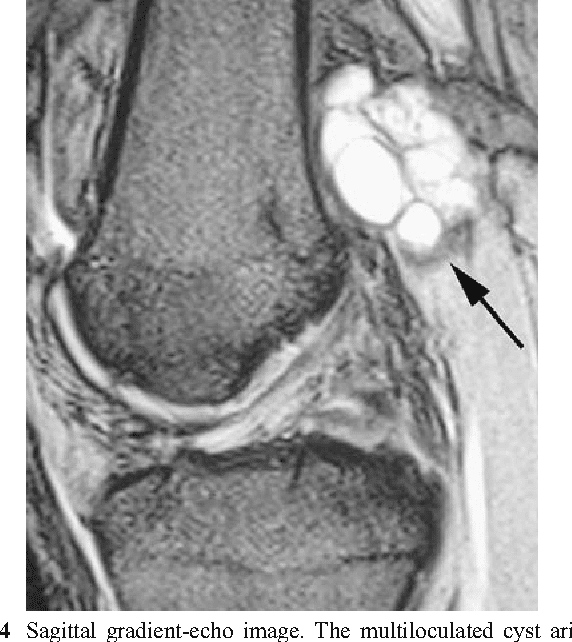
The cause of ganglion cysts is not known. One theory suggests that trauma causes the tissue of the joint to break down, forming small cysts that then join into a larger, more obvious mass. The most likely theory involves a flaw in the joint capsule or tendon sheath that allows the joint tissue to bulge out.
Ganglion cysts are more common in women, and 70% occur in people between the ages of 20-40. Rarely, ganglion cysts can occur in children younger than 10 years.
Don’t Miss: How To Soothe Knee Pain
Recovery After Ganglion Cyst Removal
After your surgery, rest as much as you can for a few days. This will encourage the site of your cyst removal to heal. Limit movement of your hand and wrist to minimize pain and avoid irritation of the removal site.
Minimal, nonrepetitive activity is okay after a cyst removal, such as writing or carrying light objects. Your doctor may recommend finger exercises involving stretching your fingers and thumb as far out as possible and then bending them as much as is comfortable.
You may experience localized pain after surgery, which can be relieved by numbing medications, over-the-counter pain medications, or prescription pain medications.
You may also experience swelling at the removal site. Swelling can be treated with ice and will eventually go away.
In rare cases, infection may occur after ganglion cyst removal. Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic to prevent the infection from spreading. Keep your dressings and wounds clean to prevent infection and limit scarring. Once the surgical site has healed, rub lotion into your skin to ensure that scars heal and keep your nerves stimulated.
Symptoms Of Ganglion Cysts
The symptoms of a ganglion cyst include:
- Noticeable swelling or lump.
- The lump is able to change its size, including going away completely only to return.
- The lump is usually soft and immobile.
- In some cases, the lump is painful and aching, particularly those at the base of fingers.
- The ache and pain is made worse by moving any nearby joints.
- The affected tendon may cause a sensation of muscular weakness.
- The back of the hands and wrists are most commonly affected.
- Other sites include the back of the knee , ankle, foot, palm and fingers.
Also Check: What Can I Do About Fat Knees
Symptoms Of The Knee Cyst
In the initial stages, the knee cyst does not manifest itself in any way, or it is manifested by slight sensations of discomfort. But when it begins to increase in size, it accordingly begins to press on nearby blood vessels and nerves , which leads to painful sensations in the knee, numbness and tingling in the sole area, a feeling of constant cold in the area below the knee. Movements in the knee become difficult and painful. In more rare cases, the knee cyst may press so strongly on the popliteal vein that it causes deep vein thrombosis, or varicose veins of the subcutaneous veins, which is accompanied by swelling, a feeling of heaviness and discomfort. Among all admissible complications of the knee cyst there is a rupture of its wall, the cause of which is high fluid pressure in the knee cyst itself. The rupture is accompanied by severe and severe pain, redness of the skin, swelling and local fever.
Diagnosis Of The Knee Cyst
Diagnosis of the knee cyst is performed by a trauma doctor or orthopedist. The knee cyst is a secondary disease, therefore for the diagnosis it is taken into account the medical history, patient complaints, laboratory and instrumental methods of research. To date, the most popular and accurate methods of instrumental diagnosis are MRI and ultrasound of the knee joint, they can accurately determine the size and position of the cyst. Sometimes in very severe cases resort to the use of arthroscopic diagnosis through a small incision with an optical tube examine the joint cavity. A popular laboratory method of diagnosis is a puncture of the knee cyst with subsequent examination of its contents. Due to accurate diagnosis and correctly diagnosed treatment of knee cyst will have a positive result.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Rebuild Cartilage In My Knee
Home Remedies And Tips
If a cyst causes discomfort, the following can help:
- Adapting footwear: If the cyst is on a foot or ankle, shoes should not rub or irritate it. It may help to wear soft or open shoes, insert padding, or lace the shoes in a different way.
- Immobilization: Moving the affected area may increase the cysts size. Wearing a splint or brace can help limit movement, and this may cause the cyst to shrink.
- Pain relief: If the cyst is painful, over-the-counter pain medication, such as ibuprofen, can help.
Also Check: What Causes Left Leg To Swell Below The Knee
Synovial Cyst Of The Knee Joint
Synovial cyst – a disease that is characterized by a hernia or hypertrophy of the synovial membrane of the joint. To date, medicine is not able to name the exact cause of the disease, but there are several risk factors, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic joint damage. Treatment of this knee cyst in most cases is operational, since conservative treatment methods do not represent high efficiency. The operation consists in the complete removal of the synovial cyst and with the subsequent stitching of the weak site of the capsule with a special suture that helps to strengthen it. To date, a popular method is endoscopic removal of the knee cyst, for the reason that this method is less traumatic and the recovery period is faster and more efficient. But in any case, to delay the visit to the doctor is not worth it, since the synovial cyst may break and this in turn will complicate the whole process of treatment and recovery several times.
Also Check: Should I Get An Mri On My Knee
What Is A Bakers Cyst Is This Another Type Of Ganglion
A Bakers Cyst is a collection of fluid that develops from the knee joint and is often associated either with torn cartilage in the knee or arthritis in the knee. When the fluid presents at the front of the knee it is known as swelling. If it presents at the back of the knee it is known as a Bakers cyst.
A Bakers cyst is a mostly superficial issue. Excising the Bakers cyst does not fix the underlying problem, and may result in continued leakage through the skin. The Bakers cyst is also close to the major neurological structures near the knee. Purely excising a Bakers cyst does not produce any benefit and can have some significant side effects.
A Bakers cyst is commonly associated with degeneration of the knee, and the treatment is to treat the degeneration either by an arthroscopic debridement of the torn cartilage or in the case of an arthritic knee, if the symptoms warrant it, a total knee replacement.
At Glenelg Orthopaedics we provide a balanced approach to assessment of an orthopaedic condition with the aim of providing quality orthopaedic care, treating the patient as we would expect to be treated.
What Is A Ganglion
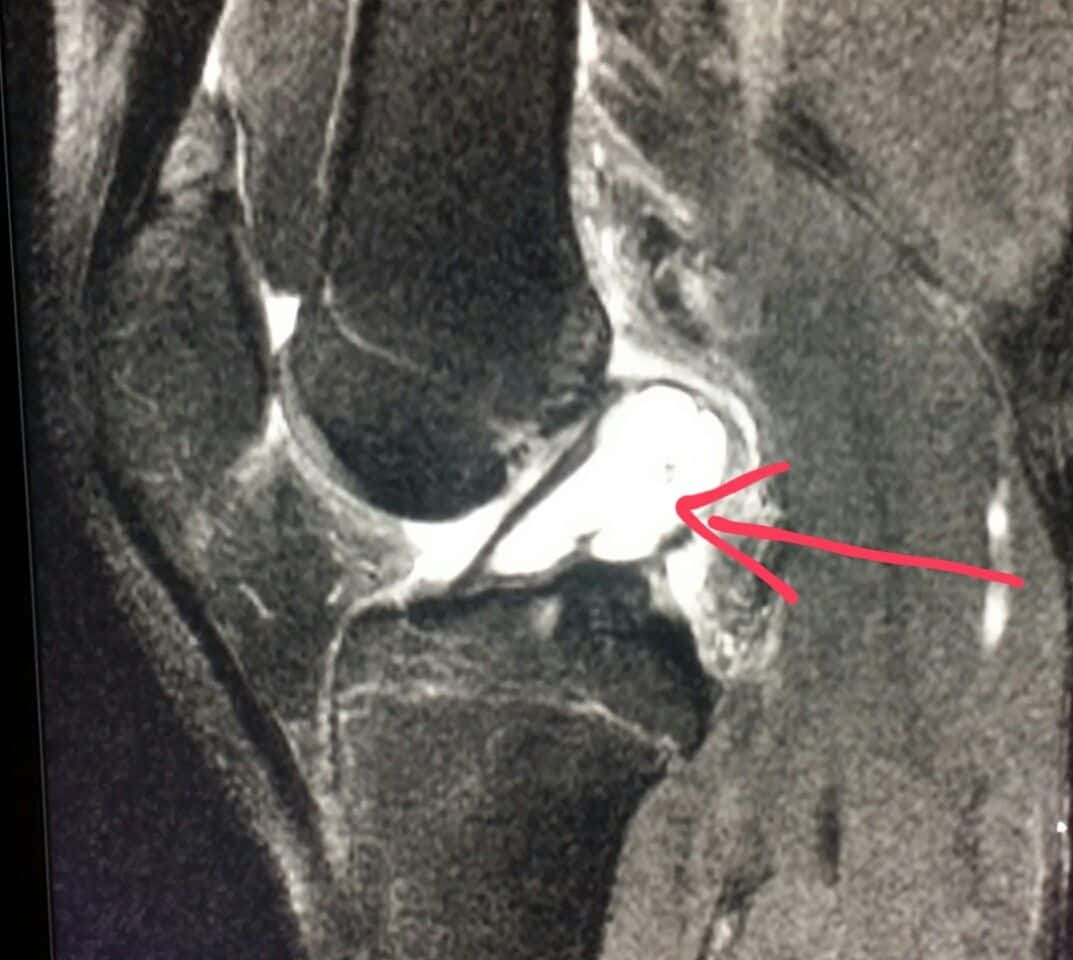
A ganglion is an out-pouching of fluid enclosed by a capsule of tissue, arising from a structure in the body. It can arise from a joint or from a tendon. They usually occur in areas of inflammation either from stress on a structure or from degeneration . They commonly occur around the wrist where there are many tendons that can become inflamed, or can arise from an arthritic joint.
It may present as a lump which incurs insidiously and is often diagnosed by an ultrasound which is ordered by the General Practitioner, although it can also be seen on MRI scan.
You May Like: Can Arthritic Knees Cause Back Pain
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have a ganglion cyst, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Do I need treatment right now?
- Which treatment options do you recommend I try first, and why?
- What are the chances a cyst will come back after treatment?
- When would you consider surgery to treat ganglion cysts?
- What are the risks and benefits of ganglionectomy surgery?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have a ganglion cyst, you may not need treatment right away. If the lump doesnt bother you, your provider may follow you over time to check for any concerning changes. Ganglion cysts are benign, which means these lumps arent cancer. They pose no long-term threat to your health. Many ganglion cysts go away on their own. If a ganglion cyst affects your quality of life in any way, ask your provider about treatment options. Splints, over-the-counter pain medication or surgery may provide relief.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/23/2020.
References
You May Like: Pain Behind And Side Of Knee