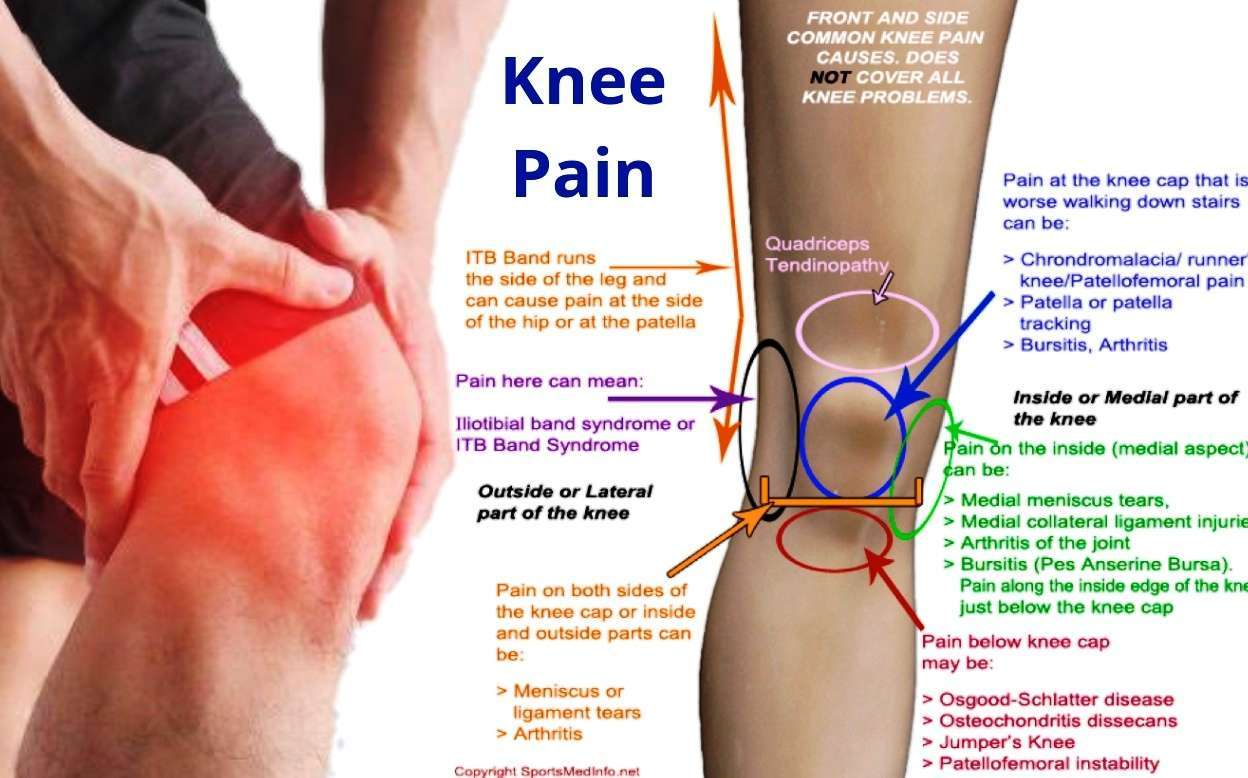
What Causes Sharp Burning Pain In The Knee
Before you identify the cause of sharp burning pain, you need to identify the pain and the location. What does burning pain in the knee mean?
It means that your pain does not just generally ache. You have a sharp, burning sensation in the front, on the side, or on the back of your knee. You can have it while you’re kneeling, while you’re just standing still, and even when you’re sleeping.
What Causes Patellofemoral Pain
It is probably due to a combination of different factors which increase the pressure between the kneecap and the lower part of the thighbone . This may happen during running, cycling, squatting and going up and down stairs. It is likely that the cause is not the same in everyone affected.
Situations where this can occur include:
- Overuse of the knee, such as in certain sports – particularly at times of increased training.
- Cycling when the saddle is too low or too far forward.
- Some people may have a slight problem in the alignment of the patella where it moves over the lower femur. This may cause the patella to rub on, rather than glide over, the lower femur . It may be due to the way the knee has developed. Or, it may be due to an imbalance in the muscles around the knee and hip – for example, the large quadriceps muscle above the knee and the muscles that stop the hips from tilting when standing on one leg.
- Weak hip muscles may cause patellofemoral pain by causing the thighbone to be slightly turned inwards, leading to the patella being pulled slightly to one side.
- Foot problems may also play a part – for example, where the feet do not have strong arches . This makes the foot roll inwards , which means the knee has to compensate for the inward movement. However, it is unclear whether this causes the knee problems or may be caused by the knee problems.
- Injury to the knee – including repeated small injuries or stresses due to sports, or due to slack ligaments .
There Are Many Possible Causes Of Knee Pain Radiating Down Shin:
The knee joint can become inflamed and inflamed arthritis, which can lead to stiffness and pain. Sometimes the pain can be debilitating and lasting for a long time. Arthritis in the knee usually results from wear and tear, osteoarthritis but other forms of arthritis can affect the knee joint, such as blood pressure and gout uric acid crystal buildup, and pseudo-gout calcium crystal buildup. Severe complications that cause joint knee pain may include fractures and infections septic arthritis.
Myofascial pain occurs due to stress with the surrounding muscles, ligaments and tendons of the knee. Muscles can develop small thin knots taut bands that are called interesting myo-fascial markers. Stimulant components are unsightly spots in the fascia covering that surrounds the muscles and can be very painful and completely debilitating. When a touch cell is touched or examined, it can cause severe pain in and around the area.
Injury of the frontal ligament ACL can be demolished by sports such as football, basketball and skiing.
Meniscus The meniscus is a hard, soft cartilage that acts as a knee joint. It is similar to a record within the spine. The meniscus can break in some cases as with a sudden knee.
Patellar Tendonitis pain in the patella tendon can occur when the kneecap tendon is swollen and swollen. Sometimes the patella may disintegrate.
Also Check: How To Whiten Knees And Elbows
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Sprain/strain
Cause & Symptoms
If you watch or play sports you are probably quite familiar with ACL injuries. These injuries typically occur during player on player contact , or noncontact, occurring at high speeds where an athlete attempts to brake or change direction .9 Women are almost twice as likely to experience an ACL injury. Pain and dysfunction localized at the front of the knee will begin immediately after the injury. Additionally, due to the nature of the injury, other knee structures such as the lateral and medial collateral ligamentsoften experience trauma as well.
Treatment
Over 70% of ACL injuries require surgery.9 One common issue after injury and the subsequent surgery is poor proprioception your ability to sense the position of a joint in time and space. Ligaments are rich in receptors that enable proprioception. As a result, when you injure your ACL you will experience joint instability. Overcoming this requires months of commitment to strengthening and balancing exercises.
What Is Anterior Knee Pain
It is pain that is experienced in the front of the knee, and can sometimes feel quite diffuse or localised . Its common to experience some amount of swelling when it first happens or when it flares up. This might be accompanied with some amount of stiffness, typically first thing in the morning or after prolonged sitting.
This pain typically worsens when doing activities involving repeated weight bearing like walking, stairs, running/jogging, jumping.
Very rarely will you experience clunking or locking of the knee .
You May Like: Can You Use An Inversion Table After Knee Replacement
Common Knee Injuries And Causes Of Knee Pain
by Ethan Anderson PT, DPT, ATC | Arrowhead
Knee injuries are some of the most common occurrences in sports and athletics. The knee is one of the most significant weight-bearing joints of the body, meaning that it undergoes a lot of pressure when we run, jump, or do other physical activities, like heavy lifting. The structure of the knee joint is relatively simple, essentially only straightening and bending with a small amount of rotation. Excessive rotation or twisting during activity is a very common mechanism for knee injuries in addition to heavy loading on the joint and muscles.
There are a vast number of injuries or conditions that can impact the knee and/or cause pain. This article will cover anatomy of the knee, causes of knee pain, and common sports injuries.
Blood Clot Giving Rise To The Back Of Knee Pain
There is a major blood vessel present at the back of the knee, known as the popliteal vein. If a clot forms in this vessel, the blood flow to the lower leg is restricted and pain might occur.
The clot can be formed due to many reasons, including smoking, obesity or a major injury.
The most-occurring symptoms are:
The blood clot behind the knee is treated in the following ways:
- Anticoagulant medication: These blood thinners like warfarin and heparin stops the blood clots from growing.
- Thrombolytic therapy: Involves the intake of drugs that dissolve the blood clot.
- Compression bandages and warm compressions: To regulate the blood flow in the legs.
Don’t Miss: How To Whiten Knees And Elbows
What Are The Symptoms Of Patellofemoral Pain
- Pain around the knee. The pain is felt at the front of the knee, around or behind the kneecap . Often, the exact site of the pain cannot be pinpointed instead the pain is felt vaguely at the front of the knee.
- The pain comes and goes.
- Both knees are often affected at the same time but one is usually worse than the other.
- The pain is typically worse when going up or, in particular, going down stairs.
- Running, especially downhill, squatting and certain sports can all set it off – anything that leads to the patella being compressed against the lower part of the thighbone.
- The pain may be brought on by sitting still for long periods. For example, after going to the cinema or for a long drive, when it will be worse when starting to move about again.
- There may be a grating or grinding feeling or a noise when the knee bends and straightens. This is called crepitus.
- Sometimes there is puffiness or swelling around the kneecap.
What Causes Pain In The Leg Below The Knee
Leg pain can strike anytime. The area of the leg directly below the knee includes tendons, ligaments and bone. Physio Advisor suggests that MCL tendinitis arises gradually from the frog-kicks repetitive propulsion, which requires the quadriceps and hamstring muscles to whip the lower legs backwards and together.
Don’t Miss: Can You Use An Inversion Table After Knee Replacement
Medial Collateral Ligament Injury
The medial collateral ligament runs along the outside of your inner knee to stabilize the joint. If the ligament overstretches, you may have an MCL sprain.
The MCL can also tear partially or fully. An MCL injury most commonly occurs after force is applied to the outer knee, such as in contact sports.
Symptoms of an MCL injury include:
About Our Health Information
At Bupa we produce a wealth of free health information for you and your family. This is because we believe that trustworthy information is essential in helping you make better decisions about your health and wellbeing.
Our information has been awarded the PIF TICK for trustworthy health information. It also follows the principles of the The Information Standard.
Read Also: Do Compression Sleeves Help With Knee Pain
Repetitive Strain Injury Of The Quadriceps
Repetitive strain injury of the upper leg is caused by consistent repetitive use.
Rarity: Uncommon
Top Symptoms: upper leg numbness, thigh weakness, thigh pain from overuse
Symptoms that always occur with repetitive strain injury of the quadriceps: thigh pain from overuse
Symptoms that never occur with repetitive strain injury of the quadriceps: upper leg injury, severe upper leg pain
Urgency: Self-treatment
How Is Knee Pain In Teens Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will ask about your teens knee pain:
- Is there a known cause for the knee pain does it happen with certain movements or is there no specific known event?
- How long has the pain been present?
- Where on or around your knee do you feel pain?
- Does the pain wake you up at night?
Your provider will perform a physical exam, checking:
- Kneecap and knee stability.
- Alignment of lower leg, kneecap and thigh.
- Range of motion of hips and knees.
- Thigh muscle strength, flexibility, firmness.
Your provider may order imaging tests including X-rays or a CT scan or MRI .
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Limping After Knee Surgery
Symptoms Of Pain At The Front Of Your Knee
Pain at the front of your knee can feel different for different people and will depend on whats causing it. You may have pain below your kneecap, around it, on either side of it or behind it. You may have a dull ache or a sudden, sharp pain.
Youll often get pain in both knees at the same time, unless its due to a particular injury. Pain at the front of your knee is often made worse by:
- standing up after sitting for a long time
- squatting or kneeling
- using stairs
- running downhill
Jumpers knee may cause pain only when youre active, but if it gets worse, it may be painful all the time.
Pain from an anterior cruciate ligament injury is usually sudden and you may hear a pop. Your knee is likely to swell up quite quickly and may feel as if it is going to give way.
Osteoarthritis in your knee usually causes pain when you put weight on the affected leg and gets better when you rest it. You may have stiffness and loss of movement first thing in the morning or after sitting for a while.
OsgoodSchlatter disease and Sinding-LarsenJohansson disease cause pain, tenderness and swelling just below your kneecap, at the top of your shin bone. Symptoms are usually brought on by running or jumping.
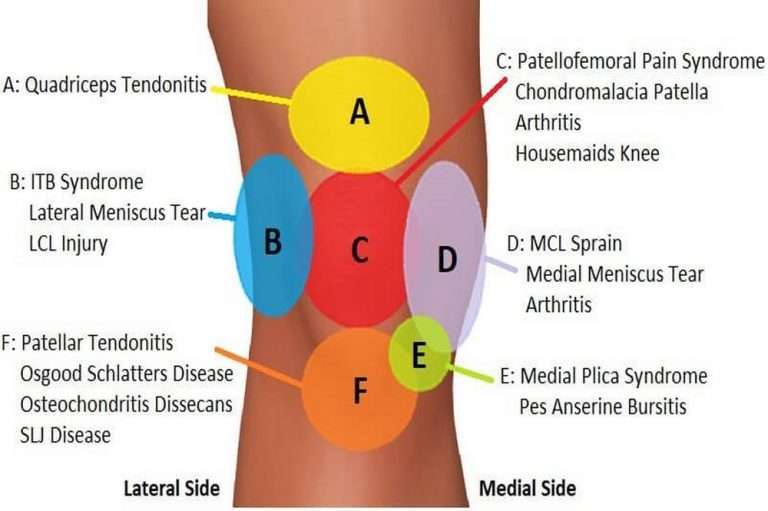
What Are The Types And Causes Of Knee Injuries
While direct blows to the knee will occur, the knee is more susceptible to twisting or stretching injuries , taking the joint through a greater range of motion than it was meant to tolerate.
If the knee is stressed from a specific direction, then the ligament trying to hold it in place against that force can stretch or tear. These injuries are called sprains. Sprains are graded as first, second, or third degree based upon how much damage has occurred. Grade-one sprains stretch the ligament but don’t tear the fibers grade-two sprains partially tear the fibers, but the ligament remains intact and grade-three tears completely disrupt the ligament.
Twisting injuries to the knee put stress on the cartilage or meniscus and can pinch them between the tibial surface and the edges of the femoral condyle, potentially causing tears.
Injuries of the muscles and tendons surrounding the knee are caused by acute hyperflexion or hyperextension of the knee or by overuse. These injuries are called strains. Strains are graded similarly to sprains, with first-degree strains stretching muscle or tendon fibers but not tearing them, second-degree strains partially tearing the muscle tendon unit, and third-degree strains completely tearing it.
There can be inflammation of the bursas of the knee that can occur because of direct blows or chronic use and abuse.
Read Also: Fluid On The Knee Remedies
How Does It Happen
Anterior knee pain usually happens over time. Its often difficult to pinpoint a specific incident that caused it.
However, the weeks or months before it starts is pretty telling Was there something new that you started doing? Or was there some change in your usual routine which involves significantly more load through the knee? Usually this indicates much more load going into the tissues around the knee which are unable to adapt quickly enough.
* This is assuming there has been no direct trauma to the knee. If there is, you should see a qualified healthcare professional about this.
Burning Pain When Sitting Still
Some people feel more pain at night than during the day.
You might feel more pain when you’re sitting still. Some of us are just too busy to monitor pain. We need debilitating pain to tell us to slow down and be still.
So when you sit down and take a break, do not be surprised if the little niggles of pain begin to visit you.
Your nightly knee pain can also come from reduced hormone signals. When you rest, your hormone signals are reduced. These reduced hormone signals give way for pain signals to reach the brain.
So you’ll feel pain as you try to nod off.
Your blood vessels may also be the culprit for pain at night. When you sleep, your blood vessels increase in diameter. This is a natural process that allows more blood to come to muscles, allowing them to heal.
However, those expanding blood vessels can put pressure on your nerves. This will cause pain such as pain in your knee even as you try to sleep.
Don’t Miss: What Do You Do For Water On The Knee
How Do Doctors Diagnose Knee Injuries
The initial evaluation by the health care professional will begin with a medical history. Whether the evaluation is occurring immediately after the injury or weeks later, the physician may ask about the mechanism of injury to help isolate what structures in the knee might be damaged. Is the injury due to a direct blow that might suggest a fracture or contusion ? Was it a twisting injury that causes a cartilage or meniscus tear? Was there an injury associated with a planted foot to place stress and potentially tear a ligament?
Further questions will address other symptoms. Was swelling present, and if so, did it occur right away or was it delayed by hours? Did the injury prevent weight-bearing or walking? Does going up or down steps cause pain? Is there associated hip or ankle pain? Is this an isolated injury, and have there been other occurrences?
Past medical history and information on medications and allergies will be helpful information to learn about the patient.
Sometimes X-rays of the knee are required to make certain there are no broken bones, but often with stress or overuse injuries where no direct blow has occurred, plain X-rays may not be initially needed and imaging of the knee may wait until a later date. Standing X-rays of the knees are used to assess the joint space and compare the injured knee to the uninjured one. An MRI might be considered to evaluate the ligaments and cartilage within the knee joint.
If You Have Jumpers Knee
Immediately take rest from the activity that caused it: basketball, netball or any other sport you might be playing. The knee is a complex machine and needs rest if it incurs complications.
It is the first step of the R.I.C.E process which is common for treating a Jumpers knee.
R= Rest
C= Compression
E= Elevation
Apply an icepack on the knee area which will compress it and then elevate the knee using a splint, stool or with the help of a wall.
This elevation increases the blood flow to the knee to help in the healing. When you are involved in some light activity, make sure to wear a supporting knee brace to reduce the amount of weight applied on the knees.
As for the rehabilitation process, several exercises are recommended by the doctors.
Sandra Curwin and William Stanish especially recommended drop squats and came up with a 6-week program that helped the patients in increasing the tendon strength years ago.
There are other exercises as well, like the:
- Short-leg raises:
Lie on the floor with your good leg bent as shown above.
Tighten the muscles of the affected knee by straightening it and raise it 30 cm above the ground.
Hold there for 6-10 seconds before lowering the leg and repeat for 10-15 times.
- Step-up & step-down
Have a raised platform in front of you. Get on top of it and then descend. Repeat if for 10-15 times.
- Side-lying leg lift:
Lay on your good leg and raise the other leg at least 3-4 feet from it.
- Prone hip extension
Recommended Reading: Nano Knee Cost