What Can You Do For The Pain
Your plan will depend on your specific injury. Mild to moderate issues will often get better on their own. To speed the healing, you can:
- Rest your knee. Take a few days off from intense activity.
- Ice it to curb pain and swelling. Do it for 15 to 20 minutes every 3 to 4 hours. Keep doing it for 2 to 3 days or until the pain is gone.
- Compress your knee. Use an elastic bandage, straps, or sleeves to wrap the joint. It will keep down swelling or add support.
- Elevate your knee with a pillow under your heel when you’re sitting or lying down to cut down on swelling.
- Take anti-inflammatorymedications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or naproxen will help with pain and swelling. Follow the instructions on the label. These drugs can have side effects, so you should only use them now and then unless your doctor says otherwise.
- Practice stretching and strengthening exercises if your doctor recommends them. You may want to do physical therapy, too.
Make an appointment with a doctor if you still have pain after 2 weeks of home treatment, if the knee becomes warm, or if you have fever along with a painful, swollen knee.
Some people with knee pain need more help. For instance, if you have bursitis, your doctor may need to draw out extra fluid from the bursa in your knee. If you have arthritis, you may need an occasional corticosteroid shot to settle down inflammation. And if you have a torn ligament or certain knee injuries, you may need surgery.
Osteonecrosis Of The Knee
Osteonecrosis is a condition in which bone tissue dies due to a lack of adequate blood supply. People typically notice severe pain on the inside of the knee with tenderness and joint swelling as well as pain when bending or straightening the knee. These symptoms may cause a person to limp when walking.
Osteonecrosis in the knee is not common. It is most likely to occur after an injury, but it can also develop gradually in absence of a trauma. Older women who have osteoporosis are at the greatest risk for osteonecrosis.
Causes Of Inner Knee Pain
The inside or medial part of the knee contains a wide variety of bones, ligaments, and soft tissue structures, all contained within a relatively small area. Because of this, pain in this area of the joint can be tough to diagnose.
Several of the most common conditions that cause medial knee symptoms are listed below.
Recommended Reading: How To Whiten Knees Fast
Chronic Idiopathic Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy refers to the feeling of numbness, tingling, and pins-and-needles sensation in the feet. Idiopathic means the cause is not known, and chronic means the condition is ongoing without getting better or worse.
The condition is most often found in people over age 60. Idiopathic neuropathy has no known cause.
Symptoms include uncomfortable numbness and tingling in the feet difficulty standing or walking due to pain and lack of normal sensitivity and weakness and cramping in the muscles of the feet and ankles.
Peripheral neuropathy can greatly interfere with quality of life, so a medical provider should be seen in order to treat the symptoms and reduce the discomfort.
Diagnosis is made through physical examination blood tests to rule out other conditions and neurologic and muscle studies such as electromyography.
Treatment involves over-the-counter pain relievers prescription pain relievers to manage more severe pain physical therapy and safety measures to compensate for loss of sensation in the feet and therapeutic footwear to help with balance and walking.
Rarity: Rare
Top Symptoms: distal numbness, muscle aches, joint stiffness, numbness on both sides of body, loss of muscle mass
Urgency: Primary care doctor
Tendon And Muscle Injuries Causing Pain Behind Knee

Tendon injuries often occur in runners due to overload. The tendons most likely to be affected include the hamstring on the inside or outside . Rarely, a small tendon called the popliteus wrapping around the outside of the knee joint can become swollen and painful.
In addition, hamstring muscle tears can occur close to the outside of the knee. Usually, these tears occur about 5cm above the knee joint. It is important to define the exact location of the tear, as location determines the time to return to sport.
Finally, a pulled calf muscle near the knee can also cause pain in this area.
Read Also: Dcf Compression Knee Sleeve
Investigation Of Pain Inside The Knee
Your doctor will ask you about the type of pain you are feeling, and also note the size of your affected knee compared to your unaffected knee. Any discolouration and warmth will be noted as will the range of movement you are able to effect. The doctor may need further investigation in the form of medical imaging to detect fluid or a possible fracture, and perhaps a blood test to identify any rheumatoid factor or antinuclear antibodies. Fluid may also be drawn from the knee to test for uric acid or bacteria if an infection or inflammation is suspected.
Inner Knee Pain: Why Does The Inside Of My Knee Hurt 5 Common Causes
Do you have pain on the inner part of your knee? Well, theres five Common causes for pain on the inside of the knee. And theres a specialist physical therapist, I often see people are mis diagnosed by their healthcare professional, because really, their healthcare professional just doesnt do a whole lot of examination, they wont physically examine their patients most of the time. And even then, theyre not specialists in physically checking the knee and knowing the ligaments, the tendons, the cartilage, all the stuff thats in there.
Theyre more specialists or experts in issuing out pain medication, which really does not solve any sort of knee problem for the long term. Today, Ill be explaining to you the five Common causes for knee pain so that you can best determine which one you have. And watch out because some of these problems can overlap, there is a possibility that you might have two of them happening at the same time, so you have to use your best judgment to figure out whats going on.
For most of these problems, Ive got a separate video that shows you exactly how to test yourself. In some of these videos go into the treatment that you can do on your own, so that you can begin to get relief for this specific problem thats causing your inner knee pain. The videos are linked in the description below. So lets get into the first of the five reasons for inner knee pain.
Read Also: How Do I Get Rid Of Fat Around My Knees
Kneecap To Shinbone Pain: Jumper’s Knee
Pain from the top of the kneecap to the top of the shinbone may be an indication of patellar tendinitis, a common overuse injury. The condition is also called jumper’s knee because it is common in sports that involve jumping.
Those who have jumper’s knee feel pain, tenderness, and possibly swelling near the patellar tendon . When the condition is in its early stages, you might only notice it when running. As it gets worse, however, you’ll notice it throughout the day, even when you are not exercising.
Patellar Tendonitis Tendinosis And Tears
Patellar tendonitis occurs when the patellar tendon becomes inflamed and irritated. This problem is most often seen in athletes who do repetitive jumpingthe reason patellar tendonitis is often called “jumper’s knee.” Patellar tendonitis is most often seen in participants of sports such as basketball and volleyball, although it can also be seen in runners and other types of athletes.
Patellar tendinosis is different from tendonitis in that it is a chronic condition. Instead of the tendon becoming inflamed and irritated, the condition is more gradual in development and characterized by microscopic tears and thickening of the tendon. Patellar tendinosis causes similar symptoms, but the treatment of this condition is different from that used for tendonitis.
Partial patellar tendon tears, a finding sometimes described on an MRI, are usually characteristic of chronic patellar tendinosis. These tears are differentiated from a complete patellar tendon tear, in which the entire tendon is ruptured and requires surgical repair.
You May Like: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Knee Surgery
What You Can Do
Take over-the-counter NSAID drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen to ease pain and swelling. RICE — rest, ice, compression, and elevation — can often help, too: Get off your feet. Raise your leg so it’s higher than your heart. Put a cold pack in a thin cloth or towel on your knee for 10-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Wrap an elastic bandage around your knee when you’re up and about, snug but not tight.
Lower Leg Pain Caused By Veins And Nerve Issues
1. Blood Clot
When blood thickens in veins, it can develop a clot. This typically happens in the thigh or lower leg, commonly leading to pain from knee to ankle. There is a higher risk if you are overweight, on certain medicines, or inactive for a long car ride or flight.
2. Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are caused by weakness in the vein walls or valves and can lead to a dull ache, particularly after standing.
3. Lower-Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease
This occurs if your legs arteries get damaged and harden. The legs begin to miss needed blood flow, leading to pain or cramps when walking or climbing stairs.
4. Narrowed Spinal Canal and Sciatica
When the spinal canal narrows due to a herniated disc, arthritis of the spine, or another cause, it can lead to weakness, fatigue, numbness, tingling, or cramping, burning leg pain when you sit or stand. It may start in the hip and the back before extending down the leg.
5. Diabetic Neuropathy
This diabetes complication can be due to high blood sugar levels and leads to pain in both legs. It also features less sensation and numbness in lower legs.
When to See a Doctor
You should see your doctor for pain from knee to ankle if you have the following symptoms:
Read Also: Inversion Table Knees
Coping Strategies For Runners With Anterior Knee Pain:
- A shorter stride: a shorter stride allows you to control your pelvic drop better.
- A higher cadence : This also minimizes your pelvic drop and other gait abnormalities.
- Avoiding hilly terrain until the pain has lessened.
- Progressive, intelligent training. Consider using apps such as HRV4Training, Training Peaks or TrainAsOne.
- Patella taping: See the video at the end of this post.
- Orthotics or shoe inserts: These have been shown to work in some of you.
- Prevention: Keep your glutes/ hip abductors / core strong. See the exercise videos at the end of this post.
Anterior Knee Pain: The Basics
Pain in the front of the knee or anterior knee pain can affect people in all age groups. Approximately 25% of people will suffer from pain in the front of their knees at some time in their lives. I have seen teenagers who can longer participate in sports, and I have 70 years olds who can no longer walk downstairs without fear of their knee giving way. Why is our kneecap or patella so prone to bothering us like this?
The cause of anterior knee pain might vary based on your age, level of activity, and your chosen sports. We can see people who are inactive and suffer from pain in the front of the knee, and we can also see people who are highly trained and disciplined who are suffering from pain around the kneecap. The majority of people who have pain in the front of their knee do not recall any injury.
In the majority of cases of anterior knee pain, we do not find anything significant wrong with your X-rays or MRI scans. It seems that the pain in the front of the knee is often due to imbalances, weakness patterns, movement patterns, and complex issues that can take a while to figure out. Yes, some of you might have a cartilage defect or some early arthritis in the front of your knee but believe it or not, the majority of you will have pretty normal-appearing imaging studies. That has led to a significant change in our approach to anterior knee pain over the years.
Anterior knee pain is particularly common in young women and many runners.
Read Also: Roller Knee Walker
Common Causes Of Pain Behind Knee
Where do we start with making an accurate diagnosis?
Generally, most doctors use a methodological process to confirm or rule out causes. Firstly, we perform a thorough assessment to test the joints, ligaments, and tendons that pass across the back of the knee. Then, we consider imaging to confirm our thinking. X-rays often pick up major arthritis in the knee. MRI can detect soft tissue problems such as tendonitis or muscle tear. Occasionally, we perform other tests such as blood, ultrasound, or nerve studies depending on the presentation.
Generally, the more common causes of pain behind the knee include:
What To Expect At Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam, and look at your knees, hips, legs, and other joints.
Your provider may do the following tests:
- MRI of the knee if a ligament or meniscus tear could be the cause
- CT scan of the knee
- Joint fluid culture
Your provider may inject a steroid into your knee to reduce pain and inflammation.
You may need to learn stretching and strengthening exercises. You also may need to see a podiatrist to be fitted for orthotics.
In some cases, you may need surgery.
You May Like: Inversion Table After Hip Replacement
Pain On The Outside Of The Knee
- A burning pain at the outside of the knee may be due to iliotibial band syndrome. The iliotibial band is a ligament running down the outside of the thigh to the outside of the knee which can become inflamed and irritated.
- A tear in one of the two menisci can cause pain, swelling, and a feeling that the knee is giving way or locking.
- A burning sensation at the side of the knee can indicate pressure on the menisci and sometimes can be due to a fluid filled cyst.
Treatment Options And Pain Relief
Usually, your treatment will vary depending on the severity of your injury. The inner meniscus do not have a huge blood supply and sometimes, surgery may be required. However, it isnt always necessary. Rest and ice can go a long way in helping you recover from a meniscus injury. When the pain has begun to subside, proper stretching and strengthening exercises targeting muscles around the knee can help the area heal further, as well as prevent future injury.
You May Like: Does Tommie Copper Knee Sleeve Work
How Are Knee Problems Diagnosed
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, other tests for knee problems may include:
-
X-ray. This test uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging . This test uses large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body can often determine damage or disease in a surrounding ligament or muscle.
-
Computed tomography scan . This test uses X-rays and computer technology to make horizontal, or axial, images of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
-
Arthroscopy. A minimally-invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used for conditions of a joint. This procedure uses a small, lighted, optic tube , which is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen used to evaluate any degenerative or arthritic changes in the joint to detect bone diseases and tumors to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation.
-
Radionuclide bone scan. A nuclear imaging technique that uses a very small amount of radioactive material, which is injected into the patient’s bloodstream to be detected by a scanner. This test shows blood flow to the bone and cell activity within the bone.
Symptoms Of Outer Knee Pain
The symptoms of outer knee pain will vary depending on the type of injury you have. Outer knee pain may feel dull and your knee may ache, or the pain can be sharp and limited to one area. You may have swelling from fluid that collects, or your knee may click or lock .
If you have iliotibial band syndrome, you may have pain all over the outside of your knee or the pain may be sharp and in one area. If your injury is mild, you might notice the pain come on after a certain time or distance when youre running, for example. And it may get better when you stop. If your injury is more severe, it might be painful to walk or even sit with your knee bent.
If you have a lateral collateral ligament injury, the outside of your knee will be painful. This ligament helps to keep your knee stable, so you may feel as if your knee is going to give way. You may have swelling around your knee, or pins and needles in your foot. You might find the pain is worse when you walk or run on uneven ground.
Symptoms of a torn meniscal cartilage include pain and your knee may also feel stiff, and lock or catch. There may be some swelling that may gradually get worse and you may find it difficult to fully straighten your leg. Pain can come and go, as can the swelling.
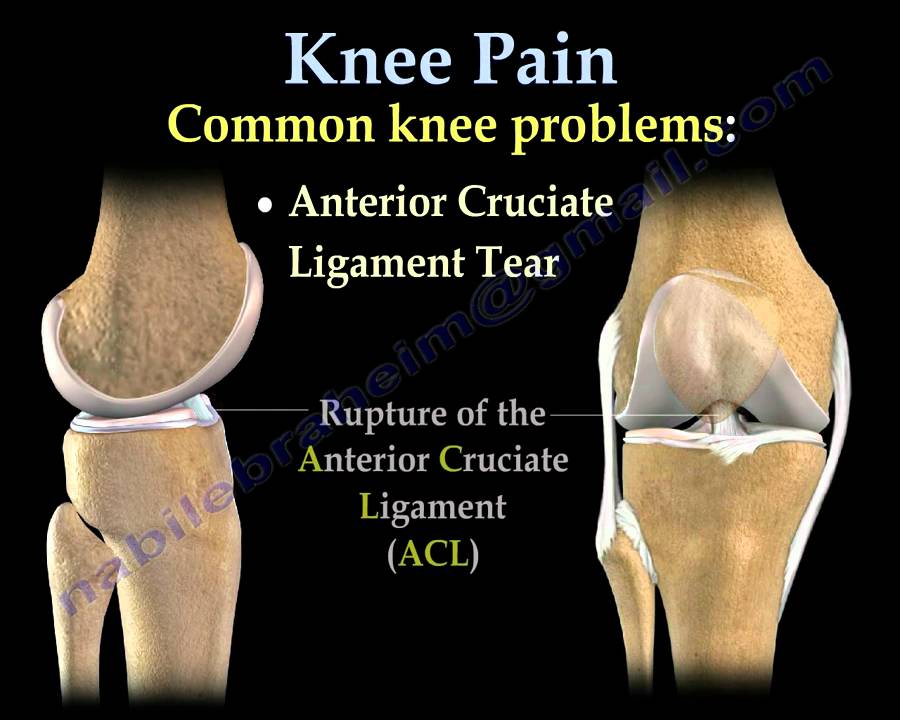
Pain from an anterior cruciate ligament injury will be sudden and you may hear a pop. Your knee is likely to swell from internal bleeding and may feel as if its going to give way.
You May Like: Inversion Table Benefits For Knees