You Felt Or Heard A Pop
Sometimes, a popping sound after a movement can indicate something is out of place.
Oftentimes this type of sound upon injury is indicative of a ligamentous injury, says Schwabe. Not all ligamentous injuries are full tears, though, and not all require surgery.
However, if you also experience excessive swelling and instability, get it checked out by an M.D. If you only have a mild sprain then you will be able to rehab it with physical therapy, he says.
The pop is what you hear as a result of a ligament tear, a meniscus tear, strained tendons, or a dislocated kneecap. Usually what happens is youll simultaneously hear and feel the pop.
If youre not familiar with the meniscus, its the cartilage in the knee that functions as a shock absorber. Each knee has two menisci, and theyre shaped like horseshoes. The medial meniscus is on the inside of the knee, and the lateral meniscus is on the outside.
The popping sensation can be difficult to explain, but youll certainly know it when it happens to you. Though the sound originates in the knee, youll hear it as though it was directly in your ear. Its as if the sensation travels up your body, and when it gets to your brain, it becomes audible.
If the pain is severe, youll want to visit a doctor as soon as possible. Surgery is often the recommended course of action, but physical therapy and other non-invasive remedies may be prescribed as alternatives.
Treatments That Have Already Been Instituted
Many patients have undergone physiotherapy, steroid injection or previous arthroscopy. The success of previous therapies guides further management.
If a patient has not undergone physiotherapy this may be the first port of call particularly in anterior knee pain related to patellofemoral joint dysfunction. History of previous surgery, in particular total knee replacement or cruciate ligament reconstruction, associated with new onset of symptoms should warrant a referral to the orthopaedic surgeon.
Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are two common types of arthritis that can lead to knee tightness. Osteoarthritis causes the cartilage in the knee to erode, leading to malalignment. Rheumatoid arthritis causes damage to the lining of the joints, which leads to inflammation. Both types of arthritis can lead to limited function and range of motion, deformity, and tightness.
Exercises that strengthen the surrounding muscle groups may help your range of motion and knee stability.
Also Check: What Is The Best Knee Walker
What Can Cause Swelling Above Knee & What Is Its Treatment
Swelling above knee is a fairly common condition and observed when knee joint or the soft tissues surrounding knee joint is inflamed or injured. Swelling above or over the knee joint is a condition often observed following the knee joint disease. It is sometimes also referred to as water on the knee.
Joints are junctions at which two bones meet with the help of soft tissues or surrounding structures. Swelling above knee indicates accumulation of fluid around the knee joint. Synovial fluid is normally present in the knee joint for lubrication, protection and nutrition of the cells in the joint.1 However, excessive accumulation of fluid in the knee joint causing knee swelling may mean some disturbance in the normal structure and functioning.
Complementary And Alternative Therapies
A number of mind-body therapies may be used to treat knee pain. These include:
- Acupuncture
- Tai chi
These are especially common for knee osteoarthritis.
The once-popular supplements glucosamine and chondroitin have fallen out of favor for knee osteoarthritis. That’s due to a lack of scientific proof. Always talk to your healthcare provider before taking any supplements or medications.
You May Like: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Knee Surgery
You Cant Put Weight On It
If its immensely painful to stand or put any weight on your injured knee, theres definitely something serious going on.
Inability to bear weight after a knee injury could be caused by a fracture, bone contusion, cartilage injury or ligament tear, explains Dr. Brown. Initial treatment includes using crutches or a steerable scooter to take pressure off the injured limb and minimize additional damage to the knee.
If this sounds like you, listen to what your body is trying to tell you. Dr. Brown warns that the old adage of no pain, no gain doesnt apply in this situation.
He advises seeking orthopedic evaluation as soon as possibleeven that same day if you can.
After a minor injury like a twist or fall, you might not be able to put weight on your leg immediately. Thats not necessarily a cause for alarm, but if you dont feel like youve recovered within a few minutes, this could indicate something more serious.
Its similar to when you injure a wrist or ankle. If you fall on your wrist or twist your ankle, you may experience searing pain for a moment or two. When the injury isnt severe, youre able to shake it off and resume your life after a few minutes at the most. However, if youve experienced a sprain, the pain doesnt subside. Instead, it gets worse.
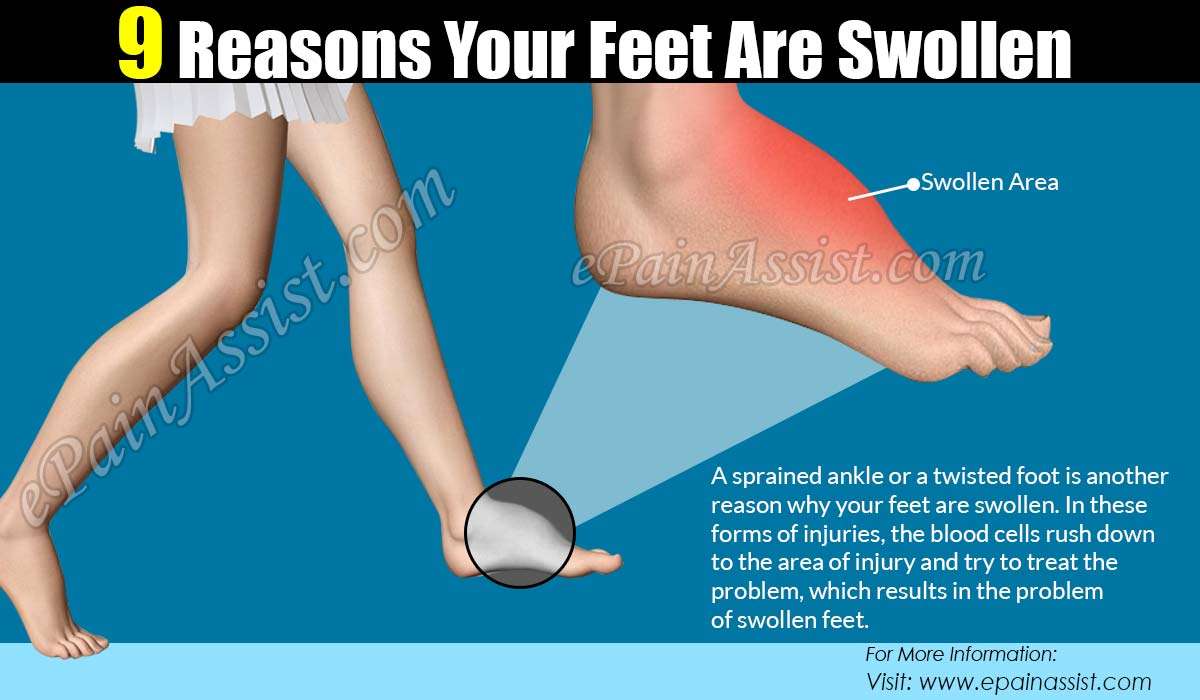
What Can Cause Swelling Above Knee
Swelling above knee appears like a puffed knee and the accumulation of fluid may give it a bulging appearance.2 Swelling above knee or swollen knee is often accompanied with pain, discomfort and inability to move the knee joint properly. The knee may appear red, warm to touch and weight bearing on the knee, walking and other activities may be difficult. Complete bending or straightening of the knee may be difficult and painful on account of swelling above knee.
There can be many causes for swelling above knee, which includes:
Swelling above Knee Caused Due to Injury or Trauma: Any injury or direct trauma to the soft tissue surrounding knee joint can result in swelling above the knee. People engaged in sports, adventure games, or an accident can experience swelling above the knee joint due to injuries to soft tissues resulting in ligament strains, tendon injuries, muscle strains, cartilage and meniscus injuries. Injuries to the knee cap and soft tissues of the knee cap can cause swelling above the knee. Serious injuries like fractures or dislocations of knee cap and knee joint too can cause swelling above the knee joint because of collection of blood. If the pain is very severe with inability to move the knee, then immediate medical attention should be sought.
Also Check: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Outpatient Surgery
Osteoarthritis The Most Common Reason For A Swollen Knee
Osteoarthritis is by nature an inflammatory condition. As your arthritis worsens you may notice that the swelling is always present in the knee. Removing the fluid from an arthritic knee will usually make you feel better. Unfortunately for many arthritis sufferers, the swelling might return very rapidly.
If your knee is swelling due to Osteoarthritis, its implied that your cartilage or the cushioning within the knee joint is wearing thin. The arthritic process also changes the chemicals within the knee and creates a rather hostile environment within the knee joint. This causes the Synovium to become irritated and produce a significant amount of fluid. Occasionally that fluid will migrate to the back of the knee and cause swelling in the back of the knee. If you have a swollen area in the back of the knee it is likely a Bakers cyst.
What Does A Knee Injury Feel Like
Obviously, it hurts! But the type of pain and where you feel it can vary, depending on what the problem is. You may have:
- Pain, usually when you bend or straighten the knee
- Swelling
- Trouble putting weight on the knee
- Problems moving your knee
- Knee buckling or âlockingâ
If you have these symptoms, see your doctor. They will check your knee. You may also need X-rays or an MRI to see more detail of the joint.
You May Like: Inversion Table After Hip Replacement
Different Causes Of Knee Pain
It is possible to sustain a specific injury to any of the above parts of your knee joint from an accident, a fall, impact, a sudden forceful movement, whilst playing sport, or doing a simple task. Acute injuries are covered in our previous article, titled Torn Knee Ligaments.
However in this article I will explain some fairly common non-injury sources of knee pain and swelling..
I have arranged the conditions relating to where you would feel the pain the most: the front, back, inside or outside of your knee
Mildly Swollen But Painless Knee: Possible Cause
The most common cause of non-traumatic knee swelling is a misalignment of the large tibia bone that comprises the lower part of the knee joint, says Eugene Charles, DC, Diplomate of applied kinesiology and author of Journey to Healing: The Art and Science of Applied Kinesiology.
This frequently happens insidiously through daily activities where you turn your leg and foot out repetitively.
These subtle movements include getting out of a chair or car seat and going up stairs.
Over time the tibia bone rotates slightly out of alignment and needs to be realigned through a precise chiropractic or osteopathic adjustment.
Resting it only helps because you are not using it, but rest alone does not fix the underlying cause of the knee problem specifically the misalignment of the knee joint itself.
Recommended Reading: Does Aflac Cover Hysterectomy
How Can I Prevent Knee Pain
Although you canât prevent all injuries, you can take these steps to make them less likely.
- Stop exercising if you feel pain in your knee.
- If you want to make your workout more intense, always do it gradually.
- Stretch your legs before and after physical activity.
- Use kneepads to prevent bursitis, especially if you have to kneel a lot.
- Wear shoes that fit well and offer enough support.
- Keep your thigh muscles strong with regular stretching and strengthening.
- If youâre overweight, work to drop some pounds so thereâs less stress on all of your joints, including your knees.
Why Would A Teenager Have Knee Pain
Knee pain isnt a condition that only happens to older people. Despite being young, your teenager can develop knee pain too.
Knee pain in teens is a common result of overuse, but also results from specific knee injuries and medical conditions that affect the knee. Knee pain can also be temporary and not related to an injury, but rather a change in your teens level of activity or sport.
Because of the many different reasons for knee pain, if your teen complains of pain, its wise to get it checked. Never think that knee pain in your teen is simply growing pains. This is not a typical cause of knee pain in a teenager.
Read Also: Nano Knee Surgery Cost
Less Common Causes Of Knee Pain
Less-common causes of significant knee pain include conditions and injuries. Injuries include:
- Dislocated kneecap: Causes are sharp blows to the knee or twisting. Severe pain in the front of the knee plus buckling, slipping, or catching during movement.
- Kneecap fracture: Causes are a direct blow or falling onto the knee. Pain, difficulty straightening the leg, bruising, and swelling can occur. Sometimes there’s visible deformity.
Conditions include:
- Gout: High uric acid levels form sharp crystals inside the joint. Affects the knee, hip, fingers, and especially the big toe. Pain can be severe.
- Plica syndrome: Irritation of the synovium . Pain is in the middle and front of the knee. Worsens with inactivity or squatting, running, or kneeling. The knee may pop when bent.
- Osgood-Schlatter disease: Strikes after growth spurts in kids between 9 and 14. Pain is in the front of the knee. It improves with rest and worsens with activities like running and jumping.
- Osteochondritis dissecans: In children, lack of blood supply weakens the bone and cartilage. The knee may separate from the underlying bone. Causes pain with activity.
- Knee joint infection: Causes significant pain, swelling, warmth, painful movements, and fever. It may result from a bacterial infection in the bloodstream.
- Bone tumor: Very rarely the source of knee pain. Symptoms include fever, unintentional weight loss, and pain that’s worse at night.
Why Does The Knee Swell
A swollen knee is a common problem that affects people of all ages. Knee swelling typically indicates a problem somewhere inside the knee joint.
The knee has a joint capsule, which is like a sac that surrounds the whole joint. The capsule contains synovial fluid which nourishes and lubricates the joint so that it can move smoothly, think of it like the oil in your car. The joint capsule acts as container, keeping the fluid within the knee joint.
A swollen knee usually develops when excess fluid builds up inside the joint capsule and is caused by either:
- Bleeding in the Joint: aka Haemarthrosis. This is normally caused by an injury and the knee swelling comes on rapidly . The swelling can be intense making the knee feel very tight.
- Accumulation of Synovial Fluid: aka knee joint effusion or water on the knee. This type of swollen knee tends to come on gradually and may come and go, varying in degrees of severity.
Usually, knee swelling remains inside the knee joint as the joint capsule acts like a barrier, preventing the fluid from escaping. However, it can also occur outside the joint capsule, known as extra-articular swelling, such as with knee bursitis.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Get Rid Of Fat Around My Knees
Acute Onset Without Injury
Rapid onset of swelling with no injury is abroad category wherein the accumulation of fluid is not due to an injury or a chronic condition, such as:
- Infection can result in joint fluid accumulation, often as a result of surgery, a knee wound, or systemic infection that spreads to the joint. Treatment can be a problem as the body has a tough time clearing infection from this space. Surgery may be required to fully clean out a .
- Gout and pseudogout involve a buildup of crystals in the knee fluid. With gout, the uric acid used to transport waste can accumulate and crystallize in various joints of the body, causing intense swelling and pain. With pseudogout, the culprit is calcium crystals.
Can Knee Pain In Teens Be Prevented
Most knee pain that is caused by injury or overuse can be prevented with some attention and work by your teen, including:
- Make sure your teen wears proper shoes for the activity/sport and wears knee pads and leg guards . Replace worn out footwear and gear.
- Engage in muscle strength training exercises. Check with a trainer to make sure proper form and body alignment are being followed. Always do warm up and cool down exercises before and after workouts.
- Keep your muscles flexible by proper stretching exercises or yoga.
- Dont engage in activities that cause or worsen knee pain.
You May Like: Cellulite Above Knees
Not To Be Missed If You Have Pain Behind The Knee Or Back Of The Leg
- It is very important to note that pain at the back of your knee may be referred pain from your lower back. This referred pain would most likely be a poorly localized, dull ache, not related to knee movements, but aggravated by movements in your lower back So do be aware of that possibility
- Deep Vein Thrombosis may occur following surgery, a period of immobilization such as a long flight or time spent on extended bed rest, following an injury, in woman taking estrogen, or in obese patients. It may present as pain in the calf, or in the back of the knee. There may be some mild swelling, tenderness or skin discoloration. If you are worried you may have a DVT, speak to your doctor to arrange for further investigations such as a Doppler ultrasound.
Bursitis Could Be To Blame
Often confused with arthritis, bursitis is another condition that can cause swollen knees. Bursitis is a reaction in which sacks of fluids, blood vessels, and nerve endings that cushion your jointscalled bursaebecome inflamed, explains Dr. Gladstone. Typically, bursitis occurs across the front of the knees as a result of excess pressure and friction on the joint over time.
Those little blood vessels bleed and the bursa produces excess fluid, which creates this giant, swollen pouchlike a bubble of fluid just below the skin, Dr. Gladstone says. These inflamed pouches, which can take on all sorts of shapes and sizes, can be incredibly painful to put pressure on.
Bursitis is most common in people who work a lot on their knees, like carpenters, plumbers, and tile-setters, says Dr. Gladstone. However, a good fall can cause bursitis, too.
Don’t Miss: Ginger Poultice For Knee Pain
How To Treat A Swollen Knee At Home
In many cases, a mild to moderately swollen knee may be treated at home. Home care typically involves Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation and medication. Read the descriptions of these treatments below to help maximize their benefit and avoid mistakes.
The 4-step R.I.C.E. Formula
1.Rest will give the joint time to repair and recover. Take a break from sports and other activities for 24 hours or longer. The joint should not necessarily be immobile people with knee swelling should try to gently flex and straighten the knee several times a day to maintain range of motion.
2.Icing is an easy, effective treatment for excess knee swelling. Cold therapy can ease symptoms by:
- Causing nearby blood vessels to constrict, decreasing blood flow and inflammation
- Slowing down the production of joint fluid in the knee
- Distracting the brain from pain signals to the brain
Apply a cold compress to the knee for no longer than 20 minutes at a time. This can be done several times a day.
Ice should not be applied directly to the skin. Prevent skin damage by placing a towel or another material in between the icepack and skin. Cold therapy may not be appropriate for people who have Raynauds Syndrome or nerve damage.
See When and Why to Apply Cold to an Arthritic Joint
3.Compression involves wrapping the affected joint in an elastic bandage . Compression may help limit or reduce swelling.
Keep in mind that a compression bandage will not support the knee or protect it from further injury.