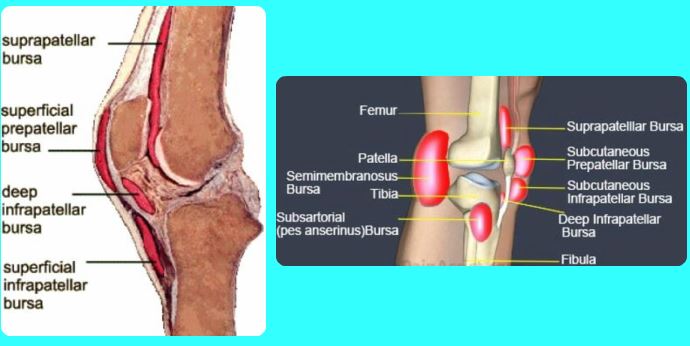
How Many Bursas Are There In The Knee
There are multiple bursas around the knee. The most important of them are the prepatellar bursa, infrapatellar bursa and pes anserine bursa. These are most commonly involved in the inflammation and the swelling. They can be caused due to daily activities like kneeling or may be caused due to pathology in the knee leading to bad biomechanics around the knee.
They can be treated usually with RICE that is rest, ice, compression and elevation along with anti-inflammatory medications. They can also be treated with cortisone shot if not improved. The patient should see a physician if the pain is not relieved with over-the-counter medications.
Recovering From Knee Bursitis
Bursitis knee symptoms usually settle within a few weeks with effective treatment. As mentioned, treatment varies depending on which bursa is affected, and you can find out more about the most common types of bursitis including treatment options and the recovery process:
- Infrapatellar Bursitis: below the knee
Common Types Of Knee Bursitis
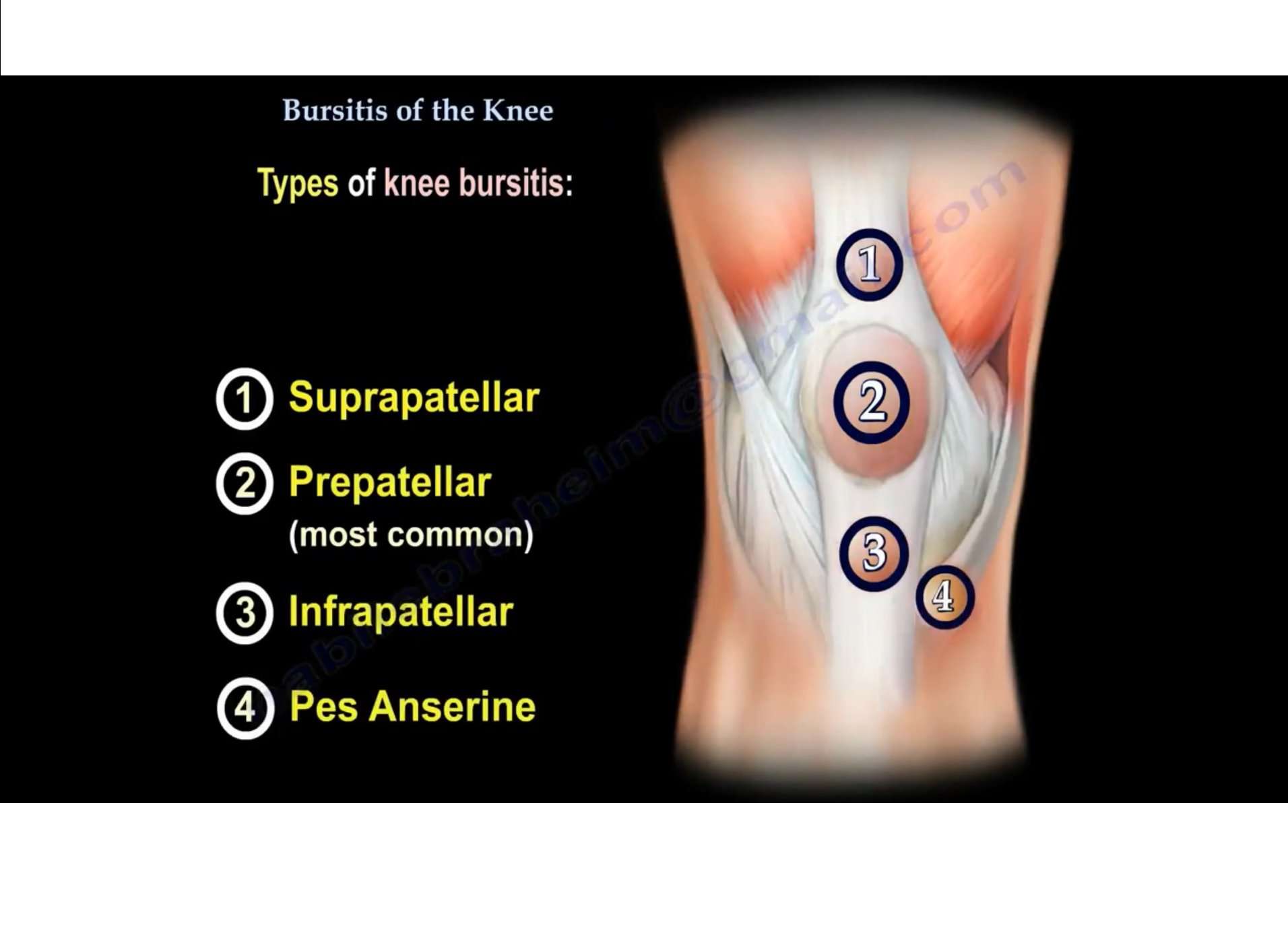
There are approximately eleven bursa located around the knee and bursitis can develop at any one of the bursa knee locations.
The five most common types of knee bursitis are:
1. Prepatellar Bursitis
The prepatellar bursa is found directly in front of the knee cap, just underneath the skin.
Irritation here is known as Prepatellar Bursitis, or more commonly Housemaids Knee, causing pain and swelling at the front of the knee.
It is a common problem for people who spend long periods kneeling e.g. carpet layers/roofers because of the continuous pressure going through the prepatellar bursa.
You can find out more about the common causes, symptoms and treatment options in the Housemaids Knee section.
2. Pes Anserine Bursitis
Pes Anserine bursitis occurs on the inner side of the knee. The pes anserine bursa sits between the medial collateral ligament and the conjoined medial knee tendons of the gracilis, sartorius and semitendinosus muscles.
Pes Anserine bursitis of the knee usually develops from overuse and most commonly affects runners.
You can find out more about the common causes, symptoms and best treatment options in the Pes Anserine Bursitis section.
3. Semimembranosus Bursitis
Semimembranosus bursitis causes pain and swelling behind the knee, often resembling a squashy orange, more commonly known as a Bakers Cyst or Popliteal Cyst.
The bursa sits behind the knee between one of the hamstring tendons, semimembranosus, and the gastrocnemius calf muscle at the back of the knee.
Also Check: What To Do When Your Knee Hurts Really Bad
What Is The Bakers Cyst On The Back Of The Knee
Bakers cyst is outpouching of the synovial lining of the knee joint. Occasionally when the patient has fluid in the knee, the fluid may track outside into this outpouching causing it to collect the fluid and swell up that can be felt as a soft swelling of the back of the knee. It is usually treated by the management of the pathology that causes the formation of the fluid as well as aspiration of the fluid from the knee joint. Rarely the Bakers cyst just needs a surgery to remove it.
When Should I See A Doctor For Knee Bursitis
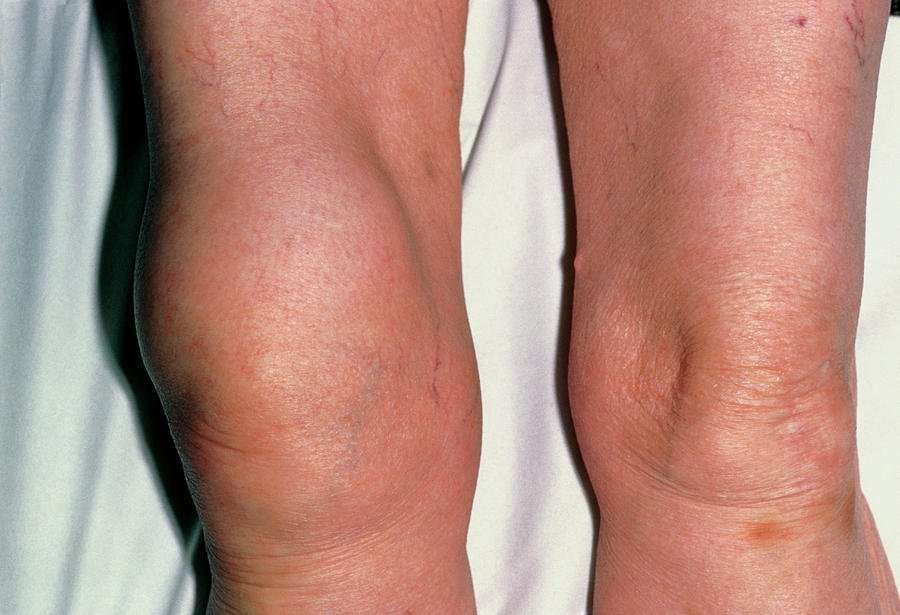
Are you experiencing an uncomfortable swelling in your knee or has the skin on your knee turned red and tender? You might have knee bursitis or inflammation of the knees bursa.
Knee bursitis can occur in any part of the kneeabove, below, or in the kneecap. Bursas are small fluid-filled sacs found in the knee joint. They prevent the various knee tissues from rubbing against each other, which can cause immobility and excruciating pain. When knee bursitis develops, a bursa becomes inflamed. Knee bursitis is typically a temporary condition, and you can recover completely after treatment.
Don’t Miss: What To Do To Strengthen Knees
What Causes Knee Bursitis
Bursitis in the knee is normally a result of either trauma due to an impact injury, overuse through work or sports or age related wear and tear. Another less recognized cause can be due to post operative irritation in the knee.
There are also certain jobs where individuals may be more susceptible to developing bursitis in the knee as they require long periods where kneeling on hard surfaces is required. These jobs may include carpenters, plumbers, gardeners and cleaners. In fact prepatellar bursitis is also known as housemaids knee.
Invasive Treatments For Bursitis
The most common invasive treatment for bursitis is a steroid injection into the gel-filled bursa sac. For serious bursitis that isnt helped by rest, physical therapy, or braces, this may be the best option. When you get a steroid shot for bursitis, the doctor first numbs the area with a topical anesthetic gel. This lessens the pain of the needle, which is inserted with a mix of fluid and steroid solution. Patients are not anesthetized for this procedure, and you will be able to leave the doctors office shortly after getting the steroid shot.
You May Like: Can You Repair Cartilage In Your Knee Naturally
Physical Therapy Guide To Knee Bursitis
Read Time:
Knee bursitis, commonly known as “housemaid’s knee” and “clergyman’s knee,” involves swelling of 1 or more of the bursae at the front of the knee. Knee bursitis is one of the most common bursitis conditions it can be painful when moving the knee, when kneeling, or even when at rest. The condition can also be painless, with only visible swelling present. Knee bursitis can have many causes. The most common is trauma, whether from a direct hit, or the result of activities that require crawling or kneeling on hard surfaces for long periods of time, such as laying carpet or tile, or scrubbing floors. Knee bursitis is most commonly seen in athletes up to 10% of runners develop knee bursitis. However, its occurrence is not related to any particular age or ethnic group, and can also be caused by infection or autoimmune conditions. Physical therapists treat individuals with knee bursitis to reduce their pain, swelling, stiffness, and any associated weakness in the knee or leg.
Physical therapists are movement experts. They improve quality of life through hands-on care, patient education, and prescribed movement. You can contact a physical therapist directly for an evaluation. To find a physical therapist in your area, visit Find a PT.
Bursitis Of The Knee: Recovery Time
How long does knee bursitis last? Recovery time varies significantly depending on the patient and treatment plan. Less severe cases may heal within a few weeks while more severe injuries may require a few months. Of course, surgery typically requires more recovery time, but mild symptoms can be managed and reduced over time rather quickly.
Bursitis of the knee can make it difficult to tolerate normal daily activities that require weight-bearing, like walking or standing. Luckily it is treatable, and a quick diagnosis and treatment is key to reducing its severity and keeping your life on track.
Don’t Miss: When To Go To Er For Knee Pain
What Are The Symptoms Of Housemaid’s Knee
Housemaid’s knee causes pain and swelling of the affected knee. You may notice redness of the skin over the knee and your kneecap may be tender. You may also have difficulty bending your knee and difficulty kneeling and walking. If housemaid’s knee is caused by infection, you may have a high temperature .
When Should I Seek Medical Advice
Most cases of bursitis improve without any treatment over a few weeks. See your healthcare provider if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Pain that interferes with your day-to-day activities.
- Soreness that doesnt improve despite self-care measures.
- Bursitis that comes back .
- Fever.
- Redness, swelling or warmth in the injured area.
For most people, bursitis is preventable. The first step is figuring out what movements caused the irritation. Then you can avoid those movements or find workarounds, like cushions or devices that can ease joint pressure. Take the necessary steps at home and get medical care, if needed, so you can regain pain-free use of your joint
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 05/29/2020.
References
You May Like: What Is Done In Knee Replacement Surgery
Causes Of Knee Bursitis
Common causes of knee bursitis include:
How To Treat Bursitis Yourself
To help bring down swelling and pain you can:
- rest try not to move the joint too much and avoid activities that put pressure on it
- use ice gently hold an ice pack wrapped in a tea towel on the area for around 10 minutes at a time and repeat every few hours during the day
- take painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, to ease any pain
It may also help to put extra cushions around the affected joint while you sleep, to help protect and support it.
Don’t Miss: Does Gout Affect Your Knees
Whats The Difference Between Arthritis And Bursitis
Arthritis and bursitis both affect the joints. But arthritis usually results from normal wear and tear on the cartilage, the smooth lining at the ends of bones. The damage is permanent.
In most cases, bursitis is short-term irritation. It doesnt create long-lasting damage unless you continue to stress the area.
Key Points About Bursitis
-
Bursitis is inflammation of a bursa, a closed, fluid-filled sac that works as a cushion and gliding surface to reduce friction between tissues of the body.
-
The most common causes of bursitis are injury or overuse, but it can also be caused by infection.
-
Pain, swelling, and tenderness near a joint are the most common signs of bursitis.
-
Bursitis can be treated with rest and medicines to help with the inflammation. Antibiotics are used if infection is found. If needed, surgery can be done to remove the bursa.
-
You can help prevent bursitis by doing things like warming up before exercise or sports, increasing activity slowly, padding joints, taking rest breaks often, and stopping activities that cause pain.
Don’t Miss: What Causes The Back Of Your Knee To Hurt
What Is The Bump Below My Knee
A bony bump just below the knee usually is a tibial tuberosity where the patellar tendon from the knee cap inserts. It acts as a point of stress because all the forces from quadriceps are passed through the patellar tendon on to the leg. It may be enlarged in patients of Osgood-Schlatter disease in which there is hypertrophy of the tibial tuberosity which is usually found in teenagers.
How Can You Prevent Bursitis
Because most cases of bursitis are from overuse, the best treatment is prevention. Its important to avoid or change activities that cause the problem. To prevent bursitis:
- Learn proper posture or technique for sports or work activities.
- Avoid sitting or kneeling too long. These positions put a lot of pressure on joints.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on joints.
- Use cushions and pads when you kneel or put weight on your elbows.
- Ease into new exercises or activities to avoid injury.
- Take breaks if youre doing a repetitive task.
Also Check: What Is The Best Running Shoe For Knee Pain
Treatment Of Kneecap Bursitis
Kneecap bursitis can be effectively treated with conservative therapy where your doctor advises sufficient rest, use of ice packs and elevation of the affected leg to reduce inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drugs may also be prescribed to alleviate pain and swelling, and antibiotics for infections. Sometimes the bursa may be aspirated with a thin needle to remove fluid and reduce swelling or corticosteroids may be injected at the region of the inflamed bursa to relieve pain. Surgery is performed only when conservative treatment is ineffective, which involves the surgical removal of the bursa.
What Are Knee Bursitis Symptoms
Early identification can help reduce the severity of bursitis and make it easier to control. Identifying symptoms of knee bursitis is very important for a speedy recoveryand for managing the injury without invasive treatments. Yet, many of these symptoms are common for other knee injuries as well. Here are common symptoms of bursitis in the knee.
- Noticeable swelling in the knee- especially when localized to one specific area in the knee
- Localized pain and tenderness
- Pain even during rest, which often increases during movement
You May Like: Can You Have Arthritis In Your Knees
Facts You Should Know About Knee Bursitis
- A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that functions as a gliding surface to reduce friction between moving tissues of the body.
- There are three major bursae of the knee.
- Localized swelling, warmth, and tenderness, as well as knee pain, often accompany bursitis of the knee.
- Bursitis is usually not infectious, but the bursa can become infected.
- Treatment of noninfectious bursitis includes rest, ice, and medications for inflammation and pain. Infectious bursitis is treated with antibiotics, aspiration, and surgery.
Braces For Bursitis Of The Knee
Fortunately, there are some very good products to help you get over bursitis. It does take awhile, like all joint issues dobut given time and good care, the pain of bursitis can be fully defeated. Today, I am pain-free, and I have stayed free of bursitis since that nasty episode. I used this high-quality bursitis knee brace, which can be found online and is easy to use. Its more comfortable than the other braces I tried, and it really made a difference for me. It’s specifically designed to soothe and support your knee as it heals from the damage of a condition like bursitis.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Strengthen My Knees
How Is Bursitis Treated
The treatment of any bursitis depends on whether or not it involves infection.
-
Aseptic bursitis. This inflammation results from local soft-tissue trauma or strain injury. The bursa is not infected. Treatment may include:
-
R.I.C.E. This stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation
-
Anti-inflammatory and pain medicines, such as ibuprofen or aspirin
-
Injection of a steroid into the affected area to help decrease pain and swelling
-
Splints or braces to limit movement of the affected joint
-
The bursa becomes infected with bacteria. This causes pain and swelling. Treatment may include:
-
Antibiotics
-
Repeated aspiration of the infected fluid
-
Surgical drainage and removal of the infected bursa. This is called a bursectomy.
Can This Injury Or Condition Be Prevented
Your physical therapist can recommend a home program to help prevent knee bursitis. It may include strength and flexibility exercises for the leg muscles.
To help prevent a recurrence of the injury, your physical therapist may advise you to:
- Avoid kneeling for prolonged periods of time.
- Use knee pads or a cushion when you do have to kneel, including during sports or other physically-challenging activities to protect your knee.
- Avoid hard hits or prolonged pressure to the front of the knee.
- Follow a consistent flexibility and strengthening exercise program, especially for the knee and leg muscles, to maintain good physical conditioning, even in a sport’s off-season.
- Always warm up before starting a sport or heavy physical activity.
- Gradually increase any athletic activity, rather than suddenly increasing the activity amount or intensity.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Dark Knees
How Is It Diagnosed
If you see your physical therapist first, your therapist will conduct a thorough evaluation that includes taking your health history. Your physical therapist also will ask you detailed questions about your injury, such as:
- How and when did you notice the swelling and/or pain?
- Have you been performing any repetitive activity?
- Did you receive a direct hit to the knee, fall on it, or kneel for a long period of time?
Your physical therapist also will perform special tests to help determine the likelihood that you have knee bursitis. Your physical therapist will gently press on the front of the knee to see if it is painful to the touch, and may use additional tests to determine if other parts of your knee are injured. Your therapist also will observe how you can move your knee, and test your strength and flexibility.
Your physical therapist will test and screen for other, more serious conditions that could cause knee pain or swelling. To provide a definitive diagnosis, your physical therapist may collaborate with an orthopedic physician or other health care provider, who may order further tests to confirm the diagnosis and to rule out other damage to the knee, such as a fracture or infection.
How Is It Treated
Home treatment is often enough to reduce pain and let the bursa heal. Your doctor may suggest physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles around your joints.
- Rest the affected area. Avoid any activity or direct pressure that may cause pain.
- Apply ice or cold packs as soon as you notice pain in your muscles or near a joint. Apply ice 10 to 15 minutes at a time, as often as twice an hour, for 3 days . You can try heat, or alternating heat and ice, after the first 72 hours.
- Use pain relievers. Use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , such as ibuprofen or naproxen, to reduce pain and inflammation. NSAIDs come in pills and also in a cream that you rub over the sore area. Acetaminophen can also help with pain. Don’t rely on medicine to relieve pain so that you can keep overusing the joint.
- Dorange-of-motion exerciseseach day. If your bursitis is in or near a joint, gently move the joint through its full range of motion, even during the time that you are resting the joint area. This will prevent stiffness. As the pain goes away, add other exercises to strengthen the muscles around your joint.
- Avoid tobacco smoke. Smoking delays wound and tissue healing.
If you have severe bursitis, your doctor may use a needle to remove extra fluid from the bursa. You might wear a pressure bandage on the area. Your doctor may also give you a shot of medicine to reduce swelling. Some people need surgery to drain or remove the bursa.
Recommended Reading: Why Is My Knee Hurting