Contact Medical Expert Today And Learn More About Free Private Treatments
There are a number of free private treatments which can be accessed across the UK for torn cartilage injuries in the knee including free provision of medical supplies and free professional physiotherapy programmes. With this free private physiotherapy treatment, the recovery time for torn cartilage in knee injuries may be shortened and your life can get back to normal once more. Contact Medical Expert on .
How Is Cartilage Damage In The Knee Diagnosed
Cartilage damage as a result of a forceful injury is often accompanied by other injuries particularly if you have wrenched or even a dislocated your knee, so its not always obvious what is causing your knee pain.
Even if you have cartilage damage due to wear and tear, the symptoms can be similar to many other knee conditions so its always best to get seen by a knee specialist.
The Capital Orthopaedics team is highly experienced at diagnosing knee conditions, starting with a history of your lifestyle or injury and a physical/biomechanical exam.
You will then be given x-ray or CT scans to assess damage to the bones in your joint, and an MRI to review cartilage damage and any other soft tissue injuries.
What Is Articular Cartilage
The matrix of cartilage is made up of collagens, proteoglycans, and non-collagenous proteins. While cartilage is a highly-organized structure, about 85% of cartilage is water. This decreases to about 70% of older people. Chondrocytes are the only cells found in cartilage and this produces and maintains;the cartilage matrix.
Articular cartilage serves as the cushion and shock absorber within the joint. It does so because it lines the ends of the two bones that form the joint.
Cartilage damage can be caused by several conditions including:
- Joint injury
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Joints affected by cartilage damage become painful, stiff, and have a limited range of motion.
Cartilage has a limited capacity to heal itself. Consequently, articular cartilage has become the focus of many researchers and tissue engineers who strive to be able to grow new cartilage and transplant it in place of damaged or worn cartilage.
Recommended Reading: How To Repair Knee Cartilage
Surgical Procedures For Knee Cartilage Restoration
Most cartilage restoration procedures can be performed arthroscopically, a minimally invasive surgery that involves making 3 small keyhole incisions around the knee joint using an arthroscope, a small flexible tube with a light and video camera at the end that enables your surgeon to view inside of the joints and perform surgery. In certain cases, open surgery may be required to access the affected area requiring longer incisions. Your surgeon will discuss the best surgical options for you based on your condition.
Usually, recovery from an arthroscopic procedure is much faster with minimal pain than a traditional, open surgery.
Some of the most common procedures for knee cartilage restoration include:
This Is How To Regenerate Your Knee Cartilage
Proper diet is vital in keeping your joints problem free, but it also has a crucial role in revitalizing hip, knee and spine cartilage.
Moreover, maintaining optimal weight reducing excessive physical strain every day will keep things on track to keep your knee cartilage healthy.
Symptoms of Damaged Knee Cartilage
In order for you to fully understand the importance of cartilage, especially in the knees, where it holds most of our weight, we need to explain its structure and function.
The cartilage is a type of connective tissue which prevents the bones from grinding against each other and helps their mobility. This means its role is to keep our bones from damaging.
It is part of many other bone structures in the human body, such as the nose, bronchi, ears, chest, and lines and creases of the spine, elbows, knees, hips. It can be almost as hard as bone, however not as elastic as the muscle.
Cartilage distortions can be caused by various factors such as aging process and various degenerative diseases such as osteoarthritis, which commonly affects the joints on your shoulders, neck , hip, knee, hand and foot joints.
Furthermore, there can be many other factors that can damage the cartilage, such as excessive physical activity, obesity, mechanical injuries of some kind of impact or carrying heavy loads.
The following are the best tips and natural remedies for cartilage regeneration on your hips and knees:
Rebuild the Knee Cartilage
Recommended Food for Cartilage Regeneration
Recommended Reading: What Is Nano Knee Replacement Surgery
Regrown Cartilage In The Knee
Patients have experienced regrowth of cartilage in knee joints changing the bone-on-bone situation, recreating the cartilage between the bones increasing the glide and removing the pain. The X-ray below shows the knee of a 70-year-old female who was experiencing extreme pain when walking because the cartilage had degenerated. The Curatron encouraged cartilage growth between the bones removing the need for a knee replacement.
Preparation For Knee Cartilage Restoration
Preoperative preparation for knee cartilage restoration will involve the following steps:
- A thorough examination by your doctor to check for any medical issues that need to be addressed prior to surgery.
- Depending on your medical history, social history, and age, routine blood work and imaging may be ordered for safely conducting surgery.
- You will be asked if you have any allergies to medications, anesthesia, or latex.
- You should inform your doctor of any medications, vitamins, or supplements that you may be taking.
- You should refrain from medications or supplements such as blood thinners, aspirin, or anti-inflammatory medicines for a week or two prior to surgery.
- You should refrain from alcohol or tobacco at least 24 hours prior to surgery.
- You should not consume any solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to surgery.
- Arrange for someone to drive you home as you will not be able to drive yourself post surgery.
- A written consent will be obtained from you after the surgical procedure has been explained in detail.
Read Also: Can You Run Again After Knee Replacement
Problems With Replacing Worn Cartilage
Unfortunately, a cartilage replacement procedure is not as simple a task as we would hope. Cartilage cells can be cloned and reproduced in a lab. The real problem comes up when we want to place those cells in a particular location;and get them to function effectively in that area. Cartilage is a complex tissue; in order for cartilage to function, it must be able to withstand tremendous forces. Simply injecting cartilage into a joint would serve no useful purpose, those cells would be destroyed in a short time.
The problem is that no one has been able to figure out a way for the body to accept new cartilage and allow the cartilage to adhere to the surface of the joint. Once on the joint surface, the cartilage must be able to support the weight of the body and glide smoothly to allow normal movements. Many scientists are working on ways to accomplish these goals, but there is no solution right now.
Role Of Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate
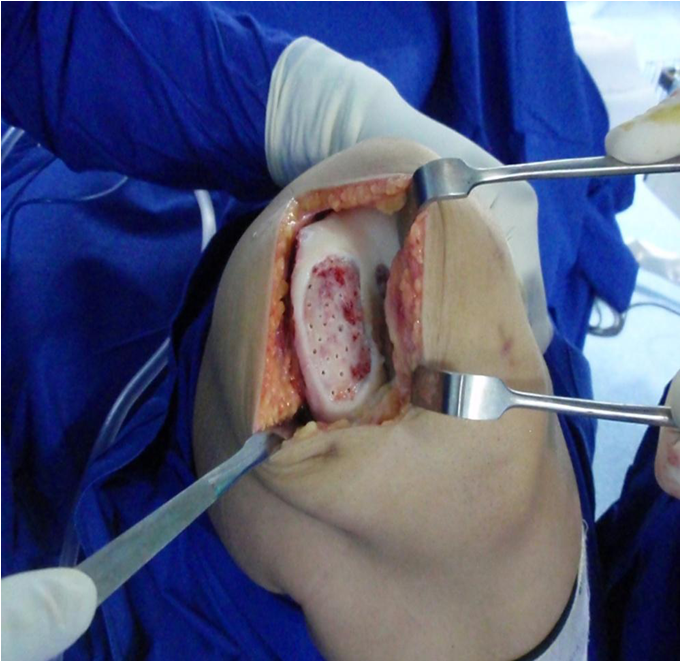
Recent studies demonstrated that marrow-derived stem cells secrete bioactive molecules that stimulate angiogenesis and mitosis of tissue-specific and -intrinsic progenitors and reduce T cell surveillance and inflammation, and some authors have also recognized that the presence of other nucleated cells is able to restore the damaged tissue.- The authors from Milan are performing a single-step surgery utilizing autologous BMAC containing MSCs and growth factors for cartilage repair in large osteochondral lesions measuring even up to 22 cm2 in size. In a prospective study, we followed up a group of 15 athletes operated on for grade IV cartilage lesions. The average size of the lesions was 9.2 cm2 . We harvested 60 mL of BMAC from the ipsilateral iliac crest using a dedicated aspiration kit and centrifuged using a commercially available system .3C). The cartilage defect was templated and the collagen membrane fashioned according to the defect size. Using Batroxobin enzyme , the BMAC was activated and produced a sticky clot material which was implanted into the prepared cartilage defect . Finally the defect was covered with a collagen membrane in order to protect MSCs .
Grade IV chondral lesion of patella, bone marrow aspiration, centrifugation, BMAC clot after activation, implantation and coverage with collagen scaffold, and biopsy at 2-year follow-up.
Don’t Miss: How To Avoid Knee Replacement Naturally
Why Choose Johns Hopkins
- Our team includes experts with years of experience in cartilage regeneration surgery a complex set of procedures who specialize in minimally invasive approaches.
- Our orthopaedic surgeons at Sibley Memorial Hospital approach cartilage regeneration surgery with cutting-edge technology, incorporating the latest methods into their practice.
- Not everyone is a good candidate for cartilage regeneration. These procedures are ideal for active people under age 55. Our experienced team will assess your condition and help you make an informed decision.
How Is Damaged Cartilage Regenerated
Cartilage is regenerated according to what food you eat.;One of the other most common conditions that affects the ankle, knee, wrist, elbow, and shoulder;cartilage is arthritis,;currently a very well-known disease that affects almost everyone older than forty.
For this reason, it is necessary to have proper nutrition so that cartilage tissue can regenerate quickly.
One of the most important;amino acids for the rapid regeneration of damaged cartilage is lysine. It is;responsible for;absorbing calcium and producing collagen that rebuilds damaged tissue.;It also improves appearance of your skin and strength of your tendons.
Read also:;Everyday Habits that Cause Knee Pain
Recommended Reading: What To Do If Your Knee Hurts
Originally Posted In Mayo Clinic News Network May 13 2017
DEAR MAYO CLINIC:;Im interested in a procedure approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration that can repair cartilage in the knee. How does it work? Whos a good candidate for this procedure?
ANSWER:;The new technique is called matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte implantation, or MACI. It can be effective for repairing isolated cartilage damage in the knee, but its not useful for people whose knee cartilage is diffusely damaged due to arthritis.
Your knee has two kinds of cartilage: the articular cartilage and the meniscus. Matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte implantation is used to repair articular cartilage damage, which can come from an isolated injury or defect, or as a result of arthritis.
Of these two problems, isolated injuries and defects are much less common than;arthritis. They usually happen due to an athletic injury or another medical condition, such as;osteochondritis dissecans. Both isolated cartilage defects and arthritis have similar symptoms, including knee pain, swelling and loss of motion.
With matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte implantation, the new cells are grown on a membrane scaffold in the lab. Thats different than the cartilage repair techniques previously used. In the older approaches, cartilage cells were grown in a lab and implanted into the knee under a patch created from a membrane taken off the outer surface of a bone, called the periosteum, or implanted under a membrane made of collagen.
Vitamin D And Osteoarthritis
Vitamin D is crucial for the development and maintenance of healthy bones. Adequate amounts enable proper absorption of calcium, which is necessary to support the structure and function of bones and teeth. It may also play a role in the prevention and treatment of cartilage deterioration, although using vitamin D for joint pain is unlikely to have immediate or verifiable results.
According to authors of a research review published in the Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine in June 2017, vitamin D levels play a role in the development and progression of osteoarthritis. Their findings show that people with osteoarthritis typically have low levels of the nutrient, while individuals with sufficient blood levels have a lower risk of developing the condition and the associated cartilage degeneration.
The recommended daily intake for vitamin D is 600 international units for all adults. NIH reports that there are few dietary sources of vitamin D, which can make it difficult to get adequate amounts through diet alone. Your body can synthesize vitamin D from reactions within the skin when exposed to UVB rays from the sun. But due to widespread sunscreen use and less time outdoors, many people aren’t meeting the requirement.
You can increase your vitamin D stores by eating more fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna, and fortified milk, juice and cereal. If you think you are not meeting your vitamin D needs, speak with your doctor about whether you need a supplement.
Read Also: Why Does My Knee Click When I Walk
Eat Fruits Nuts And Dairy
Fisher-Titus Medical Center also recommends that your knee cartilage repair food plan includes creamy avocados. These tasty fruits are loaded with essential fatty acids and antioxidant-rich oils, both of which help combat joint inflammation and facilitate cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis patients might find this versatile fruit especially helpful.
Beneficial fruits also include grapefruit, which is rich in bioflavonoids and vitamin C. These nutrients team up to strengthen cartilage and fight inflammation. Choose red grapefruit as it contains more antioxidants compared to the yellow variety. These refreshing fruits are also foods good for the joints and cartilage.
Compact little berries pack a big antioxidant punch too. Raspberries, cherries and elderberries contain anthocyanins that help knock down various chemicals associated with inflammation. If you suffer from gout, consider noshing on black cherries, which may help prevent that painful condition.
Add more anti-inflammatory foods, such as extra-virgin olive oil and walnuts, to your meal plan. Brazil nuts are packed with selenium, a mineral that may improve the quality of cartilage protein. Yogurt and kefir are rich in probiotics that may help relieve rheumatoid arthritis joint inflammation.
Read more:14 Inflammation-Fighting Foods to Eat Every Day
Vitamin D For Bones Joints And Cartilage
A study distributed under the title Arthritis and Rheumatism affirms that daylight and vitamin D frankly contributed to better joint mobility.
Outcomes of the study demonstrated that its important to bring a necessary quantity of vitamin D in the body if we want to prevent the occurrence of osteoarthritis. We can find Vitamin D in milk, bread, oats, and in greasy fish, for example, salmon, herring, and in oysters.
Foods that are rich in vitamin D can stimulate the cartilage renewal on the knee and hip.
Recommended Reading: What Does Constant Knee Pain Mean
What Causes Cartilage Loss In Your Joint
To fully understand why cartilage loss can be such an issue, you first have to understand why its important. Cartilage is the tissue that covers the ends of your bones where they meet together in your joint. It allows the bones to glide over each other smoothly and fluidly.
If your cartilage has worn away, your bones wont be able to move as smoothly and in severe cases can cause bone on bone friction and intense pain. This may also cause you to have swelling, stiffness, or grinding in your joint. There are three main reasons that you may experience loss of cartilage, including:
Build Knee Cartilage Naturally
If you’re searching for ways to reduce your knee discomfort, Dr. Lars Richardson, an orthopedic surgeon with Harvard Medical School-linked Massachusetts General Hospital, describes a three-part strategy that may help.
First, he recommends that you drop some weight. If you’re packing some extra pounds, each added pound means you’re exerting four pounds of pressure on the joints.
To accomplish that goal, follow a well-balanced diet that includes foods good for the joints and cartilage. Engage in low-impact exercise regularly. After you lose those pesky pounds, your joints will experience decreased pressure and pain. Dr. Richardson notes that when your body mass index reaches a healthy range, your knees should feel the benefits.
Next, partner up with a physical therapist to develop a muscle-strengthening program that results in better knee function. Target your body’s core muscles along with the hip, quadriceps and hamstrings. With stronger muscles supporting your knees, they won’t feel as much stress, and your knee joint will be better stabilized.
Work with your physical therapist to improve your knee’s range of motion. By working to straighten your knee and achieving better overall motion, you’re likely to experience fewer troublesome symptoms, Dr. Richardson points out.
Read more:Exercises That Improve Muscular Strength
Read Also: Is It Possible To Regenerate Knee Cartilage
Foods That Help Your Joints
Eating foods good for joints and cartilage may help relieve the symptoms of arthritis and other inflammatory conditions, including osteoarthritis and gout. In some cases, you might even be able to prevent or delay their progression.
Miriam E. Nelson, Ph.D., of Tufts University, states that eating to protect your joints can potentially reduce painful inflammation and annoying stiffness. By adding exercise to a healthy diet, you’ll likely lose weight, which also helps ease the stress on your hip and knee joints. Even a small reduction in body weight is a step in the right direction.
Per Dr. Nelson, you should consume one or more servings of fish, nuts, soy and legumes each day. Limit meat, eggs and poultry to two servings daily. Add three servings of vegetables, three servings of fruits and four to nine servings of starches, with at least half from whole grain sources.
Between two and three servings of reduced-fat milk, cheese and yogurt cover the dairy category. Omega-3 oils are very desirable, but you should limit all other oils and fats. It’s also advisable to limit your consumption of sugary foods.
Dr. Nelson’s recommendations are based on smaller size “servings” rather than heaping portions that often fill diners’ plates. Also, making these healthy foods a priority means your plate won’t have much room for calorie-packed processed foods that don’t provide much nutrition. These principles also provide a good foundation for an osteoarthritis diet.
How Long Is The Recovery Period After Surgery
The best results are in patients who follow the rehabilitation guidelines well. Following the surgery, the area that has been treated must be protected using a brace, crutches and protected weight-bearing for six weeks followed by a rehabilitation process going on for up to six months or more. Cartilage cells are slow-growing and can take up to 18 months to fully form new cartilage. Therefore, strict adherence to rehabilitation programmes is very important.
Mr Barkatali performs all types of knee surgeries with the latest techniques. To find out how he can help you and to arrange your appointment, visit his profile click;here.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Black Knees