Calf Or Hamstring Strain Or Cramp
Sudden activity and overuse are two leading causes of pain behind the knee due to a calf or hamstring strain or cramp, according to Dr. Tanaka. Movements that require pushing off or severe knee bending cause this calf and hamstring pain, respectively. Both can be managed with ice, rest, gentle stretching, and anti-inflammatories; however, one should seek care if there is swelling or persistent pain associated with this to rule out blood clots, Dr. Tanaka says. Dr. Lyons adds that although an orthopedist could treat this, if you cant bear weight on the knee or are at risk of falling, then its time to go to the emergency room. Heres what else could be causing pain in your calf.
Posterolateral Corner Injury Causing Behind The Knee Pain
Experiencing stiffness and pain behind the knee could be due to injuries to the delicate structures in the knee. These types of injuries are referred to as posterolateral corner injuries.
According to the journal Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia, PLC injuries are common if the ligaments of the knee have been damaged by trauma. This can result in severe pain and inability to put pressure or weight on the damaged knee. In some cases, PLC injuries occur without damaging any of the knee ligaments.5
How Common Is Gout In The Knee
As a general rule of thumb, if left untreated, gout tends to work its way up the body, Dr. Keenan explains.
For example, he cites research that shows 50 percent of patients experience their first gout attack in the big toe. If gout worsens, 35 percent of secondary flares occur in the knee, 40 percent in the midfoot and ankle, 30 percent in elbows and wrists, and 15 percent in fingers.
Its not uncommon for a person to experience their first gout flare in their knee and, after an X-ray or ultrasound, show signs of gout in the foot, he adds.
Gout can afflict both knees, but typically is felt more strongly in one knee where arthritis from general wear is worse.
Recommended Reading: What Does It Mean When Your Knees Crack
How Are Knee Problems Diagnosed
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, other tests for knee problems may include:
-
X-ray. This test uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging .;This test;uses;large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body; can often determine damage or disease in a surrounding ligament or muscle.
-
Computed tomography scan .;This test uses;X-rays and computer technology to make horizontal, or axial,;images of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
-
Arthroscopy.;A minimally-invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used for conditions of a joint. This procedure uses a small, lighted, optic tube , which is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen; used to evaluate any degenerative or arthritic changes in the joint; to detect bone diseases and tumors; to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation.
-
Radionuclide bone scan.;A nuclear imaging technique that uses a very small amount of radioactive material, which is injected into the patient’s bloodstream to be detected by a scanner. This test shows blood flow to the bone and cell activity within the bone.
What Causes Pain Behind The Kneecap
Pain behind the kneecap is usually caused by a problem with the cartilage that lines the back of the kneecap. It may be Runners Knee, where a problem with how the kneecap glides causes friction and pain behind the kneecap.
In teenagers, pain behind the kneecap is often caused by Chondromalacia Patella, a condition where there is thinning of the cartilage on the back of the kneecap.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Best Volleyball Knee Pads
Diagnosis Of Knee Pain
Doctors may examine the knee movement and local signs of inflammation during physical examination. The following imaging tests are often ordered to identify the cause .
- X-ray imaging of knee joint helps to visualize degenerative joint diseases and fractures.
- Computed tomography scan may help visualize subtle fractures and gout.
- Ultrasound imaging of the knee helps to look at the soft tissues around the knee.
- Magnetic resonance imaging may also be used to visualize soft tissues, such as tendons, ligaments, cartilages, and muscles in the knee.
- Blood tests may help to identify infection or inflammation markers.
- Arthrocentesis involves needle aspiration of synovial fluid from the knee joint and its laboratory analysis.
Blood tests, X-rays, and physical examination of knee flexibility, range of motion, and strength may often confirm the diagnosis. Other tests are usually ordered if these examinations are not enough for diagnosis.
How To Identify The Culprit And Which Drugs Injections And Habits Will Bring You The Most Relief
by Alison Gwinn, AARP, September 20, 2019| 0
En español | Oh, my aching knees! If that’s your daily refrain, whether you’re walking the dog, climbing stairs or just sleeping, you’re not alone.
For many, the culprit behind that nagging soreness is osteoarthritis, which affects an estimated 31 million Americans quite often, in this particular joint according to the Arthritis Association.
But there are other common causes of knee pain, stemming from the fact that knees are our largest, most complex joints. Knee joints allow you to stand up straight, walk stairs and get up and down from sitting, says Daniel Saris, an orthopedic surgeon at the Mayo Clinic and professor of orthopedic surgery at the Mayo Medical School. But they are also the most difficult joint because they’re not stable. Hip joints and ankles are both pretty stable by themselves, but the knee is just three bones trying to be good friends, and they need muscles and ligaments for stability.”
Knee pain is not to be taken lightly. A Japanese study, published last year in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, found a link between the onset of knee pain in people 65 or older and depression. And a recent study from the University of North Carolina School of Medicine Thurston Arthritis Research Center and Harvard’s Brigham and Women’s Hospital found that knee pain in men and women over age 45 correlated with higher rates of death.
Don’t Miss: How To Whiten Knees And Elbows
Osteoarthritis And Pain In The Back Of The Knee
Osteoarthritis is a widespread cause of pain behind your knee. ;Some of you might also note that you have a loss of motion and can not fully bend the knee. ;The pain from arthritis can be due to inflammation of the structures behind the knee. ;That irritates the lining or inside of the knee joint and makes the joint stiff and painful. ;
;If osteoarthritis is causing pain in the back of the knee you might note that the pain can refer up the back of the thigh, or down into the calf. ;Many of you with arthritic knee pain will benefit from wearing a compression sleeve or brace. ; You will also find that gentle stretching, an ice pack, or a warm compress can help calm arthritic pain. ;
If the pain does not improve over a few days, consider seeing your doctor to look into why the back of your knee hurts.
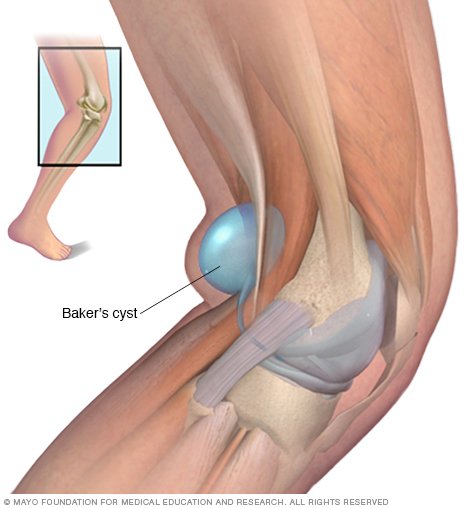
How Is A Bakers Cyst Treated
Treatment of a Bakers cyst usually starts with nonsurgical options. One time-honored method that sports doctors and orthopaedic surgeons have relied on for decades to soothe swelling from joint damage is the RICE method: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation.
Nonsurgical treatment.
Often, your healthcare provider will suggest that you start with a nonsurgical treatment of your Bakers cyst. These are generally things you can do at home and on your own that can improve your symptoms.
Nonsurgical treatment options can include the RICE method:
- Resting your leg whenever possible.
- Applying ice to your knee.
- Using compression wraps on your knee to decrease the amount of joint swelling.
- Elevating your knee while you are resting.
Other nonsurgical treatment options for a Bakers cyst can include:
- Taking an anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen.
- Maintaining a healthy body weight, which can help put less pressure on your joints.
- Avoiding activities that strain your knee. This includes avoiding high-impact sports like jogging.
- Using a crutch or cane when you walk.
- Getting a referral for physical therapy from your healthcare provider to help strengthen your knee and body.
Your healthcare provider may also give you a steroid injection. This involves cortisone being injected into your knee joint, which can reduce inflammation and pain.
Surgical treatment.
Your provider might suggest a surgical option to you if:
- Your knee pain is severe.
- Youre unable to move your knee well .
Read Also: How To Exercise With Knee Pain
How The Spine Causes Knee Pain
The nerve roots that transmit the sensation of pain to the legs and feet are located in the lower back. Occasionally with age or injury, the discs between the vertebrae can degenerate or bulge out and press on these nerves.
When this occurs, the nerve becomes irritated and sends out pain signals. The location of the pain depends on which disc is protruding.
The severity of the pain depends on how much of the disc is pressing on the nerve. The nerves that send fibers to the knee are located at the second, third, and fourth lumbar vertebral levels in the lower back area.
If a bulging disc, bone spur, or arthritic joint in the second, third, or fourth lumbar vertebra compresses a nerve, the referred pain will often be felt in the knee.
Referred pain;is;pain;perceived at a location other than where the cause is situated. It is the result of pain signals being sent along the network of interconnecting sensory nerves.
This condition can be diagnosed by your physician with a thorough history and physical exam. If the nerve that travels to your thigh and knee is irritated or pinched, you may feel a host of symptoms, including:
- Pain in the front of your thigh
- Knee pain
- Numbness or tingling in your thigh
- Weakness in your hip or quadriceps muscles
If you have any of these symptoms, see a doctor. In some cases, the hip may be the culprit, so a careful examination is necessary to find the true cause of your knee pain.
Muscle And Tendon Conditions
The shallow depression formed at the back of the knee is called the popliteal fossa; it is formed at the junction of the femur and tibia. There is a muscle here on the floor of the popliteal fossa which is the deepest muscle of the knee joint. It works on the femur to rotate it on the tibia when walking. Through the popliteal depression a bundle of muscles run from the pelvis to the knee and attach to the tibia and fibula respectively by tendons. These three muscles are collectively called the hamstring muscles, and function to extend the leg and bend the knee.
At the back of the lower leg the calf muscles are composed of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles which flex the leg at the knee and flex the ankle via the achilles tendon.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Your Knee To Stop Hurting
Blood Clots Behind Knee
It is important to note that pain and swelling behind the knee may be associated with blood clots. Blood clots behind the knee are especially common for those on bed rest or prolonged laying down, recovering from surgery or who have experienced trauma to the knee. Age and weight may also be a factor in blood clots. If you are experiencing behind knee pain, see a doctor to diagnose your situation, especially as you may be experiencing a blood clot behind knee.
Urgent Advice: Get Advice From 111 Now If:
- your knee is very painful
- you cannot move your knee or put any weight on it
- your knee is badly swollen or has changed shape
- you have a very high temperature, feel hot and shivery, and have redness or heat around your knee this can be a sign of infection
111 will tell you what to do. They can tell you the right place to get help if you need to see someone.
Go to 111.nhs.uk or .
You can also go to an urgent treatment centre if you need to see someone now.
They’re also called walk-in centres or minor injuries units.
You may be seen quicker than you would at A&E.
Read Also: Can Cortisone Shots Help Knee Pain
Managing Pain Behind The Knee
You can help yourself by keeping weight off your leg as far as possible, using an ice pack and taking painkillers, such as ibuprofen. If you cant put weight on your leg, you may need crutches.
Popliteal cysts often get better on their own and you may not need any further treatment. But its a good idea to see a doctor if you have pain behind the knee. It may be something more urgent . With posterior cruciate ligament injury, you can develop complications later if you are not treated. You should see a doctor if:
- you cannot put weight on the affected leg
- you have severe pain, even when not bearing weight
- your knee buckles, clicks, or locks
- your knee is deformed or misshapen
- your knee is hot, red or very swollen or you have a fever
- you have pain, swelling, numbness, tingling, or a bluish discoloration in your calf
- youre still in pain after three days
Sciatic Nerve Links The Back To The Legs
The most common back ailments that cause pain in the knees are related to the sciatic nerve. If you have back pain and feel a shooting sensation originating from your lower back running down your leg and through your knee, your sciatic nerve is to blame.
As the longest and largest nerve that runs through the body, the sciatic nerve if damaged or compromised can cause debilitating pain. The condition is called sciatica, and it is often the byproduct of a degenerative nerve condition or an injury .
When any part of the spine puts pressure on the sciatic nerve, the result may be shooting pain or a tingling sensation that travels from the back down to your hips, buttocks, knees, and feet.
Read Also: What Causes Gout In The Knee
The Link Between Your Back And Knee Pain
Every part of your body has a special and unique function, but each part relies on others for optimal performance.
When your body is functioning well, you feel invincible. When you are falling short due to an injury or illness, its hard to function. The same is true with many interacting body parts. One connection, in particular, is when back pain causes knee pain. Even though the back and knee arent directly connected, there is a very real link that can help explain why when your back hurts, your knees may hurt, too.
I Only Have Pain Behind My Knee When Walking Up Or Down The Stairs What Should I Do
The act of walking up and down stairs involves straightening the knee whilst it is bearing weight, and the the most common cause of pain in this case is chondromalacia patella. This condition is brought about by the cartilage on the underside of the kneecap deteriorating and softening. Some people can ignore the condition, but in the end it will probably need to be surgically addressed. It may be that a flap of cartilage has become unstable, in which case it can be treated by a chondroplasty, repairing the damaged cartilage using keyhole surgery.
Recommended Reading: What Does Cortisone Do For The Knee
Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries
The posterior cruciate ligament plays a similar role to the ACL, though it is less likely to become injured than the ACL.
PCL injuries may happen during traumatic events, such as falling directly onto the knee from a height or being in a vehicle accident. With enough force, the ligament may tear completely.
PCL injuries cause symptoms such as:
- knee pain
- stiffness in the knee if bending
- difficulty walking
- swelling in the knee
Completely resting the knee may help a PCL strain heal. However, a severe PCL injury may require surgery.
What Are Some Common Knee Problems
Many knee problems are a result of the aging process and continual wear and stress on the knee joint . Other knee problems are a result of an injury or a sudden movement that strains the knee. Common knee problems include the following:
ACL Tears in Female Athletes: Q&A with a Sports Medicine Expert
Sports injury prevention isn’t a one-stop shop, especially for injuries like ACL tears, which are four to eight times more common among women than men. Discover ways for women to help prevent this common injury.
Don’t Miss: Why Does My Knee Keep Popping Out Of Place
Complementary And Alternative Therapies
A number of mind-body therapies, such as acupuncture and tai chi, may be used to treat knee pain, especially knee osteoarthritis.
While once popular, the dietary supplements glucosamine and chondroitin have fallen out of favor for treating knee osteoarthritis. This is due to their lack of benefit based on scientific studies; although, some people may obtain mild relief. Like any medication, vitamin, or supplement, be sure to talk with your doctor first before taking it to be certain it is safe for you.
If You Feel Pain Behind Your Knee When Bending Or Squatting:
You may be feeling a symptom of Patellar Tendonitis . This is caused by repetitive activity like kicking, jumping or running. The repetitive exercise puts a lot of strain on the tendon resulting in tiny tears and inflammation along the patellar tendon. Other symptoms include pain just below the kneecap, pain with any pressure to the knee, aching and stiffness after activity, knee stiffness in the morning and thickening of the patellar tendon.
Also Check: How Do They Do Knee Replacement Surgery