Time Frame: Recovery From Hyperextended Knee Injury
A mild hyperextension of the knee may require only two to four weeks to heal. Rest and physical therapy will be the primary modes of treatment, and knee pain medicines may be prescribed. A knee that has experienced a ligament tear during the injury may require surgery and will likely require physical therapy and six to nine months of convalescence before returning to athletic activity.
Treatment For Severe Cases
In more extreme cases, a hyperextended knee will require surgery to fix the ligaments or alignment of the knee.
A torn anterior cruciate ligament is the most common complication, but other tendons and structural supports can be damaged. The ACL is a pair of ligaments in the knee.
It is possible that multiple areas of the knee will require surgery to repair.
What Is The Treatment Of A Hyperextended Knee
Typical treatment of a hyperextended knee is based on the RICE principle, which includes:
- Rest: The activity that caused the hyperextended knee must be immediately stopped, and the knee should be rested. Its necessary to seek medical assistance. High-intensity activities and contact sports must be completely avoided during rest. The doctor may give anti-inflammatory medications and pain medications to help reduce swelling and pain.
- Ice: A piece of ice placed inside a small towel or piece of cloth should be applied to the affected knee for up to 15 minutes several times a day to reduce swelling and get some relief from pain.
- Compression: Wrapping the knee with a compression wrap or elastic support bandage reduces swelling and pain.
- Elevation: Elevate the injured knee above the heart whenever possible. This can be done by lying down on a bed with the leg resting on a pillow or comfortable support.
Treatment of severe cases of a hyperextended knee
- Surgery: Although surgery is less common, in severe cases, a hyperextended knee can result in tendon tear, tissue damage, or misalignment of the knee that requires surgical repair. Common surgical procedures include:
- Arthroscopy: Arthroscopic surgery involves inserting a small endoscopic camera through a small incision to get a clear view of the affected area and repair knee damages.
- Reconstruction: Reconstructive surgery may be performed to repair tissue damage caused by a hyperextended knee.
Prevention of a hyperextended knee
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Dark Spots On Your Knees
Treatment For Less Severe Cases
Most of the hyperextended knee cases that occur on the sportsfield are treatable without surgery. The depth of care depends from case to case, but the following elements are normally helpful:
Getting plenty of rest with your leg elevated is a must. Youve got to give the ligaments enough time to heal. For minor cases, recovery time can be between 2-4 weeks.
Ice and compression should be part of your treatment. They speed up the healing process and provide relief from the pain and inflammation.
If the pain is too much to bear, you can take over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen.
You may benefit from the use of a knee brace while you get back on your feet. Knee braces help prevent further injury.
You should definitely consider a chiropractor. Contrary to popular belief, chiropractors arent just for your spine. A chiropractor who works with all joints can be of invaluable assistance.
The Anatomy Of The Knee
As shown in figure 4a, there is no bony stop at the back of the knee, as there is in the elbow joint. The ligaments, joint capsule, and tendons restrict posterior movement. One study found that 85% of the stress pulling the tibia forward is absorbed by the ACL. Another study, however, found that the oblique popliteal ligament was the main ligament preventing hyperextension of the knee, contributing about 37% of the resistance. This latter study began with the complaint that a primary stabilizer against knee hyperextension has not been identified.
FIGURE 4. The ligaments of the knee: anterior/lateral oblique view . The plateau at the top of the tibia is angled downward from front to back.
Also Check: Can Knee Replacement Cause Neuropathy
Causes Of A Hyperextended Knee
Hyperextension typically occurs when the knee absorbs strong, sudden force while the leg is straightened. This can happen for a variety of reasons:
- During activities such as basketball or sports that involve a lot of jumping and changes in direction at high speeds
- During sports that revolve around flexibility such as gymnastics
- During a car accident when the knee is smashed
- Falling while the foot is caught
- Having weak quad muscles unable to support the knee
- Instability of the knee joint from previous ligament injuries
What Causes Hyperextended Knee
Youre probably wondering why do you get hyperextended knee?
Your knee hyperextends, or goes beyond its appropriate range of motion, when inordinate stress is placed on your knee joint ligaments. The most commonly affected ligaments are anterior cruciate ligament and the posterior cruciate ligament .
The kind of force strong enough to provoke hyperextended knee is usually related to sports and accidents.
Contact sports like football and lacrosse are common culprits. But even running can lead to hyperextended knee if you push yourself beyond your limits or dont use proper technique.
Many times, hyperextended knee incidents are caused by an athlete unexpectedly placing all their weight on one leg. This can happen in basketball, for instance, when he goes to make a shot.
Naturally, the impact of being tackled in football or rugby can be enough to push the femur over the patella in a way that puts excess stress over the ligaments in your joint.
The most serious cases of hyperextended knee typically happen during car accidents. Automobile collisions are massive impacts that can cause major damage to your knees surrounding tissue and cartilage.
Also Check: Knee Brace Support Meniscus
What Is A Hyperextended Knee
Mayo Clinic explains that you sustain a hyperextended knee when the knee lands improperly and gets bent backward, damaging the ligaments, cartilage and other stabilizing structures. An especially bad hyperextension can even result in an injured anterior cruciate ligament . Penn Medicine adds that a hyperextended knee can also refer to an injury of the posterior cruciate ligament .
Read more:How to Strengthen Tendons and Ligaments
These injuries can be partial or complete tears or stretches. Knee injuries like hyperextensions are troubling because, depending on the severity, they could last anywhere from a few weeks to a year, according to Harvard Health Publishing. In some cases, such as severe injuries where the ligament is completely torn and the knee is unstable, a patient might require surgery.
However, Harvard Health Publishing notes, a mild or moderate injury can usually be treated with RICE and a rehabilitation program provided by a doctor or therapist. In fact, 80 percent of people with PCL injuries can fully recover with the help of a physical therapy program.
How Do You Diagnose A Hyperextended Knee
Typically an MRI and/or x-rays are performed. In some cases, imaging will not need to be used for a doctor to diagnose an athlete with a hyperextended knee. If, however, surgical intervention is expected to be used as treatment, imaging will be necessary in order to develop plans for the procedure and recovery.
You May Like: What Is Chondrocalcinosis Of The Knee
Does Hyperextension Cause Injuries
Researchers are quite divided as to whether hyperextension of the knee predisposes us to injury. While everyone with lax knee ligaments hyperextends, not everyone who hyperextends has lax ligaments. Despite the view in the yoga community that the 180° alignment of the knee is ideal, allowing the knee to be slightly hyperextended is actually necessary for human bipeds.
Even though it sounds negative to lock the knees and hang out in the ligaments when we stand, we reduce muscular energy therebyallowing the ligaments, rather than the muscles, to do the work of supporting our posture. Our species evolved to do this. Walking chimpanzees expend far more energy than walking humans, because the chimps have to keep their knees constantly bent. Humans can extend the knee, and this saves on calories.
We hyperextend around 5° when we walk, which is, not surprisingly, right around the amount that average people can do. If we did not slightly hyperextend the knees while standing or walking, the quadriceps would be constantly working to hold our posture, which would be tiring and could lead to chronic shortening of the quadriceps.
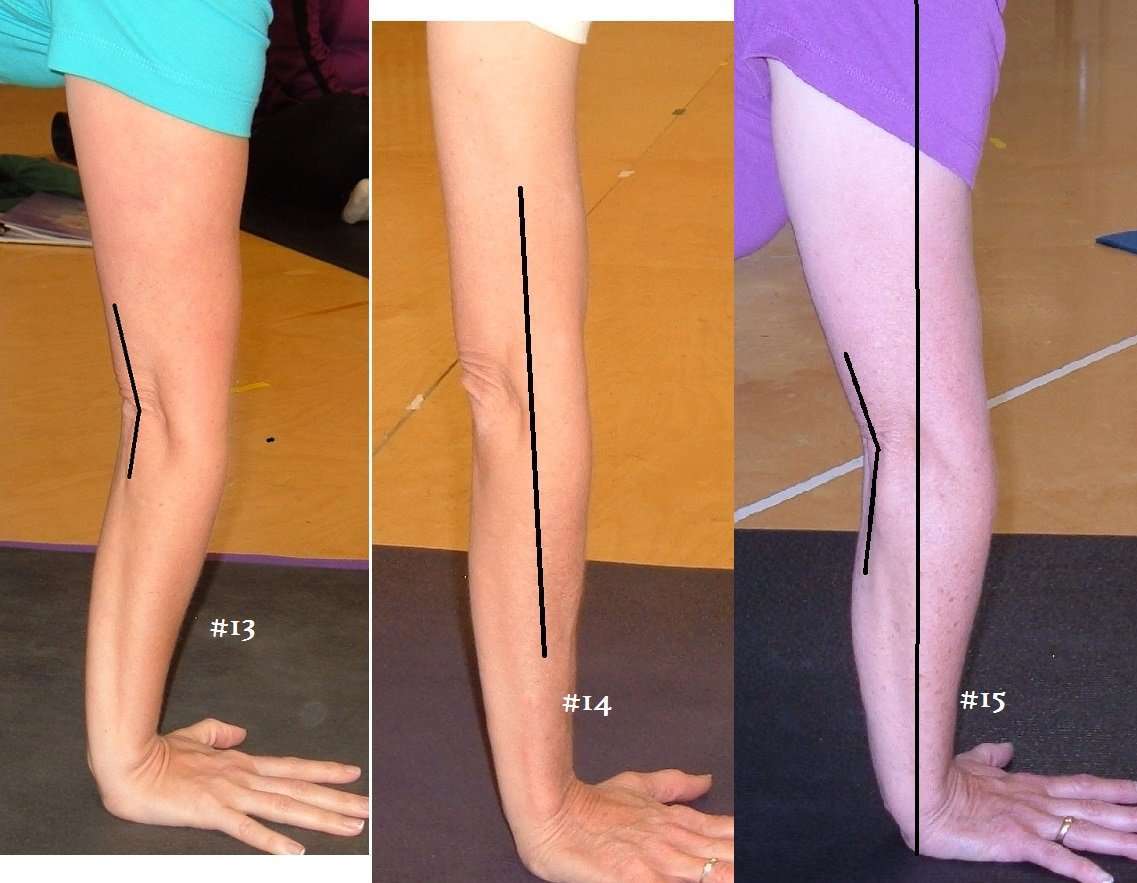
In figure 2 below, we see two yogis in natarajasana: Are they at risk? Perhaps, but not necessarily!
FIGURE 2.Both yogis are hyperextending at the knee, but the yogi on the left has the most hyperextension: 12°. This may or may not be a problem for herit depends on the health of her ligaments.
Causes Of Knee Hyperextension
When too much weight or pressure forces the knee into extension, the joint can extend further than its true range of motion, causing soft tissue damage, swelling, and potentially tears or strains of the MCL, LCL, ACL, or PCL. Common causes of knee hyperextension include:
- Pushing the femur or patella over the tibia and placing excess stress upon one or more of the major ligaments within the joint. This sort of impact might be experienced by a basketball player stopping unexpectedly and placing all of their weight on one leg to do so.
- Unexpected impact to the front of the knee, causing backward movement of the knee joint, may cause the ACL to strain or tear. This sort of impact would occur in traumatic physical situations, such as a football player being tackled by the legs or a soccer player being slid into.
advertisement
The method by which a knee hyperextension is caused can predict the severity of the condition. In minor cases, an athlete will notice small amounts of pain or swelling. In traumatic injury, however, hyperextension of the knee may also cause damage to the surrounding ligaments, cartilage and soft tissues.
Also Check: Nano Knee Replacement Surgery
When To Seek Care
If your hyperextended joint causes mild pain or swelling, you may be able to treat the injury at home with the self-care measures as described above. However, if the pain, swelling, or bruising is more severe, its a good idea to call your doctor.
Your doctor will want to perform a physical examination and examine the injured joint as well as the surrounding muscles, ligaments, and tendons. They may also order a set of X-rays to help confirm the diagnosis.
If you dont have any other injuries, your doctor may suggest some self-care measures that you can do at home.
Seek medical attention immediately if a bone is protruding through your skin or if your joint looks twisted or deformed. These types of severe injuries often require more significant treatment, including surgery.
A hyperextension injury to the neck can be mild, but theres also the potential for damage to the spinal column. As a general rule, its always a good idea to seek medical attention for any type of neck injury.
Its all too easy to say, Ill just be careful. Sometimes that works, but sometimes you need to be more proactive to minimize your risk of a hyperextension injury.
Here are some other steps you can take to reduce your risk:
Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tears

The PCL crosses over the ACL and prevents forward shifting of the shin bone. The PCL is typically injured by falling and landing directly on the front of the knee joint.
PCL tears can often be treated with nonsurgical treatment when sustained as an isolated injury, but are more commonly treated surgically when combined with other injuries.
Also Check: Is Nano Knee Covered By Medicare
Dynamic Versus Static Hyperextension
There are two ways we can hyperextend the knee: dynamically or statically. In dynamic hyperextension, the knee is forced backwards due to a sudden trauma or movement. The most frequently damaged ligament in knee injuries is the anterior cruciate ligament , and a common cause of ACL injury is a sudden stress on the knee while it is hyperextended .
Note that the ACL prevents the femur from sliding backward over the tibia, and the posterior cruciate ligament prevents the tibia from sliding backward under the femur. Knee injury most often occurs when we make a sudden stop while running, especially when combined with a change of direction, or when we jump and land with the legs extended. Unfortunately, women are two to eight times more likely to damage their ACLs than men, and this happens most often in the landing that follows a jump.
Excessive hyperextension of a knee bearing a load increases the risk of ACL damage. If in addition to the hyperextension, the knee is twisted, the risk of damage increases. Interestingly, the incidence rate of ACL injuries is far lower in gymnastics than in skiing, handball, soccer, basketball, or contact sports.
FIGURE 3. Hyperextension between 5° and 7° is normal. B.K.S. Iyengar hyperextended his knees in half moon pose and king dancer.
How Do I Treat Knee Hyperextension
Knee hyperextension is a condition in which the knee is straightened beyond the normal limits of the joint. When this happens, the possibility of some type of knee injury is greatly increased. Even a mild and momentary bend of this type can result in straining knee ligaments, especially the anterior cruciate ligament, or ACL. The main focus of treating knee hyperextension involves relieving the unnatural stress at once, as well as minimizing swelling and inflammation. In some cases, surgery may be needed if the knee ligaments are badly damaged.
In the event that knee hyperextension occurs due to some type of exercise or an accident that bends the knee in an awkward position, there is a good chance that one or more ligaments will be strained or possibly torn. Swelling is likely to begin immediately, which only places additional stress on the already damaged ligaments. Applying ice as quickly as possible will help to reduce the swelling, and also help to ease the pain that is probably shooting up and down the leg.
Also Check: Is Nano Knee Covered By Medicare
Isometric Strengthening Of The Quadriceps
This is easiest way to strengthen your quadriceps muscle especially when you are still too weak to do strenuous exercises. Roll a towel and put that in the space behind your knee. Then lie down and press it backwards with your knee. Hold for 6 seconds and repeat 10-20 times. Dont forget to breath while doing this exercise! To prevent holding your breath, count from 1 to 6 while doing each repetition.
What Are Its Primary Causes
Knee hyperextension injuries typically occur in a sporting activity that involves contact, jumping, or cutting sports . Forceful knee hyperextension via contact or non-contact injuries commonly injure the ACL, PCL , and other structures such as meniscus, and can even cause bone contusion in the femoral condyle or tibial plateau. The extent of the damage can be as little as a small sprain or strain but other high force injuries can cause complete tears in the ligaments.
Don’t Miss: How To Whiten Knees And Elbows
How To Treat A Hyperextended Knee
Hyperextended knee is a condition in which the knee gets stretched or twisted in such a way that its ligaments tear, and cause severe pain and discomfort while walking. Even a minor bend can cause extreme trouble for the patient, which needs to be treated as soon as possible. The major focus of knee hyperextension treatment is to minimize inflammation and swelling, and relieve the stress immediately. In severe cases of serious damage to the knee ligaments, surgery may be recommended by the physician. We have already told you how to treat swollen joints of the knees. Here at OneHowTo.com, we are going to discuss about how to treat a hyperextended knee.
Diagnosing The Knee That Is Hyperextended
Most of the time, a musculoskeletal physician such as a sports medicine specialist, an orthopedic surgeon, or a physiatrist can evaluate the knee and should use a diagnostic ultrasound with which they can classify the injuries. After the evaluation, if intra-articular damage is supected, they can send you for an MRI on the knee!
BUT, there are some simple things you can do on your own to see if you need to see a specialist to further investigate. Consider the following tests.
- Weight-bearing If you can stand on a single leg then that is a good sign, but if you are unable to weight bear on that leg, then potentially a bone bruise or ligament damage causing substantial instability can be present so you should see a specialist.
- Tenderness to palpation Compress the tissue around the knee and if you are not able to tolerate deep palpation without significant pain, the potential for high-grade injuries to the ligaments/tendons surrounding the knee exists.
- Swelling / bruising Inspect the top of the knee cap with the leg extended and if you are able to make out the quadriceps muscle and knee cap then significant swelling in the joint is unlikely, but if the contour is gone and puffy then its recommend to have a physician check it out!
Recommended Reading: Can You Use An Inversion Table After Knee Replacement
Hyperextended Knee Specialist In Dallas
Our board certified orthopedic surgeons see hundreds of patients with hyperextended knee conditions. If your knee bends backwards, you likely have a hyperextended knee injury and should consult a physician immediately. At SPORT Orthopedics in Dallas, we do offer Urgent Care for emergency hyperextended knees treatment in Dallas and Frisco.