Arthrosis Vs Arthritis: Whats The Difference
What are arthrosis and arthritis?
Arthritis and arthrosis sound similar. Both of them affect your bones, ligaments, and joints. They also share many of the same symptoms, including joint stiffness and pain. But the difference between the two is important.
Arthritis is an umbrella term. Its used to describe several conditions that cause inflammation in your joints. In some cases, the inflammation can also affect your skin, muscles, and organs. Examples include osteoarthritis , rheumatoid arthritis , and gout.
Arthrosis is another name for OA, one type of arthritis. Its the most common type of arthritis, according to the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases . Its caused by normal wear and tear on your joints and cartilage. Cartilage is the slippery tissue that covers the ends of your bones and helps your joints move. Over time, your cartilage can deteriorate and may even disappear completely. This results in bone-to-bone contact in your joints, causing pain, stiffness, and sometimes swelling.
Arthrosis can affect any joint in your body. Its most likely to affect the joints of your hands, neck, knees, and hips. Your risk of developing it increases with age.
The symptoms of arthritis vary from one type to another. Joint pain and stiffness are the two most common. Other common symptoms of arthritis include:
- swelling in your joints
- redness of the skin around affected joints
- reduced range of motion in affected joints
- joint pain
Chronic Osteoarthritis Knee Symptoms
- In chronic cases, bony tips, called osteophytes, begin to grow on the edge of the knee joint.
- As a result of the knee becoming stiff and immobile, the patient experiences sharp pain and severely restricted mobility.
- The joint is compromised and requires external support to avoid buckling. In the worst-case scenario, a patient might need a complete knee replacement.
Description Of The Condition
A thin layer of cartilage covers all joint surfaces. This acts like a shock absorber and ensures optimum sliding of the individual bone components in the joint. Osteoarthrosis is associated with a deterioration in quality of the cartilage. This causes the joint to move less smoothly and the shocks are not absorbed as effectively. Loss of cartilage can result in chronic knee symptoms.As the cartilage is gone, bone-to-bone contact can occur in the joint. This is painful and makes the joint less mobile. The body responds by forming osteophytes. This means that abnormal bony growths occur along the edges of the joint. This is the body’s repair response to combat the effects of osteoarthrosis. By making the joint wider, this distributes the pressure over a greater surface area.
Recommended Reading: Cellulite Above Knees
What Stages Does Arthrosis Go Through In Its Development
The effectiveness of knee treatment depends on the degree of development of arthrosis diagnosed in the patient:
- First degree of knee arthrosis. The pain at this stage is not felt much. The patient can endure discomfort for years, while he is in no hurry to contact specialists or to carry out any kind of treatment. A person needs help during an exacerbation. A sharp onset of pain is not typical for arthrosis of the knee.
- Arthrosis of the knee joint of the 2nd degree. The intensity of the discomfort increases. Pain occurs not only after physical exertion on the knee joint, but also at rest. To get rid of unpleasant sensations, you have to rest more. In the area of the knee joint, swelling appears, the patient hears a crunch. The x-ray shows a narrowing of the joint space, a slight deformation of the knee joint.
- Arthrosis of the knee joint of the 3rd degree. In this case, knee mobility is severely limited, and sometimes the leg cannot fully straighten. The pain in the joint becomes severe and constant, it appears as a response to changing weather conditions. The discomfort is aching in nature, and it is difficult to get rid of it even at rest. Often the patient’s sleep is disturbed, and in order to alleviate his condition a little, he uses NSAIDs. A person develops lameness, and the deformity of the joint is very noticeable.
What Exactly Is Athrosis
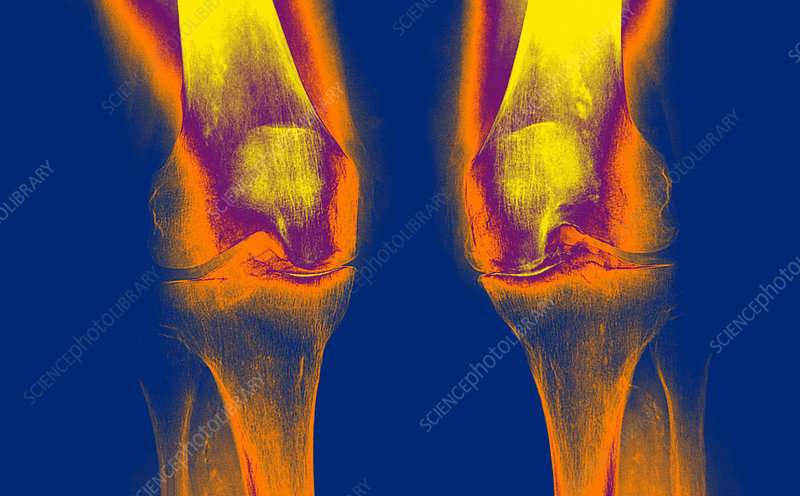
Arthrosis is a type of rheumatism in which the cartilage in the joint deteriorates in quality. It becomes thinner, softer and crumbly. This leads to deformation of the bone directly underneath the cartilage. There are visible and tactile nodules called osteophytes at the edge of your joint. These nodules limit the mobility of your joint.
Sometimes there is inflammation in the joint. Also nerves are sometimes pinched, causing pain, sensory disturbances and loss of strength. Arthrosis is the most common rheumatic disorder of the musculoskeletal system.
Arthosis is a condition that involves the entire joint and can occur in all joints. There are joints in which it occurs more frequently, such as in the neck, lower back, knees, hips, thumb, fingers and big toe. The condition is relatively common. The international name of Arthrosis is osteoarthritis.
Also Check: Inversion Table Knees
Radiographic Findings Of Oa
- Joint space narrowing
- Advice on weight loss
- Knee bracing
- The first-line treatment for all patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis includes patient education and physiotherapy. A combination of supervised exercises and a home exercise program have been shown to have the best results. These benefits are lost after 6 months if the exercises are stopped.
- Weight loss is valuable in all stages of knee OA. It is indicated in patients with symptomatic OA with a body mass index greater than 25. The best recommendation to achieve weight loss is with diet control and low-impact aerobic exercise.
- Knee bracing in OA can be used. Offloading-type braces which shift the load away from the involved knee compartment. This can be effective when there is a valgus or varus deformity.
Other non-physiotherapy based interventions include pharmacological management:
Imaging For Diagnosing Advanced Knee Osteoarthritis
X-rays are very helpful in diagnosing advanced knee osteoarthritis because the joint will have specific characteristics, including:
- Bones that are closer to each other than they should be: As cartilage wears away, the joint space between them often narrows.
- Cysts: As the body responds to cartilage destruction and attempts to stabilize the joint, cysts or fluid-filled cavities can form in the bone.
- Increased bone density or uneven joints: When bones are no longer cushioned by cartilage, they can rub against one another, creating friction. The body responds by producing more bone tissue, which increasing bone density. Increased bone creates uneven joint surfaces and bone spurs at the joint.
Don’t Miss: Inversion Table Knee Pain
Do You Have These Symptoms
You experience weakness when you get up from a sitting position? You feel pain when you walk up or down the stairs? Or, do you feel knee stiffness when you bend or stretch your leg? If so, its possible that you have knee arthrosis.
If you have any doubts, contact us for an appointment in one of our five locations on the North Shore, in Montreal and on the South Shore.
Difference Between Arthrosis And Arthritis
- Arthritis is an inflammatory condition, arthrosis is non-inflammatory.
- Arthrosis involves the articular cartilage and sometimes bone whereas arthritis involves the joint lining.
- Arthrosis usually does not present with significant joint swelling, whereas swelling is prominent in arthritis.
- Arthrosis is due to wear and tear often related to age and overuse whereas arthritis is inflammation mediated by autoimmune, infectious and other inflammatory factors.
References
Recommended Reading: Bleach Dark Knees
What Is Knee Arthrosis
Knee arthrosis affects around 10 % of Canadians. In the case of arthrosis, the knee is the most affected articulation, in 80 % of the cases.
The average age at diagnosis is 50.4 years old. When your knees are in good health, they show a joint space between the femur and the tibia which is filled by meniscus. But when the alignment of the knee is not optimal, the meniscus wears, causing friction of bone on the other. This knee arthrosis is called osteoarthritis or gonarthrosis.
Causes Of Knee Joint Arthrosis
It is difficult to say what causes early cartilage deficiency in some people. It is generally believed that disturbed metabolism is to blame, where the metabolism of essential amino acids and micronutrients occurs slowly or incorrectly.
Here, in turn, the following reasons are to blame:
What are the symptoms that make it possible to suspect this bad pathology?
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Knee Walker
How To Fix Osteoarthritis In The Knee Using Orthosis
Exercise and restrengthening is a tried and tested remedy in treating gonarthrosis pain.
- A medical knee brace, like Bauerfeinds GenuTrain OA, is instrumental in a speedy recovery as it provides the knee with support and stability.
- Developed specifically for knee osteoarthritis, the GenuTrain OA knee brace features an unloading and stabilizing system which noticeably reduces the pain experienced within the knee joint.
- With the addition of the Boa closure system, the patient can easily adjust the amount of unloading required to adapt to a wide range of daily activities, including walking or hiking.
What Questions Might A Healthcare Provider Ask To Diagnose Arthritis Of The Knee
Your healthcare provider will interview you when you report your symptoms. Some questions might include:
- Does anyone in your family have arthritis of the knee?
- Does your knee swell up?
- Is your skin often red?
- Is your skin often warm?
- Do you have symptoms in one knee or both?
- How long have you had these symptoms?
- What medications do you take?
- How severe is your pain?
- Do you struggle to walk?
- Do the symptoms interfere with your daily activities?
You May Like: Nano Knee Surgery Cost
Consequences Of Neglected Gonarthrosis
The advanced stage of gonarthrosis is almost always characterized by the following unfavorable symptoms:
- round-the-clock pain, from which no pain reliever can save
- loss of support for a limb
- immobilization of the articular block
- pronounced curvature of the bones around the knee
- severe swelling around the affected area.
Gradual Increase In Pain
Arthritis pain usually starts slowly, although it can appear suddenly in some cases.
At first, you may notice pain in the morning or after youve been inactive for a while.
Your knees may hurt when you:
- climb stairs
- stand up from a sitting position
- walk on a flat surface
- sit down for a while
Knee pain that wakes you up from sleep can be a symptom of OA.
For people with RA, the symptoms often start in the smaller joints. They are also more likely to be symmetrical, affecting both sides of the body. The joint may be warm and red.
With OA, symptoms may progress rapidly or they may develop over several years, depending on the individual. Symptoms can worsen and then remain stable for a long time, and they can vary day to day.
Factors that may cause worsening of symptoms include:
- cold weather
- stress
- excessive activity
With RA, symptoms usually appear over several weeks, but they can develop or worsen in a few days. A flare can happen when disease activity increases. Triggers vary and can include changes in medication.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Knee Fat And Cellulite
Complications Of Arthrosis Of The Knee Joints
Advanced arthrosis can lead to dislocations and subluxations of the knee joint. With dislocation, the epiphysis of the femur extends completely outside the joint, due to which movement in the joint becomes impossible, and the axis of the leg is substantially shifted to the side. Fortunately, such a negative variant of the development of the disease is rather rare.
Subluxations are more common. They are characterized by a partial displacement of the joints relative to each other and a slight deviation of the tibia axis. In this case, subluxations are accompanied by severe pain and dysfunction of the joints.
The neglect of the disease can lead to a complete loss of functionality of the lower limb.
ATTENTION! The habit of sparing a sore leg sometimes causes deformation of the intervertebral discs and the appearance of hernias.
Mild Osteoarthritis Knee Symptoms
- Even in mild cases, the underlying condition still exists. Immediate treatment is highly recommended to stop the progression of the disease. The earlier the diagnosis, the better the prognosis!
- If left untreated, the gradual wear and tear of the cartilage reduce the joint gap. Long term wear and tear of the buffer causes the upper and lower leg bones to grind against each other.
- The patient consequently experiences pain and discomfort. The skin around the knee then begins to turn red and there may be swelling present.
You May Like: Whiten Knees Fast
What Is The Difference Between Gonarthrosis And Knee Osteoarthritis
The degeneration of the knee joint, due to this long term wear and tear, is often referred to as gonarthrosis. Knee Gonarthrosis is a non-inflammatory condition related to the aging population.
In mild cases, a patient experiences episodic pain after long periods of inactivity, like a long day seated at work. Gonarthrosis is fairly common in elderly adults but is not exclusively a disease of old age.
In chronic cases, the entire knee joint can be compromised and in the worst-case scenario, a knee replacement may become necessary.
Electrotherapy For Patients With Gonarthrosis
Another rehabilitation option is functional electrical stimulation. The electrical stimulation of muscles can provide important support in every phase of rehabilitation.
By selecting different programmes, the stabilising and protective muscles on the knee joint can be stimulated to prevent muscle atrophy , which is caused by an adaptive posture in everyday life or after surgery.
Stimulation of an isolated muscle with simple muscle strengthening programmes, the combined stimulation of several muscles in a specific motion sequence, or EMG-triggered stimulation may simplify and accelerate the treatment of gonarthrosis. Pain can also be treated using TENS programmes.
Read Also: Bioknee Cost
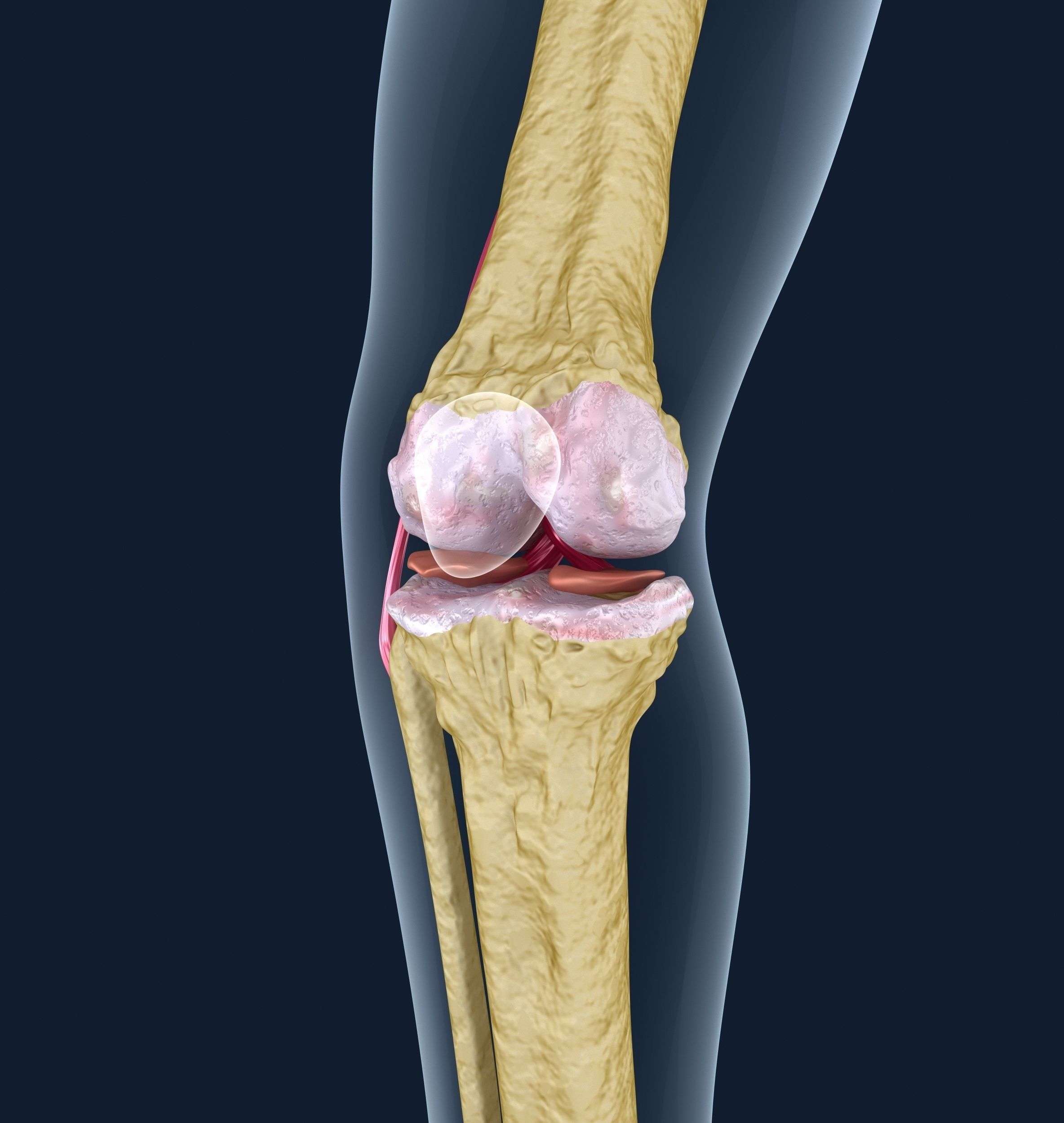
What Is The Knee Joint
Three bones come together to form your knee joint. They include the:
- Thighbone .
- Shinbone .
- Kneecap .
A smooth substance called cartilage covers the ends of each bone. Its a cushion between the bones that keeps them from rubbing together. The synovial membrane, a type of tissue that surrounds the joint, lubricates the cartilage.
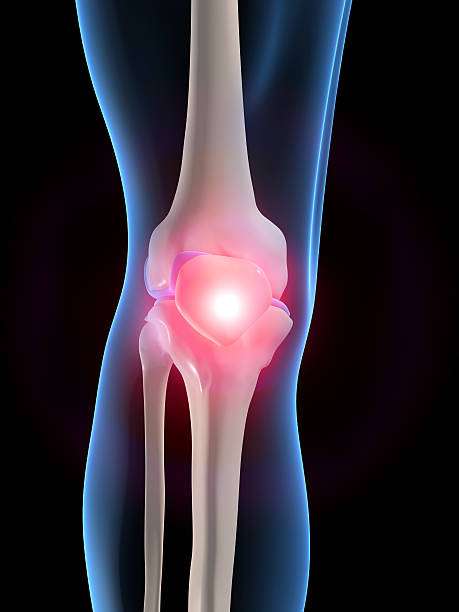
Arthritis of the knee causes pain and swelling in the joint
How Is Osteoarthritis Of The Knee Diagnosed
The diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis will begin with a physical exam by your doctor. Your doctor will also take your medical history and note any symptoms. Make sure to note what makes the pain worse or better to help your doctor determine if osteoarthritis, or something else, may be causing your pain. Also find out if anyone else in your family has arthritis. Your doctor may order additional testing, including:
- X-rays, which can show bone and cartilage damage as well as the presence of bone spurs
- magnetic resonance imaging scans
MRI scans may be ordered when X-rays do not give a clear reason for joint pain or when the X-rays suggest that other types of joint tissue could be damaged. Doctors may use blood tests to rule out other conditions that could be causing the pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, a different type of arthritis caused by a disorder in the immune system.
You May Like: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Ambulance Ride
What Are The Symptoms Of Knee Osteoarthritis
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee may include:
- pain that increases when you are active, but gets a little better with rest
- swelling
- feeling of warmth in the joint
- stiffness in the knee, especially in the morning or when you have been sitting for a while
- creaking, crackly sound that is heard when the knee moves
Causes And Consequences Of Arthrosis
For patients with arthrosis, the articular cartilage loses its strength, as does the bone tissue, all of which is located under the cartilage, which compresses at the heavily stressed areas. The cartilage is roughened and cracks develop in cartilage tissue. Consequently, the bone is exposed and damaged. In the advanced stage of the disease, the cartilage can completely disappear. The affected bone then rubs on bone and sometimes causes great pain. Arthrosis can be defined as cartilage damage in combination with bone alteration or damage.
Arthrosis can arise from a variety of causes. A congenital malformation or weakness of the joints can cause the cartilage to dissolve and the bone to change as a result. One cause of arthrosis can be the long-term consequences of an accident – during sports, at work or in traffic. However, the main cause of joint wear and tear is excessive long-term stress on the joints and incorrect movement.
Also Check: Where To Get Knee High Converse
Causes & Types Of Knee Osteoarthritis
Knee Osteoarthritis is described as the damage to the cartilage inside the knee joint. The damage is irreversible and can significantly restrict ones mobility.
Based on the root of the disease, there are two distinct types:
- Primary and
- Secondary .
Primary Knee Osteoarthritis is rather mysterious. The true root of the disease is unknown however, scientists suspect that pre-existing conditions and a hereditary disposition could be the trigger. Not all carriers of the gene manifest symptoms. Lifestyle choices, including lack of exercise and obesity, are also suspected triggers.
Secondary Knee Osteoarthritis is easier to diagnose and has a clear origin. Risk factors for developing secondary gonarthrosis include:
- Sporting accidents or physical trauma to the knee.
- High-intensity physical activity, which laborers and tilers experience.
- Long periods of inactivity like in long hours at a desk job.