Normal Anatomy Of The Knee
The knee joint is made up of three bones: the femur , the tibia , and the patella . There is a fourth bone, the fibula which lies along the side of the tibia, but it has only a small role in the function of the knee joint. These three bones work together to allow for flexing and extending the leg at the knee joint. The lower part of the femur connects to the upper part of the tibia and to the patella with ligaments, tendons, and other connective tissues. Amongst these connective tissues is a 2-part structure called the meniscus. The two parts are the inner side and the outer side. The meniscus helps to reduce friction, balance out the weight distribution in the knee, and acts as a shock absorber. The surfaces of the bones where they meet in the knee joint are covered in a special type of cartilage called articular cartilage. This cartilage is very strong and smooth, and it acts to reduce the friction in the knee joint even more. The patella is vital for knee function. Without the patella the knee joint would have a much more difficult time bending and straightening. You can think of the patella like a fulcrum and the leg bones like levers. You use a lot less energy to lift something using a lever with a fulcrum under it than just trying to move it with a lever alone. Since our knees have to support virtually all of our body weight, and have a lot of stress upon them during daily activities, things can sometimes go wrong.
Are There Randomized Controlled Trials For Total Knee Replacement
A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Total Knee Replacement In patients with knee osteoarthritis who were eligible for unilateral total knee replacement, treatment with total knee replacement followed by nonsurgical treatment resulted in greater pain relief and functional improvement after 12 months than did nonsurgical treatment alone.
Whats The Difference Between Partial Knee Replacement And Total Knee Replacement Ive Also Heard Of Resurfacing The Knee What Does That Mean
Urquhart: A partial knee replacement is performed on patients who have intact ligaments and pain isolated to the inside portion of the knee. Performing surgery on that inside portion of the knee, called the medial compartment, can result in relief of symptoms and the patient not needing surgery on the entire knee joint, thus the partial title.
All knee replacement surgeries involve some amount of resurfacing, or replacement of the knees cartilage. Patients usually hear about resurfacing for hips, which is a type of total hip replacement surgery. At Michigan Medicine, we dont currently recommend hip resurfacing for a variety of reasons and encourage patients who need surgery to have a stemmed total hip replacement with implants that have a good registry track record instead.
Also Check: Does Copper Infused Fabric Really Work
What Is Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement
Several surgical approaches to knee replacement are considered “minimally invasive.” What characterizes a less invasive surgery is that the surgeon makes a smaller incision and works within a smaller surgical area than a traditional knee replacement surgery.
Below are four examples of how traditional and minimally invasive knee replacements are different from one another:
Less invasive knee replacements can differ in the exact location of the incision, the shape of the incision , and how the muscles and other soft tissue are cleared out of the way to make room for the surgical procedure. The type of minimally invasive approach used typically depends on the surgeon’s experience and preference. The patient’s anatomy may also be a factor.
What To Expect The Day Of Your Kneecap Replacement
In general, the day of your surgery you can expect to:
- Talk with a preoperative nurse. The nurse will perform an exam, ensure all necessary tests are in order, start an IV, and answer questions. Youâll also sign medical consent forms.
- Remove all clothing and jewelry and dress in a hospital gown. It is a good idea to leave all jewelry and valuables at home or with a family member. The surgical team will give you blankets for modesty and warmth.
- Talk with the or nurse anesthetist about your medical history and the type of anesthesia you will have.
You will likely have sedative medication before the team takes you to the operating room . The anesthesiologist or will start your anesthesia once youâre in the OR. The surgical team will monitor your vital signs throughout the procedure and during your recovery. The surgery takes about an hour.
Also Check: Get Rid Of Knock Knees
When Surgery Is Recommended
There are several reasons why your doctor may recommend knee replacement surgery. People who benefit from total knee replacement often have:
- Severe knee pain or stiffness that limits everyday activities, including walking, climbing stairs, and getting in and out of chairs. It may be hard to walk more than a few blocks without significant pain and it may be necessary to use a cane or walker
- Moderate or severe knee pain while resting, either day or night
- Chronic knee inflammation and swelling that does not improve with rest or medications
- Knee deformity a bowing in or out of the knee
- Failure to substantially improve with other treatments such as anti-inflammatory medications, cortisone injections, lubricating injections, physical therapy, or other surgeries
Total knee replacement may be recommended for patients with bowed knee deformity, like that shown in this clinical photo.
Conditions That Can Be Treated With Knee Replacement
Knee replacement can be used to replace a knee joint affected by a range of conditions including:
- Severe osteoarthritis
- Ligament damage or infection that leads to severe osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Crystal deposition diseases such as gout and pseudogout
- Avascular necrosis death of bone following loss of blood supply
- Bone dysplasias disorders of the growth of bone.
Don’t Miss: Flying After Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee Replacement Alternatives To Consider
Crunching sounds as you climb stairs, chronic aching and swelling: Knee osteoarthritis is a real pain. If youre suffering with it, you may be considering surgery.
Getting a knee replacement is one approach, but you may not need surgery, at least not right away. And some patients cannot undergo knee replacement surgery for various reasons. Other people with knee pain are too young for a knee replacement the artificial knee is only likely to last 15 or 20 years, after which the person may need revision surgery.
There are several things you can try first, on your own or with a professionals help, that can help with knee pain and even delay the need for replacement.
Arthritis doesnt go away, but there are things you can do to lessen the pain and stay more active.
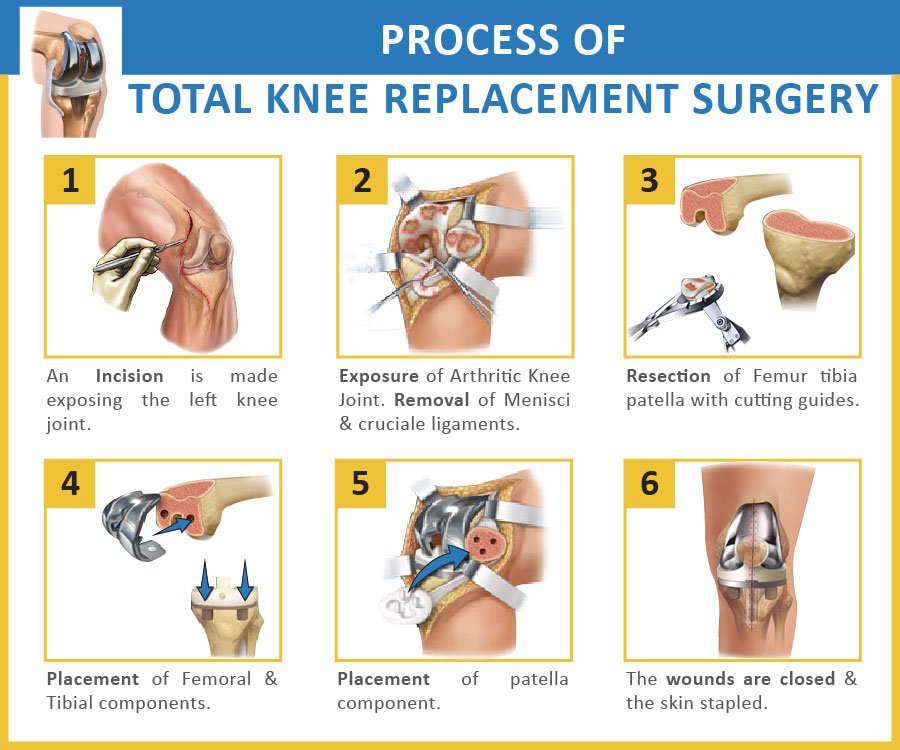
How Is A Total Knee Replacement Performed
First, the orthopedic surgeon makes an incision in the knee and moves the patella to the side. If are any bone spurs are present, as sometimes occurs in osteoarthritis, they will be removed.
Next, the two menisci between the femur and tibia are removed, as are the anterior cruciate ligament and, in some cases, the posterior cruciate ligament . In some types of knee replacement, the PCL is retained.
During the main phase of the operation, the surgeon cuts and remove cartilage and some bone from the upper part of the tibia and lower sections of the femur. The femoral sections removed are two knobby protuberances called the femoral condyles. The tibia and femur are then be capped with metal implants to create new surfaces for the joint. The surface of the femoral component mimics the shape of the original femoral condyles. If the kneecap has also degraded, the surface on its underside may also be cut away and replaced with a polyethylene implant.
Finally, the various layers of tissue are repaired with dissolvable sutures and the skin incision is closed with sutures or surgical staples. A bandage will be wrapped around the knee and the patient is be taken to recovery.
Fixed-bearing knee implant with a polyethylene articulating surface sandwiched between the metal tibial implant and metal femoral implant.
Side-view illustration of a knee with a fixed-bearing knee implant in place.
X-ray of a knee after total knee replacement, showing the implanted prosthesis)
Recommended Reading: How To Whiten Knees Fast
Schedule An Appointment With A Leading Orthopedic Surgeon
Dr. Likover is an expert orthopedic surgeon who has practiced for nearly four decades in Houston. He has successfully treated a wide range of knee conditions, including patellofemoral arthritis.
Dr. Likover will examine your knees to determine whether you suffer from isolated patellofemoral arthritis. If you are only experiencing pain in your kneecaps, he can repair the affected joint you may not need a total knee replacement.
Submit an online form or call his office at 713-465-0696 to schedule an appointment with Dr. Likover today.
Types Of Knee Implants
There are multiple types of knee implants that doctors and patients can discuss before choosing the best option.
Regardless of type, all knee implants have certain things in common.
All consist of a component that attaches to the thigh bone and one that attaches to the tibia, one of the two lower leg bones. A knee replacement implant may or may not have a patellar component mimicking the kneecap.
Some components, particularly the bearings, may be made of ceramics or a mixture of ceramics and metal. The materials have to be biocompatible meaning they cannot trigger the bodys rejection response. Knee implants are relatively lightweight usually between 15 and 20 ounces.
You May Like: Inversion Table Knee Pain
Injections For Knee Pain
There is good science behind cortisone shots and other injections, such as hyaluronic acid injections, that lubricate the inner workings of the knee and help relieve arthritis pain.
According to experts, there is less evidence supporting the benefits of other injectable substances, including platelet-rich plasma and concentrated bone marrow or stem cells, but further studies will reveal more about their efficacy in treating knee arthritis.
Injections can provide temporary relief typically a few months which can help you stay on your feet and postpone surgery.
The Pros And Cons Of Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement Surgery
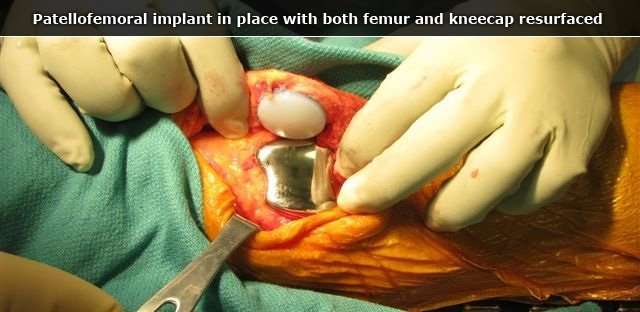
Both minimally invasive knee replacements and traditional knee replacements are performed to alleviate chronic knee pain due to arthritis, and both surgeries require the cutting of soft tissue and bone in order to implant prosthetic knee joint components. The difference is that a minimally invasive knee replacement uses a smaller skin incision and tends to require less cutting of other soft tissue, such as muscles, tendons and ligaments.
The expectation is that less invasive knee replacement techniques will allow for an easier post-surgical recovery in the short term and provide equal or better results in the long term. Whether this expectation is realistic is a matter of ongoing research. To date, experts have found minimally invasive knee replacement surgery has both advantages and disadvantages, and it is not appropriate for all knee replacement patients.
Also Check: Ginger Poultice For Knee Pain
Do You Have To Come To The Hospital For Total Knee Replacement Surgery
Urquhart: Knee replacements in healthy patients do not require a hospital stay. In fact, we now offer the surgery at the Brighton Center for Specialty Care, one of our outpatient specialty clinics.
Patients have the surgery performed in one of the operating rooms at the facility and then are moved into a recovery area where they are monitored and work with physical therapy to be safe to go home. The center has the ability and staffing to monitor patients overnight, if needed. Then the patient is able to finish their recovery at home.
What Was The Pain Before Total Knee Replacement
My knee has got worse. Good to walk around on but I get severe shooting pain at night turning in bed, the opposite of the situation before surgery. Apart from the night pain, severe with movement, daily are activities easier. I had TKR of the right knee in June 20, similar situation to the above, only 30 percent as bad.
Total knee replacement is a type of surgery to replace a damaged knee joint. A minimally invasive surgery uses a smaller cut than a traditional total knee replacement. This type of surgery typically requires special tools so that the surgery team can see and do the procedure through the smaller incision.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Dark Spots On Knees Fast
Complex Or Revision Knee Replacement
This procedure is done when the original knee replacement surgery has either failed or has reached the end of its useful life. Sometimes, an artificial joint can become infected necessitating removal and replacement of the implanted components. Another reason for a revision knee replacement is a fracture of the bone in the area of an implant component. A revision knee replacement procedure is more complicated as the knee has previously been surgically altered. Specialized implants need to be used, and there is a lot more planning involved for this procedure. Often these implants have thicker stems that fit deeper into the bones of the femur and tibia.
Types Of Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement can be total or partial.
Total knee replacement : Surgery involves the replacement of both sides of the knee joint. It is the most common procedure.
Surgery lasts between 1 and 3 hours. The individual will have less pain and better mobility, but there will be scar tissue, which can make it difficult to move and bend the knees.
Partial knee replacement : Partial replacement replaces only one side of the knee joint. Less bone is removed, so the incision is smaller, but it does not last as long as a total replacement.
PKR is suitable for people with damage to only one part of the knee. Post-operative rehabilitation is more straightforward, there is less blood loss and a lower risk of infection and blood clots.
The hospital stay and recovery period are normally shorter, and there is a higher chance of more natural movement.
Read Also: What Rebuilds Cartilage
How Long Is The Recovery
All patients heal from surgery at their own pace. Your doctor will tell you when it is safe to go back to your normal activities. Here are some guidelines:
- Household chores: 3-6 weeks
- Work: 4 weeks or more- depending on your job requirements
- Swimming: 6-8 weeks
- Driving: Before you can drive, will need to be off pain medicine and be abele to get in and out of the car. You may be able to start driving within 2 to 6 weeks–even if your driving leg was operated on.
Rising Number Of Knee Replacement Surgeries
When medications, therapies and other treatments dont work, surgery is the next step to reclaiming mobility. A total knee replacement can get a patient back to work or back to a better quality of life.
The amount of knee replacement surgeries continue to grow in the U.S. and are projected to near 3.5 million procedures each year by 2030. This significant increase, in large part, can be attributed to the growing number of baby boomers reaching retirement age when the chance of a worn-out joint is higher and a rise in obesity and an increased need for follow-up procedures .
Most patients who undergo total knee replacement are between 50 and 80, but recommendations for these procedures are based on a patients pain and disability, not age.
As the number of knee replacements has increased, so has the number of problems reported with knee implants. Manufacturers have issued nearly 1,000 knee replacement recalls since 2003. But not all defective implants were included in those recalls.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Knee Fat And Cellulite
How Do Artificial Knee Joints Work
The knee joint forms where the femur meets the tibia and fibula . The patella , located on the front of the knee, moves up and down against the femur. These bones are connected by ligaments, muscles and cartilage that help form the joint hinge and give the joint its flexibility.
Although there are four bones around the knee joint, only the femur, tibia and patella are affected by an implant.
While many device companies design and manufacture knee implants, which in turn can be made from a variety of metals, plastics and ceramics, artificial knee joints consist of three components.
The three components of a knee implant include:
- Femoral component
- This metal piece attaches to the end of the femur. It has a groove that allows the patellar component to slide up and down smoothly as the knee bends and straightens.
- Tibial component
- This flat, two-piece metal and polyethylene part is attached to the tibia. The metal part sits on top of the tibia and has a stem that is inserted into the tibia for stability. The plastic part, or tibial spacer, acts as a cushion between the metal tibial component and the metal femoral component.
- Patellar component
- This plastic piece is dome-shaped to match the resurfaced shape of the patella. Because the patella rests against the femur, the alignment of the patellar component and femoral component is crucial for proper function. The patella is held in place by the quadriceps tendon and patellar tendon.