Rest Ice Compression Elevation
Your doctor may recommend following the RICE principles: rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Give your joint plenty of time to rest, and elevate your leg when possible, especially at night. Holding an ice pack or bag of frozen peas wrapped in a dishcloth to the affected area for 10 to 20 minutes can help reduce swelling. Compression bandages, wraps, sleeves, and braces can also help support the knee joint.
One member shared their tips: Ice helps. Put ice up on a pillow at night time. Lie flat on your back.
Common Treatments For Osgood
Osgood-Schlatter disease is easily treated, and most athletes recover entirely by the time their tibia completes its development. Resting from activities that stress the patellar tendon is usually the first step to reducing the pain and inflammation of Osgood-Schlatter disease. Other standard therapies include:
- Ice
- Over-the-counter medication, specifically NSAIDs
- Stretching and physical therapy, aimed at increasing the flexibility of the thigh muscles
- Straps or bands that put pressure on the patellar tendon may help control pain during activities
What Are Possible Complications Of A Baker Cyst
In rare cases, a Baker cyst may cause complications. The cyst may enlarge, which may cause redness and swelling. The cyst may also rupture, causing warmth, redness, and pain in your calf.
The symptoms may be the same as a blood clot in the veins of the legs. Your healthcare provider may need imaging tests of your leg to make sure you dont have a clot. Rupture can also lead to its own complications, such as:
- Trapping of a tibial nerve. This causes calf pain and numbness behind the leg. It can be treated with arthrocentesis and steroid injections.
- Blockage of the popliteal artery. This causes pain and lack of blood flow to the leg. It can also be treated with arthrocentesis and steroid injections.
- Compartment syndrome. This causes intense pain and problems moving the foot or toes. Compartment syndrome is a medical emergency. It needs immediate surgery. It can lead to permanent muscle damage if not treated right away.
Also Check: Nano Knee Surgery Cost
Should You Remove Bakers Cyst
In principle, treatment of Bakers cysts in the initial phase or when it is smaller and does not cause symptoms is not necessary. At that point, surgical procedures are out of question. In the younger population, there is even a high probability that they will disappear on their own.
The most important thing to be aware of is that Bakers cyst is only the result of some other pathology in the knee joint. That is why it is first necessary to pay attention to the primary problem. The cyst itself is of secondary importance and requires special attention only in rare cases.
If symptoms occur, problems with Bakers cyst are alleviated conservatively as follows:
- taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Causes Of A Bakers Cyst
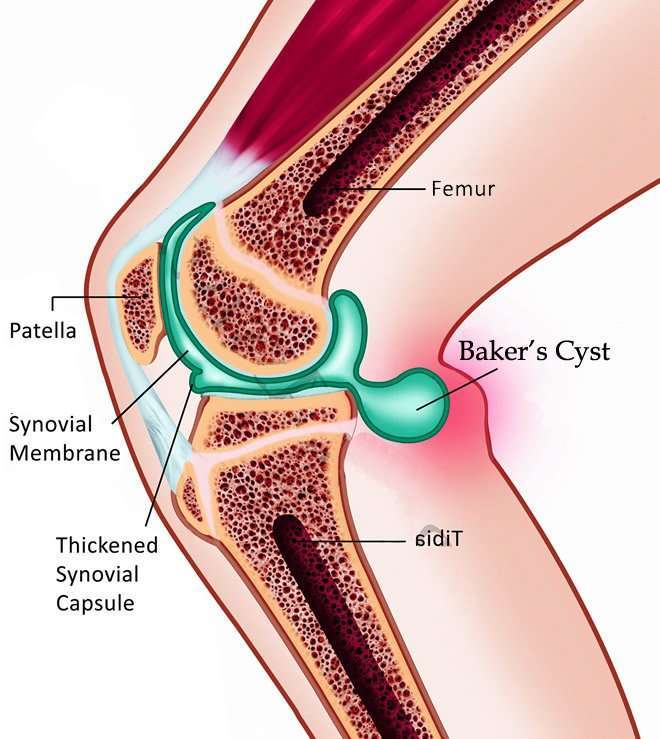
Knee damage caused by a sports-related injury or a blow to the knee can lead to a Bakers cyst developing.
A Bakers cyst can also sometimes occur if you have a health condition such as:
Bakers cysts are more common in women than men, probably because women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. They usually develop in people aged over 40, although can affect people of any age, including children.
Also Check: Bioknee Cost
Are There Any Complications That Can Develop
The most common complication of a Baker’s cyst is for it to split open . If this happens, the fluid from inside the cyst can leak out into your calf muscle. This can cause swelling of your calf. You may also develop itching and redness of the skin of your calf because of irritation caused by the fluid that leaks out from the cyst. About 1 or 2 in 20 Baker’s cysts are thought to rupture.
If a Baker’s cyst ruptures, it can be quite difficult to tell the difference between the ruptured cyst and a deep vein thrombosis in the leg. A DVT is a blood clot that forms in a leg vein. In these cases, it is important that investigations are carried out to exclude a DVT because it can be a serious condition that needs treatment. See the separate leaflet called Deep Vein Thrombosis for more detail.
Very rarely, a Baker’s cyst may become infected.
Bakers Cyst Treatment And Home Treatment
You may not need any treatment for a Baker’s cyst. They arenât dangerous and tend to go away on their own. But there are things you can do at home to ease your pain and make yourself more comfortable:
- Keep it cold. Apply a cold pack to the affected area. Itâll help keep the swelling down. A compression wrap might also help.
- Take medication. For pain , take an over-the-counter medication like ibuprofen.
- Rest your leg. Keep it raised above your heart level when possible. This will keep down swelling. You may want to use a compression bandage, and a cane or crutch when you walk, to keep pressure off your leg.
If these at-home treatments donât work, see your doctor. They may suggest:
- Steroids. These can help lessen inflammation.
- Exercise. A physical therapist can teach you gentle exercises, to help improve your range of motion, and strengthening moves, to build up the muscles around your knee. This could ease your symptoms.
- Aspiration. Your doctor can drain the cyst. Theyâll likely do it with the aid of an ultrasound. This treatment may not work if your case is severe.
- Surgery. If youâre in serious pain or if the cyst makes it hard for you to move your knee, this might be an option. But itâll work only if your doctor also treats the issue that caused the Bakerâs cyst to begin with, such as arthritis.
Also Check: Ginger Poultice For Knee Pain
Lump Behind Knee Treatment
Depending with causes of the lump different treatment would be applied. You need to see you health care provider who will assess you and prescribe the best medication possible. The treatment therefore will depend on the causes of the lump, how long you have had the lump and the size of the lump. The most common treatment include:
Treatment for bakerâs cyst due to knee cancer depends on the type of cancer, how far it has spread and your general health
- Surgery, done especially if the cyst is very large or painful and other treatments have not worked. At times a keyhole method is used to close of the connection between the bakerâs cyst and the knee joint. The cyst may also be removed at times using open surgery. surgery might help treat an underlying problem for example, repairing a meniscal tear
- Chemotherapy, this is done with medicine to kill the cancer cells, by damaging them so they canât reproduce and spread. It is used if a cancer has spread or there is a risk that it will.
- Radiotherapy, this is the treatment of cancer involving high-energy radiation. It commonly used to tear the cancer. It would also work to treat other condition such as thyroid disease and some blood disorders.
Treatment for a lump due to lymphoma would include
What Causes A Baker’s Cyst
Knee damage caused by a sports injury or a blow to the knee can lead to a Baker’s cyst developing.
A Baker’s cyst can also sometimes occur if you have a health condition such as:
- osteoarthritis usually caused by age-related “wear and tear” of joints it particularly affects the knees, hips, hands and big toe
- inflammatory arthritis including rheumatoid arthritis, which is a less common type of arthritis and is caused by the immune system attacking the joints
- gout a type of arthritis that usually affects the big toe and is caused by a build-up of the waste product uric acid in the blood
Baker’s cysts usually develop in people aged 30 to 70, although they can affect people of any age, including children.
Don’t Miss: Lock Knee Joint
Common Treatments For Ligamentous Strains Or Tears
The most common treatment for mild to moderate ligament strains is the RICE method, which is resting the area, applying ice to reduce swelling, applying compression via braces or bandages and elevating the area. Pain relievers may also be used to alleviate symptoms.
In moderate to severe cases, including those involving a tear, other treatment might be considered. Physical therapy, reconditioning and even surgery might be options, depending on the severity of the injury.
Recommended Reading: Nano Knee Surgery Cost
Treating A Baker’s Cyst
Treatment will not usually be necessary if you have a Baker’s cyst that is not causing any symptoms.
Painkillers such as paracetamol and ibuprofen can be used to reduce the swelling and relieve any pain. A knee support or an ice pack may also help. A bag of frozen peas wrapped in a tea towel works well as an ice pack.
If you have an underlying condition that’s causing your cyst, it’s important that the condition is properly managed. The cyst may disappear when the condition causing it has been treated.
In some cases, it may be possible to drain the cyst. Surgery may also be needed to repair any significant damage around the knee joint.
Page last reviewed: 04 October 2021 Next review due: 04 October 2024
Also Check: How To Reduce Swelling In Knee Quickly
What Is The Treatment For A Baker’s Cyst
A Baker’s cyst often gets better and disappears by itself over time. Primary Baker’s cysts in children all usually disappear with time. However, the cyst may persist for months or even years before it goes. In a lot of people it causes little in the way of symptoms and no specific treatment is needed.
There are various treatment options that may help if you do have symptoms associated with a Baker’s cyst. These include:
Can A Bakers Cyst Be Prevented
The best way to prevent a Bakers cyst is to prevent knee injuries. A few ways you can prevent an injury to your knee include:
- Using the balls of your feet to turn instead of your knees.
- Warming up properly before you exercise and cooling down afterward.
- Stopping immediately when you get a knee injury. Its important to ice, rest, wear a compression wrap and elevate your injury when it happens. Talk to your healthcare provider about any knee injuries to make sure youre caring for them correctly.
You May Like: Knee Brace Infomercial
The Swelling Occurs Due To The Accumulation Of Synovial Fluid Inside A Small Sac Known As A Bursa
A Bakers cyst is a painful condition that can be characterized by swelling in the back of the knee.
If you are not yet familiar, a bursa is a small balloon-like structure that is found throughout the body and acts as a cushion between bones, tendons and muscles.
When this condition develops, the synovial fluid accumulates in a bag and protrudes from behind the knee.
This is also known as a popliteal cyst because it directly affects the popliteal region of the knee .
If it is not treated, it may break. A broken Bakers cyst can cause the collected synovial fluid to transfer and travel through the calf muscles of the legs. This can trigger a rapid swelling of the leg that can cause more complications.
Read Also: How To Whiten Knees And Elbows
Treatment For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Treating a Bakers cyst often involves treating the underlying cause of the cyst in this case, rheumatoid arthritis. There are several types of treatments for RA, including oral medications, injections, surgery, and lifestyle changes like diet and exercise. You and your rheumatologist can work together to find the right treatments for you.
Don’t Miss: Knee Walker Mobility Scooter
What Can A Sports Injury Specialist Or Doctor Do
- They will examine the knee and diagnose what is causing the swelling in the first place.
- For more serious cases a surgeon may operate to correct whatever might be causing the swelling including cartilage meniscus, foreign bodies or bursa that may need removing.
- The patient is likely to be out of action for 8 to 12 weeks following surgery.
Be aware that lumps in the back of the knee are most likely a Popliteal Cyst but might possibly be a tumor or an aneurysm . If unsure always seek professional advice.
Causes Of A Baker’s Cyst
Knee damage caused by a sports-related injury or a blow to the knee can lead to a Baker’s cyst developing.
A Baker’s cyst can also sometimes occur if you have a health condition such as:
Baker’s cysts are more common in women than men, probably because women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. They usually develop in people aged over 40, although can affect people of any age, including children.
Read Also: How To Whiten Knees Fast
It Is A Common Occurrence In Humans
Bakers cyst is a fairly common pathology of the knee joint in children. Fortunately, it resolves spontaneously by the 20th month. In adults, however, it is different.
The appearance of popliteal cysts in the knee is strongly associated with effusion in the joint, with meniscus damage and degenerative changes in the knee . In addition, Bakers cyst in the knee often occurs in people with:
- rheumatoid arthritis,
- patients with chronic renal failure,
- hypothyroidism,
- sarcoidosis,
- haemophilia.
Doctors check for the presence of cyst with the help of ultrasound diagnostics and magnetic resonance imaging.
Ultrasound examination of the Bakers cyst is the best noninvasive imaging tests.
What Is A Baker Cyst
A Baker cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms behind the knee. It’s also known as a popliteal cyst or popliteal synovial cyst.
The knee is a complex joint that has many parts. The lower end of the thighbone rotates on the upper end of the shinbone . The knee joint is filled with a special fluid that cushions the joint.
A Baker cyst forms when an injury or disease causes extra synovial fluid to leak into the extra space behind the knee.
Baker cysts are common in both adults and children. But theyre more common as a person gets older.
Recommended Reading: What Is Nano Knee Replacement
The Most Common Causes Of Bakers Cysts
Neil, Facty Staff
Bakers cysts, also called popliteal cysts, form when fluid collects behind the knee. Many people have no symptoms, while others may experience pain or stiffness when fully flexing or extending the knee. If the cyst bursts, the calf may swell, and more intense pain can develop. Generally, treating the cause of Bakers cysts provides relief and alleviates the symptoms. There are many possible causes, but the vast majority are varieties of arthritis. Anything that can cause inflammation of the knee can cause a Baker’s cyst.
How Is A Bakers Cyst Diagnosed
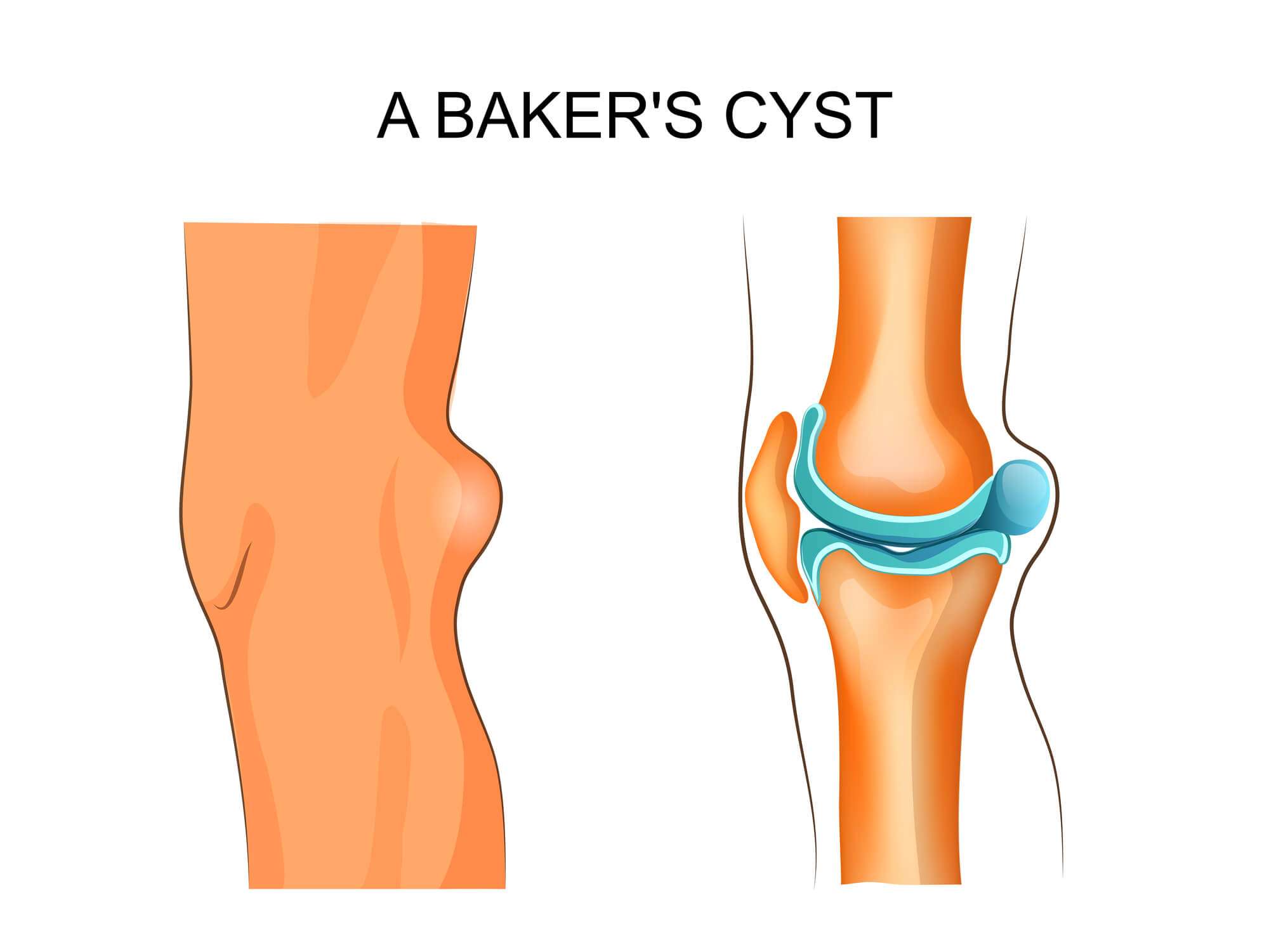
You need a professional medical exam to diagnose a Bakers cyst. During your appointment, your healthcare provider may do several tests to both confirm the Bakers cyst and figure out what might be causing it, including:
- Taking a medical history: Your healthcare provider will ask you about any previous injuries you may have had to your knee and go over your entire medical history.
- X-ray: This test wont necessarily show the Bakers cyst itself, but it can be used to see if you have arthritis in your knee. Arthritis is one of the possible causes of a Bakers cyst.
- Magnetic resonance imaging scans: An MRI uses magnetic waves instead of X-rays to show detailed images inside the body. This test can give your provider even more information about what might be causing the Bakers cyst.
- Ultrasound: A simple and painless test, an ultrasound uses sound waves to determine if the lump is solid or fluid.
Don’t Miss: Inversion Table After Hip Replacement
When To See Your Gp
See your GP if you have a lump behind your knee that’s causing problems and does not clear up on its own. They’ll usually be able to diagnose a Baker’s cyst by examining the back of your knee and asking about your symptoms.
Your GP will ask you whether you have any associated health conditions, such as arthritis.
Tests may be recommended to rule out other more serious conditions, such as a tumour, an aneurysm or DVT . You may need an ultrasound scan or a MRI scan.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Bakers Cyst
Sometimes youll feel no pain at all, or only a slight pain with a Bakers cyst. You may only have knee pain from the initial damage that caused the Bakers cyst, but not the lump itself. Any strain can cause this lump or your knee to swell in size. When the knee or cyst swells, this can increase your pain and limit how much you can move your knee.
Symptoms of a Bakers cyst may include:
- A fluid-filled lump behind your knee.
- Pain.
- Limited range of motion and ability to bend your knee.
- Swelling of your knee and/or leg.
Sometimes, a Bakers cyst can cause swelling and redness in your lower leg that can be similar to the symptoms of a blood clot. A blood clot is an emergency situation. If you are ever in doubt, reach out to your healthcare provider right away. Your provider can check out your symptoms and determine if its a Bakers cyst or a blood clot.
Also Check: Can Knee Cartilage Be Regrown
Symptoms Of A Bakers Cyst
The first symptom people tend to feel with a bakers cyst is a small bulge behind the knee, a bit like a small water balloon or squashy orange.
There may only be minor swelling and often a Bakers cyst is so small you dont even notice anything.
In some cases however, the popliteal cyst can get quite large, resulting in pain behind the knee, tightness and stiffness, especially when you bend and straighten the knee.
The average size of a Bakers cyst is 3cm.
The pain associated with a popliteal cyst tends to get worse with activity or when standing for long periods, easing with rest.