What Is A Knee Cartilage Transplant
Your surgeon will take healthy cartilage from one part of a joint to repair another part of the joint. The graft is taken from a non-weight bearing part of the joint, matched up to the damaged area and then put into place. The new graft will then leave a smooth exterior in the joint.
Knee cartilage transplants are only done in areas where theres smaller damage, because a graft can only be taken from a small area from the same joint. They are typically performed via a small camera called an arthroscope, meaning the incision will be smaller and recovery quicker and easier than with open surgery.
When the damaged area is too big for an autograft, you may have to undergo an allograft, which will require open surgery. An allograft is tissue taken from a cadaver donor. Just like an autograft, its taken from cartilage and bone. It is sterilized and tested for any possible disease. An allograft allows your surgeon to more accurately cut and place the cartilage in your damaged joint.
Other names that refer to a type of knee cartilage transplant include:
- Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation
- Carticel
- Osteochondral Allograft Transplantion Surgery
- MACI
How To Regrow Collagen In The Knee
Fact Checked
Collagen is a plentiful protein and vital component of muscles, organs, skin, tendons and connective tissue, such as cartilage. Cartilage, found in the knee and throughout the body, acts as shock-absorbing padding between bones, protecting joints and facilitating movement. With age, collagen production slows and cartilage degenerates, often resulting in pain, stiffness and inflammation that can lead to osteoarthritis. Food alone can’t replace collagen in your knee joints, but certain nutrients can help preserve the collagen you have and optimize your bodys own collagen synthesis.
Knee Conditions We Treat
Cartilage Damage: the slippery cartilage that coats the bones in your knee joint can get torn as a result of an impact, a wrenching movement, repetitive actions or wear and tear. It can cause problems with mobility, pain, swelling and can lead to arthritis if left untreated. We treat cartilage damage with physiotherapy, injection therapy and arthroscopic surgery.
ACL Tears: a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament can be caused by a sharp twisting motion, an impact or by a sudden force through a bent knee. It leads to symptoms of pain, swelling and instability. ACL tears can be treated with physiotherapy or keyhole surgery.
Torn Meniscus: the semi-circular rubbery pads in your knee joint provide cushioning. They can get torn as a result of twisting injuries, or an impact on the knee joint. Minor tears can be managed with physical therapy, while more severe tears may be repaired or removed using minimally invasive keyhole surgery.
Knee Fractures: a fracture to any of the bones of the knee can occur as a result of a major impact, or severe wrenching action. Other injuries to soft tissues often occur at the same time, so a careful diagnosis is needed. Some fractures require stabilisation while they heal , but displaced or shattered bone will require surgery.
Don’t Miss: Why Does My Knee Pop When I Do Squats
Knee Cartilage Repair Surgery: Main Procedures
Surgical repair service may be done by open surgery, in which a small incision is made and the knee is opened up so that the cosmetic surgeon can see inside the knee and the meniscus can be repaired. Significantly, specialists make use of arthroscopic surgery to fix the meniscus. The surgeon inserts a thin tube consisting of a camera and a light through small cuts near the knee and has the ability to see inside the knee without making a huge cut. Surgical instruments can be placed through other small incisions. The surgeon repair works the meniscus making use of stitches or anchors.
Other knee injuries-most frequently to the anterior cruciate ligament -might occur at the same time as a torn meniscus. In these cases, the treatment strategy is modified. Normally, your orthopedist will fix your torn meniscus, if required, at the same time ACL surgery is done. In this case, the ACL rehabilitation plan is followed.
What Surgical Procedures Are Available
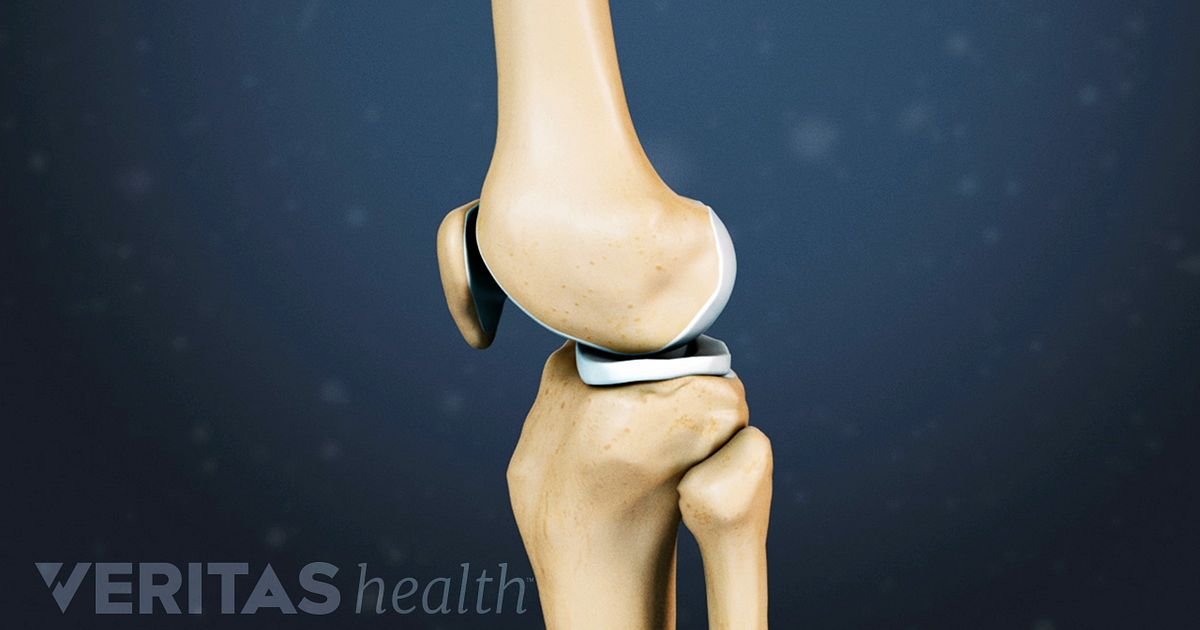
Many procedures to restore articular cartilage are done arthroscopically. During arthroscopy, the procedure is done through 2 small incisions . Some procedures require direct access to the affected area via an open incision . In general, recovery from an arthroscopic procedure is quicker and less painful than traditional, open surgery. Your doctor will discuss the options with you to determine what kind of procedure is right for you.
The most common procedures for damaged cartilage are:
- Chondroplasty
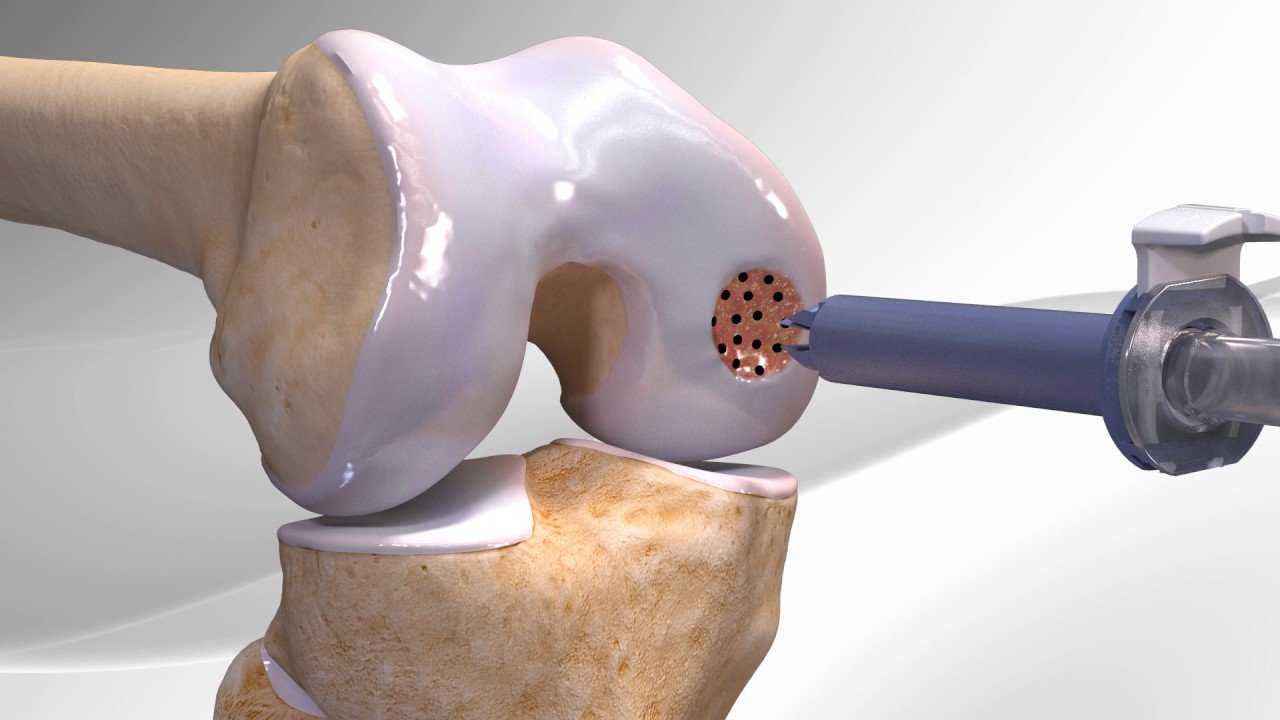
- Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation
Don’t Miss: How Do You Pop Your Knee
What To Expect During Knee Cartilage Surgery
You will be given a general anaesthetic and the operation takes about 45 minutes, depending on the extent of the damage.
Your surgeon will make a series of small incisions over your knee and insert a camera on a flexible tube, then use special tools to repair the cartilage.
They may also make small abrasions in the bone surface underneath the cartilage to increase blood flow and stimulate new cartilage growth.
Recovering From Knee Cartilage Surgery
You may not be able to fully weight bear until four weeks after surgery, although you should be able to drive after week two.
In the first week, your rehabilitation will focus on increasing your range of motion through manual manipulation and gentle exercises.
From then on, the physiotherapy programme will work on improving strength and mobility.
Most people are able to return to physical activity after six weeks, but it can take three to six months before you can fully recover.
Physiotherapy is very important in the recovery period, as building up the muscles and mobility is key to the long-term effectiveness of cartilage repair.
Also Check: How To Pop Your Knee
Why Is Cartilage So Important
Cartilage is the strong, pliable, and slippery substance that covers bones at joints. Cartilage has two primary functions:
- Eliminating friction between a joints bones during joint flexing and extending.
- Providing a protective cushion between bones during high-impact activities, such as running and jumping.
This slick, smooth articular cartilage can measure anywhere from less than 1 mm to more than 6 mm thick.2–4 The cartilage is bathed in a joint fluid, called synovial fluid, which further decreases friction and allows for pain-free range of motion.
Our Unique Approach To Articular Cartilage Repair
Early identification and treatment of articular cartilage damage can have a significant effect on outcomes for patients. We address cartilage damage as part of our biologic joint replacement procedure. By repairing or replacing the damaged cartilage before it completely wears out, the arthritic damage can be reversed and the joints preserved.
If this step is not taken, eventually the cartilage wear will progress so much that the bones will touch on each side of the joint, called bone on bone wear. At this stage, artificial joint replacement becomes necessary.
Recommended Reading: Why Does My Knee Stiffen Up After Sitting
Restoration Of Cartilage Can Be A Successful Alternative To Knee Replacement
The University Medical Center in Utrecht, the Netherlands, has developed a new treatment to restore cartilage in the knee. This can result in postponing a knee replacement for years. For the 54-year-old Jan de Wit it is a godsend. My knee is worn out to a degree that doing nothing was no longer an option, he says at a radio interview with Radio EenVandaag. You can listen to the full radio interview in Dutch here.
There is a growing a demand for joint-preserving techniques, such as knee joint distraction , to treat knee osteoarthritis . Because of the increased risk for revision surgery and the lower clinical efficacy in especially younger adults patient group, it is important to avoid knee arthroplasty.
With the new treatment method of the UMC Utrecht, patients can continue for years longer without knee replacement. An example of the application of this technique can be viewed here:
Cartilage can come back and regenerateThe method revolves around a metal frame that very slowly pulls the upper and lower legs of patients with osteoarthritis apart for 6 weeks. This gives the broken cartilage in the knee a chance to regenerate.
A prosthesis only lasts 15 to 20 years, and a second prosthesis is much more expensive and has less chance of success. This means that people can keep their own knee for as long as possible.
For further reference, links and research:
Can Knee Cartilage Repair Without Surgery
Can knee cartilage repair without surgery? Cartilage is essential for the free and painless movement of any joint. A common injury to the knee is to the cartilage in the joint. Cartilage often referred to as hyaline cartilage in the knee is soft and spongy and has a number of functions. Firstly, it acts as a shock absorber, absorbing pressure and stopping bone on bone contact during jumping walking and running. Secondly, it maintains the synovial fluid within the joint with the right concentrations of salts and other substances. Finally, it provides a smooth surface for joint movement to occur on. By having a smooth surface and stopping bone on bone contact the joint is able to move freely and without pain. As such, when this cartilage is damaged, pain and an inability to move the joint can occur. This can come on slowly, in the case of osteoarthritis or suddenly, as in the case of a meniscus injury from a twisting motion in sports like Football or Tennis. Either way, the cartilage is often repaired using surgery but this is associated with a number of risks and is not always ideal for older patients. So can knee cartilage repair without surgery?
As we have seen there are options for knee cartilage repair that do NOT involve risky surgery. Regenerative medicine could be the breakthrough many doctors have been waiting for as it is associated with so few risks and has so many benefits.
Read Also: What Causes Burning In The Knee
Build Knee Cartilage Naturally
If you’re searching for ways to reduce your knee discomfort, Dr. Lars Richardson, an orthopedic surgeon with Harvard Medical School-linked Massachusetts General Hospital, describes a three-part strategy that may help.
First, he recommends that you drop some weight. If you’re packing some extra pounds, each added pound means you’re exerting four pounds of pressure on the joints.
To accomplish that goal, follow a well-balanced diet that includes foods good for the joints and cartilage. Engage in low-impact exercise regularly. After you lose those pesky pounds, your joints will experience decreased pressure and pain. Dr. Richardson notes that when your body mass index reaches a healthy range, your knees should feel the benefits.
Next, partner up with a physical therapist to develop a muscle-strengthening program that results in better knee function. Target your body’s core muscles along with the hip, quadriceps and hamstrings. With stronger muscles supporting your knees, they won’t feel as much stress, and your knee joint will be better stabilized.
Work with your physical therapist to improve your knee’s range of motion. By working to straighten your knee and achieving better overall motion, you’re likely to experience fewer troublesome symptoms, Dr. Richardson points out.
Read more:Exercises That Improve Muscular Strength
Radiofrequency Ablation For Knee Pain
If all of these methods fail to control your knee pain from osteoarthritis, there are still options. Radiofrequency ablation controls pain in the knees by destroying the sensory nerves that carry the pain signal from the knee to the brain.
RFA is likely a temporary fix, as nerves will grow back in six months to two years, and the pain may return.
Also Check: Why Does My Knee Stiffen Up After Sitting
What Is Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery is a type of arthroplasty a surgical procedure to restore joint function by resurfacing damaged bone and replacing it with an artificial metal or plastic implant called a prosthesis. There are two types of knee replacement surgeries: total or partial. Total knee replacement involves replacing both sides of the knee joint, while partial replacement replaces only one side, removing less bone in the process.
According to , approximately 40% of the worlds population over 55 years old experience chronic knee pain at some point in their lifetime. The prevalence of knee replacement surgery has grown, with 2.6 million people opting for knee replacement surgery each year. With the advent of new technologies and techniques such as robotics and minimally invasive surgery, patients may benefit from reduced surgical trauma, and shortened operation and recovery times.
Mayo Clinic Q And A: New Technique For Repairing Knee Cartilage Damage
DEAR MAYO CLINIC: I’m interested in the new procedure approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration that can repair cartilage in the knee. How does it work? Who’s a good candidate for this procedure?
ANSWER: The new technique is called matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte implantation, or MACI. It can be effective for repairing isolated cartilage damage in the knee, but it’s not useful for people whose knee cartilage is diffusely damaged due to arthritis.
Your knee has two kinds of cartilage: the articular cartilage and the meniscus. Matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte implantation is used to repair articular cartilage damage, which can come from an isolated injury or defect, or as a result of arthritis.
Of these two problems, isolated injuries and defects are much less common than arthritis. They usually happen due to an athletic injury or another medical condition, such as osteochondritis dissecans. Both isolated cartilage defects and arthritis have similar symptoms, including knee pain, swelling and loss of motion.
With matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte implantation, the new cells are grown on a membrane scaffold in the lab. That’s different than the cartilage repair techniques previously used. In the older approaches, cartilage cells were grown in a lab and implanted into the knee under a patch created from a membrane taken off the outer surface of a bone, called the periosteum, or implanted under a membrane made of collagen.
Also Check: Do Copper Knee Braces Really Work
Foods That Help Regenerate Cartilage
To encourage better knee health, it’s important to minimize the rate of cartilage deterioration and take the steps needed for cartilage repair. Fisher-Titus Medical Center points out that consuming certain foods is a step in the right direction. On top of that, it supports your transition to a healthier lifestyle.
Examples of knee cartilage repair food include oily fish, such as sardines and salmon. Consuming these healthy proteins may help decrease joint pain and general morning stiffness due to the omega-3 fatty acids in fish. If you find it difficult to eat the recommended two weekly servings, consider taking omega-3 or krill oil supplements.
Add generous servings of antioxidant-rich vegetables like broccoli, spinach, spring greens and parsley to your diet. These leafy veggies may help slow the rate of cartilage deterioration.
Next, chop up some onions and garlic. Onions contain quercetin, an inflammation-reducing antioxidant. Garlic is rich in allicin, a compound that can provide some relief for rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
Problems With Replacing Worn Cartilage
Unfortunately, a cartilage replacement procedure is not as simple a task as we would hope. Cartilage cells can be cloned and reproduced in a lab. The real problem comes up when we want to place those cells in a particular location and get them to function effectively in that area. Cartilage is a complex tissue in order for cartilage to function, it must be able to withstand tremendous forces. Simply injecting cartilage into a joint would serve no useful purpose, those cells would be destroyed in a short time.
The problem is that no one has been able to figure out a way for the body to accept new cartilage and allow the cartilage to adhere to the surface of the joint. Once on the joint surface, the cartilage must be able to support the weight of the body and glide smoothly to allow normal movements. Many scientists are working on ways to accomplish these goals, but there is no solution right now.
Read Also: Can You Use An Inversion Table After Knee Replacement
How To Quickly Regenerate Damaged Cartilage
14 March, 2019
One of the most common injuries for people is damaged cartilage. It tends to be very painful but recent studies have conducted that your diet helps you regenerate cartilage even faster.
Cartilage is a very flexible structure that weightlessly supports certain structures like the pinna , nose, and joints. There are areas in our body that are much more sensitive to getting injured, such as the knee joints, and are always more affected in those who do daily physical activities like athletes.
It can also affect elderly people because of the natural deterioration of the body at a certain age.
Repair Damaged Cartilage In The Knee With Knee Cartilage Regeneration
Damaged cartilage cannot repair itself. However, knee cartilage restoration helps patients regain mobility by resurfacing and stabilizing the joint. Two of the most common cartilage restoration processes that are performed by our Rothman Orthopaedic Institute specialists are:
-
Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation : This process has two steps. To begin, a knee doctor will remove healthy cartilage from an area in the joint that will not harm the patient. The doctor will then send the cartilage collection to a laboratory, where the cells are cultured and can multiply over three to five weeks. The second step involves the reinsertion of the new cells. The doctor will add a layer of bone-lining tissue, then inject the cartilage cells beneath the cover.
-
Osteochondral Transplant: An osteochondral transplant may either include an autograft or allograft. In autograft transplantation, healthy cartilage from one joint in the body is transferred to the damaged area. Osteochondral autograft is typically suggested for smaller cartilage injuries because the procedure is done with an arthroscope.
For larger areas of damage, an allograft from a cadaver is used. Doctors suggest this type of osteochondral transplant after another restoration technique has failed to provide relief or if bone damage is present, in addition to cartilage damage.
Also Check: How To Pop Your Knee