How Common Is Osgood
Osgood-Schlatter disease is prevalent among active adolescents. Its most often found in individuals whose sports require a great deal of running and jumping, like volleyball and track. The onset of the condition often coincides with a growth spurt, usually between the ages of 10 and 15. Some individuals may experience the disease in both knees, but it more frequently shows up in one knee.
Also Check: What Knee Brace Is Best For Torn Meniscus
How Is A Bakers Cyst Diagnosed
You need a professional medical exam to diagnose a Bakers cyst. During your appointment, your healthcare provider may do several tests to both confirm the Bakers cyst and figure out what might be causing it, including:
- Taking a medical history: Your healthcare provider will ask you about any previous injuries you may have had to your knee and go over your entire medical history.
- X-ray: This test wont necessarily show the Bakers cyst itself, but it can be used to see if you have arthritis in your knee. Arthritis is one of the possible causes of a Bakers cyst.
- Magnetic resonance imaging scans: An MRI uses magnetic waves instead of X-rays to show detailed images inside the body. This test can give your provider even more information about what might be causing the Bakers cyst.
- Ultrasound: A simple and painless test, an ultrasound uses sound waves to determine if the lump is solid or fluid.
White Lump On Side Of Knee
Lump behind knee is caused by many different ways. A white lump on side of knee might be a symptom of gout, It is caused when the level of uric acid in the blood rise until it becomes excessive , causing urate crystals to build up around the joint. The symptoms of gout include painful swelling and inflammation in one or more of the joints. Gout can be extremely painful.
According to the UK Gout Society, gout affects around one in every 100 people. Its more common in men, particularly those aged 30 to 60, and in older people. Other symptoms of gout include: severe joint pain, swelling and warmth around the joint, red and shiny skin around the joint, mild fever, firm white lumps beneath the skin .
You May Like: Whiten Knees Fast
A Bakers Cyst Also Referred To As A Popliteal Cyst Or Bulge
A Bakers cyst, also referred to as a popliteal cyst or bulge-knee, is a fluid-filled sac located in the back of the knee. The knee joint is filled with a special type of fluid that helps cushion the spaces between the bones, ligaments, and muscles in order to prevent wear and tear on the joint. A Bakers cyst forms when synovial fluid leaks into the back of the knee. Occasionally, a Bakers cyst can rupture and cause swelling in the calf.
Diagnosis Of Bakers Cyst
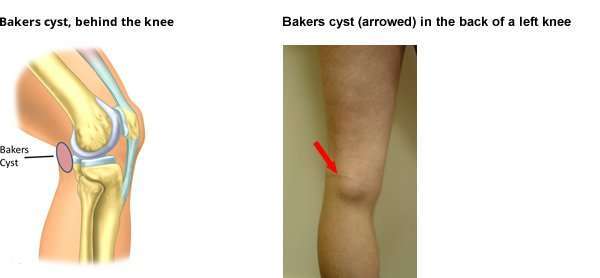
A lump at the back of the knee is a good indication that you may have a Bakers Cyst. A physical examination will help confirm it. Other problems such as a blood clot, aneurysm or tumor need to be ruled out, which makes it important for you to seek medical attention if you notice a protrusion in the hollow of your knee.
Non-invasive imaging tests may be used to rule out these other possibilities. Ultrasound scans, also called sonograms, use high-frequency sound waves to generate an image of what is going on inside the body. X-rays may also be used in the diagnosis. These produce pictures of the bones and other structures in the knee. Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, is also used to see the structures of the knee joint. This procedure uses radio waves in conjunction with a large magnet to produce the images.
After ruling out other conditions and confirming the presence of Bakers cyst, you doctor will create a treatment plan. Treatment will be determined by the size of the cyst and whether or not it is causing problems or discomfort.
Don’t Miss: Does Aflac Cover Hysterectomy
What Is The Pain At The Back Of My Knee
A swelling at the back of the knee and calf causing pain, and a feeling of tightness when straightening the leg. This may be due to a Bakers Cyst, which is an accumulation of synovial fluid in the popliteal fossa. The synovial fluid is over-produced, due often to a trauma to the knee or in conditions such as arthritis
Who Gets A Baker’s Cyst
A Baker’s cyst most commonly occurs in children aged 4 to 7 years and in adults aged 35 to 70 years. However, Baker’s cysts are much more common in adults than in children. You are more likely to develop a Baker’s cyst if you have an underlying problem with your knee.
Arthritis is the most common condition associated with Baker’s cysts. This can include various different types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis , rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and gout.
Baker’s cysts may also develop if you have had a tear to the meniscus or to one of the ligaments within the knee, or if you have had an infection within your knee joint.
Read Also: Bioknee Cost
What Causes Bakers Cyst
A Bakers cyst forms when swelling inside the knee causes synovial fluid to leak into the space behind the knee. As synovial fluid collects, a cyst or bulge forms.
Conditions that can cause swelling of the knee, and therefore may lead to the formation of a Bakers cyst include:
- Arthritis, including osteoarthritis
- An injury, such as a meniscus tear
- Rheumatologic conditions
Bakers Cyst Causes And Treatment
A Bakers cyst is a swelling in the space behind the knee. It has nothing to do with baking. The condition is named after a British surgeon, Dr. William Morrant Baker. In the late 19th century, Dr. Baker documented cases of swelling in the popliteal region, the depression in the back of the knee joint, hypothesizing that it was a result of synovial membrane herniation and cyst formation due to osteoarthritis.
Synovial fluid lubricates the knee to help the leg move and reduces friction between all of the moving parts of the knee. A Bakers or popliteal cyst is a synovial fluid filled cyst that develops behind the knee. It is usually the result of knee joint conditions, such as arthritis, torn cartilage, and gout, that cause the knee to produce excess lubricating fluid. Bakers cyst symptoms include a bulge in the back of the knee, knee joint locking or popping, and knee and calf pain. The symptoms are similar to a blood clot, aneurysm or tumor in the leg. So it is important to rule out a serious cause of your symptoms.
Usually Bakers cysts can be resolved by some self-care techniques such as icepacks, rest, compression bandages, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications.
If the swelling is particularly large and painful, other treatments include:
- A corticosteroid injection to reduce inflammation and relieve pain
- Physical therapy to strengthen knee muscles
- Fluid drainage via needle aspiration
- Arthroscopy surgery to remove the cyst and repair the joint
Don’t Miss: How To Whiten Knees Fast
Common Treatments For Ligamentous Strains Or Tears
The most common treatment for mild to moderate ligament strains is the RICE method, which is resting the area, applying ice to reduce swelling, applying compression via braces or bandages and elevating the area. Pain relievers may also be used to alleviate symptoms.
In moderate to severe cases, including those involving a tear, other treatment might be considered. Physical therapy, reconditioning and even surgery might be options, depending on the severity of the injury.
Recommended Reading: Nano Knee Surgery Cost
Are There Any Complications That Can Develop
The most common complication of a Baker’s cyst is for it to split open . If this happens, the fluid from inside the cyst can leak out into your calf muscle. This can cause swelling of your calf. You may also develop itching and redness of the skin of your calf because of irritation caused by the fluid that leaks out from the cyst. About 1 or 2 in 20 Baker’s cysts are thought to rupture.
If a Baker’s cyst ruptures, it can be quite difficult to tell the difference between the ruptured cyst and a deep vein thrombosis in the leg. A DVT is a blood clot that forms in a leg vein. In these cases, it is important that investigations are carried out to exclude a DVT because it can be a serious condition that needs treatment. See the separate leaflet called Deep Vein Thrombosis for more detail.
Very rarely, a Baker’s cyst may become infected.
You May Like: Ginger Poultice For Knee Pain
What Is The Treatment For A Baker’s Cyst
A Baker’s cyst often gets better and disappears by itself over time. Primary Baker’s cysts in children all usually disappear with time. However, the cyst may persist for months or even years before it goes. In a lot of people it causes little in the way of symptoms and no specific treatment is needed.
There are various treatment options that may help if you do have symptoms associated with a Baker’s cyst. These include:
Can You Have A Blood Clot In The Back Of Your Knee
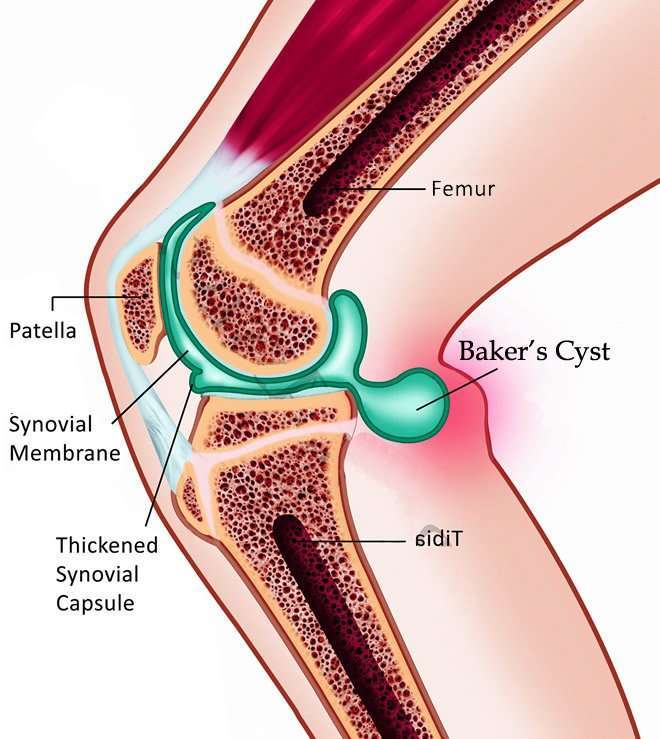
A blood clot behind the knee is a type of venous thromboembolism. It is a serious condition that can lead to life-threatening complications, such as a pulmonary embolism. The popliteal vein runs behind the knee and transports blood back up to the heart. We also cover diagnosis, treatment, complications, and prevention.
Read Also: Inversion Table Benefits For Knees
Rest Ice Compression Elevation
Your doctor may recommend following the RICE principles: rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Give your joint plenty of time to rest, and elevate your leg when possible, especially at night. Holding an ice pack or bag of frozen peas wrapped in a dishcloth to the affected area for 10 to 20 minutes can help reduce swelling. Compression bandages, wraps, sleeves, and braces can also help support the knee joint.
One member shared their tips: Ice helps. Put ice up on a pillow at night time. Lie flat on your back.
How Can Baker’s Cysts Be Prevented
Knee joints are susceptible to injury during sporting activities. Preventing knee injuries from occurring can reduce the risk of a Baker’s cyst developing in the first place or coming back.
Things you can do to prevent knee injuries include:
- warming up and cooling down before and after exercising or playing sports
- wearing supportive footwear
- trying to turn on the balls of your feet, rather than through your knees.
If you injure your knee, stop your activity immediately, apply ice packs to treat the swelling and seek medical advice.
Recommended Reading: Dcf Compression Knee Sleeve
What Are Bakers Cyst Causes
A Bakers cyst develops as a result of metabolic and dystrophic violations in joints. Most often that appear after injuries, meniscus failures, and as a result of inflammations. Rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, knee injury, damage to the cartilage, psoriatic arthritis, excessive exercise, osteoarthritis and so forth are among them. In some cases, Bakers cyst cause of occurrence is not possible to establish.
We know that the main Bakers cyst cause is an inflammation of the mucous in synovial bursa. It is between the semimembranosus muscle and the tendons of the middle of the gastrocnemius muscle head. And these synovial bursa exists in 50% of healthy people. The disease develops only due to the inflammatory process in it. It manifests with an increase of the cavity, limits of motion and pain in the knee.
When the inner synovial capsule of the joint becomes inflamed, the fluid released fill the cavity and stored in synovial bursa. The most common reason of the inflammation, which is indirectly aBakers cyst cause, is a knee disease of the synovial bursa.
Among other Bakers cyst causes, are the following the diseases. They appear in knee tissues and lead to the formation of the cyst:
- cartilage damage
- chronic synovitis
- degenerative meniscus
- patellofemoral arthrosis
Key Points About Baker Cysts
- A Baker cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms behind the knee. They usually don’t cause major problems.
- A Baker cyst is usually the result of some other problem with the knee. It may be caused by osteoarthritis or a tear of the knees cartilage.
- Many people with Baker cysts dont have any symptoms. You might have some pain behind the knee.
- Your healthcare provider will try to treat any underlying conditions. You may also need fluid removed from the knee joint space or the cyst.
- Surgery isn’t usually needed for a Baker cyst.
- In rare cases, a Baker cyst can rupture. This can cause serious complications. See your provider right away if your leg is red and swollen.
Recommended Reading: Does Aflac Pay For Sprains
What Causes A Bakers Cyst
A Bakers cyst is caused by excess fluid in the knee joint. As the joint swells, excess synovial fluid seeps backwards out of the joint and into the popliteal bursa. As the fluid enters the bursa it starts to swell resulting in bursitis.
A number of things can cause the swelling of the knee that leads to a Bakers Cyst:
- Osteoarthritis: wear and tear of the knee bones and cartilage leads to increased fluid in the knee joint. 50% of arthritis sufferers develop a Bakers cyst at some point. Osteoarthritis is by far the most common cause of Bakers cysts.
- Knee Injuries: any injury that results in swelling inside the knee joint increases the risk of developing a popliteal bursitis. The most common injury to cause a Bakers cyst is a cartilage tear.
- Inflammatory Arthritis: There are a few types of inflammatory arthritis that increase the risk of developing a Bakers cyst, the most common being gout.
How Do You Know If You Have A Torn Meniscus In Your Knee
If youve torn your meniscus, you might have the following signs and symptoms in your knee: A popping sensation. Swelling or stiffness. Pain, especially when twisting or rotating your knee. Difficulty straightening your knee fully. Feeling as though your knee is locked in place when you try to move it.
Recommended Reading: Inversion Table For Knee Pain
What Are The Symptoms Of A Bakers Cyst
Sometimes youll feel no pain at all, or only a slight pain with a Bakers cyst. You may only have knee pain from the initial damage that caused the Bakers cyst, but not the lump itself. Any strain can cause this lump or your knee to swell in size. When the knee or cyst swells, this can increase your pain and limit how much you can move your knee.
Symptoms of a Bakers cyst may include:
- A fluid-filled lump behind your knee.
- Pain.
- Limited range of motion and ability to bend your knee.
- Swelling of your knee and/or leg.
Sometimes, a Bakers cyst can cause swelling and redness in your lower leg that can be similar to the symptoms of a blood clot. A blood clot is an emergency situation. If you are ever in doubt, reach out to your healthcare provider right away. Your provider can check out your symptoms and determine if its a Bakers cyst or a blood clot.
What Is A Baker’s Cyst
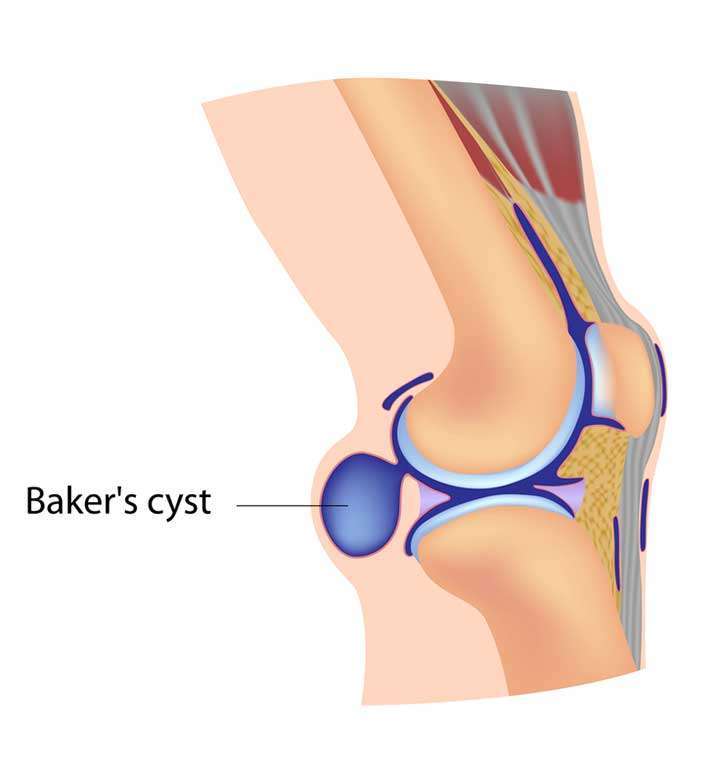
A Baker’s cyst is a fluid-filled swelling that can develop behind the knee. It is one cause of knee pain.
It is named after a doctor called William Baker who first described this condition in 1877. It is also sometimes called a popliteal cyst, as the medical term for the area behind your knee is the popliteal fossa.
The cyst can vary in size from a very small cyst to a large cyst that is a number of centimetres across. Rarely, a Baker’s cyst can develop behind both knees at the same time.
Recommended Reading: Dcf Knee Compression Sleeve
How Is A Bakers Cyst Treated
Treatment of a Bakers cyst usually starts with nonsurgical options. One time-honored method that sports doctors and orthopaedic surgeons have relied on for decades to soothe swelling from joint damage is the RICE method: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation.
Nonsurgical treatment.
Often, your healthcare provider will suggest that you start with a nonsurgical treatment of your Bakers cyst. These are generally things you can do at home and on your own that can improve your symptoms.
Nonsurgical treatment options can include the RICE method:
- Resting your leg whenever possible.
- Applying ice to your knee.
- Using compression wraps on your knee to decrease the amount of joint swelling.
- Elevating your knee while you are resting.
Other nonsurgical treatment options for a Bakers cyst can include:
- Taking an anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen.
- Maintaining a healthy body weight, which can help put less pressure on your joints.
- Avoiding activities that strain your knee. This includes avoiding high-impact sports like jogging.
- Using a crutch or cane when you walk.
- Getting a referral for physical therapy from your healthcare provider to help strengthen your knee and body.
Your healthcare provider may also give you a steroid injection. This involves cortisone being injected into your knee joint, which can reduce inflammation and pain.
Surgical treatment.
Your provider might suggest a surgical option to you if:
- Your knee pain is severe.
- Youre unable to move your knee well .
Some Knee Joint Anatomy
The first diagram below illustrates a typical normal knee joint looking from the side.
The joint capsule is a thick structure that surrounds your whole knee and gives it some support. It is lined by a special membrane called the synovium. The synovium produces a fluid called synovial fluid. This fluid acts as a lubricant within your knee joint and helps to cushion it during movement.
There are also various tissue pouches called bursae next to the knee. A bursa is a small sac of synovial fluid with a thin lining. Bursae are normally found around joints and in places where ligaments and tendons pass over bones. They help to reduce friction and allow maximal range of motion around joints. The bursa at the back of your knee is called the popliteal bursa.
Each knee joint also contains a medial and a lateral meniscus. These are thick rubber-like pads of cartilage tissue. The menisci cartilage sit on top of, and are in addition to, the usual thin layer of cartilage which covers the top of one of the bones of the lower leg, called the tibia. They act as shock absorbers to absorb the impact of the upper leg on the lower leg. They also help to improve smooth movement and stability of the knee.
Read Also: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Outpatient Surgery