What Makes Me Susceptible To Arthritis Of The Knee
Inherited bone structure or genetic mutations can contribute to the development of knee arthritis, as well as repetitive injury from a profession or sports. Age-related arthritis becomes common after 45 years of age.
Weight is also a factor, since the knee bears much of the bodys weight. The constant pounding pressure that is placed on the knee when walking, which becomes greater with more weight, causes the cartilage in the joint to break down over time. When the cartilage disintegrates, bone-on-bone scraping occurs whenever you move your leg.
Orthopedic Knee Surgery In Macomb County Mi
Fortunately, the days of suffering with knee pain associated with arthritis are over. Movement Orthopedics treats knee arthritis with state-of-the art surgical and nonsurgical methods, and our orthopedic team can help you get back to an enjoyable lifestyle again.
If you have any questions about our practice, or if you would like to schedule a consultation with one of our skilled orthopedic surgeons, contact our friendly staff today by calling us at 436-3785 or by filling out our easy-to-use online appointment request form now. We look forward to being your partner in total health and wellness!
Special Cartilage In The Knee
Each knee has two moon-shaped sections of cartilage, each called a meniscus. The lateral meniscus is located in the outer knee near your hands when you are standing up with your arms at your sides and the medial meniscus is in the inner knee. When someone has a torn ACL in the knee, they are also likely to have a torn meniscus.
The more wear-and-tear and injury that is caused to this cartilage, the more likely you are to develop arthritis in the knee. This is because the menisci cannot fully perform their job as a cushion between the knee bones.
Recommended Reading: How To Fix Knee Pain From Basketball
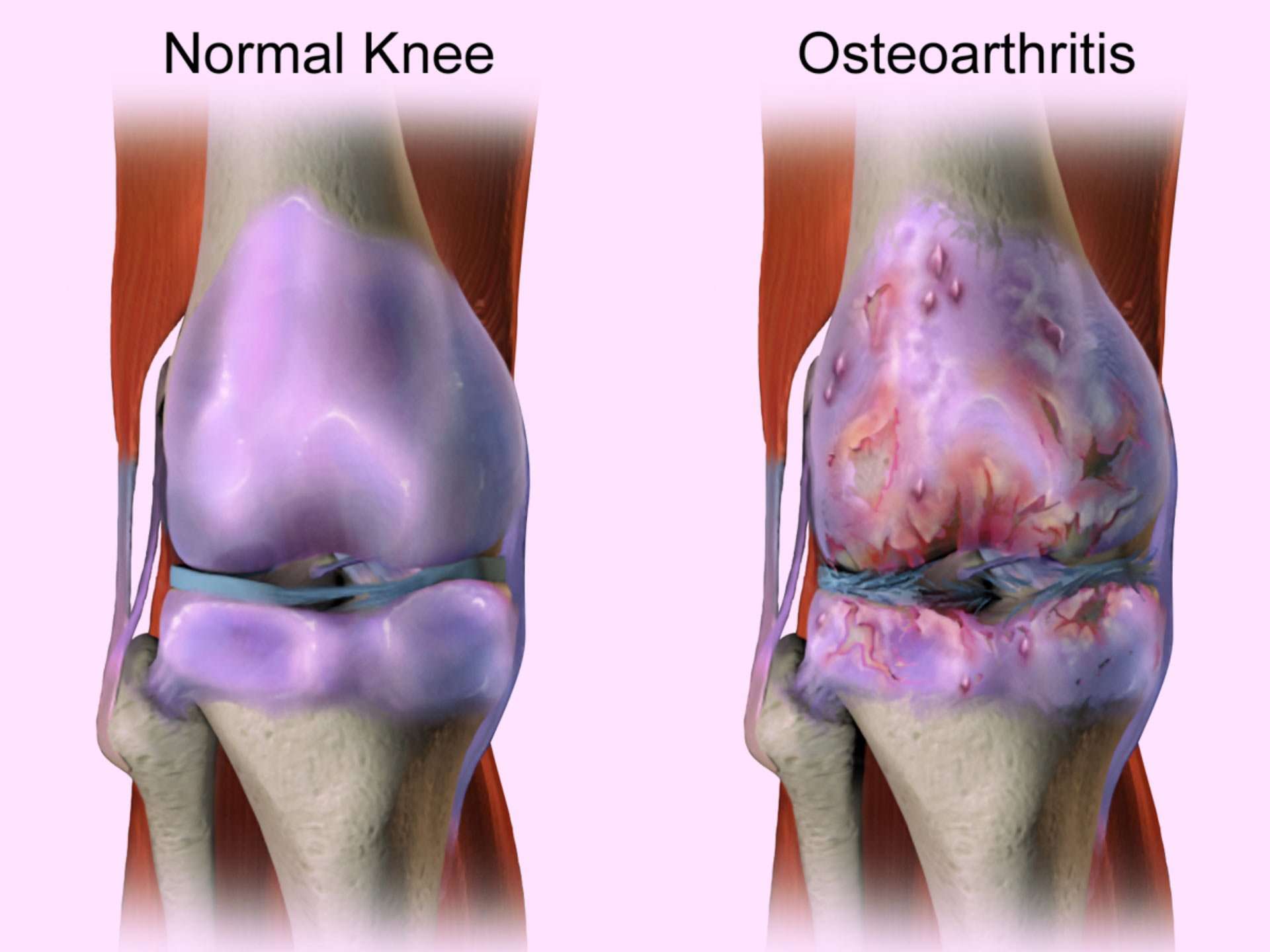
Types Of Arthritis That Affect The Knee
Osteoarthritis is characterized by cartilage degeneration and bony protrusions called osteophytes . In the knee, the most common sites of osteoarthritis include the tibia , femur , and patella .
The most common type of arthritis affecting the knee is osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis occurs when a joints articular cartilage breaks down. In the knee, articular cartilage covers the top of the tibia , bottom of the femur , and back of the patella .
Not everyone with knee osteoarthritis will get knee pain. Pain may occur if the loss of healthy cartilage:
- Causes the bones of the joint to rub against one another.
- Compromises the joints biomechanics in some other way.
See Knee Osteoarthritis Symptoms
Post-traumatic knee arthritisPost-traumatic arthritis is a type of osteoarthritis. It develops after a meniscus tear, ligament injury, or other trauma. The injury may heal but wear-and-tear on the articular cartilage can accelerate. Post-traumatic arthritis may not become symptomatic until years after the injury.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that targets the synovial membrane surrounding many joints of the body. Some of the most common areas affected include the wrists, knees, and ankles.
Knee pain can be caused by an autoimmune disease called rheumatoid arthritis . RA causes joint inflammation that can make the knee feel swollen, stiff, warm, and painful. Over time, untreated RA can cause permanent knee joint damage.
See What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis ?
Where Can Arthritis Occur In The Knee
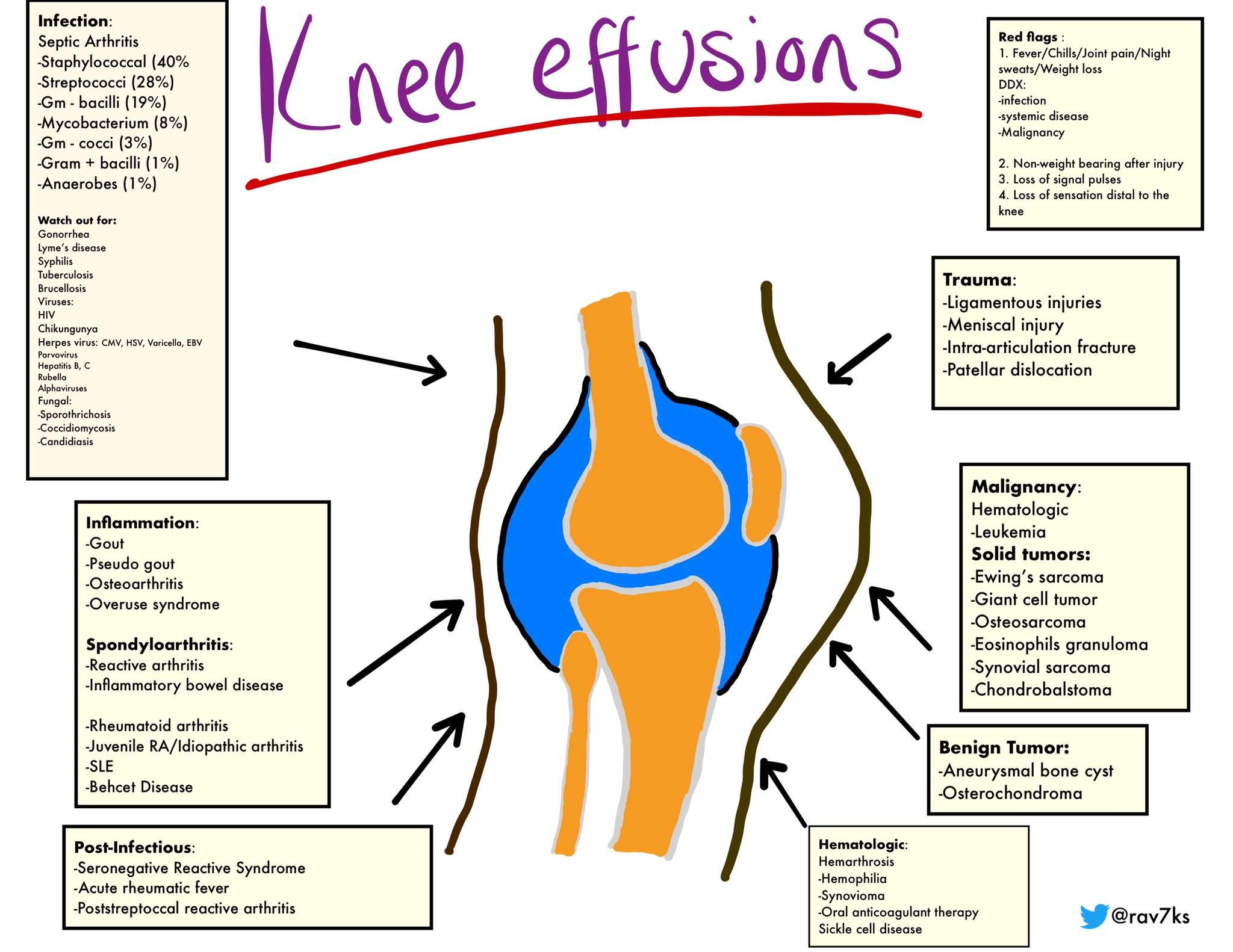
Cartilage loss can occur between the thighbone and the shinbone in the medial portion , lateral portion and under the kneecap.
- Thinning of the cartilage under the kneecap is called patellofemoral arthritis .
- Some patients have cartilage loss in one, two or all of these areas. When all three areas are affected, this is called tricompartmental arthritis.
Recommended Reading: Why Does My Knee Hurt For No Reason
Other Causes Of Calf Pain
So weve looked at the most common causes of calf muscle pain, but there are a few other less common causes of pain in the calf region.
1. Deep Vein Thrombosis
A deep vein thrombosis can be a very serious cause oflower leg pain. A DVT is the formation of ablood clot in a deep vein, usually in the calf or thigh.
A DVT requires IMMEDIATE medical attention as it reduces the blood flowto the foot, and there is the risk that the blood clot could break off andtravel through the bloodstream to the heart or lungs which can cause a heartattack or pulmonary embolus.
The commonsigns of a DVT are pain, redness, warmth and swelling in the calf region. The pain often gets worse if your dorsiflex your foot .
DVTs often develop after surgery or periods of inactivity e.g. plane journeys, and there can be a genetic link.
2. Trapped Nerve
Compression of the nerves of the lower leg can cause pain, pins and needles and numbness in the calf region.
The nerve compression may be coming from the lowerback where the nerve originates from, or at any point along the nerve itself.
Trapped nerves are usually accompanied by changes in sensation such as pins and needles, tingling or numbness and lower leg pain often spreads.
Any symptoms of nerve compression should bechecked out by your doctor. You can find out more in the nerve pain section on our sister site.
3. Muscle Imbalance
4. Peripheral Vascular Disease
Knee Pain At A Glance
- The knee joint has three compartments.
- Causes of knee pain include injury, degeneration, arthritis, infrequently infection, and rarely bone tumors.
- Ligaments within the knee and on the inner and outer sides of the knee stabilize the joint.
- Surgical repair of ligament injury can involve suturing, grafting, and synthetic graft repair.
- Routine X-rays do not reveal meniscus tears, but can be used to exclude other problems of the bones and other tissues.
- The knee joint is commonly involved in rheumatic diseases, immune diseases that affect various tissues of the body including the joints.
Show Sources
Dont Miss: Nano Knee Surgery Cost
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Black Knees
Is Surgery Used To Treat Knee Osteoarthritis
If your doctor wants to treat the osteoarthritis in the knee with surgery, the options are arthroscopy, osteotomy, and arthroplasty.
- Arthroscopy uses a small telescope and other small instruments. The surgery is performed through small incisions. The surgeon uses the arthroscope to see into the joint space. Once there, the surgeon can remove damaged cartilage or loose particles, clean the bone surface, and repair other types of tissue if those damages are discovered. The procedure is often used on younger patients in order to delay more serious surgery.
- An osteotomy is a procedure that aims to make the knee alignment better by changing the shape of the bones. This type of surgery may be recommended if you have damage primarily in one area of the knee. It might also be recommended if you have broken your knee and it has not healed well. An osteotomy is not permanent, and further surgery may be necessary later on.
- Joint replacement surgery, or arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which joints are replaced with artificial parts made from metals or plastic. The replacement could involve one side of the knee or the entire knee. Joint replacement surgery is usually reserved for people over age 50 with severe osteoarthritis. The surgery may need to be repeated later if the prosthetic joint wears out after several years. But with today’s modern advancements, most new joints will last over 20 years. The surgery has risks, but the results are generally very good.
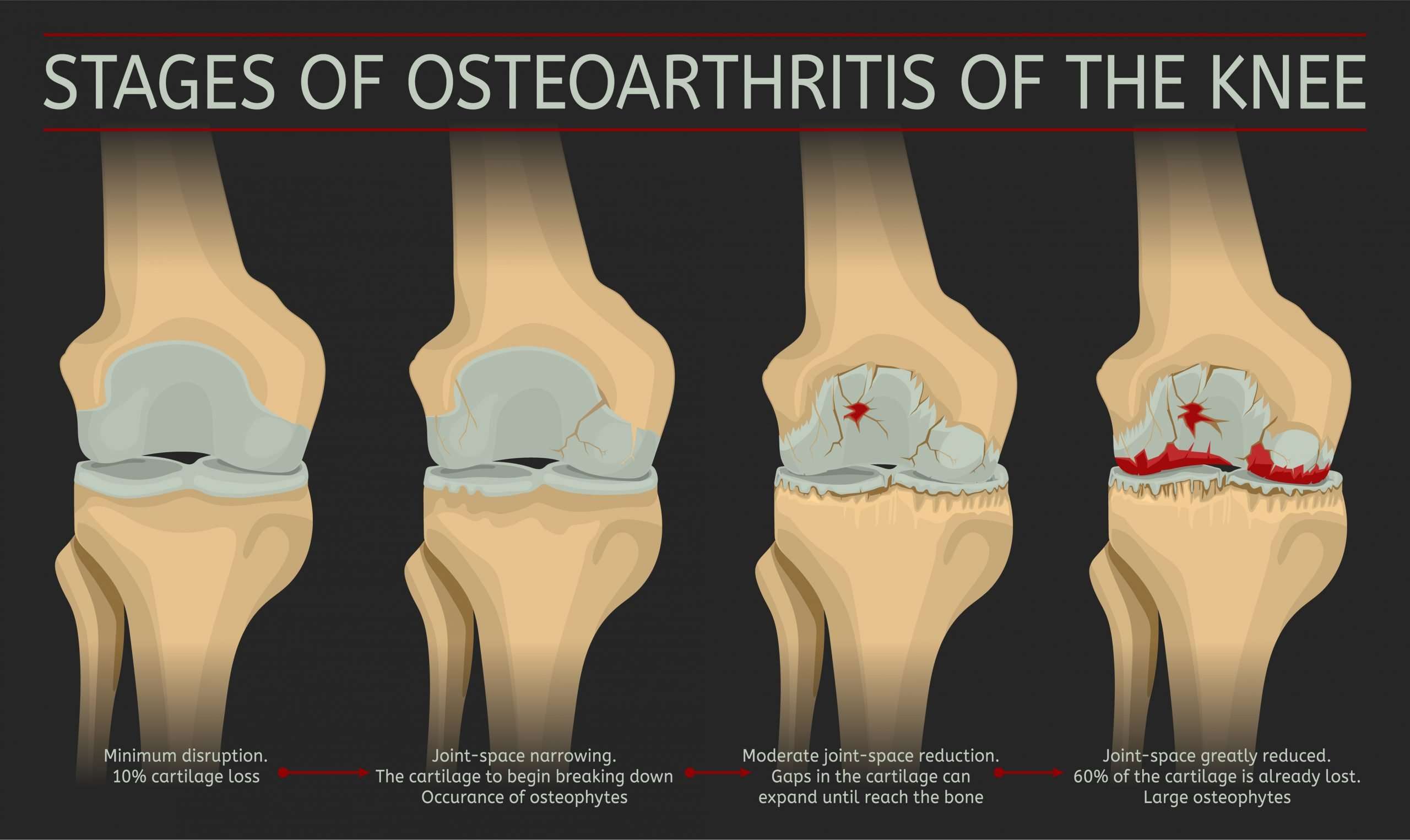
Imaging For Diagnosing Advanced Knee Osteoarthritis
X-rays are very helpful in diagnosing advanced knee osteoarthritis because the joint will have specific characteristics, including:
- Bones that are closer to each other than they should be: As cartilage wears away, the joint space between them often narrows.
- Cysts: As the body responds to cartilage destruction and attempts to stabilize the joint, cysts or fluid-filled cavities can form in the bone.
- Increased bone density or uneven joints: When bones are no longer cushioned by cartilage, they can rub against one another, creating friction. The body responds by producing more bone tissue, which increasing bone density. Increased bone creates uneven joint surfaces and bone spurs at the joint.
Recommended Reading: What Can I Use For Knee Joint Pain
Gradual Increase In Pain
Arthritis pain usually starts slowly, although it can appear suddenly in some cases.
At first, you may notice pain in the morning or after youve been inactive for a while.
Your knees may hurt when you:
- climb stairs
- stand up from a sitting position
- walk on a flat surface
- sit down for a while
Knee pain that wakes you up from sleep can be a symptom of OA.
For people with RA, the symptoms often start in the smaller joints. They are also more likely to be symmetrical, affecting both sides of the body. The joint may be warm and red.
With OA, symptoms may progress rapidly or they may develop over several years, depending on the individual. Symptoms can worsen and then remain stable for a long time, and they can vary day to day.
Factors that may cause worsening of symptoms include:
- cold weather
- stress
- excessive activity
With RA, symptoms usually appear over several weeks, but they can develop or worsen in a few days. A flare can happen when disease activity increases. Triggers vary and can include changes in medication.
Knee Arthritis In Young People Often Result Of Previous Injury
Osteoarthritis of the knee is usually thought to affect only senior citizens. Thats because it is often associated with aging, genetics, and gradual wear and tear on weight bearing joints over time. But osteoarthritis which is marked by joint pain and stiffness can also affect much younger people.
Research shows a joint injury suffered at any age increases the risk of early onset osteoarthritis. In the knee, for example, sports injuries such anterior cruciate ligament and meniscus tears are associated with rapid or early onset post-traumatic arthritis, a form of osteoarthritis.
Because these type of injuries occur in our prime athletic years during high school and college, its not uncommon for people in their 40s and 50s to have advanced stages of osteoarthritis, says William Bugbee, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Scripps Clinic.
Early diagnosis important
It can take a while for old knee injuries to cause ongoing symptoms. Symptoms can usually be managed but damage to joints cant be reversed. That is why early diagnosis is critical for effective treatment.
Medical treatment of knee osteoarthritis in young people does not differ from its management in the general population, says Dr. Bugbee.
In many cases, people with knee osteoarthritis can make lifestyle changes to help reduce pain, slow progression of the disease and help improve joint function. If symptoms become severe, knee replacement is an option, but this is generally reserved for older adults.
You May Like: How To Get Fluid Out Of Knee
You Arent Exercising Which Is Bad For Your Knees
It may seem counterintuitive to exercise if you have joint pain, but the Arthritis Foundation tells people to be active. The knee joint loves motion, says Brian Halpern, MD, a sports medicine physician with the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City and author of The Knee Crisis Handbook. The challenge is to find the best types of activities for you. Dr. Halpern recommends bicycling, swimming, and elliptical trainers, as well as strengthening exercises that help muscles support the knee joint.
Also Check: How Do You Treat Arthritis In The Hip
What Other Symptoms Are Linked With Knee Joint Pain
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee are generally limited to the joint itself, whereas inflammatory arthritis causes a wider array of issues. Unlike OA, inflammatory arthritis is a systemic disease, which means it affects the whole body, says CreakyJoints Medical Advisor Vinicius Domingues, MD, a rheumatologist in Daytona Beach, Florida.
In fact, it would be less common for someone with a form of inflammatory arthritis to experience pain in just one knee. Thats because symptoms are usually symmetrical whats more, inflammatory arthritis symptoms usually dont start in the knee.
For example, rheumatoid arthritis generally strikes the small joints in the fingers and toes first, while someone with ankylosing spondylitis is more likely to complain of low back and buttock pain, with knee arthritis pain developing later.
Depending on the type of inflammatory arthritis you have, you may experience other symptoms beyond knee joint pain. People with psoriatic arthritis exhibit the telltale scaly rash and plaques of psoriasis eye inflammation can be a problem for those with psoriatic arthritis as well as ankylosing spondylitis, and people with rheumatoid arthritis may experience weight loss and fevers.
Read Also: How To Fix Damaged Cartilage In Knee
What Type Of Doctor Treats Knee Arthritis
Osteoarthritis of the knee may be treated by a sports medicine physician or an orthopedic surgeon, depending on your particular condition. A physical therapist may be able to treat less severe cases to help reduce pain and increase your mobility. If your knee pain is a result of rheumatoid arthritis, gout or other form of inflammatory arthritis, you should consult a rheumatologist. “” rel=”nofollow”> Find a doctor who diagnoses and treats knee arthritis.)
Special Devices And Footwear
Walking sticks can help to reduce the load on your knees and reduce pain when moving about. Other ways to improve symptoms of osteoarthritis include taping the joint, wearing braces, or using shoe insoles that improve your body alignment when standing and walking. Check with your physiotherapist for advice about using aids or supports.
Recommended Reading: How To Relieve Chronic Knee Pain
What Questions Might A Healthcare Provider Ask To Diagnose Arthritis Of The Knee
Your healthcare provider will interview you when you report your symptoms. Some questions might include:
- Does anyone in your family have arthritis of the knee?
- Does your knee swell up?
- Is your skin often red?
- Is your skin often warm?
- Do you have symptoms in one knee or both?
- How long have you had these symptoms?
- What medications do you take?
- How severe is your pain?
- Do you struggle to walk?
- Do the symptoms interfere with your daily activities?
Treatment Goals: Manage Pain And Improve Function
Osteoarthritis treatment plans often include exercise, rest and joint care, pain relief, weight control, medicines, surgery, and complementary treatment approaches. Current treatments for osteoarthritis can relieve symptoms such as pain and disability, but there are no treatments that can cure the condition.
Although health care professionals can prescribe or recommend treatments to help you manage your arthritis, the real key to living well with the disease is you. Research shows that people with osteoarthritis who take part in their own care report less pain and make fewer doctor visits. They also enjoy a better quality of life.
Read Also: Can I Regrow Cartilage In My Knee
Also Check: How Much Range Of Motion After Knee Replacement
What Is The Treatment For Knee Arthritis
Nonsurgical methods to relieve pain and stiffness should are usually tried first. These may include physical therapy, and/or oral pain medications or injections of corticosteroid or other agents. Advanced knee osteoarthritis may require surgery such as a partial or total knee replacement or patellofemoral joint replacement. Inflammatory arthritis in the knee is usually managed medically rather than surgically.
In cases of â inflammation of the synovium â or effusion , a and/or to aspirate the joint may be appropriate.
What Are The Parts Of A Joint
Joints get cushioned and supported by soft tissues that prevent your bones from rubbing against each other. A connective tissue called articular cartilage plays a key role. It helps your joints move smoothly without friction or pain.
Some joints have a synovial membrane, a padded pocket of fluid that lubricates the joints. Many joints, such as your knees, get supported by tendons and ligaments. Tendons connect muscles to your bones, while ligaments connect bones to other bones.
Read Also: How To Lighten Dark Knees
What Does The Procedure Involve
You can usually receive a knee injection in your doctors office. The procedure only takes a few minutes.
Youll be seated during the procedure, and your doctor will position your knee. They may use ultrasound to help guide the needle to the best location.
Your doctor will:
- clean the skin on your knee and treat it with a local anesthetic
- insert the needle into your joint, which might cause some discomfort
- inject the medication into your joint
Though you may feel some discomfort, the procedure is rarely painful if your doctor has experience administering this type of injection.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may remove a small amount of joint fluid to reduce pressure.
Theyll insert a needle attached to a syringe into the knee joint. Then, theyll draw out the fluid into the syringe and remove the needle.
After removing the fluid, the doctor can use the same puncture site to inject the medication into the joint.
Finally, theyll place a small dressing over the injection site.
Lower Leg Pain Caused By Veins And Nerve Issues
1. Blood Clot
When blood thickens in veins, it can develop a clot. This typically happens in the thigh or lower leg, commonly leading to pain from knee to ankle. There is a higher risk if you are overweight, on certain medicines, or inactive for a long car ride or flight.
2. Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are caused by weakness in the vein walls or valves and can lead to a dull ache, particularly after standing.
3. Lower-Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease
This occurs if your legs arteries get damaged and harden. The legs begin to miss needed blood flow, leading to pain or cramps when walking or climbing stairs.
4. Narrowed Spinal Canal and Sciatica
When the spinal canal narrows due to a herniated disc, arthritis of the spine, or another cause, it can lead to weakness, fatigue, numbness, tingling, or cramping, burning leg pain when you sit or stand. It may start in the hip and the back before extending down the leg.
5. Diabetic Neuropathy
This diabetes complication can be due to high blood sugar levels and leads to pain in both legs. It also features less sensation and numbness in lower legs.
When to See a Doctor
You should see your doctor for pain from knee to ankle if you have the following symptoms:
You May Like: Is Knee Replacement Major Surgery