How Long Will A Knee Replacement Last
It varies depending on the type of knee replacement procedure you have, the implant used, and the patients age, weight, and activity level.
Although there is no guarantee of how long the medical device will last, typically a total knee replacement with a cemented implant lasts about 15-20 years.
For patients under 60, Dr. Likover has performed a porous bone in-growth Regenerex implant that does not use cement and has the potential to last a lifetime.
In cases of a partial knee replacement, the Oxford implant has a limited lifetime warranty.
Looking After Your Knee Replacement
Your new knee will continue to improve for as much as two years after your operation as the scar tissue heals and;you exercise your muscles. You’ll need to look after yourself and pay attention to any of the following problems:
Stiffness Sometimes the knee can become very stiff in the weeks after the operation for no obvious reason. Try placing your foot on the first or second step of the stairs, hold on to the banister and lean into your knee. This should help to improve movement and flexibility in your knee. Its very important to continue with the exercises you were working on in the hospital.If the stiffness doesnt improve after about six weeks your surgeon may need to move or manipulate your knee. This will be done under anaesthetic.
Pain Pain caused by bruising from the operation is normal in the first two months, and you’ll probably still need to take;painkillers at six weeks to help you sleep through the night. You may still have some pain for as long as six months. If you still have pain after this, speak to your;physiotherapist or GP.
Infection You should speak to your GP or hospital if you notice any signs of infection, for example:
- breakdown of;the wound with oozing/pus or sores
- increased pain
- redness and the affected area feeling warmer than usual or smelling unpleasant.
You should also look after your feet see a doctor or;podiatrist if you notice any problems such as ingrown toenails that could become infected.
Reasons For The Procedure
Knee replacement surgery is a treatment for pain and disability in theknee. The most common condition that results in the need for kneereplacement surgery is osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis is characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage.Damage to the cartilage and bones limits movement and may cause pain.People with severe degenerative joint disease may be unable to donormal activities that involve bending at the knee, such as walking orclimbing stairs, because they are painful. The knee may swell or”give-way” because the joint is not stable.
Other forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and arthritis thatresults from a knee injury, may also lead to degeneration of the kneejoint. In addition, fractures, torn cartilage, and/or torn ligaments maylead to irreversible damage to the knee joint.
If medical treatments are not satisfactory, knee replacement surgery may bean effective treatment. Some medical treatments for degenerative jointdisease may include, but are not limited to, the following:
-
Anti-inflammatory medications
-
Cortisone injections into the knee joint
-
Viscosupplementation injections
-
Weight loss
There may be other reasons for your doctor to recommend a knee replacementsurgery.
Read Also: How To Fix Injured Knee
Care After The Operation
Please give some thought as to how you will be looked after once you have had the operation, well in advance. Most people like to be independent, but you are going to need support with day-to-day activities for a while. If you have an able-bodied partner, this might fall to them, but otherwise you may need a friend or relative to come to stay with you for a while. Some people may arrange to stay in a care home until they have their mobility and independence back.
S To Take After Surgery
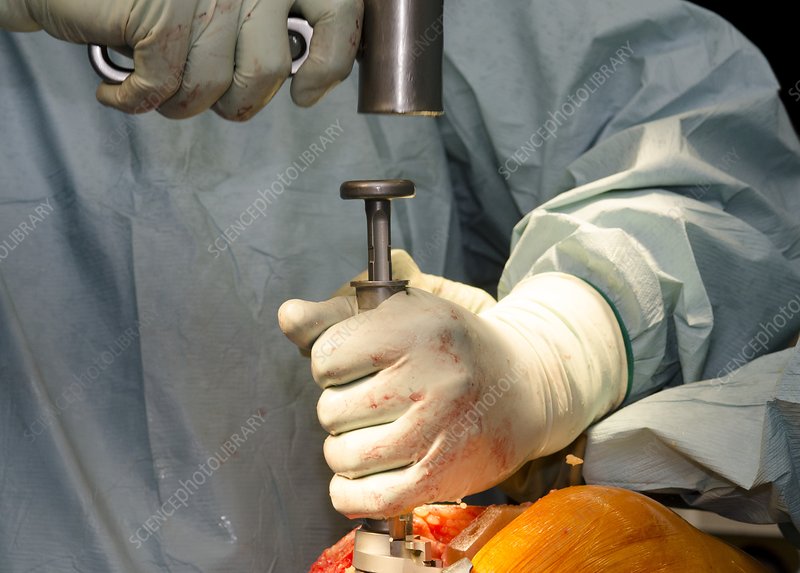
After surgery, the following steps can help reduce the chances of infection:
- Follow your surgeons guidance on how to take care of your incision.
- Treat any cuts, wounds, burns, or scrapes as soon as they happen. Clean with an antiseptic product and then cover it with a clean bandage.
- Keep up with preventive dental health and dont delay in seeing your dentist. Your dentist or orthopedic surgeon may want you to take antibiotics about an hour before any dental procedures to reduce your chance of infection.
See your doctor if you think you might be developing any kind of infection after total knee replacement, including urinary tract infections, ingrown toenails, and skin infections.
Don’t Miss: What Is Nano Knee Replacement Surgery
Surgical Treatment Of Knee Pain
Partial knee replacement: The surgeon replaces the damaged portions of the knee with plastic and metal parts.
Total knee replacement: In this procedure, the knee is replaced with an artificial joint. It requires a major surgery and hospitalization.
What Is Involved With The Pre
Before surgery, the joints adjacent to the diseased knee are carefully evaluated. This is important to ensure optimal outcome and recovery from the surgery. Replacing a knee joint that is adjacent to a severely damaged joint may not yield a significant improvement in function as the nearby joint may become more painful if it is abnormal.
- Furthermore, all medications that the patient is taking are reviewed. Blood-thinning medications such as warfarin and anti-inflammatory medications such as aspirin may have to be adjusted or discontinued prior to knee replacement surgery.
- Routine blood tests of liver and kidney function and urine tests are evaluated for signs of anemia, infection, or abnormal metabolism.
- Chest X-ray and EKG are performed to exclude significant heart and lung disease that may preclude surgery or anesthesia.
- Finally, a knee replacement surgery is less likely to have a good long-term outcome if the patient’s weight is greater than 200 pounds. Excess body weight simply puts the replaced knee at an increased risk of loosening and/or dislocation and makes recovery more difficult.
Another risk is encountered in younger patients who may tend to be more active, thereby adding trauma to the replaced joint.
Also Check: How To Relieve Pain From Twisted Knee
Immediately After The Operation
After the operation, you can expect:
- Your knee is covered with a dressing and a drainage tube removes excess fluids from the wound.
- You are monitored by nursing staff who regularly check your vital signs .
- You are given antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection.
- You are given medications to thin your blood and reduce the risk of clots both during and after the operation.
- Strong pain relief can be given via an epidural or drip.
- You can start eating again on the second day after your operation.
- Nurses encourage you to move your feet and bend your other leg as soon as you can this helps to reduce the risk of clot formation.
- You are encouraged to walk around on the second day after surgery.
- Physiotherapists show you how to perform knee exercises.
- Occupational therapists advise you on how to best modify your home to make daily life easier during your recovery .
- Knee replacement surgery without complications usually involves a seven to 10 day hospital stay.
- Your stitches are removed about 10 days after surgery.
How Long Will My New Joint Last
In recent years, improvements in medical equipment and surgical techniques have meant that many knee replacements last longer than they did in the past.
A new study looking at over 6,000 people who have had knee replacement shows:
- More than 4 in 5 people who have total knee replacements can expect them to last for at least 25 years.
- 7 in 10 people who have a unicompartmental knee replacement can expect it to last for at least 25 years.
Clearly this will vary between different people, and you still need to take care of your new knee.
You May Like: Can Knee Replacement Cause Neuropathy
Infection After Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery is a common procedure performed on more than 500,000 patients a year in the United States. While the majority of patients have no problems after surgery, there are risks of knee replacement that cause concern for anyone thinking of having this procedure. One of the most concerning complications associated with a knee replacement is an infection.
Infection after knee replacement surgery is rare. In the first 2 years after surgery, the chance of developing an infection is estimated at 1.5%. After 2 years, the chance of infection goes down to about 0.5%. While these numbers are exceedingly small, they are not zero, and people having a knee replacement need to know everything they can do to prevent this serious complication.
What About Exercise Following A Knee Replacement
Exercise and sport are recommended after knee replacement, apart from;contact sports,;which may weaken the cement and lead to loosening of the joint components.;Recreational sports including golf, tennis and skiing will gradually become possible depending on how fit and sporty you were before the operation. Cycling is a very good way of building up strength and mobility after knee surgery.
Exercising the main muscle groups around your knee is very important both before and after having a;knee replacement. You can download a selection of exercises that are designed to stretch, strengthen and stabilise the structures that support your knee. Try to perform these exercises regularly, for instance for 10 minutes six to eight times a day. However, its important to find a balance between rest and exercise so you dont overwork your knee. Its a good idea to get advice from your doctor or;physiotherapist about specific exercises before you begin.
Read Also: What Are Gel Injections For The Knee
Complications That Can Arise
Just like any surgical procedure, knee replacement surgery can have complications. Complications are more likely to occur when having a total knee replacement than a partial knee replacement. Some of these complications occur because of the surgery itself. Others occur because of a faulty implant and are the subject of ongoing litigation.
Common complications include:
- Nerve damage
- Different leg lengths
If the person has a chronic illness, the risk of complications increases. For example, a person with sleep apnea a sleep disorder that causes a person to have pauses in breathing while asleep has a higher in-hospital mortality risk following joint replacement surgery.
If the person has revision surgery a second surgery required to adjust or replace an implant if it fails the risk of complications increases.
More serious complications, like joint infection, occur in less than 2 percent of patients. Infection is considered one of the most serious complications that can occur after surgery. When organisms enter the wound during surgery, they can attach to the prosthesis and are difficult to kill with antibiotics.
Symptoms of early joint infection include pain and swelling in the joint, a leaking wound and fever. Depending on the type of bacteria, infections can be dealt with one of two ways: Debridement, washing out the infection, exchanging the plastic spacer and leaving the metal implants intact; and staged surgery, where the implant is completely removed.
What Is A Total Knee Replacement Whats The Difference
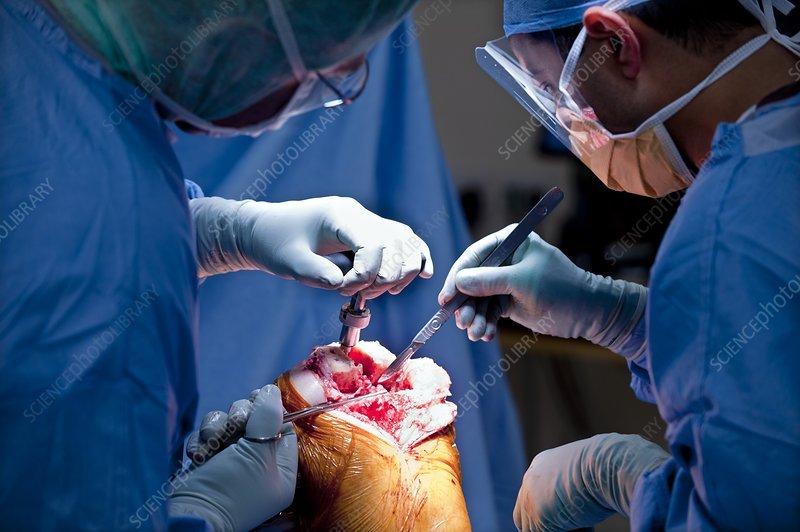
If more than one part of your knee is worn out, you may need a total knee arthroplasty .
In a total knee replacement, which is a more invasive surgical procedure, the damaged cartilage and bone are removed and replaced with an implant system.
Basically, the whole knee joint is replaced. The surgical incision is larger, the surgery is more complex, and the recovery takes longer.
Read Also: How To Whiten Knees And Elbows
What Is Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement is where portions of the bones that form the knee joint are removed and replaced with artificial implants. It is performed primarily to relieve knee pain and stiffness caused by .
Most people who get this surgery have advanced knee arthritis, in which the knee cartilage is worn away and the surface of the knee becomes pitted, eroded, and uneven. This causes pain, stiffness, instability and a change in body alignment. Knee replacement surgery can also help some people who have a weakened knee joint caused by an injury or other condition.
Why Might I Need A Total Knee Replacement
You might need a total knee replacement if you have significant damage to your knee joint. Different types of medical conditions can damage this joint, such as:
-
Osteoarthritis
-
Injury or fracture of the knee joint
-
Bone tumor in the knee joint
This damage might be very painful and limit your normal activities. The procedure may help decrease your pain, improve your joint mobility, and quality of life. Usually, healthcare providers only recommend total knee replacement when you still have significant problems after trying more conservative treatments, like pain medicines and corticosteroid shots .
Talk with your doctor about the benefits and risks of having minimally invasive total knee replacement instead of traditional total knee replacement. Minimally invasive total knee replacement uses a smaller incision than a traditional knee replacement, so it may lead to less pain and decreased recovery time. It is not yet clear whether the procedure leads to an increased risk of certain complications, though.
In some cases, you may have other surgical options, like shortening the bone or a partial knee replacement. Talk with your doctor about the risks and benefits of all your options.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Knee Fat And Cellulite
Minimally Invasive Total Knee Replacement
Some medical centers perform minimally invasive surgery for a total knee replacement, also called min-incision joint replacement.
This surgery allows surgeons to cut less muscle and tissue, which leads to less blood loss, increased range of motion and a shorter hospital stay. Many patients go home the same day and the recovery process is usually much quicker than traditional total knee surgery.
However, minimally invasive knee replacement is not for everyone. In general, the best candidates for this kind of surgery are younger and in better health. Older patients, those who are overweight or patients who have undergone knee surgeries in the past may be less suitable for minimal incision procedures.
Because it uses a much smaller incision, minimally invasive knee replacements have a higher risk for poor implant placement compared to traditional total knee surgery. Other common complications include nerve and artery injuries, wound healing problems and infection.
Only specialized medical centers typically offer this surgical option. An orthopaedic surgeon should explain the complete process, the benefits and the potential risks to help the patient decide which surgical option is the best fit.
Feel Free To Contact Us Or Make An Appointment
- walk within hours, and go home
- are driving on their own within 7-10 days,
- are going for extended walks outside, and start golf-range levels of activities within 2 weeks
- add back most all other physical activities at their own pace as comfort allows
- recover with no restrictions on weight bearing or range of motion and
- progressively achieve normal or near normal range and knee function within 4-6 weeks
Read Also: What’s The Best Knee Brace
How To Encourage Healing
For anyone who has had knee surgery, it is essential to keep the wound as dry as possible until it has thoroughly healed. Covering the wound with a bandage will also help prevent irritation from support stockings and other clothing.
Having a healthful, balanced diet helps encourage healing, though a person may have a poor appetite for the first few days after their surgery.
The AAOS recommends exercising in the first few weeks after the operation. A physical therapist may recommend specific exercises that help restore movement and build strength in the knee, and a person may need to do these several times a day.
Otherwise, the best approach to aftercare largely depends on the type of surgery that a person has had.
Anyone who has undergone arthroscopy should exercise regularly. A doctor or physical therapist usually recommends 2030 minutes of exercise two or three times a day and walking for 30 minutes two or three times a day during early recovery.
A physical therapist may design a personalized activity program. This may involve gradually increasing the amount of walking and a timetable for resuming everyday activities, such as climbing stairs. They will also recommend rehabilitation exercises.
Hip And Knee Joint Replacement Surgery: How Is It Done
Total joint replacement is a surgical procedure where parts of an arthritic or damaged joint are removed and replaced with a metal, plastic or ceramic device called a prosthesis or implant. The prosthesis is designed to reproduce the shape and motion of the normal joint.
A joint is an area in the body where two or more bones join together to allow motion. The surfaces of the bones are covered with cartilage to form a normal smooth gliding joint. Over time this cartilage can break down, leading to bone-on-bone friction which can cause inflammation and pain.
The most common conditions that lead to joint replacement surgery are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. There are, however, other causes of joint pain that may also lead to joint replacement including hereditary disorders, developmental problems, and trauma. Joint replacement is performed only after other conservative treatments have failed such as medications, physical therapy, and injections.
You May Like: How To Tape An Arthritic Knee
Total Knee Arthroplasty Procedure
The total knee replacement procedure is performed in a hospital under general anesthesia. During the procedure, an incision is made in the knee to access the joint so the damaged bone and cartilage can be removed. Once the damaged tissue is removed, the prosthetic device is inserted and may be either cemented or pressed into place. Cemented knee replacements are most commonly used, and are fixed into the joint for immediate support. Press-fit knee replacements are designed to have the surrounding bone grow into the implant for long-term joint stability.
Recent advances in surgical technology make it possible to perform minimally invasive joint replacements. Various minimally invasive techniques allow the joint to be replaced with less cutting and manipulation of muscles, tendons and ligaments around the joint. There are other potential advantages to minimally invasive surgery, including smaller incisions, less bleeding, less scarring, less pain and a speedier recovery.