How Is Osteoarthritis Of The Hip Diagnosed
There is no single test for diagnosing osteoarthritis, but often it is diagnosed by an abnormal X-ray that shows characteristic features such as narrowing of the joint and spurring of the joint margins. Your doctor will take your medical history and perform a physical examination. This will include a check of how your hip is functioning and may uncover loss of motion.
Find Out What Type Of Arthritis You Have
Learn about the type of arthritis you have and your treatment options. Ask your doctor about creating a tailored management plan and team care arrangement for you. This includes subsidised care from a team of healthcare professionals such as physiotherapists, dietitians, and others. Your local Arthritis office may also run self management courses to help you develop skills to manage your symptoms, communicate with your healthcare team and lessen the impact of arthritis on your life.
Vive Copper Full Finger Arthritis Gloves
- Constructed with a soft breathable blend infused with copper for soothing relief from arthritis
- Easily use smartphones, tablets and other touchscreen devices with the unique fingertip design
- Gloves feature minimal stitching to eliminate irritation and provide longer usability and are machine washable
- Each palm and finger is lightly textured with nonslip dots to provide a secure grip
Don’t Miss: What Causes Knees To Ache
How Common Is Osteoarthritis
Women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis than men. Australian studies show that about 1 in 10 women report having the condition, compared with about 1 in 16 men.
Osteoarthritis can develop at any age, but it is more common in people aged over 40 years or in those who have previously injured a joint. One in 5 Australians over the age of 45, and one in 3 over 75 years have osteoarthritis.
What Are The Stages Of Arthritis Of The Knee
There are five stages of osteoarthritis, the most common type of arthritis that affects your knees:
- Stage 0 . If youre at stage 0, your knees are healthy. You dont have arthritis of the knee.
- Stage 1 . Stage 1 means that youve got some wear and tear in your knee joint. You probably wont notice pain.
- Stage 2 . The mild stage is when you might start to feel pain and stiffness, but theres still enough cartilage to keep the bones from actually touching.
- Stage 3 . If youre at the moderate stage, youll have more pain, especially when running, walking, squatting, and kneeling. Youll likely notice it after long periods of rest . You’re probably in a great deal of pain because the cartilage has narrowed even further and there are many bone spurs.
- Stage 4 . Severe osteoarthritis means that the cartilage is almost gone. Your knee is stiff, painful and possibly immobile. You might need surgery.
Recommended Reading: Does Plantar Fasciitis Cause Knee Pain
Risk Factors For Hip Arthritis
- Age. The older you are, the more likely you have worn out the cartilage in your hip joint.
- Excess weight. Being overweight or obese puts additional stress on the hips.
- Injury. Severe injury, such as a hip fracture or labral tears, can cause arthritis years later.
- Overuse. Jobs and sports that require physically repetitive motions that place stress on the hip can increase risk for developing osteoarthritis.
- Gender. Women who are postmenopausal are more likely to develop hip osteoarthritis than men. Rheumatoid arthritis affects women more than men.
- Structural or developmental abnormalities. Irregularly shaped bones forming the hip joint, such as with hip dysplasia and impingement, can lead to abnormal stress on the cartilage.
- Autoimmune triggers. While the causes of rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis remain unknown, triggers of autoimmune diseases are an area of active investigation. For example, infection is believed to be one of the triggers for psoriasis.
- Genetics. Certain autoimmune conditions that lead to hip arthritis may run in the family.
- Other health conditions. People with diabetes, high cholesterol, hemochromatosis and vitamin D deficiency are more likely to develop osteoarthritis.
How Is Osteoarthritis Treated
There is no cure for osteoarthritis. Mild to moderate symptoms are usually well managed by a combination of pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic treatments. Medical treatments and recommendations include:
- Healthy eating, managing diabetes and cholesterol.
- Supportive devices such as braces, orthotics, shoe inserts, cane, or walker.
- Intra-articular injection therapies .
- Complementary and alternative medicine strategies, including vitamins and supplements.
Surgery may be helpful to relieve pain and restore function when other medical treatments are ineffective or have been exhausted, especially with advanced OA.
The goals of treatment are to:
- Improve mobility and function.
- Increase patients’ quality of life.
The type of treatment regimen prescribed depends on many factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, activities, occupation, and severity of the condition.
Medications
Although many of these medications are available in over-the-counter preparations, individuals with osteoarthritis should talk to a health care provider before taking the medications. Some medications may have dangerous or unwanted side effects and/or may interfere with other medications that are being taken. Some over the counter medications still require routine laboratory testing.
Supportive devices
Exercise
Hot and cold therapies
Weight control
Surgery
Alternative medicine
Other modalities of alternative medicine include acupuncture, acupressure and meditation.
Don’t Miss: Tom Ford Over The Knee Boots
Diagnosis Of Ra In The Hips
If you suspect RA in the hip, medical tests can help confirm or rule out this condition. The doctor will conduct a physical examination and ask questions about your symptoms, medical history, and family history.
A physical examination helps your doctor assess your pain level and joint mobility. Knowing your family history is also helpful because genetics may play a role in this disease. Your risk for RA increases if a family member has the condition.
RA can be difficult to diagnose because it can mimic other diseases like lupus and fibromyalgia in the early stages. There isnt one single test to diagnose this condition. Even so, blood tests can check for autoantibodies and markers of inflammation.
Imaging studies are also used to detect inflammation and joint damage. Your doctor may order an X-ray, MRI, or ultrasound of the affected joints.
Reducing The Strain On Your Knees
Apart from keeping an eye on your weight, there are a number of other ways you can reduce the strain on your knees.
- Pace your activities dont tackle all your physical jobs at once. Break the harder jobs up into chunks and do something gentler in between. Keep using your knee even if its slightly uncomfortable, but rest it before it becomes too painful.
- Wear shoes with thick soles and enough room for your toes. Wearing the right shoes can reduce the shock through your knees as you walk and prevent any changes to your feet.
- If you need extra support for your feet or knees when you walk, speak to your physiotherapist, occupational therapist or doctor about getting insoles made for your shoes.
- Use a walking stick if needed to reduce the weight and stress on a painful knee. An occupational therapist can advise on the correct length and the best way to use the stick.
- Use a handrail for support when going up or down stairs. Go upstairs one at a time with your good leg first.
- Think about making changes to your home, car or workplace to reduce unnecessary strain. An occupational therapist can advise you on special equipment that will make things you do every day easier.
Using a heat pack or something similar on a painful knee might help to relieve the pain and stiffness of osteoarthritis. An ice pack can also help but be careful not to put ice or heat packs or hot water bottles directly on your skin wrap them with a tea towel or cover.
You May Like: Is Bone On Bone Arthritis
You May Like: Right Knee Pain Right Side
Knee Cartilage Repair Without Surgery
Rest, ice, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , and physical therapy can all be prescribed by your doctor to help your joints return to their proper working order. They have the advantage of being less painful for many patients than surgery and can be used by a wide range of people.
The cartilage in the knee joint is frequently the source of an injury to the knee. Any joints free and painless movement can only be achieved by wearing long sleeves and cartilage. The device acts as a shock absorber, absorbing pressure and preventing bone from coming into contact with the body. When this cartilage is damaged, it can cause pain as well as difficulty moving the joint. For a number of years, studies using regenerative therapies have shown their efficacy in smaller studies. Because of the fact that regenerative medicine has few risks and has numerous advantages, many doctors have been waiting for a game-changer in this field. You can learn more about rotator cuff problems, what they are, and the treatments available.
The Role Physical Therapy Plays In The Process
Physical therapy is definitely beneficial. Improving range of motion and strength in the knee are helpful, but physical therapy for knee osteoarthritis has a large focus on strengthening the hips, explains Dr. Day.
Weak hips put more pressure on the knees. If your hips are strong, when you get up from a chair or go up and down stairs your knees have less work to do.
Everyone with knee osteoarthritis should consult a physical therapist, according to Dr. Day. Not only will you be taught the right kinds of exercises, a physical therapist also provides valuable instruction about using assistive devices and modifying activities to reduce pain.
Dont Miss: Can You Get A Rash With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Also Check: What Is Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement Surgery
Cracking Or Popping Sounds
When you bend or straighten your knee, you may feel a grinding sensation or hear cracking or popping sounds. Doctors call this crepitus.
These symptoms can occur when youve lost some of the cartilage that helps with smooth range of motion. Both OA and RA can result in cartilage damage.
When cartilage is damaged, rough surfaces and bone spurs develop. As you move your joints, these irregular areas rub against each other.
Exercise And Home Remedies
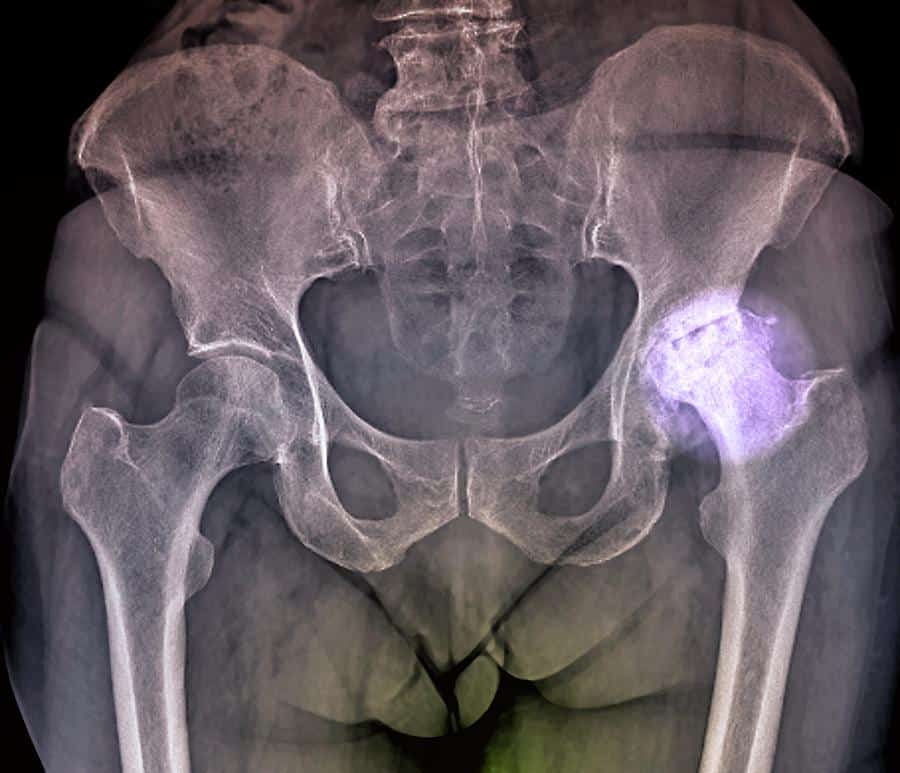
If RA in the hip limits mobility, working with a physical therapist or an occupational therapist can help improve joint flexibility and walking. Youll learn specific exercises to strengthen your hip joint. A few strategies include:
- Low impact exercises: This may help to reduce inflammation and ease hip pain. Try gentle workouts, including cycling, swimming, or water aerobics.
- Heat and cold therapy: Use heat to reduce stiffness in the joints and cold to alleviate pain.
- Meditation, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation: These can all help lessen stress. Chronic stress stimulates your body to produce more mediators of inflammation throughout your body.
Don’t Miss: What Dr Do I See For Knee Pain
What Are The Risk Factors For Oa
- Joint injury or overuseInjury or overuse, such as knee bending and repetitive stress on a joint, can damage a joint and increase the risk of OA in that joint.
- AgeThe risk of developing OA increases with age.
- GenderWomen are more likely to develop OA than men, especially after age 50.
- ObesityExtra weight puts more stress on joints, particularly weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees. This stress increases the risk of OA in that joint. Obesity may also have metabolic effects that increase the risk of OA.
- GeneticsPeople who have family members with OA are more likely to develop OA. People who have hand OA are more likely to develop knee OA.
- Race Some Asian populations have lower risk for OA.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis
While OA is considered a degenerative disorder, rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune disease in which the mechanisms that normally protect your body attack your own joints and tissues. RA causes inflammation at the joints and surrounding tissue, typically affecting the body symmetrically . It usually involves multiple joints at the same time, beginning with the small joints of the hands and eventually progressing to larger joints, such as the hip and knees.
RA is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, with smoking and obesity being two of the most common modifiable risk factors. RA is both chronic and progressive, meaning theres no cure and it usually worsens over time, with years of inflammation at the joints leading to erosion of the cartilage and eventually bone, but there are treatments available.
You May Like: What Is The Normal Range Of Motion After Knee Replacement
Knee Cartilage Damage: Causes Treatment And Prevention
The cartilage of the knee is an important component of knee function, and it can be damaged in a variety of ways. This type of damage can progress and cause arthritis if not treated. Repairing knee cartilage damage, such as surgery, is one option, but microfracture, a less invasive procedure, can sometimes be used to regenerate the cartilage. It is possible that surgery is necessary to repair knee cartilage that has been severely damaged, but there are other methods that can be used to help. Even if you are inactive and eat a healthy diet, it is possible to repair or replace knee cartilage without the need for surgery.
What Causes Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis does not have a specific, single cause. However, experts note that certain things put you more at risk of developing osteoarthritis in some joints, including:
- being overweight
- having a previous injury to the joint, such as a dislocation or a fracture
- frequent kneeling, climbing and squatting
- jobs that involve heavy lifting
- repetitive use of the hands
You may also be more likely to develop the condition if your family has a history of osteoarthritis.
You May Like: How To Treat Arthritis Knee Pain
Causes Of Hip Arthritis
Arthritis is a common medical condition that causes inflammation, and there are more than 100 different types of arthritis. The most common type, which is osteoarthritis , causes pain and swelling of the joints such as the hips and the knees.
Osteoarthritis of the hip is a degenerative joint disorder that usually develops as people become older, but it can also develop among serious athletes and frequent runners. It can also occur when an injury to the joint caused damage to the hip cartilage.
Arthritis remains a serious health issue in the United States. It is estimated that 54 million Americans suffer from arthritis, and 60% of those patients are between the ages of 18 and 64 which are generally the most productive years of our lives.
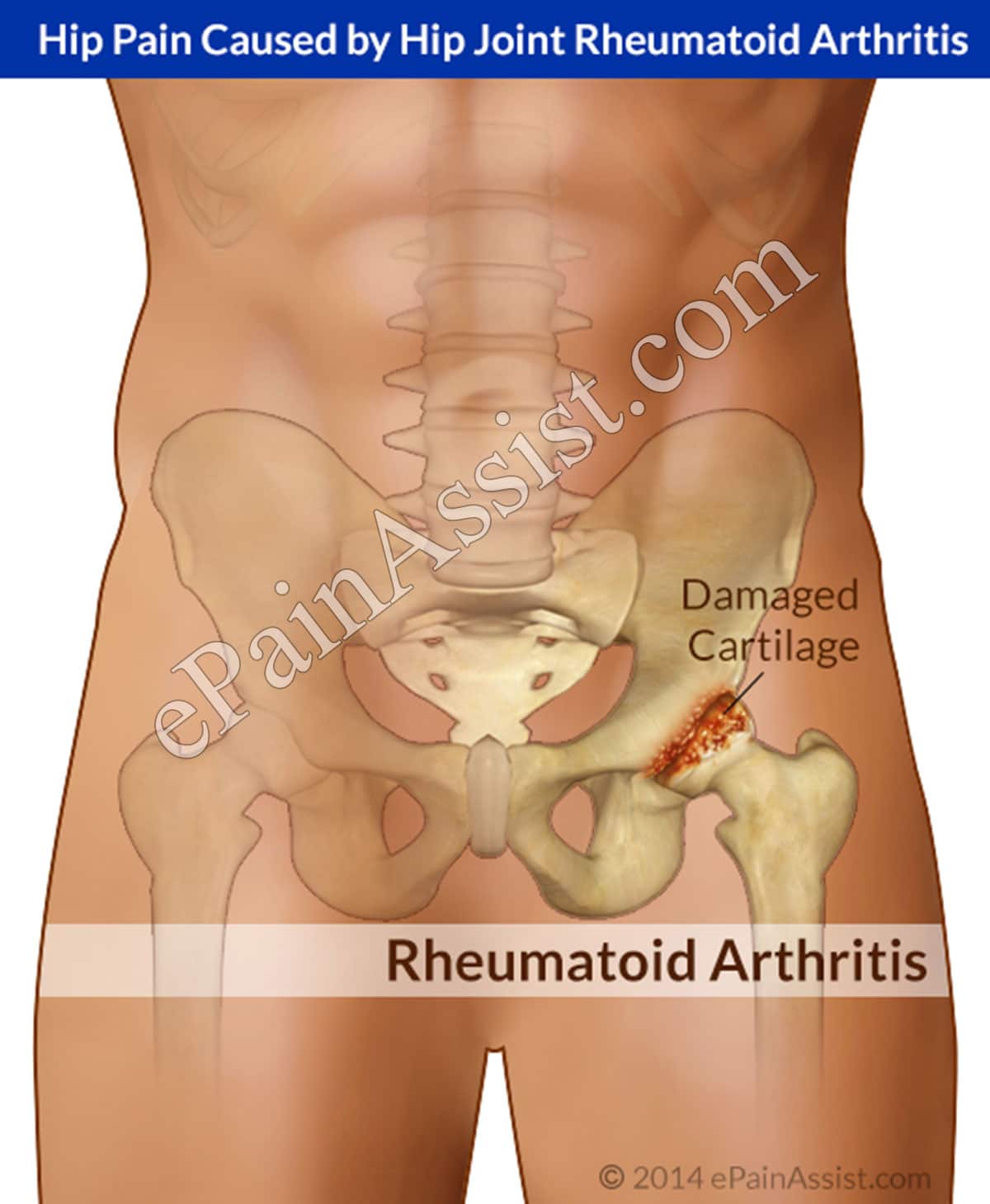
Rheumatoid Arthritis Of The Hip
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease resulting from the immune system attacking healthy tissue in the joints, including the hip. It causes inflammation of the synovial membrane, the capsule surrounding the hip joint. Inflammatory cells release substances that break down hip cartilage over time. RA typically affects smaller joints such as the wrist and fingers first, and may not be noticeable in the hip until it causes symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Quad Exercises With Bad Knees
What Exercises Should You Avoid For Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis
Experts used to ban high-impact exercises, such as running and jumping, for people with hip and knee OA. The idea was that they could overload and damage the joint. But the opposite may be true for people with mild to moderate OA. âThe impact may stimulate cells that repair in the cartilage,â Oswald says.
But this doesnât mean that you can hop on a treadmill right away. If youâre just starting out, you need to build up your strength and endurance first. This can prevent injury. âThen slowly add in high-impact exercises,â Robertson says. âFor instance, begin with just 5 minutes of jogging.â
Is your OA severe? Chances are youâll need to steer clear of high-impact exercise altogether. Be cautious about the following workouts check with your doctor if youâre able to do them.
- Running, especially on uneven surfaces
- Tennis, basketball, and other activities where you change direction quickly
- Step aerobics and other workouts that involve jumping
Show Sources
Eric Robertson, DPT, physical therapist associate professor of clinical physical therapy, University of Southern California spokesperson, American Physical Therapy Association.
William Oswald, DPT, physical therapist clinical instructor of rehabilitation medicine, NYU Langone Health.
Arina Garg, MD, rheumatology fellow, The Center for Excellence for Arthritis and Rheumatology, Louisiana University Health Sciences Center.
Arthritis Foundation: âStanding Hip Flexors and Quadriceps Stretches.â
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Arthritis Of The Knee
There are many signs and symptoms of arthritis of the knee:
- Creaking, clicking, grinding or snapping noises .
- Difficulty walking.
- Joint pain that changes depending on the weather.
- Joint stiffness.
- Knee joint pain that progresses slowly or pain that happens suddenly.
- Your knee locks or sticks when its trying to move.
Pain and swelling are the most common symptoms of arthritis of the knee. Some treatments might reduce the severity of your symptoms or even stall the progression. See your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of knee arthritis.
You May Like: Leg Pain When Bending Knee
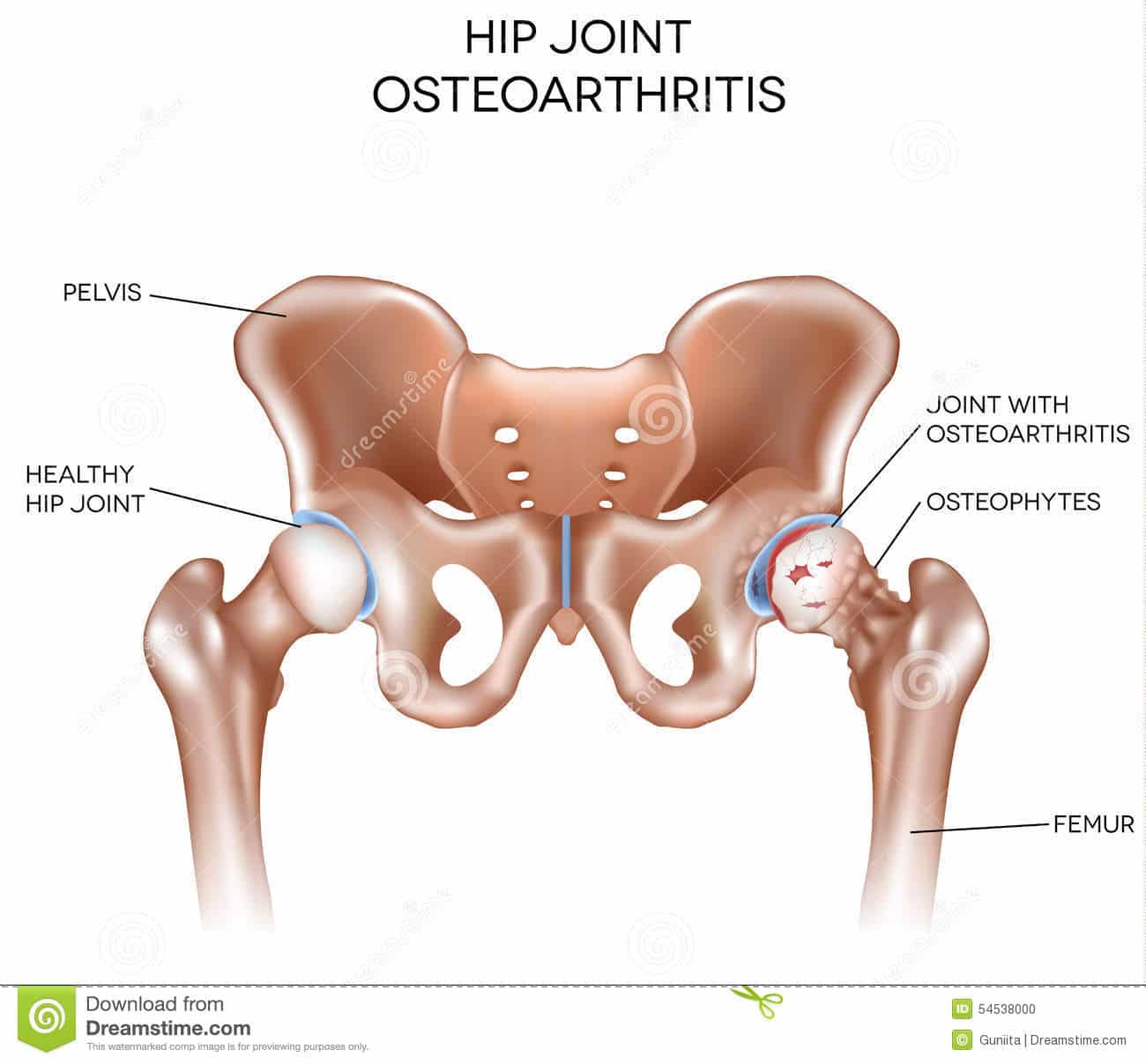
What Is Osteoarthritis
Arthritis means “joint inflammation.” It causes pain and swelling in the body’s joints, such as the knees or hips. There are many types of arthritis, but osteoarthritis is the most common. Also known as degenerative joint disease or age-related arthritis, osteoarthritis is more likely to develop as people get older.
Osteoarthritis occurs when inflammation and injury to a joint cause a breaking down of cartilage tissue. In turn, that breakdown causes pain, swelling, and deformity. Cartilage is a firm, rubbery material that covers the ends of bones in normal joints. It is primarily made up of water and proteins. The primary function of cartilage is to reduce friction in the joints and serve as a “shock absorber.” The shock-absorbing quality of normal cartilage comes from its ability to change shape when compressed. It can do this because of its high water content. Although cartilage may undergo some repair when damaged, the body does not grow new cartilage after it is injured.
The changes in osteoarthritis usually occur slowly over many years. There are, though, occasional exceptions.
The two main types of osteoarthritis are:
- Primary: More generalized osteoarthritis that affects the fingers, thumbs, spine, hips, and knees
- Secondary: Osteoarthritis that occurs after injury or inflammation in a joint, or as a result of another condition that may affect the composition of the cartilage, such as hemochromatosis