What Are The Symptoms Of A Stress Fracture
The symptoms of a stress fracture can include:
- Pain, swelling or aching at the site of fracture.
- Tenderness or pinpoint pain when touched on the bone.
- Pain that begins after starting an activity and then resolves with rest.
- Pain thats present throughout the activity and does not go away after the activity has ended.
- Pain which occurs while at rest, during normal activity or with everyday walking.
- Pain which is worse with hopping on one leg or an inability to shift weight/hop on affected leg/foot.
If a stress fracture is not treated at an early stage , the pain can become severe. There is also a risk that the fracture may become displaced . Certain stress fractures are considered high risk stress fractures because they may have a poor outcome if not identified early.
What To Discuss With Your Orthopaedic Surgeon
Treating A Stress Fracture
Your physician at Urgently Ortho reviews your medical history, physically examines the painful area, and conducts imaging tests to diagnose your condition.
The first line of defense when you have a stress fracture is using the RICE method to help heal it: rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Over-the-counter pain relievers also help reduce pain and inflammation.
Your Urgently Ortho physician determines whether you need a cast to hold the bones in place during the healing process. Your doctor may prescribe a walking boot to reduce stress on the affected area, or you may need crutches if your physician wants you to avoid weight-bearing for a period of time. She may also recommend custom orthotics to provide extra support to the injured area and your entire foot. Untreated stress fractures may lead to the need for surgical repair, so its important to seek treatment promptly.
Contact Urgently Ortho right away if you believe you have a stress fracture and for any orthopedic need.
You Might Also Enjoy…
You May Like: How To Fix Knee Problems
How Can You Prevent Stress Fractures
Stress fractures often happen in people who have dramatically raised their level of physical activity. So to prevent them, go slowly. Experts recommend that you never increase your exercise intensity by more than 10% per week. Make sure to warm up and stretch for a few minutes before exercising. Take frequent breaks to give your body a rest. And if you feel pain during exercise, stop. Don’t push through it. High-impact sports and work activities increase the risk for stress fractures.
Also, good exercise equipment can help prevent stress fractures. Don’t wear worn-out running shoes. People who have fallen arches or other anatomical problems may benefit from custom inserts or arch supports in their shoes.
Show Sources
Treatment For Knee Stress Fractures
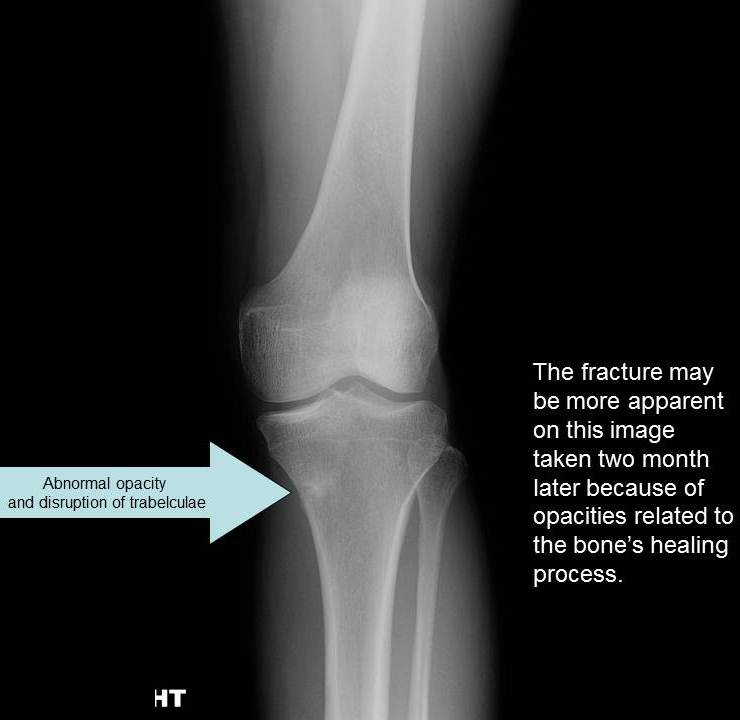
Because of the small size of stress fractures, surgery is not a common method of treatment. Instead, most physicians will recommend rest and a mechanism for bone and joint support. Treatment for knee stress fractures may involve a knee brace or sleeve that supports your knee for limited walking. While you can address the pain caused by a knee stress fracture by taking some sort of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , the only way to treat a stress fracture is with rest and patience. Methods of treatment involve:
- Resting for several weeks
Don’t Miss: How Do You Rebuild Cartilage In Your Knees
How Is A Stress Fracture Treated
Stress fractures are treated in several ways. Your doctor will discuss your options based on the location and severity of your fracture. Also, your provider will aim to treat any risk factors you have for future injuries.
Treatments your doctor may recommend can include:
- Stopping the activity that is causing pain. Stress fractures happen because of repetitive stress and overuse, so its important to avoid the activity that led to the fracture.
- Applying an ice pack or ice massage to the injured area.
- Resting for roughly two to eight weeks.
- Cross training by doing non-impact exercise after discussion with your doctor may be allowed. Eventually, once you can perform low-impact activities for extended periods without pain, you can start doing high-impact exercises. Often, physical therapy can be very helpful in returning to activities and making adjustments to avoid reinjury.
- Adjusting your position if there is swelling in your leg, ankle or foot. You can lessen the swelling by elevating your leg raising your foot above the level of your heart while youre lying on your back.
- Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines to help relieve pain and swelling.
- Using protective footwear to reduce stress on your foot or leg. This may be stiff-soled shoe, a wooden-soled sandal, or a post-op shoe which has a rigid sole.
- Using crutches to keep weight off your foot or leg until the bone heals.
Recognizing The Signs Of A Stress Fracture
If you love sports and play your sport frequently, youre susceptible to stress fractures in your feet and lower legs. A stress fracture, sometimes called a hairline fracture, is a tiny fissure in a bone.
Urgently Ortho in Scottsdale, Arizona, specializes in treating all types of orthopedic injuries, including stress fractures. Our team includes a board-certified orthopedic surgeon, a physician specializing in pain management, and a doctor trained in regenerative medicine.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If Your Knee Is Broken
What You Need To Know
- Patella fractures are common injuries. About 1% of all broken bones are broken kneecaps.
- Fractures of the patella are most often caused by a direct blow to the knee, such as a fall or motor vehicle accident.
- Kneecap fractures can be simple or complex. Complicated patella fractures, which result in displaced pieces of bone, may require surgery.
- Rehabilitation focuses on improving range of motion, building up muscle strength and decreasing knee stiffness. Recovery can take several months.
Can You Walk With A Stress Fracture In The Knee
Walking after a stress fracture is not recommended because it may reopen a partially healed injury, and you may have to begin the recovery process all over again. Despite the fact that you can walk, doctors advise you to avoid hard surfaces and avoid going long distances.
A stress fracture is a crack in a weight-bearing bone that develops during a fracture. Long marches, jumps and jumps, and long running are common causes of this condition, which is typically caused by repetitive force to the bone. Walking is not recommended if you have a stress fracture because it may reopen the partially healed fracture. When the bodys healing process fails to keep up with the increased forces on the feet, stress fractures occur. The only way to confirm a stress fracture is to have a doctor imaging it. When fracture stress occurs, it typically takes 6-8 weeks for healing to occur, and doctors advise patients to avoid weight-bearing activities during this time.
Don’t Miss: How Long Do Gel Shots In The Knee Last
What Is A Tibia Stress Fracture
The lower leg consists of two bones, called the tibia and fibula. The tibia is the larger, thicker of the two and its role is load-bearing. The fibula is the smaller, thinner bone. Its purpose is mainly as an area for muscles to attach. Either of these bones can develop stress fractures.
The most common site, however, is two to three inches above the bony bit on the inside of the ankle on the tibia bone.
Long bones such as the tibia have an outer sheath surrounding the hard compact bone called the periosteum with the inner core containing bone marrow. Continuous muscle contractions and stress forces of impact cause the tibia to overload.
In particular, fatigue causes the distribution of forces in the bone to alter. This is because your muscles are unable to absorb some of the load.
Therefore, there is more load on the bone. Lots of small impacts on the bone even though they may be very small, result in a cumulative build up.
How Is A Stress Fracture Diagnosed
Your doctor may need to do several tests to see if you have a stress fracture and the severity of the fracture. These tests can include:
- Physical examination: During your first visit, your doctor will do a physical exam and discuss your risk factors for developing a stress fracture. When discussing risk factors, you will be asked about:
- Your medical history.
- Your activities.
- Any medications you might be taking.
Read Also: What Does Knee Replacement Surgery Entail
How Did I Get A Stress Fracture
Any sport in which your feet hit the ground repeatedly from running, jumping, and pivoting quickly, such as basketball, track and field, tennis, and gymnastics, can lead to stress fractures.
These fractures are typically overuse injuries. Perhaps youve been in a three-day tennis tournament. Your muscles are overworked, and the stress transfers to the bone, leaving a small crack.
You can also get a stress fracture from suddenly increasing the amount of time you play your sport after having been sedentary for instance, returning to the court for rigorous play after youve been sick. Its important to take time to ramp up your level of activity after being out of action for a while. Perhaps youre running on worn-out shoes: Lack of the right equipment can lead to a stress fracture as well.
Study Population And Data Collection

Patients with end-stage degenerative knee arthritis associated with stress fracture of the proximal third of the tibia treated at our institute from February 2015 to December 2020 were analyzed.
All patients had varus deformity and only extraarticular stress fracture of the tibia, except one case that had both extraarticular and intraarticular fractures of medial tibial condyle . This patient had severe varus deformity in the preoperative period, which could be corrected to 6.8° hipkneeankle angle in postoperative radiograph . Despite having varus malalignment, this patient had an uneventful recovery, including fracture union, and remained asymptomatic with decent function at 5 years of follow-up. All cases were treated by single-stage TKA using a tibial component with fluted tibial extension rod.
Fig. 1
Case 1 preoperative radiographs depicting grade 4 osteoarthritis of the knee with stress fractures . The patient had history of long standing knee pain since many years, with inability to walk since the last 4 months. The tibial alignment appears to be in severe varus
X-ray findings of definite fracture line, periosteal or endosteal bone formation, or linear sclerosis were taken as an evidence of stress fracture. Preoperative metabolic workup in the form of serum calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D, alkaline phosphatase , and parathyroid hormone levels were done.
You May Like: Fell On Knee Hurts To Bend
Stress Fracture Signs To Watch For
Its important to know the signs of a stress fracture. If theyre left undetected and untreated, they can get worse and even permanently sideline an athlete.
Watch for these symptoms of a stress fracture:
- Deep aching pain within a limb or joint
- Dull pain that occurs with activity , then disappears with rest
- Pain that doesnt improve despite rest or RICE treatment measures
- Weakness or loss of performance in the affected area
- Aching pain that progressively gets worse and starts occurring not just during activity
- Pain that gets worse in the evening or at night
- Pain the starts about a week after an increase in training or intensity
See a complete symptom list: Stress Fracture Symptoms
Stress fractures are rarely treated with surgery, but the treatment process is pretty demanding and time-consuming, often involving weeks or even months of of rest, bracing, and physical therapy.
But there’s good news too: If athletes follow their treatment protocoland take steps to correct the training error that triggered the stress fracture in the first placethey have a good chance of a full recovery.
How Are Stress Fractures Diagnosed
It is very important that during the medical examination the doctor evaluates the patient’s risk factors for stress fracture.
X-rays are commonly used to determine stress fracture. Sometimes, the stress fracture cannot be seen on regular x-rays or will not show up for several weeks after the pain starts. Occasionally, a computed topography scan or magnetic resonance imaging will be necessary.
Don’t Miss: What Can I Put On My Swollen Knee
How Long Does It Take To Recover From A Stress Fracture
As long as you can feel pain, the bone is still fragile in that area, and could break again in the same place. It takes roughly six to eight weeks for a stress fracture to heal, so it is important to stop the activities that caused the stress fracture. Always ask your doctor before you fully return back to exercise to make sure the area is healed and you are ready to go.
Comminuted Noncomminuted And Hairline Kneecap Fractures
- A comminuted patella fracture is one in which the bone is shattered into three or more pieces.
- In a noncomminuted patella fracture, the kneecap is broken in two pieces.
- A hairline kneecap fracture is a simple crack in the bone . Hairline fractures are also known as stress fractures, and are rare in the kneecap. They can occur in athletes, such as marathon runners, and may be due to overuse. A stress fracture of the patella may be difficult to see on an X-ray. The main symptom is pain in the front of the knee that gets worse over time.
Also Check: Does Gout Affect Your Knees
What Is The Treatment For Stress Fractures
First aid for stress fractures
Itâs important to see your doctor, because the bone could break completely without treatment. In the meantime, follow the RICE guidelines:
- Rest. Avoid weight-bearing activities. Wear a stiff-soled, supportive shoe if necessary.
- Ice. To ease swelling, ice the area for 24 to 48 hours. Wrap an ice pack in a towel and apply for 20 minutes at a time. Never put ice directly on your skin.
- Compression. Wrap a soft bandage around the area to ease swelling.
- Elevation. Use pillows to raise your foot or leg higher than your heart.
Medications for stress fractures
You can take over-the-counter medications to manage pain. Doctors suggest acetaminophen instead of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , which may reduce your boneâs ability to heal.
Nonsurgical treatments for stress fractures
Most people donât need surgery to repair a stress fracture. Along with the RICE plan to reduce pain, your doctor may try one or more of these treatments while your fracture heals:
- Crutches or a cane for support
- Protective footwear like a boot or brace to lessen stress on the fracture
- Casts to keep your fracture in a fixed position while it heals
Theyâll also advise you to skip high-impact physical activities like running for 6 to 8 weeks. Try lower-impact exercises like swimming or cycling instead.
Surgery for stress fractures
How Long Does It Take A Stress Fracture To Heal
If you have a stress fracture, how long could it take to heal, and what can you do to protect it? At what point should a patient worry that the bone isnt healing like it should? In this Ask Dr. Geier video, I discuss healing of a stress fracture in the tibia and how you can adjust activities to help it heal.
Heidi in Davidson, NC asks: I am a runner and was diagnosed with a proximal tibial stress fracture by MRI. I have had symptoms for over a year. I stopped running because it hurt. I have followed all precautions. I dont bend past 90, no kneeling, and obviously no running, jumping, etc. That pain has improved somewhat, but it is still there with specific activities. 10 weeks after diagnosis, Im concerned that it isnt healing. Is there a time limit on this kind of healing? After this long should I just consider surgery? I feel like my current doctor is being too conservative, and I just want to get healed and back to normal routine.
The tibial plateau is the top of the tibia just below the knee. Stress fractures can occur in this area in running athletes and active people. Usually rest or modifying activities is enough to get this bone to heal.
Most stress fractures heal in 6 to 12 weeks, but every patient is different. Some stress fractures, although not generally tibial plateau stress fractures, are prone to poor healing. For those stress fractures, completely avoidance of weight on the leg and even surgery can be needed.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Knee Replacement Surgery Take