Surgeons Say One In Four Patients With Pain After Knee Replacement Had No Clear Reasoning For Their Pain It Wasnt The Hardware It Wasnt Anything Obvious That They Could See
In the research above, surgeons have a road map of where to look for pain after knee replacement. Returning to the findings released in the British Pain Journal , the doctors suggest looking for pain in other places that are usually not explored:
- Our main findings are that some patients have severe pain that interferes significantly with their lives and that a large number of them have pain sensitization problems , many of which can be classified as neuropathic pain , rather than any local, nociceptive cause .
- A heightened sense of pain following knee replacement will be discussed throughout this article.
What is the research saying?
In November 2018 a study was published in the Journal of Knee Surgery. The doctors also were looking at nerve pain after surgery.
- The study had 154 patients with 222 knee replacements
- The goal of the study was to define the prevalence of pain persisting after total knee replacement and determine the impact of neuropathic pain.
- The ratio of patients with
- moderate-to-severe pain was 28% .
- Thirteen patients experienced unclear pain.
- A significant number of patients experienced moderate-to-severe and unclear pain after total knee replacement.
It looked like neuropathy but it wasnt neuropathy.
Why Is There So Much Pain After Knee Replacement
There are a number of reasons why patients may experience pain after knee replacement surgery. In some cases, the pain is due to the surgery itself and the process of healing. In other cases, there may be an underlying condition that is causing the pain. Additionally, some patients may be more sensitive to pain than others. There are a number of ways to manage pain after knee replacement surgery. Pain medication can be prescribed by a doctor to help manage pain. Additionally, physical therapy and other forms of exercise can help to stretch and strengthen the muscles around the knee, which can help to reduce pain.
Harvard Medical Schools Findings Surrounding The Phenomena Of Continued Pain Following Total Knee Replacement
Here are some more quick facts surrounding the phenomena of continued pain following total knee replacement from researchers at Brigham and Womens Hospital, Harvard Medical School.
In this 2017 study published in the medical journal Osteoarthritis Cartilage, the doctors found:
- Approximately 20% of total knee replacement recipients have suboptimal pain relief. .
- Pre-operative widespread pain was associated with greater pain at 12-months and failure to reach a clinically meaningful difference in pain, pre and post replacement
- Patients with widespread pain along with the pain catastrophizing problems may help identify persons with suboptimal total knee replacement outcomes.
Also Check: How Long After Knee Surgery Can You Walk
Data Sources And Searches
MEDLINE and EMBASE databases were searched from inception to 31 January 2011. A general search was performed to identify quantitative research in primary total hip or knee replacement. The MEDLINE search strategy is shown in online appendix 2. Search terms related to hip or knee replacement and studies with an epidemiological design including prospective and longitudinal studies. No language restrictions were applied.
Within titles, abstracts and keywords of articles identified, we searched for text words relating to osteoarthritis and disease-specific patient-centred pain outcome measures used in osteoarthritis and joint replacement. Specifically these were Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index , Arthritis Impact , Lequesne, Oxford hip or Oxford knee score, Hip Osteoarthritis Outcome Score or Knee Osteoarthritis Outcome Score , pain visual analogue scales and self-appraisal. Outcomes not considered patient centred were Harris Hip, American Knee Society and Bristol Knee Scores. We did not include generic health measures including the Health Assessment Questionnaire, EuroQol, London Handicap Scale, Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-36 , Disease Repercussion Profile, Sickness Impact Profile and WHOQol-BREF.
We also checked citations of key articles in ISI Web of Science and reference lists. Studies reported only as abstracts were excluded. References were managed in an Endnote X3 database.
What Patients Want From Their Knee Replacement:
In the November 2017 edition of the journal Medical Care, a combined research team from the University of Illinois at Chicago, China Medical University Hospital, and National Taiwan University Hospital published their findings on what concerned patients before knee replacement and the type of pre-existing conditions these patients had.
Before the surgery concerns about successful surgery circled around these factors:
Read Also: Pain On The Top Of The Knee
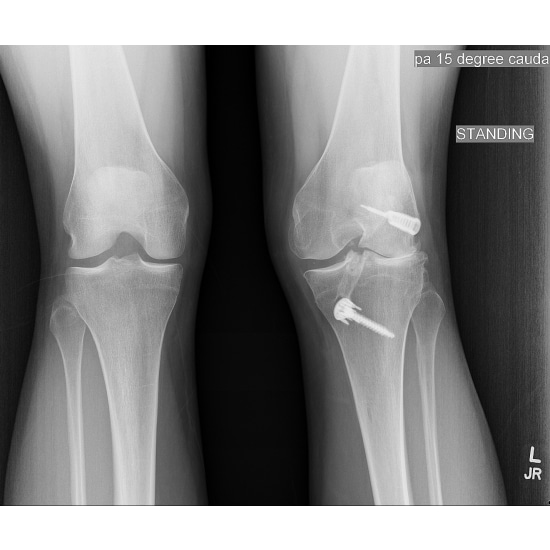
The Knee Cap Was Floating Because The Mcl Was Released Patellar Maltracking After Total Knee Replacement The Concern Of Catastrophic Laxity
Lets look at two studies surrounding the medial collateral ligament.
The first is from 2015, the second is from 2021
In June 2015 in the journal Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy researchers wrote: Medial collateral ligament release is one of the essential steps toward the achievement of ligament balancing during the total knee arthroplasty in patients with varus deformity . When the varus deformity is severe, complete release of the MCL until balanced is often required. However, it is believed that a complete MCL release may lead to catastrophic laxity.
In March 2021, a study published in the journal Knee Surgery and Related Research continued that Medial collateral ligament release during knee replacement could lead to the surviving knee cap floating around the knee. Here are the studys observations: Patellar maltracking after total knee arthroplasty can lead to significant patellofemoral complications such as anterior knee pain, increased component wear, and a higher risk of component loosening, patellar fracture, and instability. . . A complete release of the MCL during surgery was associated with patellar maltracking. Surgeons should attend to patellar tracking during surgery in medially tight knees.
What Causes Pain After Knee Replacement Surgery
Researchers continue to study the many causes of pain after knee replacement surgery. Some are biological and due to conditions present before surgery, while others are due to complications that arise during surgery.
On the biological side, patients suffering from arthritis may experience increased sensitivity because of the ongoing pain that was present before surgery. As well explain below, inflammatory responses and allergy-related problems can also contribute to persistent pain. Another source of pain is referred pain originating from the hip due to a change in alignment.
If you are experiencing ongoing pain after knee replacement surgery, but do not have a medical history of arthritis or the previously mentioned issues, you may be dealing with surgical complications. While your doctor will take steps to prevent problems, its still possible for these to rare issues to occur:
Remember to stay open and honest with your doctors. This will help them properly diagnose and treat the problem to get you the pain relief youre looking for.
Recommended Reading: Where Can I Get My Knee Drained
Establishing A Precise Diagnosis Of Where The Pain Is Coming From Can Be Challenging
Researchers at the Department of Surgery, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine offered this assessment in the medical information publication Instructional Course Lectures to guide doctors trying to help patients with pain after knee replacement.
Establishing a precise diagnosis of where the pain is coming from can be challenging.
According to the research: This is what doctors need to look for in trying to find the source of knee pain after knee replacement:
- Pain after knee replacement can be classified as intra-articular or extra-articular pain .
- After intra-articular causes , such as knee instability, aseptic loosening , infection, or osteolysis , has been ruled out, extra-articular sources of pain should be considered.
- Extra-articular sources of pain can be found after a physical examination of the other joints which may reveal sources of localized knee pain, including diseases of the spine, hip, foot, and ankle.
- MORE: Additional extra-articular pathologies that have the potential to instigate pain after total knee replacement include cardiovascular problems, tendinitis, bursitis, and iliotibial band friction syndrome.
- Patients with medical comorbidities, such as metabolic bone disease and psychological illness, may also experience prolonged postoperative pain.
Is It Normal To Still Have Pain 6 Weeks After Knee Replacement
There is no one answer to this question as each individual heals differently and experiences different levels of pain after surgery. Some people may still have pain 6 weeks after surgery, while others may have already healed and no longer experience any pain. If you are still experiencing pain 6 weeks after surgery, it is important to talk to your doctor to see if there is any reason for concern.
Youre six weeks removed from knee surgery and youre on your way to physical therapy. Some pretty critical reasons, as well as the importance of the surgery, can result in a knee replacement for someone aged 50, 60, or 70. They begin to feel upset, if not completely depressed, after three to six weeks of recovery. They do not have to be held back by a lack of knee bending, and I know they will make a recovery. Patients have three options to avoid the Manipulation Under Anesthesia in thisrecovery no-mans land. By the end of six weeks after surgery, most knees will be showing their potential. The manner in which a surgeon performs Manipulation Under Anesthesia varies greatly from one surgeon to the next.
Read Also: What Can You Do For Osteoarthritis Of The Knee
How Can We Help These Problems The Often Overlooked And Ignored Cause Of Pain After Knee Replacement The Knee Ligaments
When a knee replacement is performed, the joint itself has to be stretched out so the surgeons can cut out bone and put it in the prosthesis. When the joint is stretched out, the knee ligaments and tendons that survive the operation will cause pain as they heal from the surgical damage. Sometimes the ligaments and tendons heal well. Sometimes they do not heal as well.
In this video, Ross Hauser, MD explains the problems of post-knee replacement joint instability and how Prolotherapy injections can repair damaged and weakened ligaments that will tighten the knee. This treatment does not address the problems of hardware malalignment that our patient Jeannette described in the video above.
Summary of this video:
The patient in this video came into our office for low back pain. I did a straight leg raise test, on this patient to help determine if his back pain was coming from a herniated disc.
- During the test I noticed a clicking sound coming from his knee. The patient had a knee replacement.
It is very common for us to see patients after knee replacement who have these clicking sounds coming from knee instability. This is not instability from hardware failure. The hardware may be perfectly placed in the knee. It is instability from the outer knee where the surviving ligaments are. I believe that this is why up to one-third of patients continue to have pain after knee replacement.
What Are The Signs Of Knee Replacement Failure
The most common symptoms of a failed knee implant are pain, decrease in joint function, knee instability, and swelling or stiffness in the knee joint.
Persistent pain and swelling can indicate loosening, wear or infection, and the location of the pain can be all over the knee or in one particular area . A decline in knee function may result in a limp, stiffness or instability. Patients who demonstrate these symptoms and signs may require revision joint surgery.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Reason For Knee Joint Pain
Is It Normal To Have Knee Pain Years After Surgery
While it is extremely rare, a small percentage of patients who have had knee replacement continue to experience chronic pain after the procedure. Nonetheless, when this happens, you donât have to give up. If your situation is unsatisfactory, it is best to have it evaluated. Additional treatment options may be beneficial after knee replacement for patients who suffer from chronic knee pain.
Your pain level and recovery time will differ depending on whether or not you have a total or partial knee replacement. The average time required for total knee replacement after a walker or cane is one to three months. Patients who have a partial knee replacement have fewer invasive procedures, and they typically walk without assistance within two weeks. When you have a knee replacement, there are several different types of pain. It is expected as a result of the surgery itself, which entails swelling, bruising, and the use of prosthetics. There is also the possibility that you may experience pain in other parts of your body, such as your hips. Chronic pain is defined as pain that persists for three months or longer.
If you have knee pain or swelling, a Corticosteroid injection is a viable option. An anesthetic is injected into a genicular nerve block to interrupt pain signals being sent to the brain. There is a chance you will need to undergo revision surgery for your knee replacement.
What Causes A Knee Replacement To Become Loose
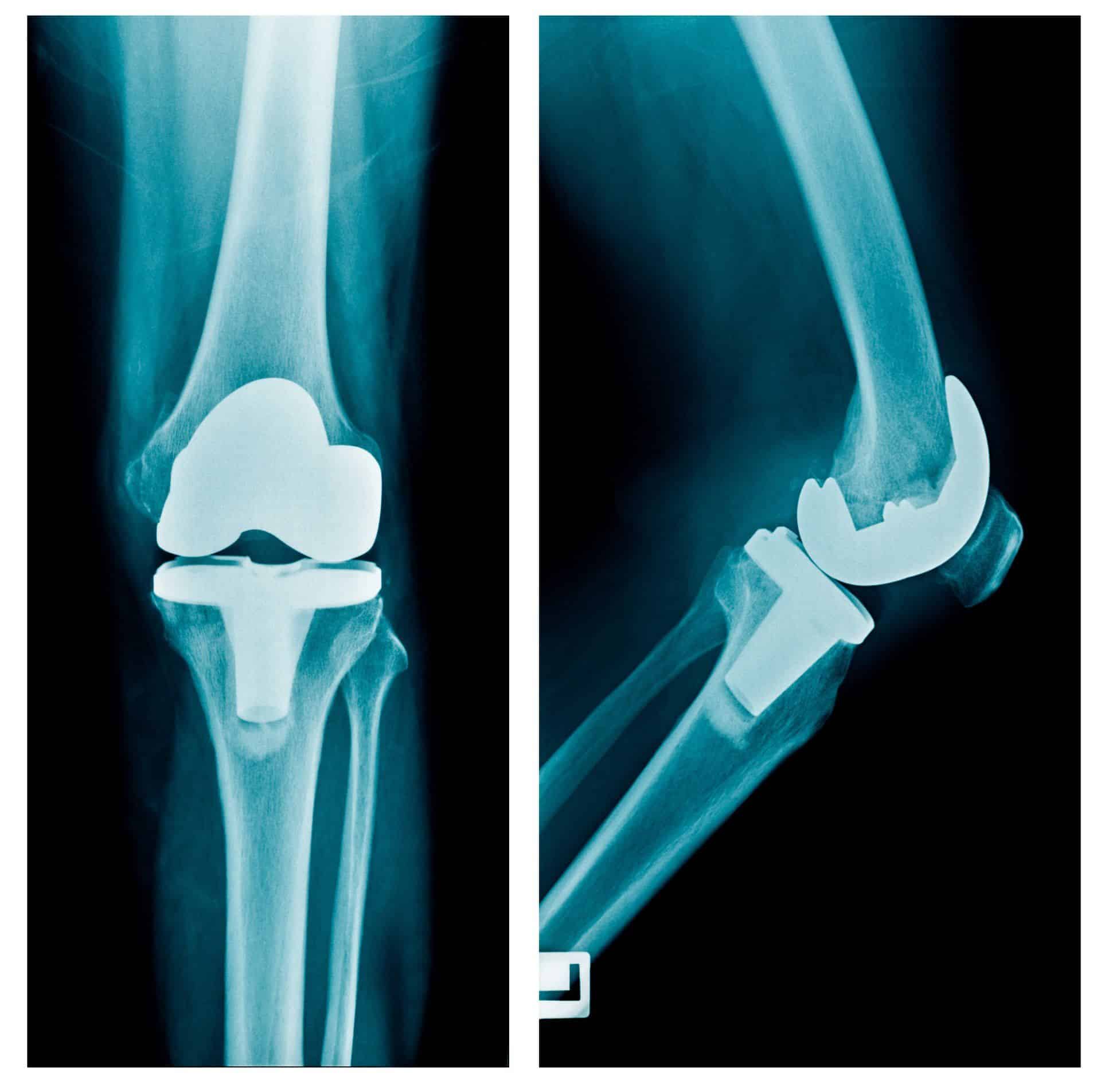
Loosening is one of the most common complications of total knee replacement surgery. Patients usually need revision surgery to fix it. What that means is another surgery is required to address the loose knee replacement. There are many causes for a knee replacement to become loose. The 6 most common are:
Excessive Wear
Knee replacements do not last forever. The longevity of knee replacement depends upon many factors including the type of implant, age, and gender of the patient, diagnosis, and type of fixation . The majority of knee replacements last approximately 20-25 years . The actual implant can become worn out.
Infection
Infection can occur immediately after surgery or years later. The infection can affect the skin, muscles, and the artificial joint. This can compromise the cement that glues the artificial joint to the bone. When this occurs the knee replacement can become loose.
Fractures
Fracture on the thigh bone
During knee replacement surgery, the end of the thigh bone is amputated. A hole is then drilled into the end of the thigh bone. A metal stud is then hammered into the thigh to which the new knee joint is attached. If the bone is weak such is the case with patients with osteoporosis or if too aggressive, a fracture can occur. The end result can be a loose knee replacement.
Poor Alignment
Technical Failure
Rejection
Also Check: Can Physical Therapy Help Arthritic Knees
What Are The Diseases That May Necessitate A Knee Replacement Procedure
-
Osteoarthritis is an age-related “wear and tear” type of arthritis. It is usually seen in patients 50 years of age and older but may occur in younger people. The articular cartilages that act as cushions between the bones soften and wear away with time. The friction between the bones leads to knee pain and stiffness.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease where the synovial membrane surrounding the joint becomes inflamed. This can damage the cartilage. Eventually, this leads to cartilage loss, pain, and stiffness, termed “inflammatory arthritis.”
-
Post-traumatic arthritis following a severe knee injury due to fractures of the bones around the knee. Tears or damage to the knee ligaments may damage the articular cartilage over time, causing knee pain and limiting knee function.
Complication Of A Second Knee Replacement In Obese Patients
A February 2022 study of 605,603 revision total knee arthroplasty surgeries published in the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Global research & reviews examined the postoperative outcomes of obesity and morbid obesity patients after revision total knee arthroplasty. The researchers here found obese and morbidly obese patients were at significantly higher risk for complications than non-obese patients. Morbidly obese patients had a significantly longer length of stay than both obese and not obese patients, while no significant difference in length of stay was observed between obese and not obese patients.
You May Like: Will Walking Help Knee Pain
Problem: Difficulty And Pain In Kneeling
Most people had difficulty kneeling because of pain or discomfort in the replaced knee. Many patients described how this limitation affected their daily lives, including housework, gardening, religious practices, leisure activities, and getting up after a fall. Patients often adapted to these limitations by finding alternatives to kneeling, assistance from others, or home adaptations. Many patients had accepted that they could not kneel, however some still expressed frustration. Few patients had consulted with healthcare professionals about kneeling difficulties, and unmet needs included the provision of information about kneeling and post-operative physiotherapy.
Can A Total Knee Replacement Wear Out
Knee replacements don’t last forever and you may need another surgery. Many patients have knee replacements that last for 20 years or more. But the longer and harder you use your replacement joint, the more likely it becomes that you’ll need a second knee replacement surgery to replace a worn out implant.
Continued Pain 5 Years After Knee Replacement
Also Check: How To Build Muscle Around Knee
When Is Joint Replacement Surgery Necessary
A joint disorder can cause pain, stiffness, and a loss of function and mobility in the knee joint. Over time, this can become increasingly disabling, preventing a person from carrying out even simple day-to-day activities. Joint damage can result from a number of factors, including aging, wear and tear, injuries, and conditions such as osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is a common type of arthritis that causes the protective cartilage that lines the joints to wear away gradually. It can result in pain, stiffness, and inflammation, and often affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips.
Nonsurgical treatment methods such as medication, cortisone injections, physical therapy, and platelet-rich plasma therapy, can help relieve pain associated with joint disorders, but if they no longer provide symptom relief, joint replacement surgery may be recommended.
Joint replacement surgery involves replacing all or part of a joint with prosthetic components. They are designed to replicate a natural, healthy joint as much as possible, allowing normal activities to be resumed once fully healed. With advances in technology and surgical techniques, it now means joint replacement procedures are becoming more popular and successful than in previous years, with a faster recovery and less risk of complications.