How Can I Prevent Fluid On The Knee
One of the best ways to prevent this condition is to take care of your joints. Maintain a healthy weight, practice exercises to keep the surrounding muscles strong, flexible, and supportive.
Consider low-impact activities such as cycling, swimming, or moderately challenging walking avoid steep hills. Make sure you use the correct form with any exercises to protect your knees and other joints.
Youre Getting An Injection
A doctor may recommend injecting an arthritic joint with cortisone, hyaluronic acid, or another therapeutic liquid into a joint capsule as part of treatment. A joint aspiration may be performed before the injection. Aspirating excess fluid makes room for the therapeutic liquid and helps ensure that it is highly concentrated in the joint.
Joint aspirations can be done on almost any joint, most often the knee joint. Many people recover right away, while others may need to rest the affected joint for a couple of hours.
See Therapeutic Injections for Knee Arthritis
For most people, joint aspiration is a safe and uneventful procedure. Contact your doctor if you experience moderate to extreme re-swelling, discoloration or rash around the injection area, fever, bleeding or discharge from the needles entry point, or pain that is not adequately controlled with over-the-counter pain medication and ice packs.
How Does Arthrocentesis Work
Fluid buildup in joints puts pressure on the joint. Excess fluid causes pain and swelling. You may find it difficult to bend and move the joint.
Your healthcare provider may drain the fluid and send a sample to a lab. Tests can determine the cause of the fluid buildup.
As a treatment, joint aspiration eases swelling and joint pressure. You should have less pain and find it easier to move after this procedure. Excess fluid often comes back. You may need joint aspiration again.
Healthcare providers typically use arthrocentesis on the:
- Hips, knees, ankles and feet.
- Elbows, shoulders, wrists and hands.
Also Check: Can You Rebuild Cartilage In Your Knee
How Are Arthrocentesis And Joint Injections Performed
Joint aspirations and injections take place in your healthcare providers office. Your provider may use images from an ultrasound or X-rays to guide procedures.
First, your provider disinfects the skin. For smaller joints, your provider applies a numbing cream to the skin. You may need a local anesthetic to numb a bigger joint section like the hips or shoulders.
During joint aspiration and injection, your provider:
Symptoms Of A Swollen Knee
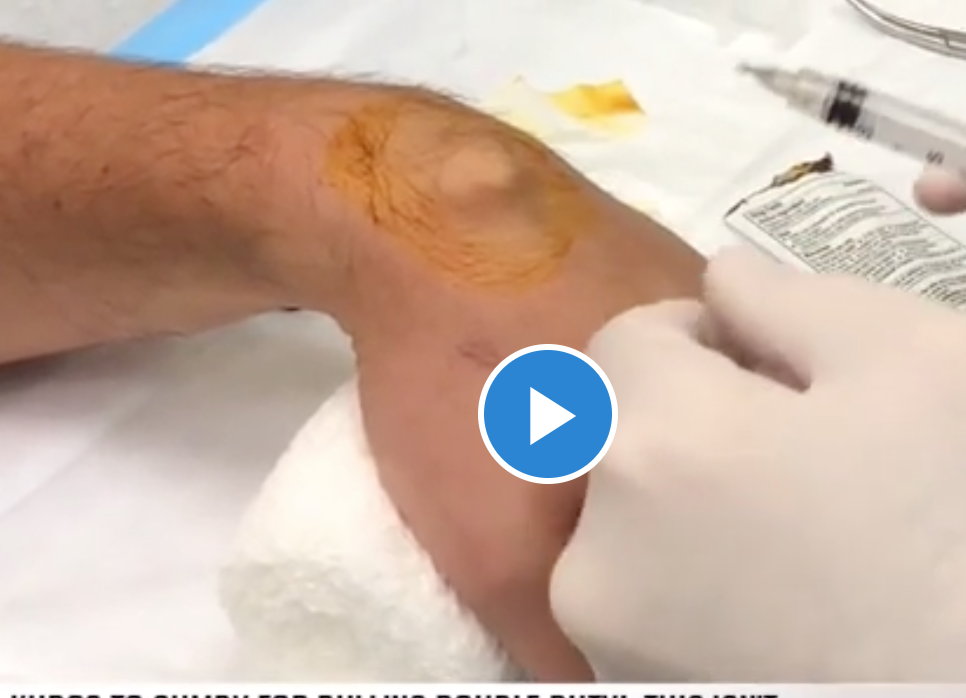
- The skin around the kneecap is puffy
- The knee is stiff and its difficult to bend or straighten it
- Its painful and bearing weight is difficult or impossible
- Redness or warmth
Swelling that does not go away, also known as chronic swelling, can lead to joint damage, cartilage degradation, or bone softening.
You May Like: What Knee Brace Is Best For Torn Meniscus
What Are Potential Risks Or Complications Of Arthrocentesis And Joint Injections
Joint aspirations and injections are relatively safe. Rarely, these complications develop:
- Allergic reaction: Some people are allergic to the anesthetic or the injectable medication. In very rare instances, this can cause anaphylaxis, a life-threatening response.
- Infection: Rarely, people develop infections after getting steroid injections.
- Post-injection flare: An estimated 1 in 50 people develop post-injection flare several hours after getting an injection. It causes joint swelling and pain that subsides in a few days.
Indications Of Knee Aspiration For Diagnostic Purposes Include
- To evaluate joint effusion
- To assess unexplained monoarticular arthritis
- To evaluate possible infective or septic arthritis
- To evaluate type of arthritis and joint related conditions
- To determine presence of crystal induced conditions like gout
- To determine the nature of accumulated fluid and cytology studies in synovial fluid analysis.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Black Marks On Knees
What Are Joint Injections
After joint aspiration, your healthcare provider may inject corticosteroids into the joint. This anti-inflammatory medication eases pain, swelling and stiffness. The drugs may also slow the return of excess fluid to the joint.
Steroid injections work best for inflammatory conditions like arthritis and tendonitis. Treatment effects last a couple of months. You shouldnt get more than four injections in the same joint within a year. Steroid overuse can damage the joint and weaken supporting tendons and ligaments.
What Should I Do After Getting Arthrocentesis And Joint Injections
Depending on the treatment area, you may need to:
- Not lift anything heavy or put weight on the treated area for 48 hours.
- Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to ease discomfort.
- Your provider may ask you to report back on the immediate and long-term effects of the procedure. This may help in diagnosis.
Also Check: What Causes Your Knee To Lock Up
Reasons You May Need A Joint Aspiration
Arthritis, infection, and joint injuries are associated with inflammation and swelling. This swelling occurs when excess fluid collects inside a joint capsule. Your physician may remove the excess fluid using a needle and syringe. This procedure is called joint aspiration or arthrocentesis.
Joint aspiration is generally considered a quick, safe procedure. It typically involves a local anesthetic, so youll feel minimal pain and discomfort. It may be done in your doctors office or a hospital setting. Medical imaging, such as ultrasound, may be used to ensure that the needle enters the joint capsule, minimizing the potential risk of damage to other tissues.
This page describes a joints anatomy and three reasons why your doctor may recommend an aspiration.
Aspiration Of Synovial Fluid From Knee
Knee arthrocentesis may be done via a parapatellar approach , , a suprapatellar approach, or an infrapatellar approach. Once the insertion site is chosen, prepare the skin with sterile solution, allow drying, and then drape.
Using a sterile technique, attach the 18- or 20-gauge needle to the 20-mL syringe, and pull the plunger in order to break resistance. Because the knee may hold up to 70 mL of fluid, using a larger syringe is advisable in certain cases accordingly, an extra syringe should be available for use if necessary.
Stretch the skin over the insertion site, and insert the needle briskly into the joint space while gently aspirating until synovial fluid enters the syringe . Relaxation of the quadriceps muscle facilitates insertion of the needle. Placement of a towel under the popliteal region to flex the knee to 15-20° may facilitate entry by opening up the joint space.
For the parapatellar approach , identify the midpoint of either the medial or the lateral border of the patella. Insert an 18-gauge needle 3-4 mm below the midpoint of either the medial or the lateral border of the patella . Direct the needle perpendicular to the long axis of the femur and toward the intercondylar notch of the femur.
If a bone is encountered during needle insertion, pull the needle back, verify the anatomic landmarks, and advance the needle in a corrected direction.
Once aspiration is complete, the needle is removed and a bandage applied .
Recommended Reading: What Is Chondrocalcinosis Of The Knee
Drain Fluid From Knee Recovery Time
Naturally, since knee effusion can have such varied origins, one of the first things medical care providers must do is to attempt to identify the cause. Take it easy for at least a couple of days after you drain the fluid from your knee.
Ultrasonic or radio imaging will regularly be used to assess the situation better. Magnetic resonance imaging can also be used if the suspected reason lies in a damaged ligament or tendon. Laboratory tests such as the C-reactive protein blood exam can be performed if the infection is thought to be the cause of the swelling.
Once a clearer picture of the underlying source of the knee effusion has been identified, the most common course is prescription of some form of analgesic and steroidal treatment.
Unfortunately, these steroidal therapies often have secondary effects that can adversely affect the general health of patients. Some reported side effects of steroid therapy include elevated high blood pressure, increased risk for infection, and even osteoporosis.
Some studies have also suggested that steroid therapy is no better than a placebo for alleviating knee pain in patients with osteoarthritis.
To drain fluid from the knee naturally, there are a few methods that have shown excellent results. The most common way is called the I.C.E approach. ICE stands for Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
Symptoms Of Water On Knee
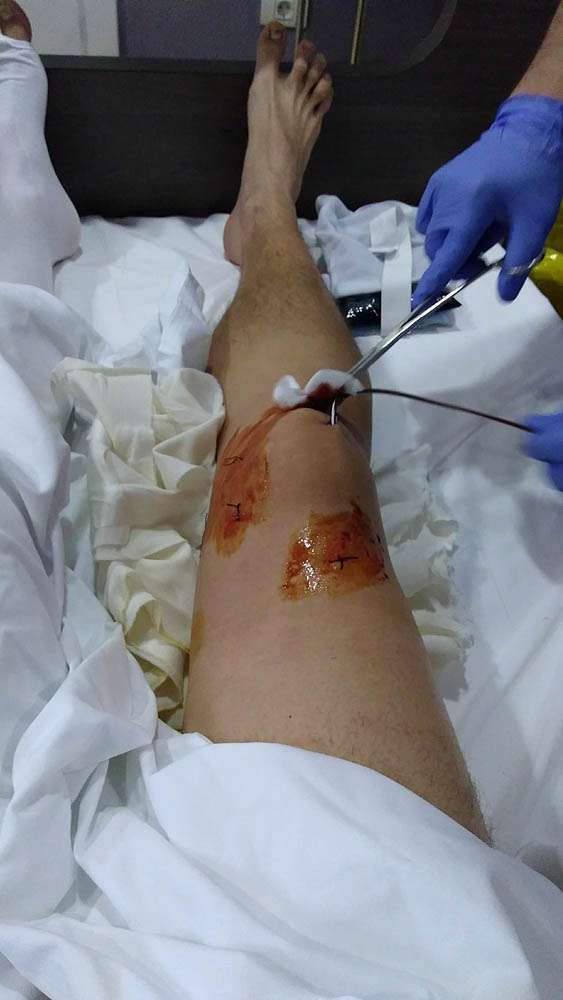
Synovial fluid can be used for diagnostic purposes. The exact symptoms of knee fluid effusion will depend on the medical cause of the accumulation. Identification of specific properties such as density, color, viscosity, and white blood cell count, can help a medical doctor determine the presence of injury or other medical conditions.
Knee fluid effusion can be the cause of high discomfort, both physical and psychological. Pain can vary from mild to severe, with some rare patients reporting no pain whatsoever. Frequently, placing any weight on the affected knee will cause significant discomfort and difficulty with mobility will be present. The proliferation of synovial fluid under the patella will usually cause considerable stiffness. This process can have a substantial and far-reaching impact on your daily life, and so it is crucial that we study ways in which to alleviate its effect.
Don’t Miss: Is Nano Knee Covered By Medicare
Treatment For Fluid In Knees
As with any injury, it’s important to consult your doctor for the appropriate treatment for your situation. Here are some treatments and pain management options you may expect for fluid on the knee:
Aspiration – Your doctor may drain the knee to relieve the pressure of the knee fluid. If blood is present, then it is often sent to the lab to analyze the fluid to ensure that infection is not present. The knee may continue to fill with fluid after being aspirated.
PRICE Method – If knee trauma or injury is the cause of the knee fluid, then your doctor may recommend that you use the PRICE method of Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation. The combination of these is often used as first aid treatment to minimize fluid in the knee after a traumatic injury.
Medications – There are different types of medications that may be used to treat the excess of knee fluid, depending on the cause of the issue. For example:
- Over-the-counter medications – Pain medications such as ibuprofen or aspirin may be used to help reduce inflammation
- Steroids – These may be taken orally or injected directly into the knee joint. This may be used if over-the-counter medications are not effective at reducing pain.
- Antibiotics – If your knee fluid is caused by infection, then antibiotics may be necessary to fight the bacteria
When To Consider Knee Drainage
Knee swelling can be a painful, functionally debilitating condition and should not be ignored. Many cases of knee swelling can be resolved with rest, ice, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medication. However, if the swelling begins to restrict movement or becomes increasingly painful, you may be eligible for knee drainage.
Knee drainage can both diagnose the source of swelling and provide effective pain relief and improved mobility. Moreover, it is a simple in-office procedure requiring very little downtime. If you are experiencing pain and swelling in your knee, drainage may be the most effective option to get you back to performing your daily activities pain-free.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Dark Spots On Knees
What Causes A Swollen Knee
There are many causes of swelling in the knee, but often it is due to an injury. Damage to ligaments, especially the anterior cruciate ligament, or ACL, causes fluid to build up around the knee. Tearing the cartilage, overuse, and breaking bones can also cause fluid buildup.
However, other underlying conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, infection, gout, pseudo-gout, bursitis, cysts, and tumors, can also cause swelling.
When To See A Doctor
If the swelling doesnt go down in one to three days of using the RICE method, its time to call a doctor.Also, call a doctor immediately if there are any of these symptoms:
- The knee is severely swollen or has a pronounced abnormality
- The knee cannot fully straighten or flex
- The knee is severely painful
- The knee feels like it will give out or cannot support any weight at all
- The skin near the knee is hot or red
- A fever
- Swelling has not gone down after three or more days
If youre experiencing knee swelling that will not go away or have pain, connecting with a specialist is always a good idea. Theres no need to rush into surgery. At Flexogenix, we specialize in cutting-edge, non-surgical treatment options, and can help you move past achy knees and into your best lifewithout invasive surgery. Contact us today to schedule your free consultation.
Recommended Reading: How Long After Knee Replacement Can You Fly
What Happens During A Joint Aspiration
A joint aspiration may be done on an outpatient basis or as part ofyour stay in a hospital. Procedures may vary depending on yourcondition and your healthcare providers practices.
Generally, a joint aspiration procedure follows this process:
You will be asked to remove clothing and will be given a gown to wear.
You will be positioned so that the healthcare provider can easily reach the joint that is to be aspirated.
The skin over the joint aspiration site will be cleansed with an antiseptic solution.
If a local anesthetic is used, you will feel a needle stick when the anesthetic is injected. This may cause a brief stinging sensation.
The healthcare provider will insert the needle through the skin into the joint. You may feel some discomfort or pressure.
The healthcare provider will remove the fluid by drawing it into a syringe that is attached to the needle.
The needle will be removed and a sterile bandage or dressing will be applied.
The fluid sample will be sent to the lab for examination.
Drain/injection Joint Without Ultrasound Guidance
About This Procedure:
To drain fluid from the knee a needle is inserted into the knee joint and the fluid is removed with a syringe. For some patients the procedure is to relieve pain and swelling in a joint. For others, the fluid is tested to learn the cause of the inflammation. After the knee fluid is drained some people get a cortisone shot to reduce the inflammation.
This procedure is done outpatient or in the doctors office and the patient returns home the same day. Patients can save money by shopping for this service as there may be many office and outpatient centers locally that offer this care.
Treating the knee by draining the fluid is not always needed. Some people get better with rest and icing the area, over-the counter medications, physical therapy, a cortisone shot, and using a cane for support.
These are 2019 prices. Use the link below to see if you can get a current, personalized cost estimate from your health insurer.
You May Like: How To Regrow Cartilage Naturally
Arthrocentesis Of The Knee
|
The knee and connecting suprapatellar pouch can be punctured while the patient is supine and the knee is extended. The needle, 18- or 20-gauge, can be inserted anteromedially, under the cephalad half or third of the patella. Alternatively, the needle can be inserted laterally, just under the cephalad edge of the patella . |
Can Fluid On The Knee Get Worse
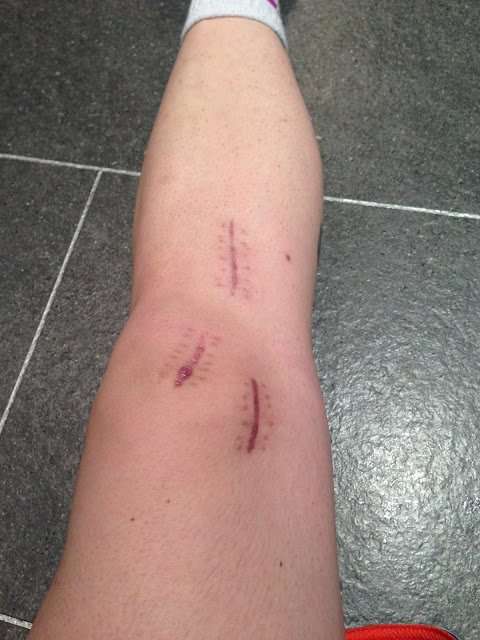
Yes. Its important to get a correct diagnosis of why your knee is swollen and follow proper treatment. A bacterial infection could spread and lead to permanent cartilage damage. If the problem is an internal tear, youre likely to have long-term, progressively more debilitating pain and loss of mobility if its not treated.
Recommended Reading: What’s Good For Arthritis In The Knee
Seeing A Doctor Is Important
Because of the detrimental and debilitating effect that knee synovial fluid accumulation can have on a patients life, it is essential to do everything possible to avoid it in the first place. Caution is always recommended when practicing any brusque physical activity. Weight management is also a valid preventative technique as excess weight puts an unnecessary strain upon the joints of the body.
It is also important to listen to your bodys signals and warnings. If you feel pain or discomfort on the knee joint, stop whatever it is you are doing and give your body a chance to rest. Doing this will significantly reduce the risk of suffering any eventual pain, stiffness, and swelling.
REFERENCES:
You Need An Accurate Diagnosis
The fluid inside the affected joint can be examined, providing important clues to help confirm or rule out a diagnosis. For example, microscopic crystals in joint fluid indicate gout or pseudogout.
A doctor can send the aspirated fluid to a lab. The lab may be asked to:
- Examine the fluid under a microscope
- Run a chemical analysis
- Perform a culture and gram stain
A doctor may also learn things just by looking at the aspirated fluidfor example, pink or red fluid indicates the presence of blood and suggests an injury, and opaque, yellowish fluid suggests .
See Diagnosis through Synovial Fluid Analysis
Don’t Miss: Why Does My Knee Hurt When It’s Cold
How Is Knee Aspiration Performed
Using aseptic precautions, the swollen knee joint is examined and appropriate site is chosen. The area is cleaned with an antiseptic and a local anesthetic is used to make the site numb. The needle is inserted into the joint space and the synovial fluid is drained out. Medications may be injected into the space if required and the needle is taken out.