The Benefits Of A Holistic Approach To Treating The Knee Can Be Clearly Seen In The Definition Of Knee Osteoarthritis:
Knee Osteoarthritis is destruction to the whole knee
- Knee swelling is the result of a slow, progressive, degenerative disease that:
- destroys articular cartilage,
- causes destructive changes to the knees lubricating and protective synovial membrane,
- damages and causes the death of subchondral bone,
- causes weakness, damage, and laxity in the knees supporting ligaments and tendons,
- destroys and causes the death of the meniscus,
Symptoms Of A Swollen Knee
- The skin around the kneecap is puffy
- The knee is stiff and its difficult to bend or straighten it
- Its painful and bearing weight is difficult or impossible
- Redness or warmth
Swelling that does not go away, also known as chronic swelling, can lead to joint damage, cartilage degradation, or bone softening.
Chronic Knee Swelling Is Developing And Worsening Knee Osteoarthritis
In this video Danielle R. Steilen-Matias, MMS, PA-C offers a brief summary of the constant degenerative process going on in your knee that shows itself every day to you as swelling.
Summary and learning points:
- Many patients tell us that their other health care providers and doctors dismiss or ignore their complaints of knee swelling. However, as research suggests, such as the research examined in this article, is that chronic knee swelling signifies the early development of osteoarthritis.
- The reason the knee is swelling relates to the strength or integrity or lack thereof of the soft tissue around the knee. So the knee swelling can be coming from knee ligament injury or instability. Your body, in an attempt to provide stability for the unstable knee, will swell the knee as a protective mechanism to provide stability to the need temporarily. It should be temporary. Your body is swelling the knee until healing of an injury can take place. The fluid fills the knee to also prevent excessive movement to accelerate healing. When the injury is healed the swelling goes away.
- If you do a job that is very physically demanding, you are on your feet all day, you climb ladders or steps, etc, that is a lot of strain to be putting on your knees and your body does the best it can to provide the swelling necessary to keep your knee together. The problem is chronic swelling is causing a rapid degeneration in the knee.
Read Also: Inversion Table For Knee Pain
S For Reducing Fluid In The Knee
Step 1 Stop any activity that may have caused the knee to swell, like running, jumping or twisting. Terminate action that makes your knee swell or hurt. You might have to avoid driving if it causes discomfort to run the brake or gas pedals.
Step 2 Rest with the leg elevated to reduce swelling naturally. This allows fluid to drain away, and reduces pressure on the joint. Dont walk or put weight on the knee unnecessarily until the pain and fluid have gone away.
Step 3 Use a cold pack to reduce pain and reduce fluid accumulation. You can use a wash cloth taken in cold water, or an industrial cold pack kept in the freezer. Do not use ice or freezer loads directly on the skin instead, wrap the frozen item in a towel and cover it around the knee. Apply this cold pack for 15 to 20 minutes every two to four hours as needed for pain.
Step 4 Wrap the leg with an elastic bandage. This must reduce build-up of fluid on the knee. Do not wrap the knee so securely that it cuts off circulation get rid of the bandage if numbness or tingling in the foot happens, or if the foot feels warm.
Step 5 Take a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory like ibuprofen or naproxen to decrease or prevent inflammation, MayoClinic.com recommends. Trademark name medications that include NSAIDs can include Advil, Motrin or Aleve. Take them with food to prevent stomach inflammation. A painkiller, such as acetaminophen or Tylenol, can likewise be used to relieve pain, but will not reduce the inflammation in the knee.
Arthritis Is Wearing On Your Joints

A catch-all term for inflammation of a joint, arthritis is particularly common in the knee. It develops over time and typically causes knees to swell, stiffen, and become painful or difficult to move.
Per the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, knees are most often affected by two forms of arthritis: osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. In osteoarthritis , cartilage throughout the knee jointwhich protects the ends of your boneswears away over time. Meanwhile, in rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system attacks the joint, damaging its connective tissues and bones.
You May Like: Is Cycling Good For Arthritic Knees
Read Also: How Do I Get Rid Of Fat Around My Knees
Common Causes Of Fluid In The Knee
There are various issues that may cause fluid in knees. Here are some of the most common:
Knee Trauma or Injury – Trauma occurs when the knee joint is impacted from an outside force, resulting in injury to the knee. The type of fluid to enter the knee from a traumatic injury is usually blood or excess joint fluid, though other types of fluid in the knee may be present. The most common forms of knee injury to cause fluid in knees are:
- Meniscus Tears
- Ligament Injuries, such as ACL Tears
- Overuse Injuries
Arthritis – The are several types of arthritis that may cause fluid on the knee. The most common types that cause excessive knee fluid are:
- Osteoarthritis – the natural wear and tear of the cartilage around the knee due to aging
- Rheumatoid arthritis – a chronic inflammation of the joints due to an autoimmune disease
- Gout – a type of arthritis where a patient’s nutritional intake may cause uric acid to build up in the joints
Infection or Inflammation – When areas of the knee are inflamed, this causes the knee to swell with fluid as the body combats the injury or bacteria in the area. A common form of inflammation that causes fluid in knees is bursitis. Bursa are cushioning sacs around the body which when inflamed may cause swelling or excess knee fluid.
The Bakers Cyst What Is It And Will It Go Away
Published on: 25th June 2020
No two ways about it: when a Bakers Cyst really gets going, it can look and feel pretty alarming.
This kind of swelling occurs behind the knee, often in the middle or slightly to the inner side, and in some cases can swell to the size of a grapefruit.
Not surprisingly, a lump on that scale even though its usually quite harmless can be debilitating to live with. Especially if its accompanied by pain.
So what causes these things? And what can be done about them?
Don’t Miss: Does Aflac Pay For Sprains
Diagnosing An Infused Knee
Your doctor will ask you about any past injuries. If youâre not sure when the swelling began or what caused it, your doctor will consider your age and activity level. If you do sports regularly, that may be a factor. If youâre overweight or obese, extra weight may add stress to your knee joint and increase the swelling.
Acute Onset Without Injury
Rapid onset of swelling with no injury is abroad category wherein the accumulation of fluid is not due to an injury or a chronic condition, such as:
- Infection can result in joint fluid accumulation, often as a result of surgery, a knee wound, or systemic infection that spreads to the joint. Treatment can be a problem as the body has a tough time clearing infection from this space. Surgery may be required to fully clean out a .
- Gout and pseudogout involve a buildup of crystals in the knee fluid. With gout, the uric acid used to transport waste can accumulate and crystallize in various joints of the body, causing intense swelling and pain. With pseudogout, the culprit is calcium crystals.
You May Like: Why Does My Knee Stiffen Up After Sitting
Recommended Reading: Nano Knee Surgery Cost
Treatment For A Swelling On Side Of Knee
With those that have a history of osteoarthritis and swelling after strenuous activity, like a workout or run, over-the-counter medications will help alleviate the pain. Patient may also apply compression sleeves to decrease the swelling during and after activity. Another way to decrease swelling at home is to use R.I.C.E.: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
Knee is swollen from Bursitis
- Rest Rest the joint and refrain from hard workouts, sports, and prolonged activity for 24-48 hours. Normal range of motion should continue to decrease joint stiffening.
REST for the RICE Protocol
- Ice Ice can be applied to the knee 3-4 times a day for 15-20 minutes at a time. Ice should never be applied directly to the skin.
Ice for the RICE Protocol
- Compression An ace bandage, compression sleeve or socks may not only reduce swelling already present, but may limit knee swelling during activity.
Compression Socks for the RICE Protocol
- Elevation Reducing blood flow to the area by sitting with the leg on a stool or lying down with the foot on a pillow, will reduce swelling.
Elevation Above Your Heart for RICE
Image of a swollen knee
Inflammation Comes Before Cartilage Breakdown Inflammation Therefore Causes Bone On Bone Not The Other Way Around
Here is what this paper said:
- . . . our results suggest that inflammation of the synovium, which occurs prior to cartilage degradation, is an early event during osteoarthritis initiation and progression.
- Note: Inflammation comes before cartilage breakdown. Inflammation, therefore, causes bone on bone, not the other way around.
Also Check: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Ambulance Ride
Home Remedy To Remove Fluid Around The Knee
The knee is the largest joint in the body and is prone to injury. It endures tremendous stress, and a person does not have to be a sports enthusiast to injure their knee. Most often, when an injury occurs, there is pain and swelling. Occasionally, fluid can build up around the knee. Knowing how to get rid of this using simple home remedies can really help.
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, seek emergency treatment immediately.
Will It Go Away Naturally
Normally, yes it will. Though in some cases it may take a few weeks. The first thing to do with bursitis is rest. Give your knee a break from whatever it was doing. Avoid other activities that tax the joint, especially repetitive ones, such as squatting. The second line of attack is anti-inflammatory pain relief such as ibuprofen, if youre able to take it. These two things should help the swelling to ease so that the fluid begins to reduce.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Outpatient Surgery
How To Drain Fluid From Knee At Home
While you technically cant drain fluid without the help of a professional, there are a few home remedies that can reduce inflammation at the site of your injury. These include the following:
- RICE method
- Massage , and
- Isometric exercises
For more information on how to drain fluid from knee at home, theres a section near the top of this page that describes these methods in detail.
That Being Said You Can Basically Group Effusions Into 2 Kinds:
Small and large.
According to a study, small joint effusions dont show any symptoms, can happen to anyone, and typically resolve on their own.
Large effusions, on the other hand, are what you have to watch out for because theyre clear giveaways that something is wrong, which brings us to the next part of our discussion.
Also Check: Inversion Table Benefits For Knees
Your Doctor May Not Want To Give You Cortisone If Knee Replacement Is Seen As Ultimately Your Only Answer
We see many patients who tell us that they have gone to their doctors and have asked for one more cortisone injection because of the amount of pain and swelling that they were suffering from that day. You know that the call to the doctors office for an appointment usually comes on the day when your knee hurts worse. The doctor, to his/her credit in many cases, has declined to give his/her patient this one more cortisone shot because their concern is that if you get cortisone injections into your knee prior to surgery, you will have a greater risk of complications after the surgery. There is a lot of debate around this subject.
A December 2020 study published in the medical journal Rheumatology gives this overview assessment of the debate surrounding the use of cortisone for a bone on bone knee. Here are the summary learning points:
- Existing data indicate that intra-articular corticosteroids in knee osteoarthritis provide short-term pain relief and functional improvement which may last from one to several weeks.
- At present, synovitis is the most important predictor of treatment response, and also a target for anti-inflammatory treatment for intra-articular corticosteroids.
- Our explanatory note: If you have a lot of knee swelling, cortisone may be of benefit.
Complications Of An Infused Knee
An infused knee can lead to other health concerns if left untreated. This includes loss of muscle in the affected leg. Persistent swelling may leave you using your knee less and losing muscle mass in that leg. Or you may develop a Baker’s cyst, which is a sac filled with fluid that forms behind your knee.â
Diseases or health conditions that may make your swelling worse include:
- Bursitis
- Tumors
You May Like: How To Whiten Knees Fast
The Problems Of Excess Weight And Obesity Causes More Inflammation
When we suggest to the patient that their knee can benefit from weight loss, we typically hear, I know, I know, or I have been trying. These are the typical responses of someone who has tried to lose weight and is tired of being lectured. Weight gain, like knee osteoarthritis, is a slow methodical problem that cannot be made to go away overnight. To lose weight you must find the inner motivation to do so. Maybe research can help.
In July 2020, researchers writing in the medical journal Skeletal Radiology looked at three patient groups. All the patients had knee osteoarthritis. The three groups were: people with normal weight people who were overweight people who were obese. What they were looking for was a relationship between excess weight and increases knee inflammation. Here are the results:
- Being overweight or obese was significantly associated with a greater prevalence and severity of synovial inflammation imaging biomarkers. Substantial reproducibility and high correlation with knee structural, cartilage compositional degeneration, and pain scores validate the synovial inflammation biomarkers used in this study.
What does all this mean? The more weight, the more inflammation, the more pain, the greater the need for medication, the greater the knee pain, the greater the eventual need for knee replacement.
Will The Cyst Just Go Away In Time
The first thing anyone with a Bakers Cyst wants to know is whether it will go away by itself. The answer is: it might. Some naturally dissipate over time, particularly if we address the underlying cause. Sometimes the cyst bursts and this can cause discomfort, which spreads into the calf muscle. Thats why we usually recommend conservative treatment for the cyst itself. Simple painkillers like paracetamol and ibuprofen can be helpful. Ice packs can sometimes reduce the swelling and discomfort. Nine times out 10, conservative is the way to go. This might mean waiting for six months or so to see how it develops.
Recommended Reading: Where To Get Knee High Converse
How Does An Orthopedist Treat Fluid On The Knee
The team of orthopedic knee specialists begins with a thorough exam and testing to identify the underlying condition causing the liquid accumulation.
They review your health information and symptoms and complete a physical exam. When necessary, your physician may order blood tests, other lab work, X-rays, and magnetic resonance imaging scans.
Once your orthopedist understands your needs, they may recommend an aspiration treatment to extract fluid from the swollen knee joint.
During this process, your doctor numbs the site and uses a hollow needle to drain fluid from the knee. They may also provide a knee brace to stabilize and support your leg.
Your doctor can also recommend treatment for the underlying issue causing your symptoms.
These Problems Are Getting Worse Despite Years Of Medications
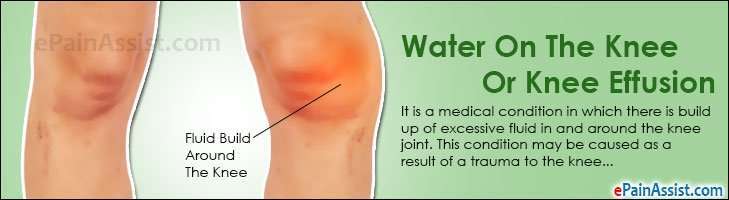
When we see a patient in our clinic with knee swelling, we ask, what have you been taking for this?
Typically the first line of treatment will include the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. The list includes many familiar names, medications you may already be on as well.
- Most common : aspirin, ibuprofen , naproxen
- Prescriptions: celecoxib, diclofenac indomethacin, oxaprozin , piroxicam
You May Like: Cellulite Above Knees
What Causes A Seroma
A seroma may form after a surgical procedure. In some cases, a seroma may form after a very minor surgery. Most seromas, though, will appear after a rather extensive procedure, or one in which a lot of tissue is removed or disrupted.
Your surgical team will place drainage tubes in and around the incision to try to prevent a seroma. The drainage tubes may remain in your body for a few hours or a few days after the surgery in order to prevent fluid buildup.
In many cases, the use of drainage tubes will be sufficient for preventing a seroma. However, thats not always the case, and a week or two after the procedure you may begin noticing the signs of fluid buildup near the incision.
The most common types of surgery that result in seromas include:
- body contouring, such as liposuction or arm, breast, thigh, or buttocks lifts