How To Treat Patellar Tendonitis
Patellar tendonitis can worsen without proper treatment. It will eventually result in degeneration of the tendon. This condition is common in many athletes and affects more than 20 percent of all jumping athletes. Your doctor may prescribe over-the-counter pain relievers, a patellar tendon strap, or cortisone injections. In rare cases, surgery may be recommended. You will be required to stay off the knee as much as possible while it heals, significantly limiting your activity.
What Is Jumpers Knee
Jumpers Knee, AKA patellar tendonitis, is caused by overuse or injury to the patellar tendon. When you overuse your knee, it can cause tiny tears to form in the patellar tendon, causing jumpers knee. This injury is more common in sports with a lot of running and jumping, including basketball, volleyball, and track and field.
Jumpers Knee is graded from 1 to 4 depending on how severe the injury is. Grade 1 means you have some pain when performing an activity, while grade 4 means you have constant pain. Noticing the symptoms and treating the injury early can prevent further damage!
In the diagram above, the first picture shows where patellar tendonitis is most likely to occur. If left untreated, patellar tendonitis can lead to a patellar tendon tear where the patella is pulled upward by the quadriceps.
Common Symptoms of Jumpers Knee
- Pain when bending the knee
Instability And Weakness In The Knee
Instability and weakness in the knee is caused by restricted glutes, leg muscles , and hamstring muscles. The quads are the power muscles of the thigh. The hamstrings are the stabilizing muscles of the thigh.
The hamstrings, along with the leg muscles, help stabilize the knee. When the hamstrings and leg muscles become restricted, it causes instability and weakness in the knee. To fix and get rid of instability and weakness in the knee, we need to target and release the hamstrings and leg muscles.
The Fastest Way To Eliminate Weight Training Tendonitis.
Get instant access to my BRAND NEW Titanium Physique program. The simple step-by-step solution I used to fix and cure my knee pain.
A young man performing traditional back squats at gym. The traditional squat exercise involve the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, hip flexors, spinal erectors, and leg muscles. Traditional squats and other squat variations can aggravate quadriceps tendonitis and patellar tendonitis. Athletes and weight lifters might also experience instability and weakness in the knee during squats.
A man and woman performing dumbbell walking lunges. The lunge exercise involve the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, hip flexors, and leg muscles. Lunges, including walking lunges, standing lunges, or lateral lunges, can aggravate quadriceps tendonitis and patellar tendonitis. Athletes and weight lifters might also experience instability and weakness in the knee during lunges.
Read Also: Is Nano Knee Covered By Medicare
Root Cause #: Muscle Restriction
When you lift weights and perform exercises that target or involve the knee, the quadriceps, glutes, and hamstring muscles contract, become stiff and tight, and after some time, lose their elasticity. Muscle restriction occurs when inelastic muscle fibers become shortened and unable to release and lengthen back to their normal relaxed state.
In the case of knee pain, lifting a weight thats too heavy, or using bad weightlifting form overstretch the quadriceps muscle and causes them to become restricted. This is usually the trigger that initiates the knee pain. When the quadriceps muscle gets restricted, they become shortened and get tighter.
Tight quadriceps muscle pulls and puts tension on the quadriceps tendon. As a result, it inflames the knee and causes knee pain when lifting weight and during exercise. In some cases, restricted muscles also causes instability and weakness in the knee.
Athletes, gymgoers, and weight lifters with restricted quadriceps experience:
- Sharp or severe pain in knee while lifting
- Burning pain in knee joint after lifting
- Instability and weakness in knee when lifting
- Difficulty and pain bending knee after working out
- Difficulty and pain straightening knee after working out
Summary: Root Causes of Knee Pain From Lifting Weights
The Fastest Way To Eliminate Weight Training Tendonitis.
Conservative Treatment Of Tendonitis
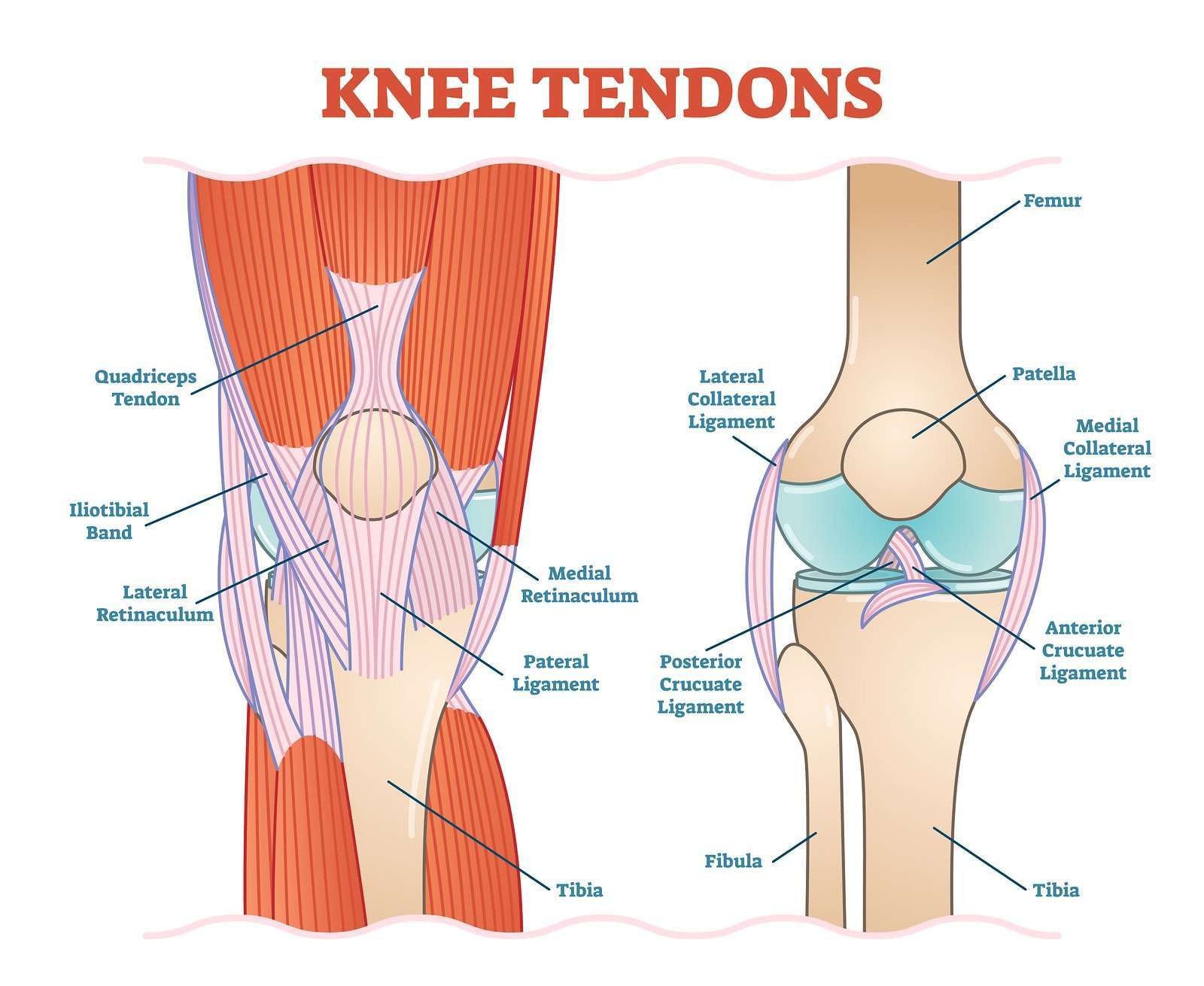
There are several conservative treatment options for tendonitis.
A common recommendation is the RICE-protocol , combined with the use of NSAIDs .
Other modalities used to deal with knee tendonitis include ultrasound treatment, deep friction massage, shockwave therapy and plasma-rich platelet injections. Speaking of injections: in his book Framework for the Knee, Nichalos DiNubile, MD, explicitly warns against cortisone shots, as they can cause a rupture of the tendon .
In physical therapy, the rehab protocols for tendonitis revolve around strengthening and stretching of the leg muscles, with a focus on stretching the quadriceps muscle group.
Keeping these traditional approaches in mind we can build on them to create an even better program for knee tendonitis. This will help us to deal with jumpers knee more thoroughly and also seems necessary, as the traditional methods of treatment apparently only provide temporary relief.
You May Like: Intellicast Aches And Pains
Can Patellar Tendonitis Lead To A Tendon Tear
Yes. Patellar tendon tears are acute injuries that happen suddenly. In some cases, repeated overuse over a long time can cause the patellar tendon tissue to abruptly tear.
Patellar tendon tears often happen when you land from a jump or suddenly change direction while running. A rip may go partway or all the way through tendon tissue.
Physio Programme For Runners Knee: Exercises For Patellar Tendonitis
Important information: slight pain may occur when performing exercises. As the healing process takes place over 12-16 weeks, its possible that you may not notice any improvement in the first four weeks, possibly even a slight worsening, due to the unfamiliar stain. Please be patient and consistently perform the exercises.
If the pain becomes too much, reduce the number of sets. If no improvement occurs or symptoms increasingly occur in everyday life, stop the exercises and please contact your treating doctor.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Dark Spots On Knees Fast
Whats A Typical Treatment Plan
Treatment depends on the severity of your injury.
Conservative measures to reduce pain, rest your leg, and stretch and strengthen your leg muscles are generally the first line of treatment. Your doctor will usually advise a period of controlled rest, where you avoid activity that puts force on the knee.
How Long Does It Take For Patellar Tendonitis To Heal
Healing takes time. The details of your recovery will depend on many factors that are specific to you.
You may start feeling better after a few weeks of taking it easy. Yet someone with more severe patellar tendonitis may find it challenging to stay on top of chronic pain.
Try not to rush your body through recovery. Pushing your body before its fully healed can damage tendon tissues more, which may set your recovery back.
Read Also: Getting Rid Of Fat Around Knees
Treatment For Tendonitis From A Gp
A GP may prescribe a stronger painkiller or suggest you use a NSAID cream or gel on your skin to ease pain.
If the pain is severe, lasts a long time, or your movement is limited, you may be referred for physiotherapy. You can also choose to book appointments privately.
If physiotherapy does not help, you may be referred to a doctor who specialises in muscles and bones or a local musculoskeletal clinic.
Some people with severe tendonitis may be offered:
- steroid injections, which may provide short-term pain relief
- shockwave therapy, which may help with healing
- platelet rich plasma injections , which may help with healing
- surgery to remove damaged tissue or repair a ruptured tendon
Treatment For Knee Tendonitis
Knee tendonitis, also called patellar tendonitis, is an inflammation of the tendon that links your patella to your tibia . People who have knee tendonitis usually experience worsening pain in the knee area until they receive treatment.
This is a frequent injury among athletes, which is why its often called jumpers knee. It is usually due to overuse or repetitive stress on the knee. Small tears develop in the tendon and become inflamed, eventually weakening the muscle and causing pain.
Also Check: How To Use Ginger For Knee Pain
What Might Be Causing The Tightness In Your Knee: Two Major Reasons
It goes without saying that the feeling of tightness in your knee may be caused by many reasons. That doesnât mean that thereâs no way of categorizing them, though. No matter how long the list gets, the truth is, you can attribute the majority of those recognized causes for knee tightness to one of the categories listed below.
Now, before we dive into the world of possible causes, Iâd like to take a moment to give you a piece of advice. As someone whoâs leading a very active lifestyle , you should probably do a little research on the topic of the best knee sleeve for running.
Why Are Exercises For Knee Tendonitis Helpful
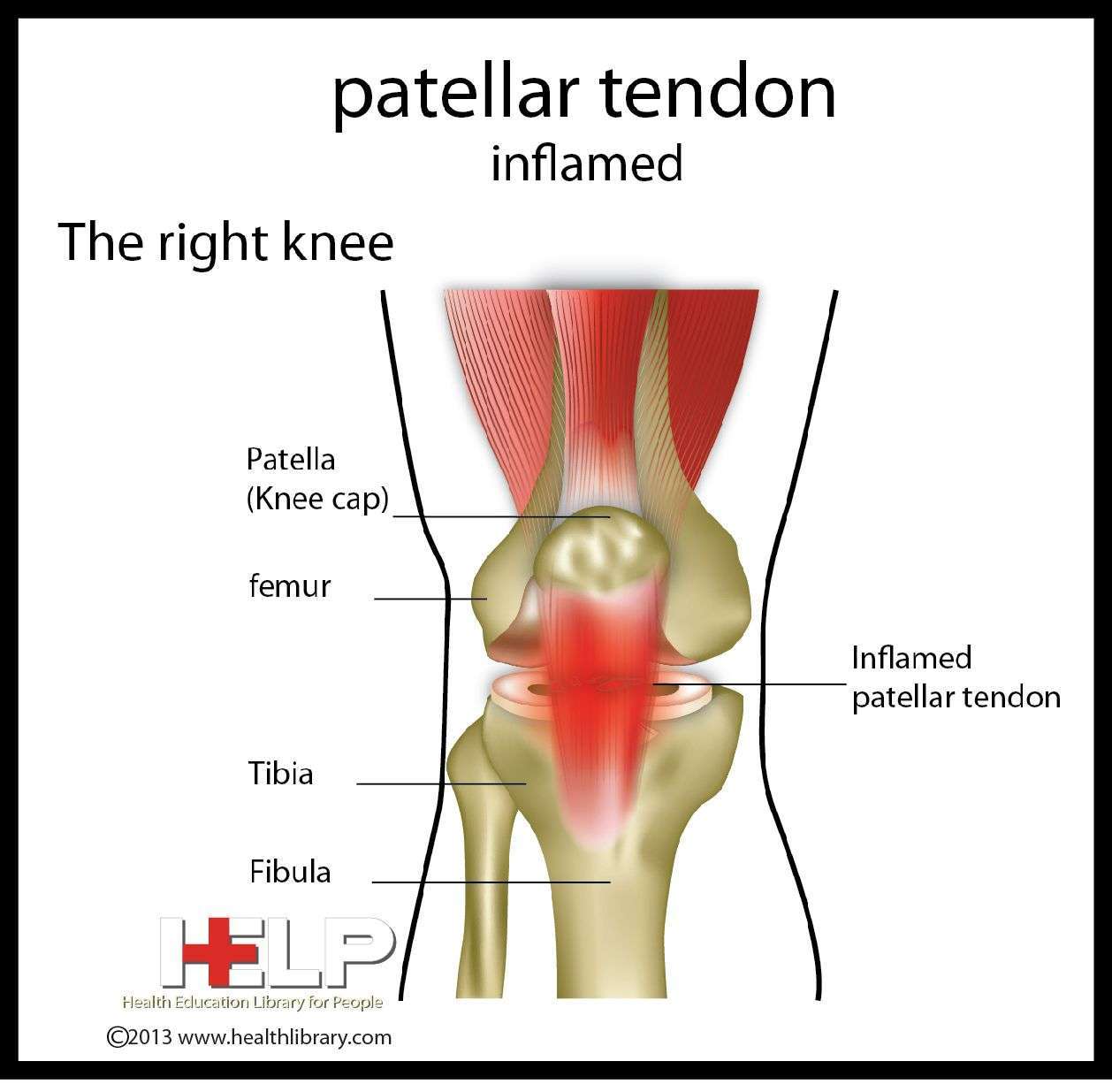
Multiple muscles overlap the knee joint like quadriceps, thigh, hamstrings, calf, gastrocnemius and soleus. All these muscles work together to flex, extend and stabilize the knee.
Strengthening and stretching the muscles will not only stabilize the knee. It will also stimulate
tendons and ligaments to become more flexible, durable and resistant to stress. While repetitive activities cause microtears, inflammation and degeneration of structures of the knee, stretching and strengthening will stimulate the structures to regenerate, take more stress without further damage and prevent injuries.
This is the reason why you should exercise all muscles that are connected to knee joint and not just certain groups of muscles.
Recommended Reading: How To Whiten Knees And Elbows
Increase Risk Of Patellar Tendonitis
The cause of patellar tendonitis in athletes is often multifactorial. However, some factors that may increase the risk of this injury include:
Overuse, particularly with recurrent jumping activities. Inadequate conditioning or stretching an abnormal length-tension relationship and compliance of the thigh and calf muscles can increase strain on the patellar tendon and increase the risk of injury. Obesity small increases in weight place dramatically increased stress on the kneecap and extensor mechanism. In fact, a gain of one pound can manifest as 8 to 10 more pounds of force on the knee with certain activities. Patella alta a higher than normal kneecap position may increase the strain and risk of injury to the patellar tendon.
Physiotherapy For Patellar Tendinopathy
Your physio will carefully assess your knee and then plan an individual programme of rehabilitation exercises to help strengthen your knee and leg muscles gradually. Treatment may involve stretching, and specific strengthening exercises.
Make sure you follow these exercises as theyre an important part of your recovery. Most people completely recover if their tendon isnt torn your physio will let you know how long it will take.
Your physio may suggest you wear patellar straps or braces, to help support your knee when youre active. They may also offer you treatment with extracorporeal shockwave therapy . This involves applying shockwaves to the affected area in order to reduce your pain.
Also Check: How To Whiten Knees Fast
Treatments For Tendonitis In The Knee
Early treatments for patellar tendonitis include resting the leg and knee and anti-inflammatory medication.
Nonsurgical treatments for patellar tendonitis:
- Physical therapy the goal of physical therapy or rehabilitation is to strengthen the leg and knee muscles and reduce the pain.
- Brace during physical therapy, your physician may prescribe a brace or crutches to facilitate healing.
- PRP injections a PRP injection uses a patients own blood, puts it in a centrifuge to centralize the growth factors and then injects it back into the affected area of the knee to promote healing.
Surgery is indicated when less invasive treatments are not successful. Your physician will determine if you require traditional open knee surgery or minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery. Arthroscopic surgery requires less recovery time.
Patellar Tendonitis Symptoms: 3 Red Flags You Need To Know
Patellar tendonitis is a deceitful injury. It will trick you into letting it weaken your knees until youll eventually need months of rehab.
This article will show you the symptoms of patellar tendonitis and the three red flags that tell you how serious your patellar tendonitis has become.
Keep reading to learn how you can get rid of patellar tendonitis symptoms and stop this injury dead in its tracks.
Disclaimer:
Don’t Miss: Mini Knee Replacement
How Is Patellar Tendonitis Treated
Patellar tendonitis treatments mostly focus on managing your symptoms and strengthening the soft tissues in your knee. At first, your provider may ask you to try conservative therapies, such as rest. In minor cases, these measures may be enough to relieve your pain.
If the condition doesnt go away, your provider may recommend you:
- Take it easy: Avoid the activities or movements that trigger your symptoms. Pushing through pain may cause more damage to tendon tissues.
- Rest: Stay off your feet as much as you can. Rest gives your body time to heal.
- Apply ice: If you have swelling around your knee, placing an ice pack on the area for 15 minutes at a time, a few times a day, may reduce inflammation.
- Take pain relievers: Taking over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medicines as needed may be enough to relieve minor aches or knee pains.
- Support your knee: Your provider may recommend you wear a support device over the knee, such as a knee brace. Support devices may relieve the pain.
- Try physical therapy: A trained professional will guide you in doing special exercises and stretches. These motions slowly increase the strength and flexibility of injured tendon tissues. Physical therapy may also relieve some of your discomfort.
- Have surgery: Surgery to treat patellar tendonitis is rare. However, if imaging tests show a tendon tear, your provider may recommend surgery to repair the damaged tissues.
Reduce The Weight You Are Lifting
Instead of complete rest, you need to consider relative rest. This means that you dont stop squatting, instead you just reduce the weight you are lifting. By reducing the weight lifted, you reduce the load placed through the sensitive area.
You need to aim for a weight that you can currently tolerate. It might take some trial and error to find. Generally, to avoid another flare up, it is best to start off lighter and build up to find the suitable weight.
Read Also: What Is The Best Knee Walker
Treatment For Tendonitis Side Of Knee
Common treatments for the treatment of tendonitis, such as knee tendonitis, roton cuff tendonitis or patellar tendonitis, include RICE therapy, ice, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy and cortisone injections. The problem with this method is that they do not repair or rebuild the weak tendon and, therefore, do not reduce the chronic pain that people with this condition experience.
When ice, anti-inflammatory drugs and cortisone bullets have been shown to provide short-term pain relief, it causes prolonged loss of function and more lasting pain by inhibiting the healing process of soft tissues and accelerating cartilage reduction. If a person with tendonitis receives cortisone injections into the tendon, or if he or she takes anti-inflammatories for too long, the tendonitis will be tendinosis. This means the tendon is increasingly weakening.
Other treatment options include cryotherapy and massage. But again, although they can provide pain relief, they do not address the root of the weak tendon problem and injured arteries. When a patient tries these treatments and the pain persists, patients who develop tendonitis may be referred to a surgeon. Unfortunately, surgery has side effects and side effects and can cause the problem to worsen.
Knee Pain After Running Here Is What To Do About It
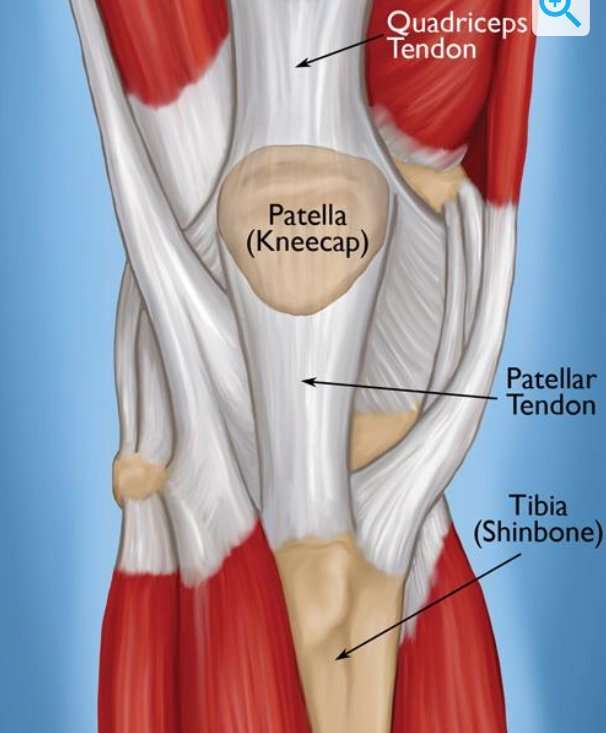
Do your knee hurt after going for a run? How about knee pain after playing basketball or jumping?
Patellar tendinitis is an injury to the tendon connecting your kneecap to your shinbone. The patellar tendon works with the muscles at the front of your thigh to extend your knee so that you can kick, run and jump.
Patellar tendinitis, also known as jumperâs knee, is most common in athletes whose sports involve frequent jumping â such as basketball and volleyball. However, even people who donât participate in jumping sports can get patellar tendinitis.
In children, patellar tendonitis is called Jumperâs Knee.
It is an inflammation or injury of the patellar tendon, the cord-like tissue that joins the patella to the tibia . Jumperâs knee is an overuse injury .
Constant jumping, landing, and changing direction can cause strains, tears, and damage to the patellar tendon. So kids who regularly play sports that involve a lot of repetitive jumping â like track and field , basketball, volleyball, gymnastics, running, and soccer â can put a lot of strain on their knees.
Also Check: Can You Rebuild Cartilage In Your Knee
Types Of Knee Tendonitis
Some of the specific types of of tendonitis that you might group under “knee tendonitis” include patellar tendonitis , quadriceps tendonitis, and iliotibial band friction syndrome.
Patellar tendonitis or jumper’s knee is the most common type of tendonitis of the knee, and it’s the kind of tendonitis most likely to be referred to simply as knee tendonitis in some cases. Athletes and others involved in sports such as running, jumping and other movements of the legs that put high pressure on the knees or result in extensive usage of the knee joint are more prone to patellar tendonitis, which is an inflammation of the tendon that links your patella to the tibia or shinbone.
When these structures are exposed to heavy and frequent pressures, it can commonly result in microscopic tears which tend to increase over time and finally resulting in inflammation of the tendons. Knee tendonitis may also be noticed in people living with chronic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, which is characterized by inflammation of multiple joints in the body.
Aging, in general, affects the functioning of different parts of the body and may also play a role in the development of knee tendonitis. It has also been noted that knee tendonitis is commonly seen in individuals and athletes in whom the muscles of the knee have been matured to the maximum extent. Trauma or injury to the knee due to a fall or awkward extension of the knee joint may also result in knee tendonitis in certain instances.