What Is The Cost Of A Gel One Injection
Is Gelsyn covered by Medicare?Euflexxa, Gel-One, Genvisc 850, Hyalgan, Hymovis, Monovisc, Orthovisc, Supartz, Supartz FX, Synojoynt, Triluron, TriVisc, or Visco-3 may be covered when any of the criteria listed below are satisfied: Trial and failure of all of the following: Durolane, Gelsyn-3, and Synvisc/Synvisc-One, resulting in minimal clinical
Review Of Key Questions
AHRQ posted the key questions on the Effective Health Care Web site for public comment. The EPC refined and finalized the key questions after review of the public comments, and input from Key Informants and the Technical Expert Panel . This input is intended to ensure that the key questions are specific and relevant.
Meniscus Tears Of The Knee
The meniscus can be torn with the shearing forces of rotation that are applied to the knee during sharp, rapid motions. This is especially common in sports requiring reaction body movements. There is a higher incidence with aging and degeneration of the underlying cartilage. More than one tear can be present in an individual meniscus. The patient with a meniscal tear may have a rapid onset of a popping sensation with a certain activity or movement of the knee. Occasionally, it is associated with swelling and warmth in the knee. It is often associated with locking or and unstable sensation in the knee joint. The doctor can perform certain maneuvers while examining the knee which might provide further clues to the presence of a meniscal tear.
Routine X-rays, while they do not reveal a meniscal tear, can be used to exclude other problems of the knee joint. The meniscal tear can be diagnosed in one of three ways: arthroscopy , arthrography, or an MRI. Arthroscopy is a surgical technique by which a small diameter video camera is inserted through tiny incisions on the sides of the knee for the purposes of examining and repairing internal knee joint problems. Tiny instruments can be used during arthroscopy to repair the torn meniscus.
Read Also: Dcf Compression Knee Sleeve
What Is The Generic Name For Synvisc
What is the cost of a gel one injection?How Much Does a Gel One Injection Cost? On MDsave, the cost of a Gel One Injection ranges from $1,591 to $2,914. Those on high deductible health plans or without insurance can save when they buy their procedure upfront through MDsave.How Much Does an Gel One Injection Cost Near Me? MDsave
Risk Factors For Osteoarthritis Of The Knee
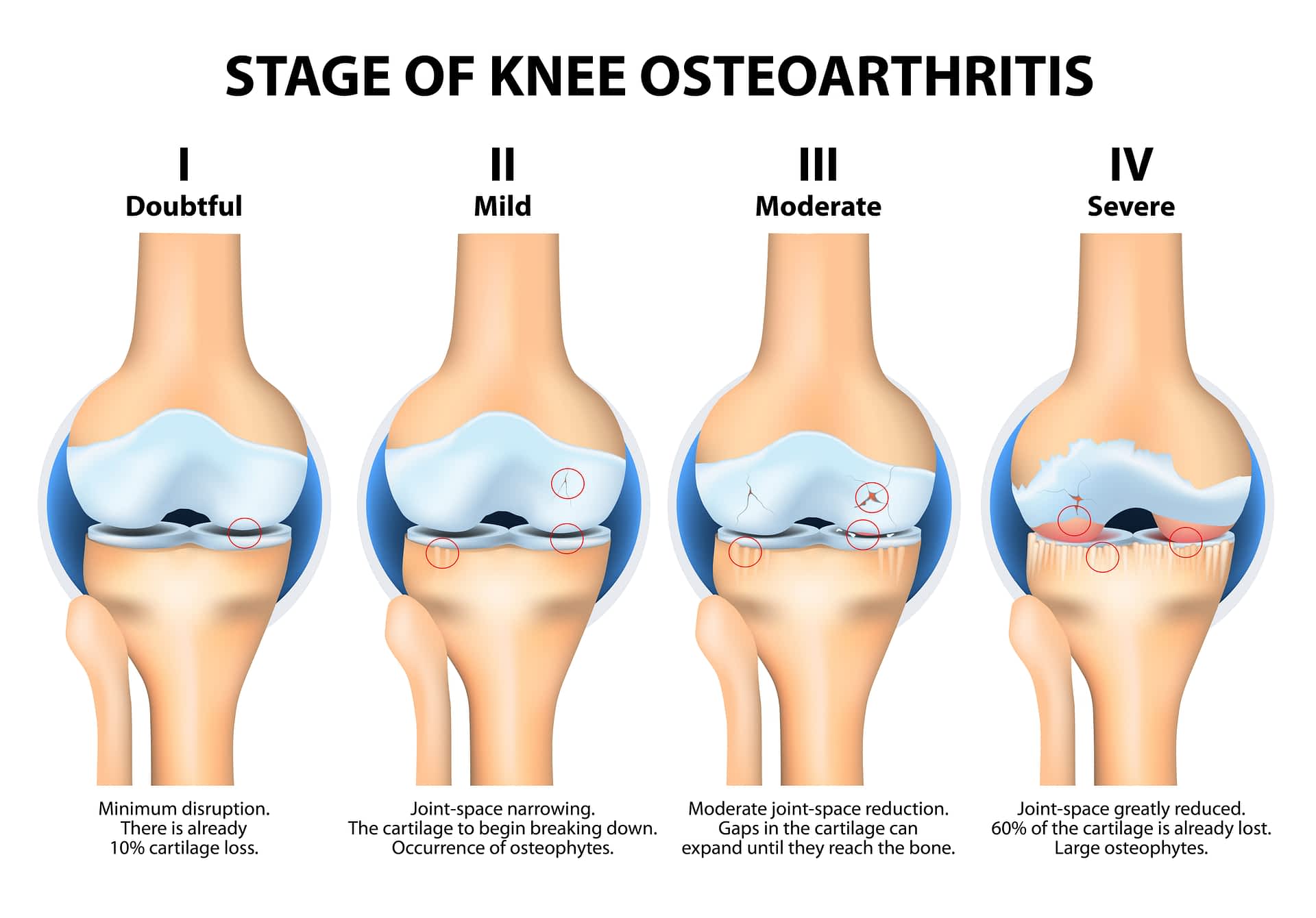
Factors increasing the risk of osteoarthritis of the knee include:
- Gender. Women develop osteoarthritis of the knee faster to men, though the reason is unclear.
- Occupations. In case your job demands repetitive stress on joints, it may develop knee osteoarthritis.
- Age. Knee Osteoarthritis risk increases with age.
- Genetics. This knee osteoarthritis is inherited and this is common.
- Obesity. The body weight results in osteoarthritis. This adds stress on joints, such as knees and hips. The fat tissue causes harmful inflammation, as it produces proteins around your joints.
- Joint injuries. People playing sports cause knee injuries and even due to accidents hurting the knee increases osteoarthritis risk.
- Deformities of bone. People born with defective cartilage or malformed joints are prone to knee osteoarthritis risk.
- Other reasons. People having rheumatic disease or diabetes also elevate the osteoarthritis risk.
Read Also: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Knee Surgery
Can Osteoarthritis Be Prevented
You can reduce your risk of developing osteoarthritis by avoiding significant damage or overuse of a joint. Maintaining a healthy weight will make osteoarthritis easier to manage if it develops in a weight-bearing joint, such as the knees, hips or feet.
Be careful of any product or treatment that claims to prevent osteoarthritis completely check with your doctor or pharmacist before taking any medication or supplement.
Does Osteoarthritis Of The Knee Cause Bone Pain
Osteoarthritis of the knee causes your leg bones to rub together, which can lead to painful bone spurs.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Osteoarthritis of the knee develops over time. You might not notice the twinge or ache that could be the first sign of knee osteoarthritis. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have knee pain thats getting worse. Your provider can help you treat your symptoms and keep you moving. Early treatment can ease the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee and slow its progress.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 09/08/2021.
References
Recommended Reading: Whiten Knees Fast
What Causes Arthritis Of The Knee
Experts have identified some genes that might cause arthritis, including arthritis of the knee. They predict that there are more genes not yet discovered. You could have a gene linked to arthritis without knowing it and a virus or injury could trigger arthritis of the knee.
Though the cause is unknown, some risk factors increase the possibility of arthritis of the knee. Risk factors of osteoarthritis, specifically, include:
- Age. Osteoarthritis happens to older adults more often than younger adults and children.
- Bone anomalies. Youre at a higher risk for osteoarthritis if your bones or joints are naturally crooked.
- Gout. Gout, also a type of inflammatory arthritis, might lead to osteoarthritis.
- Injuries. Knee injuries can cause arthritis of the knee.
- Stress. A lot of stress on your knees from jogging, playing sports or working an active job can lead to osteoarthritis of the knee.
- Weight. Extra weight puts more pressure on your knees.
Ligament Injury Of The Knee
Trauma can cause injury to the ligaments on the inner portion of the knee , the outer portion of the knee , or within the knee . Injuries to these areas are noticed as immediate pain, but are sometimes difficult to localize. Usually, a collateral ligament injury is felt on the inner or outer portions of the knee. A collateral ligament injury is often associated with local tenderness over the area of the ligament involved. A cruciate ligament injury is felt deep within the knee. It is sometimes noticed with a “popping” sensation with the initial trauma. A ligament injury to the knee is usually painful at rest and may be swollen and warm. The pain is usually worsened by bending the knee, putting weight on the knee, or walking. The severity of the injury can vary from mild to severe . Patients can have more than one area injured in a single traumatic event.
Ligament injuries are initially treated with ice packs and immobilization, with rest and elevation. At first, it is generally recommended to avoid bearing weight on the injured joint and crutches may be required for walking. Some patients are placed in splints or braces to immobilize the joint to decrease pain and promote healing. Arthroscopic or open surgery may be necessary to repair severe injuries.
Also Check: Flying After Knee Replacement Surgery
What Is Osteoarthritis Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
Osteoarthritis develops over time from normal wear and tear on joints or from injuries.
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, or inflammation of the joints .
It is also called degenerative joint disease or “wear and tear” arthritis because it most often develops slowly over time as people age.
Strength Exercises For Knee Osteoarthritis
Aging doesnt just cost you articular cartilage flexibility. It also takes a toll on your muscles, too and that can lead to knee instability.
Sarcopenia is the natural loss of muscle mass that comes with age. The process typically starts around age 30. On average, adults lose 3% to 5% of their muscle strength every decade after that birthday.
A strength program targeting your lower body helps limit the decline in muscles supporting your knee. Think of those muscles as load-sharing cables, says Dr. Orlandi. They work to limit stress and pressure on the joint.
Workout equipment offers numerous ways to build strength through exercises such as leg presses, hamstring curls and quad extensions.
If you dont have equipment or a gym membership, no worries! Try these simple exercises:
- Bodyweight squats. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, with your feet turned out slightly. Keeping your heels on the ground, bend your knees while dropping your butt and lowering your body. Pause before returning to standing. Repeat.
- Stair stepping. If you have stairs in your home, tackle those flights a few times a day. Stepping up and down off of a stool or block also is an option if youre living in a one-floor residence.
- Leg extensions. Sit on the edge of your bed or a chair and alternate kicking out your left and right legs.
Don’t Miss: Inversion Table Knees
To 2years Before Radiographic Osteoarthritis Onset
Clinical
Between 2 to 1year before disease onset people who develop AKOA are more likely to report greater knee pain than earlier assessments . Chair-stand pace and self-reported global impact of arthritis also start to worsen among those who develop AKOA while those with typical knee osteoarthritis stay the same or improve slightly . These worsening symptoms correspond to the start of a dramatic rate of changes within the joint.
Structural alterations
During the 2years before radiographic disease onset, adults who develop AKOA have, on average, a 4.6 times greater increase in effusion-synovitis volume compared with their peers with typical knee osteoarthritis . Additionally, they experience, on average, a 13 times greater increase in bone marrow lesion volume and a greater loss of articular cartilage than adults with typical knee osteoarthritis . Unlike typical knee osteoarthritis, which may be conceptualized with focal cartilage damage, adults who develop AKOA experience diffuse cartilage changes throughout the knee . Overall, these early changes characterize the start of a downward slope towards joint failure. It will be helpful to learn whether an intervention could halt or slow this progression or if they have already passed a point of no return.
Less Than 1year Before Radiographic Onset
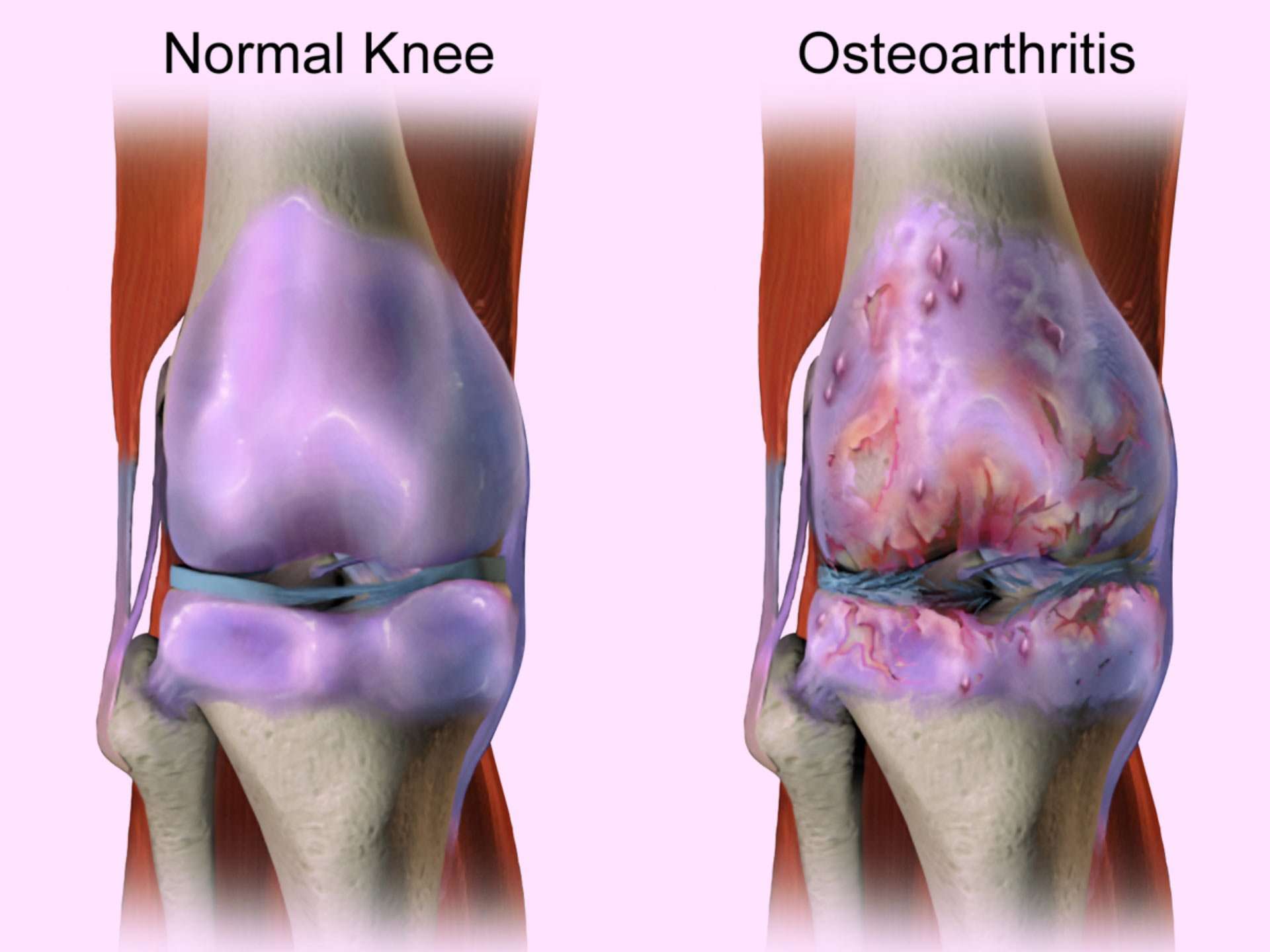
Clinical
Within the 12-months before disease onset, people who develop AKOA or typical knee osteoarthritis are more likely to report frequent use of medication for pain, aching, or stiffness compared with those with no knee osteoarthritis . Despite the frequent use of medication to manage symptoms, people who develop AKOA or typical knee osteoarthritis during the next 12months report greater symptoms in most activities than those without incident knee osteoarthritis. More specifically, people who develop AKOA are more likely to report greater difficulty with lying down, pain with straightening the knee, pain walking, daily knee pain, and frequent knee swelling compared with peers who will develop typical knee osteoarthritis .
Structural alterations
This peak in prodromal symptoms corresponds to continued worsening throughout the knee including worsening bone marrow lesions, increasing effusion-synovitis volumes, and more frequent occurrence of infrapatellar fat pad signal-intensity alterations, meniscal damage in 2 or more regions, any medial meniscal pathology or extrusion, or lateral meniscal extrusion than adults with either typical or no knee osteoarthritis . These changes may be secondary to diffuse differences in tissue composition or secondary to joint instability.
Read Also: Bleach Dark Knees
Osteoarthritis Of The Knee With Crystals
Sometimes crystals are formed during osteoarthritis of the knee and it can complicate things. The crystals are calcium chalky deposits forming in the cartilage. This is referred to as calcification and in this process the crystals are apparent in x-rays and can be understood in the joint fluid samples test done. Osteoarthritis of the knee becomes severe when crystals are formed.
Stretching Exercises For Knee Osteoarthritis
Stretching can help minimize the loss of flexibility in and around your knee. You want to make sure youre stretching your hamstrings, quads, calves and hip flexors to help address any stiffness you might feel, says Dr. Orlandi.
Examples include:
- Hamstring stretch. Stand in front of a chair or steps. Place your right foot on the chair or step, with your heel on the surface and toes pointed up. Slowly bend forward at the waist, keeping your back as straight as possible. You should feel the stretch in the back of your thigh. Hold for a few at least 10 seconds before returning to standing. Alternate feet and repeat 5-10 times.
- Quad stretch. While standing, bend your left leg back, bringing your heel toward your butt. Grab your foot with your left hand and hold. Try to bring your left thigh back until its even with your right thigh. Hold for at least 10 seconds. Alternate legs and repeat 5-10 times.
- Calf raises. Stand on a step with your heels hanging over the edge. Rise up on your toes and then slowly drop your heels down until theyre below the level of the step. Hold for at least 10 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Give yoga a try, too, to keep your joints and muscles in tip-top shape.
Also Check: Cellulite Above Knees
Assessment Of Methodological Risk Of Bias Of Individual Studies
For randomized controlled trials of pharmacological interventions, glucosamine/chondroitin, and acupuncture, we will employ the Cochrane Risk of Bias Assessment tool to assess ROB of individual studies. Questions will be added to assess the type of controls used and the way that outcomes are assessed and expressed , as these factors have been shown to influence significance of effect sizes.
For trials of physical modalities, we will incorporate a small number of items from the PEDro risk of bias assessment tool. A recent analysis finds that the tools produce different assessments of the same studies, with the Cochrane tool providing a more rigorous assessment.30
For observational studies included to assess adverse events, we will use the McHarms scale for each study.
To assess the quality of prior systematic reviews that we include as sources of data, we will use the ROBIS tool.31
Or More Years Before Radiographic Osteoarthritis Onset
Clinical
Individuals destined to develop AKOA are more likely to report more knee pain and knee-specific disability, as well as walk slower than adults who will develop typical knee osteoarthritis up to 3years in advance of disease onset .
Structural alterations
Magnetic resonance images may reveal why people 2years in advance of radiographic disease onset are more likely to report greater pain and dysfunction than individuals who develop typical knee osteoarthritis. For example, adults with infrapatellar fat pad signal-intensity alteration or large effusion-synovitis volume, assessed with magnetic resonance imaging, have roughly twice the odds of developing AKOA onset over the subsequent four years . At least 2years before radiographic onset, people who develop AKOA have greater effusion-synovitis volume compared with those who developed typical knee osteoarthritis . Furthermore, adults who develop AKOA are more likely to have infrapatellar fat pad signal-intensity alteration than those with no knee osteoarthritis . Effusion-synovitis volume and infrapatellar fat pad signal-intensity alteration may be reflective of local inflammation and at least moderately related to knee pain .
Don’t Miss: Does Aflac Cover Hysterectomy
Signs And Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis
People with osteoarthritis typically have joint pain or stiffness that’s most often caused by the rubbing of joints due to damage to cartilage, the slippery tissue that covers the ends of bones in the joints.
Other common symptoms of osteoarthritis include:
- Swelling around the joint
- Reduced range of motion, which may go away with movement
- Muscle weakness around the joint
Osteoarthritis can occur in any joint, but it most commonly affects the joints of the hands, hips, and knees, as well as the lower back and neck.
Coping With Low Mood And Sleep Problems
You might find that osteoarthritis of the knee makes you feel depressed or anxious. Speak to your doctor if youre feeling low as they may be able to recommend psychological therapies to help you, such as cognitive behavioural therapy and stress-relieving techniques.
If your sleep is disturbed because of osteoarthritis of the knee, this could make your pain feel worse. However, there are things you can do for yourself that might help, such as:
- Keep a sleep diary to work out if there are any patterns to your sleep problems
- Sleep at regular times to get your body into a routine
- Avoid phones and other screens in the bedroom to help you wind down before bed.
If youre still having problems, speak to your doctor or an occupational therapist who can give you other tips and techniques to try, known as sleep hygiene.
Also Check: Roller Knee Walker
What Is The Generic For Synvisc
What is the generic name for Synvisc?Hylan G-F 20 is the generic name for Synvisc. The generic name is hylan G-F 20. It is a gel-like substance made up of two hyaluronan polymers that come from chicken combs. Hyaluronan naturally occurs in our joints, and it functions as a cushion for the joint.What is the generic name for Synvisc Hylan GF? | Muscoloskeletal Agent
Osteoarthritis Of The Spine
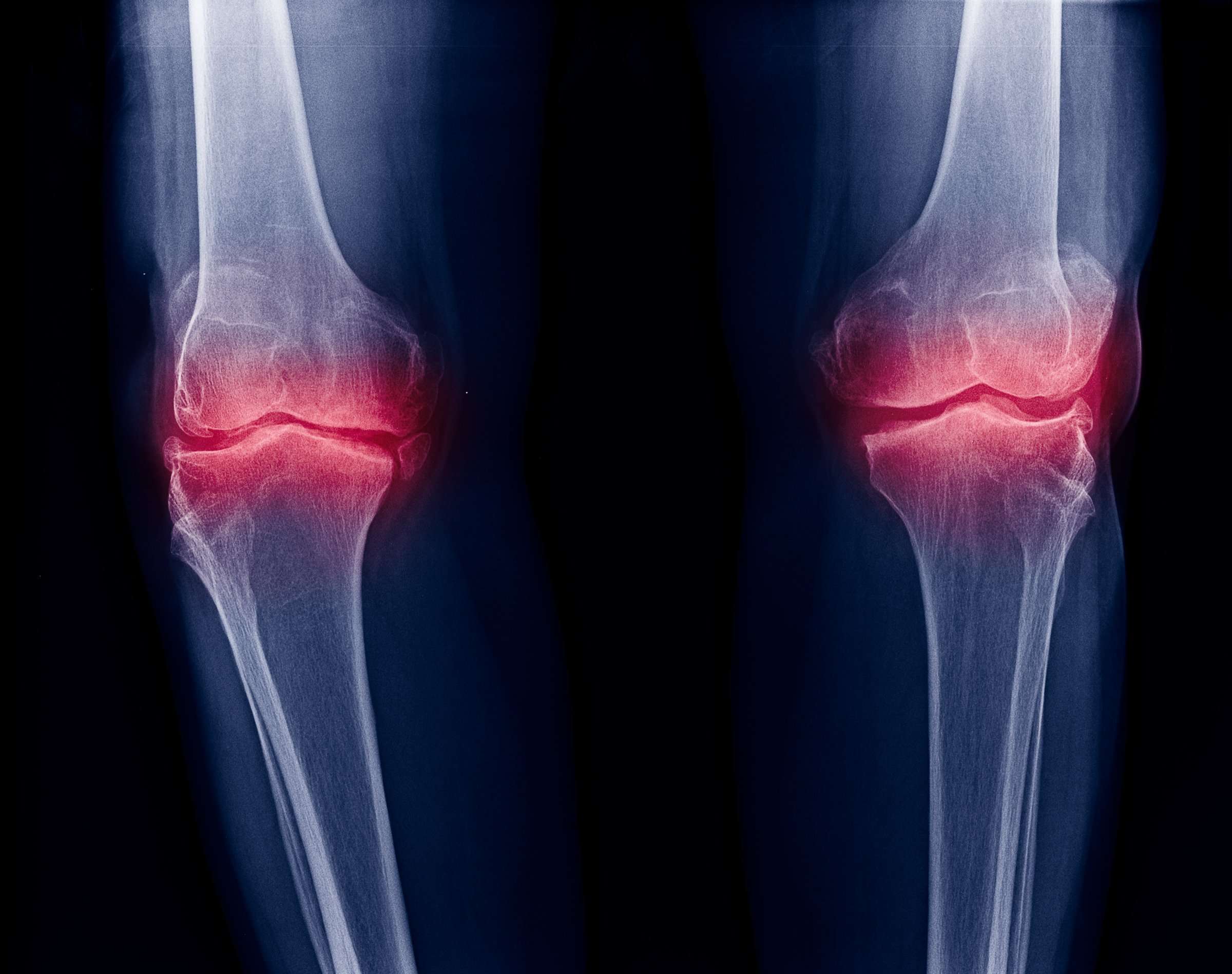
If you have back pain, it may indicate that you have spinal OA. This condition affects the facet joints located throughout the spine.
Age and trauma to the spine are both potential risk factors for spinal OA. A person who is overweight, or whose job requires squatting and sitting, may also be at increased risk.
Spinal OAs symptoms can vary in severity. They include:
- stiffness or tenderness in the joints in your back
- weakness, numbness, or tingling in your arms or legs
- reduced range of motion
Its important to pay attention to these symptoms. Without treatment, spinal OA can worsen, causing more severe symptoms and disability. Get the facts on OA of the spine.
You may have risk factors for OA that you cant change, such as heredity and age. However, other risk factors can be controlled. Managing them can help reduce your risk of OA.
The following tips can help you manage the risk factors under your control:
- Support your body. If youre an athlete or an avid exerciser, make sure you care for your body. Wear athletic supports and shoes that reduce impact on your knees. Also make sure to vary your sports, so that all of your muscles get a workout, not just the same muscles every time.
- Maintain a moderate weight. Keep your body mass index in the appropriate range for your height and sex.
- Eat a nutritious diet. Reach for a range of healthy foods, with a focus on fruits and vegetables.
- Get enough rest. Give your body ample opportunities to rest and sleep.
Don’t Miss: Inversion Table Benefits For Knees