For Ligament Cartilage And Joint Tears
Ligament, cartilage and joint tears in your knee will need to be addressed by your doctor.
After imaging diagnostics and a clinical assessment, your doctor will let you know if your treatment will include physical therapy and anti-inflammatory medication, or if youll need to undergo surgery to repair the injury.
Recovery from knee surgery can take some time. It may take anywhere from 6 months to a year to resume your normal activities.
Contributing Factors To The Development Of Mechanical Pain
There are several factors which may predispose patients to developing mechanical pain. These factors can vary depending on the tissue affected and can usually be identified and corrected with direction from a physiotherapist. Some of them may include:
- inappropriate or excessive training or activity
- inadequate recovery periods from training or activity
- work, housework or recreational activities involving repetitive, prolonged or heavy forces
- inadequate rehabilitation following a previous injury
- poor posture or biomechanics
- weight loss advice where appropriate
- a gradual return to sport or activity program
When Can I Return To Work
Its usually recommend that you return to work right away. If you cannot do your regular job, it is in your best interest to return to some kind of modified duty . Your healthcare provider can give you a prescription for a limited period of modified work duty.
It is very common to be afraid to promptly return to work and other activities because of fear of re-injury. However, if you are receiving proper treatment, your risk of re-injury should be limited. It is in your best interest to return to a normal lifestyle promptly. Early mobility has been found to directly result in a more rapid recovery. Maintaining a positive mental attitude is also imperative to a quick recovery.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/22/2020.
References
Don’t Miss: Can I Regrow Cartilage In My Knee
True Knee Locking Causes
The knee joint is designed to bend up and down, flexion and extension, and rotate slightly.;
If something gets caught inside the knee joint, it blocks the movement and the leg gets stuck. When this happens, the knee is totally blocked, unable to move at all.;It often takes a few minutes of gently moving the knee, or as patients often say waggling it about, or sometimes professional intervention is needed to get the fragment to move out of the way, before you can move the leg again.;
This is known as true locking, i.e. something is physically stopping the joint from moving. True knee locking is usually caused by:
What Are We Seeing In This Image This Is How Ligament Laxity Squeezes Your Meniscus Out Of Your Knee Joint
In the caption below are MRI like sounding terms so lets make it a little simpler to understand what its is that we are seeing in this image.
- This is an ultrasound image showing a meniscus being squeezed out of place or extruded. Extrusion is the way tooth paste comes out of a tube. For the tooth paste to come out there needs to be an unnatural pressure or an extra force exerted on the tube. That force is of course you squeezing the tube to make the tooth paste come out. Here the knee is being squeezed and the meniscus is being pushed out by valgus stress. What causes valgus stress? One answer is damage or weakness of the medial collateral ligament of the knee. Ligamentous.
Also Check: How To Fix Damaged Cartilage In Knee
Facts You Should Know About Knee Pain
- Knee pain is a common problem with many causes, from acute injuries to complications of medical conditions.
- Knee pain can be localized to a specific area of the knee or be diffuse throughout the knee.
- Knee pain is often accompanied by physical restriction.
- A thorough physical examination will usually establish the diagnosis of knee pain.
- The treatment of knee pain depends on the underlying cause.
- The prognosis of knee pain, even severe knee pain, is usually good although it might require surgery or other interventions.
What You Need To Know
- The most common causes of knee pain are related to aging, injury or repeated stress on the knee.
- Common knee problems include sprained or strained ligaments, cartilage tears, tendonitis and arthritis.
- Diagnosing a knee injury or problem includes a medical examination and usually the use of a diagnostic procedure such as an x-ray, MRI, CT scan or arthroscopy.
- Both non-operative and surgical treatment options are available to treat knee pain and problems depending on the type and severity of the condition.
You May Like: How To Restore Cartilage In Your Knee
Knee Ligament Instability The Cause Of Meniscus And Cartilage Wear And Tear And Bone On Bone
Sports medicine doctors in Europe, writing in the journal Knee surgery, sports traumatology, arthroscopy suggest that when dealing with knee instability in patients doctors should be wary that the interpretation of multidirectional knee laxity is complex and suggests the necessity for individualized care of knee diseases and injuries.
- What these researchers are saying is lets get a good physical examination and look at the knee. Please see my article Is My MRI Accurate? This includes looking for;ligament laxity.
But going a little further look at what the study suggests:
Physiological knee laxity has received little attention in spite of indications that it influences knee diseases/injuries and their outcomes. Excessive laxity has been recognized as a risk factor for non-contact ACL injuries and more importantly for worse ACL reconstruction outcomes.
Our findings may therefore stimulate the debate around the need for individualized care of knee injuries and disease. More work is needed to improve the comprehension of the role of individual knee function in the occurrence of degenerative knee diseases, knee injuries and poor treatment outcomes.
- The reason for poor outcomes, knee instability is not understood.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury
The anterior cruciate ligament is the most commonly injured ligament of the knee. The injury is common during sports. Twisting of the knee is a common cause of over-stretching or tearing the ACL. When the ACL is injured a popping sound may be heard, and the leg may suddenly give out. Besides swelling and pain, walking may be painful and the knee will feel unstable. Minor tears of the anterior cruciate ligament may heal over time, but a torn ACL requires surgery. After surgery, recovery is prolonged and low impact exercises are recommended to strengthen the joint.
Read Also: How Soon Can You Fly After Knee Replacement
Knee Pain In Children & Adolescents
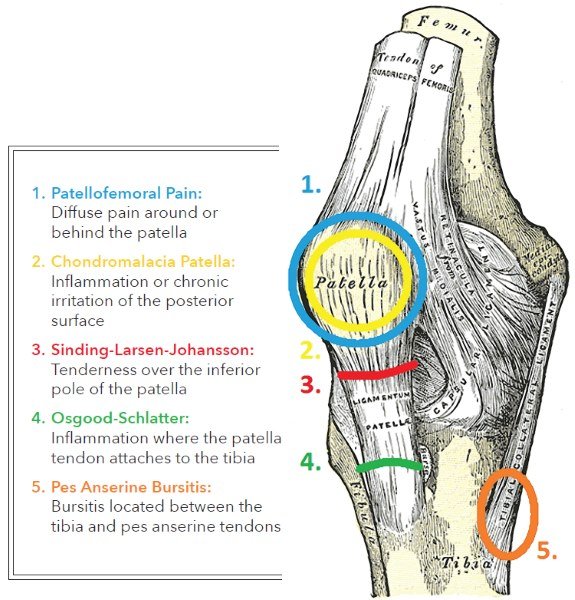
There are recognised pathological changes that are unique to the skeletally immature knee . Overuse of the knee can result in pain that only resolves after a period of rest. This is due to stress injuries from repetitive use, usually because of increased demands placed on the knee. They are also more common during growth spurts. Once the knee has been afforded time to recover from such stress then the symptoms usually resolve. The junction of the patellar ligament at the tibial tuberosity is a common site for such pain. Termed Osgood Schlatters disease, the pain is in response to repeated stress causing mild avulsion injuries. The natural history is one of spontaneous resolution before adulthood . Sinding-Larsen-Johannson disease presents as pain at the distal pole of the patella and responds to a simple non-operative therapy like Osgood Schlatter similar to the treatment of Osgood Schlatter disease.
What Is The Outlook For People With Back Pain
The prognosis for complete recovery is excellent. Most people with acute mechanical back pain respond very rapidly to treatment. About 90% of people with acute low back pain are symptom-free in one to two weeks. Many of the remaining estimated 10% recover within three months.
Recurrences of back pain are common. Continuing your home exercise program may help reduce your risk of another episode.
Don’t Miss: What Does Constant Knee Pain Mean
Bone Marrow Lesions And Osteoarthritis Progression
Figure 1.
Coronal STIR MRI showing subchondral bone oedema and synovitis
Until recently there has been much focus on articular cartilage in assessing OA severity. There is conflicting data about whether cartilage damage correlates with pain. And recent studies have tied to shift the emphasis to other pathological events such as BML and synovial effusion/synovitis in understanding the cause of OA pain. The clinical implication of BML is not clear. It is present in 78% of patients with knee OA with pain and in 30% of patients in knee OA without pain . BML is not pathognomonic of knee OA but its association is intriguing and not fully understood. This only highlights the need for more research into the matter. It is becoming more evident that pain from OA is multifactorial and that research into such new fields will help predict disease progression and alter improve treatments.
Q What Kind Of Doctor Should I See For My Knee Pain
Don’t Miss: How To Repair Knee Cartilage
What Are Treatments For Knee Arthritis
Though neither category of arthritis is curable, both kinds of knee arthritis can be managed well, particularly when caught early. Thats especially true for those with inflammatory arthritis.
We know a lot more about inflammatory arthritis than we do about OA, Dr. Domingues says. And we have drugs that target the root cause of inflammatory arthritis disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or DMARDs which decrease inflammation, help preserve the joint, and ease pain. Biologics, a more targeted type of DMARD, may be recommended for those who dont get sufficient relief of knee pain and other symptoms from traditional DMARDs.
As for what to take for knee osteoarthritis, doctors often first recommend over-the-counter analgesics such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , which are also sometimes used to alleviate the pain of inflammatory arthritis.
If those dont help your knee OA, steroid injections may be a good next step for managing knee joint pain, or your doctor might suggest hyaluronan injections, which provide some of the cushioning lost by cartilage breakdown in your knee joint.
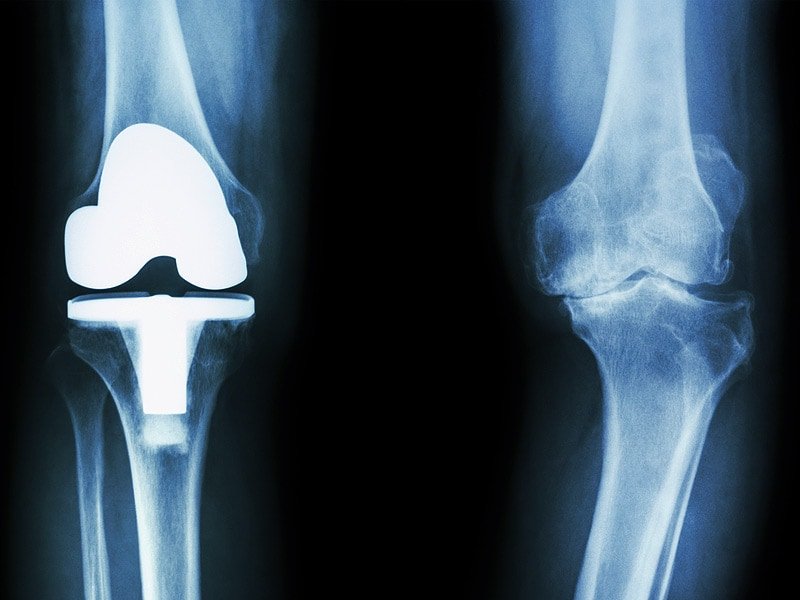
But because OA is a degenerative disease, which means it will likely get worse over time, these options mostly buy you time before you may ultimately need a knee replacement, which is the definitive treatment for moderate-to-severe knee OA, Dr. Domingues says.
You Can View The Full Infographic Here
Joint pain can be classified as either mechanical or inflammatory. Osteoarthritis the most common cause of mechanical joint pain ;is the inherent repair process of synovial joints and not a disease, as commonly thought. Sometimes this process fails and patients present with symptoms of pain and functional impairment. Joint pain classification is based on signs and symptoms; X-rays are not needed.
Flexibility exercises help to stop the joint capsule from tightening and strengthening exercises help to strengthen the supporting muscles, so reducing pain and improving function.
Also Check: How To Cure Knee Pain
What Are The Symptoms Of Mechanical Back Pain
Most people with mechanical back pain experience pain primarily in their lower back. The pain may radiate to your buttocks and thighs. Many people may also experience spasms with mechanical back pain. The symptoms of mechanical back pain are generally more noticeable with flexion of the back and when lifting heavy objects.
Being Weak In The Knees Why Does Your Knee Buckle Are You A Fall Risk
For patients who are being managed until knee replacement, or are putting off any treatment to fix his/her knee, there is the problem of knee buckling. Knee buckling is the knee giving out. Most times people will be able to grab unto something or someone close by to prevent a fall. If not, there can be a fall. People with knee osteoarthritis and knee instability are a fall risk.
Why does your knee buckle? Simply the knee at that moment cannot support your weight, your knee is collapsing under your weight.
Also Check: Can Gout Form In The Knee
What Medical Conditions Cause Knee Pain
Medical conditions
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that can affect any joint in the body. It can cause severe pain and disability, as well as swelling.
Gout is a form of arthritis that is most commonly found in the big toe, though it can also affect the knee. Gout tends to flare up and is extremely painful during the acute episodes. When there is no flare-up, the knee can be pain free.
With , the knee joint can become infected; this leads to pain, swelling, and fever. This condition requires antibiotics and drainage treatments as soon as possible.
Chronic use/overuse conditions
Patellar tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendons connecting the kneecap to the shinbone . Patellar tendinitis is a chronic condition often found in individuals repeating the same motion during exercise .
Patellofemoral pain syndrome is caused by degeneration or stress under the kneecap where it meets the thighbone . Patellofemoral pain syndrome occurs in runners and cyclists.
Osteoarthritis: a wearing down of cartilage of the joint due to use and age
Prepatellar bursitis: Inflammation to the bursa in front of the kneecap may cause anterior knee pain.
Other causes
Surgery For Mechanical Pain
A small percentage of patients who experience mechanical pain may require surgery to ensure an optimal outcome . Some common causes of mechanical pain requiring surgical intervention include:
- Certain fractures
- Severe osteoarthritis
- Severe cartilage injuries
- Full thickness muscle, tendon or ligament tears
- Joint dislocation
- Severe spinal conditions often with associated arm or leg pain
Don’t Miss: How To Fix Injured Knee
Transcutaneous Nerve Stimulators In Pain Relief Best Mechanical Relief For Arthritic Knee Pain
No Odor Pain Relief Cream Central Pain Mechanisms In Chronic Pain States Maybe It Is All In Their Head Are Back Extensions Good For Sciatica Pain Relief. Low Back Pain Right Side Relief Reviews On Omega Green For Chronic Pain. Law In Massachusetts About Chronic Pain Patients Fastest Pain Relief For Toothache.
Can You Prevent Knee Pain
There can be many reasons for knee pain. Therefore, there are different strategies to prevent the pain depending on the underlying cause. Running on soft surfaces or decreasing the amount of running can help if the pain is due to overuse. Avoiding any direct injuries to the knee including wearing a seatbelt can prevent traumatic injuries. Weight loss can be helpful for many different forms of knee pain.
Don’t Miss: Why Does My Knee Click When I Walk
Everything In The Knee Affects The Ligaments And The Ligaments Affect Everything In The Knee
Ligaments function primarily to maintain smooth joint motion, restrain excessive joint displacement, and provide stability across the knee joint.
The ligaments of the knee provide:
- Passive stability,
- guide the motion of the femur and tibia,
- define contact mechanics between the femur and tibia,
- and restrain excessive motion to prevent dislocation.
When the forces to which ligaments are subjected are too great , failure occurs, resulting in drastic changes in the structure and physiology of the joint.
Muscles Weak And Strong
Maintaining flexible muscles around your knee that are strong enough to support your body may help to alleviate or prevent tightness in the knee area. Strong legs, hips, and buttocks are thought to reduce knee tightness.
Research surrounding the benefits of strong leg muscles in relation to knee tightness varies. According to a 2010 study that looked at over 2,000 knees of men and women who had or were at risk for osteoarthritis, neither hamstring nor quadriceps strength predicted frequent knee symptoms such as pain, aching, and stiffness.
Still, having strong quadriceps may help to reduce the risk of knee problems, since stronger muscles can help to support the knee joint.
A 2014 study that was conducted over five years with 2,404 participants who also had or were at risk for osteoarthritis, found that weak quadriceps were associated with an increased risk of worsening knee pain in women but not in men. Researchers acknowledged that their longer study built on similar studies of shorter duration , and smaller group sizes, to support the link between leg muscle strength and knee pain. Their study suggests there may also be sex-specific differences in risk factors for worsening knee pain.
Read Also: Is Cycling Good For Arthritic Knees
How Is Back Pain Treated
Non-surgical treatment with limited rest and over the counter pain relievers is sufficient treatment for most patients like you. In some people, a supervised physical therapy program for ongoing mechanical pain may be recommended. Talk to your healthcare provider to see which treatment is right for you.
Evaluation Of Patients Presenting With Knee Pain: Part I History Physical Examination Radiographs And Laboratory Tests
WALTER L. CALMBACH, M.D., University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas
Am Fam Physician.;2003;Sep;1;68:907-912.
Family physicians frequently encounter patients with knee pain. Accurate diagnosis requires a knowledge of knee anatomy, common pain patterns in knee injuries, and features of frequently encountered causes of knee pain, as well as specific physical examination skills. The history should include characteristics of the patient’s pain, mechanical symptoms , joint effusion , and mechanism of injury. The physical examination should include careful inspection of the knee, palpation for point tenderness, assessment of joint effusion, range-of-motion testing, evaluation of ligaments for injury or laxity, and assessment of the menisci. Radiographs should be obtained in patients with isolated patellar tenderness or tenderness at the head of the fibula, inability to bear weight or flex the knee to 90 degrees, or age greater than 55 years.
Knee pain accounts for approximately one third of musculoskeletal problems seen in primary care settings. This complaint is most prevalent in physically active patients, with as many as 54 percent of athletes having some degree of knee pain each year.1 Knee pain can be a source of significant disability, restricting the ability to work or perform activities of daily living.
FIGURE 1.
Anatomy of the knee.
FIGURE 1.
Anatomy of the knee.
Also Check: Should I Go To Er For Knee Pain