What Does 18 Months Of Continued Inflammation Do To Your Knee When You Have A Meniscus Tear
Early in January 2019, the same research team published in the journal Arthritis & Rheumatology a study of 221 patients with knee osteoarthritis and meniscal tear. They examined these patients over a time period of 18 months.
- effusion-synovitis was persistently minimal in 45.3% and persistently extensive in 21.3% of the patients.
- The remaining 33.5% of the patients had minimal synovitis on one occasion and extensive synovitis on the other.
- Patients with extensive effusion-synovitis at baseline persistently extensive effusion-synovitis had a significantly increased risk of progression of cartilage damage depth. .
What Can Cause Knee Inflammation
Knee inflammation can be caused by a mild injury, a serious injury, arthritis, or bursitis. In addition, knee inflammation can be related to excess fluid in the knee joint, that can lead to decreased mobility and pain if it is not properly treated. Inflammation in both knees could indicate a systemic medical condition such as rheumatoid arthritis. Resting the knee joint until the inflammation subsides is typically recommended by most health care professionals.
After the pain subsides, gradual movement can be resumed. Also, icing the knee up to four times a day can dramatically reduce swelling and alleviate pain. The application of heat is generally not recommended for knee inflammation because it can promote swelling. Infrequently, knee inflammation can be caused by a joint or bone infection that will require antibiotic therapy and sometimes fluid drainage. In certain cases, the joint fluid will be drained and analyzed to test for blood and microbes.
Anti-inflammatory medications are also recommended to reduce pain and swelling of the knee, regardless of the cause. If arthritis is the cause of knee inflammation, injections of corticosteroids may be prescribed. Although effective for knee inflammation, corticosteroids can cause side effects such as irritation, weight gain, fluid retention, and swelling of the face.
Skip These Foods To Avoid Knee Inflammation
Want Less Pain? Avoid or Reduce These Repeat Offenders
Lets face it. A lot of us are brought to articles like this kicking and screaming we really dont WANT to know what foods we should be eliminating or reducing from our diets. Its just so.. so restricting! And deep down in our being, as Americans, we are all about freedom. Freedom in all things freedom to have lots of options when it comes to foods and drinks we enjoy.
Well, that is, until we start experiencing excruciating, chronic pain. Pain gets our attention, pain keeps us up at night, especially unrelenting pain that interferes with our ability to enjoy life.
Then, and usually only then, our outcry becomes, tell me, please TELL ME what I have to do to make this stopmake this pain go away! Yes, well do anything. Which usually leads to a search on the computer, which leads us to articles like this, what to do to relieve pain.
This is where Im going to say something unpopular. Pain is good and serves a purpose. Pain is trying to tell you that something is wrong or malfunctioning within your body. Yes, its a wake-up call, letting you know something needs to change, or else worse things may start happening. Pain can save you from more trouble later! And yes, its something we do not want.
You May Like: How To Whiten Knees And Elbows
Facts You Should Know About Knee Pain
- Knee pain is a common problem with many causes, from acute injuries to complications of medical conditions.
- Knee pain can be localized to a specific area of the knee or be diffuse throughout the knee.
- Knee pain is often accompanied by physical restriction.
- A thorough physical examination will usually establish the diagnosis of knee pain.
- The treatment of knee pain depends on the underlying cause.
- The prognosis of knee pain, even severe knee pain, is usually good although it might require surgery or other interventions.
What Are We Seeing In This Illustration
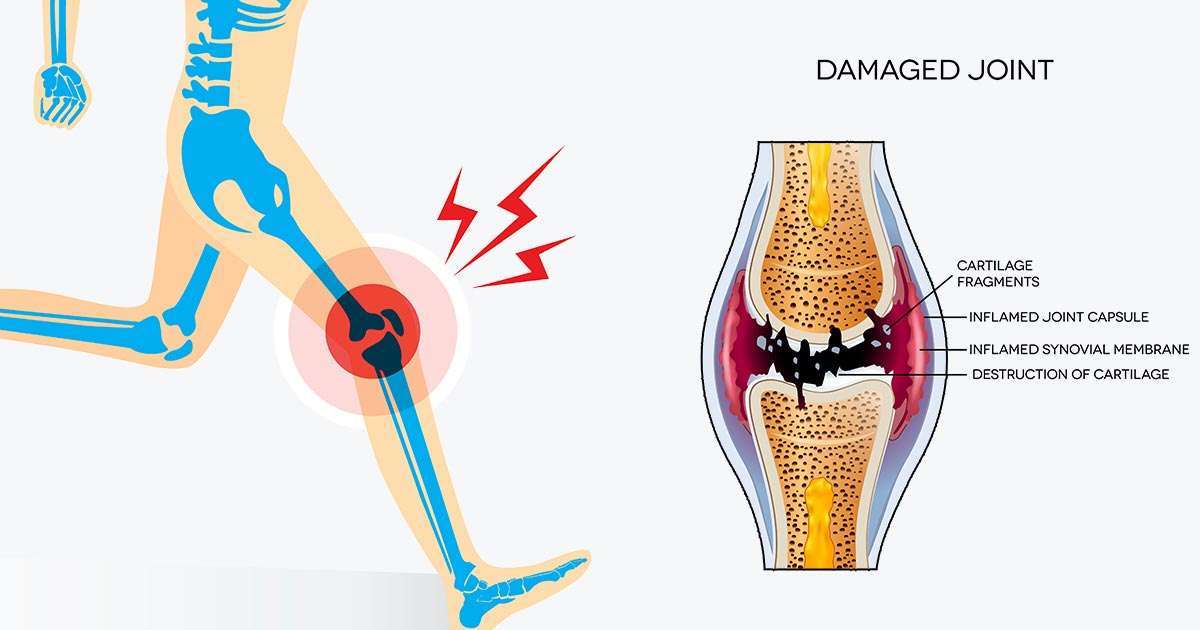
This illustration demonstrates the progression of knee osteoarthritis from a small tear or injury to degenerative joint disease. In this example a simple ligament injury, such as the medial collateral ligament depicted here) is not resolved, the resulting joint instability that this small injury can cause is the complete breakdown of the knee joint. As we are demonstrating in this article, a small unrepaired injury can spontaneously lead to osteoarthritis through swelling and inflammation.
Read Also: Inversion Table Knees
Risk Factors For A Swollen Knee
- Being overweight or obese your knees are weight-bearing so any excess weight puts more strain on them, which can damage your knee joint over time obesity also increases the risk of osteoarthritis, which is a common cause of a swollen knees
- Playing certain sports if you take part in sports that involve pivoting, rotating or twisting your knees, youre at greater risk of knee injuries, which cause swelling
- Your age your risk increases as you get older
What Is Behind Knee Swelling
A swollen area that can be felt behind the knee can be caused by several different conditions. A is a collection of synovial fluid that bulges out through the back of the knee joint and can be felt in the back of the knee as a or enlarged area. Knee injuries, , damage to the cartilage of the knee, and other problems are known to cause Bakers cysts.
Swelling behind the knee may be painful or may not produce any other symptoms. In some cases, you may notice tenderness, warmth, difficulties moving your knee joint, , or bleeding or . Injuries to the knee, including sprains can lead to diffuse swelling of the knee area.
Other possible causes of swelling behind the knee include abscesses tumors of the skin, soft tissue, or bones bleeding deep venous thrombosis or deformity of the joint after a of any of the bones of your knee joint.
Swelling behind the knee may be associated with injury and may be accompanied by more-serious injuries to the joint. Seek immediate medical care for serious symptoms, such as paralysis, loss of sensation, absent pulses in the feet, the inability to move the knee joint, severe bleeding, chest , difficulty breathing, or uncontrollable pain.
If your behind knee swelling is persistent or causes you concern, seek prompt medical care.
Read Also: Can You Rebuild Cartilage In Your Knee
B Tendonitis Of Knee Joint
- Inflammation of tendon is known as tendonitis.
- Tendonitis is caused by overuse of the muscles and tendon.
- Tendonitis follows injury or trauma of the tendon and muscles.
- Tendonitis of superior patellar tendon is known as Osgood-Schlatter Disease.
- Osgood-Schlatter tendonitis is caused by overuse, irritation or injury of the knee cap and patellar tendon.
- Inflammation of patellar tendon below patella is known as jumpers knee.
Synovial Fluid Accumulated In The Bursae Around The Knee Joint
Doctors in Taiwan publishing their study in the medical journal Experimental Gerontology examined the effects of Platelet Rich Plasma on synovial fluid volumes, protein concentrations, and severity of pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Here is their research summary:
- Patients with knee osteoarthritis are often complicated with joint soreness, swelling, weakness, and pain. These complaints are often caused by the excessive amount of synovial fluid accumulated in the bursae around the knee joint.
- They examined the effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma in treating patients with minor to moderate knee osteoarthritis combined with supra-patellar bursitis.
- Twenty-four elderly patients with minor to moderate knee osteoarthritis combined with supra-patellar bursitis were recruited.
- Aspiration of the synovial fluid was performed under ultrasound followed by subsequent PRP injections.
- Three monthly PRP injections were performed to the affected knees for a total of 3 months.
- Approximately after the 2nd PRP injection, significant decreases in synovial fluid total protein concentrations and volumes , and Lequesne index values were observed.
- Therefore, at least two monthly PRP injections may be beneficial for treating patients with minor to moderate knee osteoarthritis combined with supra-patellar bursitis.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Knee Walker
Acute Onset Without Injury
Rapid onset of swelling with no injury is abroad category wherein the accumulation of fluid is not due to an injury or a chronic condition, such as:
- Infection can result in joint fluid accumulation, often as a result of surgery, a knee wound, or systemic infection that spreads to the joint. Treatment can be a problem as the body has a tough time clearing infection from this space. Surgery may be required to fully clean out a .
- Gout and pseudogout involve a buildup of crystals in the knee fluid. With gout, the uric acid used to transport waste can accumulate and crystallize in various joints of the body, causing intense swelling and pain. With pseudogout, the culprit is calcium crystals.
Symptoms Of Knee Pain
The symptoms of knee problems can vary and will depend upon the cause and severity. However, knee pain is common.
Sudden pain in the knee can occur if you overuse it or injure it.
Instability and weakness in the knee, or the feeling that your knee is about to give way, is a common knee problem.
Other symptoms may include stiffness, popping sounds, locking of the joint and inability to straighten the knee, depending on the cause.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Limping After Knee Surgery
Bursitis Could Be To Blame
Often confused with arthritis, bursitis is another condition that can cause swollen knees. Bursitis is a reaction in which sacks of fluids, blood vessels, and nerve endings that cushion your jointscalled bursaebecome inflamed, explains Dr. Gladstone. Typically, bursitis occurs across the front of the knees as a result of excess pressure and friction on the joint over time.
Those little blood vessels bleed and the bursa produces excess fluid, which creates this giant, swollen pouchlike a bubble of fluid just below the skin, Dr. Gladstone says. These inflamed pouches, which can take on all sorts of shapes and sizes, can be incredibly painful to put pressure on.
Bursitis is most common in people who work a lot on their knees, like carpenters, plumbers, and tile-setters, says Dr. Gladstone. However, a good fall can cause bursitis, too.
The Doctor Should Consider The Problem Worse Than The Patient Is Suggesting
Getting back to the idea that the patient does not know how bad it is. In March 2019, doctors at Brigham and Womens Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston University School of Medicine, Weil Cornell Medicine, and the Mayo Clinic released their findings that basically said, patients, do not know how bad their inflammation is. When a patient reports to the doctor that they have problems with swelling, the doctor should consider the problem worse than the patient is suggesting.
Listen to the learning points of the research published in the journal Arthritis Care & Research.
- Synovitis is a prevalent feature in patients with knee osteoarthritis and meniscal tear and is associated with pain and cartilage damage.
- The researchers analyzed data from 276 patients. The patients self-reported their swelling episodes.
- Twenty-five percent of patients reported no swelling,
- 40% of patients reported had intermittent swelling,
- and 36% of patients reported had constant swelling.
When these patients had an MRI. The MRI found much more swelling than the patients reported. The conclusion of this study urged doctors to use caution against using patient-reported swelling as a proxy of inflammation manifesting as effusion-synovitis. In other words, the swelling is worse than the patients think it is. Simply, the knee is worse than they think it is.
Read Also: Cellulite Above Knees
Chronic Knee Swelling Is Developing And Worsening Knee Osteoarthritis
In this video Danielle R. Steilen-Matias, MMS, PA-C offers a brief summary of the constant degenerative process going on in your knee that shows itself every day to you as swelling.
Summary and learning points:
- Many patients tell us that their other health care providers and doctors dismiss or ignore their complaints of knee swelling. However, as research suggests, such as the research examined in this article, is that chronic knee swelling signifies the early development of osteoarthritis.
- The reason the knee is swelling relates to the strength or integrity or lack thereof of the soft tissue around the knee. So the knee swelling can be coming from knee ligament injury or instability. Your body, in an attempt to provide stability for the unstable knee, will swell the knee as a protective mechanism to provide stability to the need temporarily. It should be temporary. Your body is swelling the knee until healing of an injury can take place. The fluid fills the knee to also prevent excessive movement to accelerate healing. When the injury is healed the swelling goes away.
- If you do a job that is very physically demanding, you are on your feet all day, you climb ladders or steps, etc, that is a lot of strain to be putting on your knees and your body does the best it can to provide the swelling necessary to keep your knee together. The problem is chronic swelling is causing a rapid degeneration in the knee.
How Can I Manage Knee Pain
Treatment for knee pain depends on whats causing it and how uncomfortable it makes you.
- Mild knee injuries often improve with rest, ice and anti-inflammatory medications. Wearing a brace can stabilize your knee while it recovers.
- If arthritis is causing knee pain, your treatment may include medication and physical therapy.
- Doctors can usually repair tendon and ligament tears with minimally invasive surgery, if necessary.
- More serious knee pain may require knee replacement surgery.
No matter what caused your knee pain, physical therapy exercises can strengthen the muscles supporting your knee to help relieve discomfort.
Also Check: What Rebuilds Cartilage
Why Do We Experience Knee Pain
There are many causes of knee pain from injuries such as strains, sprains, torn ligaments and cartilage tears, to conditions such as osteoarthritis, tendonitis and bursitis .
Sports Injuries
Knee injuries are common among athletes, for example, who often experience tears in the knee ligaments, leading to sudden knee pain. Runners knee is a condition that can affect anyone who does a lot of knee bends, for example while running, walking, jumping or cycling. It is felt as pain around the kneecap and can be the result of overuse, injury, abnormalities of the leg bones or feet and weak muscles.
Other causes
Knee injuries can happen slowly because of osteoarthritis, for example. If you experience problems with your hips or feet that cause you to walk awkwardly, it can throw off the alignment of the knees leading to damage. If you have a knee injury, even if it is a minor one, it is more likely that you will have similar injuries in the future.
Locate the cause of your pain
Injuries to ligaments or tears to the menisci can cause pain in the side of the knees. Pain at the front of the knee can be due to bursitis, or cartilage problems. Osteoarthritis can lead to pain in the back of the knee.
What Causes Inflammation 7 Key Contributors
Inflammation is an important part of our immune response. It is the bodys way of healing itself after an injury, repairing damaged tissue, and defending itself against pathogens. In this way, inflammation is beneficial. However, inflammation can also be harmful to your health. Learning what causes inflammation can help you protect yourself.
There are two types of inflammation, acute and chronic. Acute inflammation is your bodys natural defense against damaged cells, viruses and other harmful invaders. It starts quickly and helps the body heal itself.
Chronic inflammation is systemic, low-grade inflammation that lasts for months or years. It is the common cause of many health issues. In fact, chronic inflammation has been linked to almost every major health condition and disease. This is partly due to an excessive production of free radicals that can be damaging to cells if not controlled.
Not just one thing causes inflammation in the body. An inflammatory diet, blood sugar imbalances, and leaky gut syndrome cause chronic inflammation. Sleep loss, chronic stress, environmental toxins, and chronic infections are additional factors that lead to chronic inflammation. It is critical to understand and address these factors to achieve optimal health.
Don’t Miss: Is Nano Knee Covered By Medicare
You May Have An Autoimmune Condition
In addition to rheumatoid arthritis, a number of other autoimmune conditionsin which the immune system attacks the body in various wayscan contribute to swelling and pain throughout the body, including in the knees.
Though less common, systemic autoimmune conditions, like lupus, may cause swelling, Dr. Gladstone says. Like Lyme, these conditions may explain inflammation in the knees when nothing else can. Along with pain and swelling, people with autoimmune conditions often experience chronic fatigue, muscle aches, and low fevers.
Stay updated on the latest science-backed health, fitness, and nutrition news by signing up for the Prevention.com newsletter here.
What Medical Conditions Cause Knee Pain
Medical conditions
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that can affect any joint in the body. It can cause severe pain and disability, as well as swelling.
Gout is a form of arthritis that is most commonly found in the big toe, though it can also affect the knee. Gout tends to flare up and is extremely painful during the acute episodes. When there is no flare-up, the knee can be pain free.
With , the knee joint can become infected this leads to pain, swelling, and fever. This condition requires antibiotics and drainage treatments as soon as possible.
Chronic use/overuse conditions
Patellar tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendons connecting the kneecap to the shinbone . Patellar tendinitis is a chronic condition often found in individuals repeating the same motion during exercise .
Patellofemoral pain syndrome is caused by degeneration or stress under the kneecap where it meets the thighbone . Patellofemoral pain syndrome occurs in runners and cyclists.
Osteoarthritis: a wearing down of cartilage of the joint due to use and age
Prepatellar bursitis: Inflammation to the bursa in front of the kneecap may cause anterior knee pain.
Other causes
Read Also: Do Compression Sleeves Help With Knee Pain