What Effects Does Fluid On The Knee Have
Since it results in knee inflammation of swelling, fluid on a knee joint may easily limit knee flexibility and also the functionality.
For instance, you may find it difficult to even bend or straighten your leg fully or completely. Indeed research has it that a swollen knee joint may only bend 15 to 25 degrees while your leg is at rest.
In addition to that, fluid on the knee might also leave you with severe pain. If left unattended, fluids that accumulate around your knee cap will cause pain. Eventually, you will be unable to settle due to the discomfort.
In the worst-case scenario, fluid retention around the knee will even prevent you from having a good night sleep.
Everything You Need To Know About Water On The Knee
What is it and how is it treated?
Your knee typically has an ounce of liquid inside of it. However, when you have an injury, arthritis, or another problem that irritates your knee, fluid accumulates to cushion and protect your joints.
Clinically, this is known as knee effusion, but most people call it water on the knee.
What Causes Fluid In The Knee
Several issues may cause fluid in knee joints. Some may be infectious. Determining what causes fluid in your knee will inform your treatment plan. Listed below are potential causes of fluid in knees.
- Injury or trauma: This happens when the knee joint receives a direct blow from an outside force. A trauma or injury to the knees tendons, bones, meniscus, bursae, ligaments, or articular cartilage can cause inflammation.
- Knee osteoarthritis: This common type of arthritis causes excessive knee fluid. Knee osteoarthritis is the degeneration of the cartilage around the knee joint due to aging and repetitive stress.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: This autoimmune disease causes the immune system to attack the bodys own cells and damage the delicate lining of the joints.
- Infection: Gonorrhea, tuberculosis, brucellosis, and lyme disease may all affect the knee.
- Gout: When levels of uric acid get too high, the acid will form into microscopic crystals and build up in the joints.
- Bursitis: An inflamed knee bursaa tiny, fluid-filled sac that separates knee bones from nearby tendons and musclescan fill with excess fluid.
- Tumor: Both benign and cancerous masses sometimes infiltrate the knee.
Read Also: Regrow Cartilage Naturally
What Causes A Baker’s Cyst
Knee damage caused by a sports-related injury or a blow to the knee can lead to a Baker’s cyst developing.
A Baker’s cyst can also sometimes occur if you have a health condition such as:
- osteoarthritis usually caused by age-related “wear and tear” of joints it particularly affects the knees, hips, hands and big toe
- inflammatory arthritis including rheumatoid arthritis, which is a less common type of arthritis and is caused by the immune system attacking the joints
- gout a type of arthritis that usually affects the big toe and is caused by a build-up of the waste product uric acid in the blood
Baker’s cysts are more common in women than men, probably because women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. They usually develop in people aged over 40, although can affect people of any age, including children.
When To See A Doctor
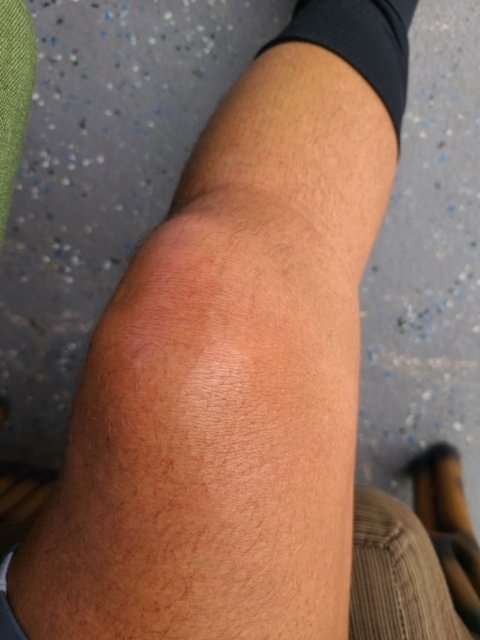
A swollen knee is a common occurrence. If mild, it can go away on its own after some good rest. However, if it persists for more than three days or gets severe, it could be a serious underlying condition. Medical attention, in this case, will be necessary. Also, see a doctor if your knee prevents you from doing things like bending, walking, or sitting.
Using heat worsens the condition? Therapeutic heat is not recommended in reducing inflammation or swelling.
Also Check: How To Stop Limping After Knee Surgery
How Serious Is A Baker’s Cyst
Baker’s cysts are fluid-filled sacs caused by excess knee-joint fluid.
This common condition occurs when excess fluid produced by the lining of the knee joint pushes through the back part of the joint capsule , forms a cyst and protrudes into the back area of the knee, known as the popliteal fossa. A Baker’s cyst may also be referred to as a “popliteal cyst.”
If you have osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, you may be familiar with this painful condition. Fortunately, there are treatment remedies available for Baker’s cysts, depending on the cause.
What Is Synovial Fluid Analysis Or Knee Aspiration Fluid Analysis
Synovial Fluid Analysis or Knee Aspiration Fluid Analysis When there is a suspicion of a particular condition, a diagnosis needs to be established. The synovial fluid, which is drained or aspirated from the joint, is examined and analyzed in the laboratory for its nature and presence of certain factors that aid in diagnosis of the condition. Specific findings help in determining the condition causing knee swelling.
The type of fluid and its detailed analysis guides in making a diagnosis of the condition. Some of the general findings include:
- Fracture or ligament injuries may show blood in the fluid.
- Meniscus injury or osteoarthritis may show straw colored or pale yellow fluid.
- Presence of crystals may mean gout or pseudogout.
- Turbid fluid or presence of pus may mean there is an infection.
- Gram staining and culture tests of the fluid can help in detecting the microorganism causing infection.
Read Also: Inversion Table Knees
S For Reducing Fluid In The Knee
Step 1 Stop any activity that may have caused the knee to swell, like running, jumping or twisting. Terminate action that makes your knee swell or hurt. You might have to avoid driving if it causes discomfort to run the brake or gas pedals.
Step 2 Rest with the leg elevated to reduce swelling naturally. This allows fluid to drain away, and reduces pressure on the joint. Dont walk or put weight on the knee unnecessarily until the pain and fluid have gone away.
Step 3 Use a cold pack to reduce pain and reduce fluid accumulation. You can use a wash cloth taken in cold water, or an industrial cold pack kept in the freezer. Do not use ice or freezer loads directly on the skin instead, wrap the frozen item in a towel and cover it around the knee. Apply this cold pack for 15 to 20 minutes every two to four hours as needed for pain.
Step 4 Wrap the leg with an elastic bandage. This must reduce build-up of fluid on the knee. Do not wrap the knee so securely that it cuts off circulation get rid of the bandage if numbness or tingling in the foot happens, or if the foot feels warm.
Step 5 Take a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory like ibuprofen or naproxen to decrease or prevent inflammation, MayoClinic.com recommends. Trademark name medications that include NSAIDs can include Advil, Motrin or Aleve. Take them with food to prevent stomach inflammation. A painkiller, such as acetaminophen or Tylenol, can likewise be used to relieve pain, but will not reduce the inflammation in the knee.
When To Contact A Doctor
Below are guidelines to help people decide if their knee swelling requires medical attention. If the person is still unsure whether to seek professional medical treatment, a phone call to a doctor or nurse can help determine whether an office visit is necessary.
A doctor should be contacted if:
- The knee is severely swollen or has a pronounced abnormality
- The knee cannot fully straighten or fully bend
- The knee is severely painful
- The person cannot bear weight on the knee, or feels as if the knee is going to “give out”
- The skin over the knee turns hot or red
- The person has a fever of 100.4° F or higher
- Knee swelling has been present for 3 days or longer
A doctor will examine the patient’s knee and ask the patient several questions. The physical examination and patient interview may provide enough information to make an accurate diagnosis. If more information is needed, the doctor may recommend medical imaging, such as an x-ray, or removing fluid from the knee using an in-office procedure called aspiration.
Leg swelling may be a cause for concernContact a doctor if the swelling affects the leg, not just the knee. Leg swelling can be a sign of a serious health problem.1,2
Seek immediate care if the leg swelling occurs suddenly with no known reason, particularly if it is accompanied by symptoms such as leg pain, chest pain, and/or problems breathing, as these may be signs of a life-threatening blood clot.
Recommended Reading: Is Nano Knee Covered By Medicare
What Are The Risks Of A Joint Aspiration
As with any surgical procedure, complications can happen. Some possiblecomplications may include:
-
Discomfort at the aspiration site
-
Bruising at the aspiration site
-
Swelling at the aspiration site
-
Infection at the aspiration site
There may be other risks depending on your specific medical condition. Besure to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider before theprocedure.
Joint Or Bursal Aspiration
When a patient has a swollen knee, a doctor may want to verify or rule out certain diagnoses by analyzing the accumulated fluid. To do this, the doctor will remove fluid from the affected knee joint capsule or bursa using a needle and syringe. When performed on a joint capsule, this process is called joint aspiration or arthrocentesis. When performed on a bursa, this process is called bursal aspiration.
The doctor will take note of the aspirated fluid’s color and viscosity and may send it to a lab for further analysis. Determining the contents of the fluid can lead to an accurate diagnosis. For example, uric acid crystals in the joint fluid indicate gout, and bacteria in the fluid indicate infection.
See The Joint Aspiration Procedure
Aspiration and examination of the fluid are important diagnostic steps because the underlying cause of knee swelling will determine the appropriate medical treatment.
Aspirated fluids are not always sent to a lab for analysis. If a diagnosis is already known, a physician may perform an aspiration to improve joint function and patient comfort.
See Diagnosis through Synovial Fluid Analysis
You May Like: How To Regrow Cartilage Naturally
When Should I See A Doctor
If you ask me, its always best to see a doctor or other reputable health and wellness professionals if youre experiencing anything thats out of the ordinary.
However, I also understand that hiring these wellness professionals is expensive. I dont even follow my own advice because of financial constraints if Im being honest.
So, below is a list of what research considers red flags. If you experience any of them, be sure to get your symptoms reviewed by medically trained folk you trust.
- Fever
- Losing pulse below your knee
- Partially or fully losing sensation below the knee
- Losing the ability to bear weight on your lef
To add, you should also seek your physicians help if neither of the home remedies and OTC meds works.
Common Causes Of Fluid In The Knee
There are various issues that may cause fluid in knees. Here are some of the most common:
Knee Trauma or Injury – Trauma occurs when the knee joint is impacted from an outside force, resulting in injury to the knee. The type of fluid to enter the knee from a traumatic injury is usually blood or excess joint fluid, though other types of fluid in the knee may be present. The most common forms of knee injury to cause fluid in knees are:
- Meniscus Tears
- Ligament Injuries, such as ACL Tears
- Overuse Injuries
Arthritis – The are several types of arthritis that may cause fluid on the knee. The most common types that cause excessive knee fluid are:
- Osteoarthritis – the natural wear and tear of the cartilage around the knee due to aging
- Rheumatoid arthritis – a chronic inflammation of the joints due to an autoimmune disease
- Gout – a type of arthritis where a patient’s nutritional intake may cause uric acid to build up in the joints
Infection or Inflammation – When areas of the knee are inflamed, this causes the knee to swell with fluid as the body combats the injury or bacteria in the area. A common form of inflammation that causes fluid in knees is bursitis. Bursa are cushioning sacs around the body which when inflamed may cause swelling or excess knee fluid.
Also Check: Can You Rebuild Cartilage In Your Knee
Fluid In Knee The Complete Injury Guide
by Jessica HeggDecember 06, 2017
Climbing stairs feels like hiking Mount Everest, and getting out of the car or going for a walk are more difficult each day. This is what having too much fluid in knee feels like, and it is something you should take seriously. In this guide, we will talk about the types, causes, and symptoms of fluid in knee. Well also discuss how to diagnose and treat the condition and ways to prevent re-injury.
Home Remedies For Water On The Knee Or Knee Effusion
In case of Water on the Knee or Knee Effusion the following steps are helpful for symptom relief:
- Rest: Take plenty of rest and avoid weightbearing activities until the swelling comes down.
- Ice and Elevation: Cold therapy is used for control of pain and inflammation. This can be done by applying ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at least three times a day. One needs to also raise the knee about the level of the heart which can be done using pillows.
- Pain Medication: Using pain medications like ibuprofen etc. can help with the pain and inflammation.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Knee Walker
Can Fluid On The Knee Get Worse
Yes. Its important to get a correct diagnosis of why your knee is swollen and follow proper treatment. A bacterial infection could spread and lead to permanent cartilage damage. If the problem is an internal tear, youre likely to have long-term, progressively more debilitating pain and loss of mobility if its not treated.
Symptoms Of Water On Knee
Synovial fluid can be used for diagnostic purposes. The exact symptoms of knee fluid effusion will depend on the medical cause of the accumulation. Identification of specific properties such as density, color, viscosity, and white blood cell count, can help a medical doctor determine the presence of injury or other medical conditions.
Knee fluid effusion can be the cause of high discomfort, both physical and psychological. Pain can vary from mild to severe, with some rare patients reporting no pain whatsoever. Frequently, placing any weight on the affected knee will cause significant discomfort and difficulty with mobility will be present. The proliferation of synovial fluid under the patella will usually cause considerable stiffness. This process can have a substantial and far-reaching impact on your daily life, and so it is crucial that we study ways in which to alleviate its effect.
You May Like: Lighten Knees Overnight
What Causes Knee Swelling
The knee has a joint capsule, which is like a sac that surrounds the whole joint. The capsule contains synovial fluid which nourishes and lubricates the joint, so that it can move smoothly . The joint capsule acts as container, keeping the fluid within the knee joint.
A swollen knee usually develops when excess fluid builds up inside the capsule and is caused by either:
a)Bleeding in the Joint: aka Haemarthrosis. This is normally caused by an injury and the knee swelling comes on rapidly . The swelling can be intense making the knee feel very tight.
b)An Accumulation of Synovial Fluid: aka knee joint effusion or water on the knee. This type of swollen knee tends to come on gradually and may come and go, varying in degrees of severity.
Knee swelling usually develops in one of four ways:
Symptoms Of A Swollen Knee
- The skin around the kneecap is puffy
- The knee is stiff and its difficult to bend or straighten it
- Its painful and bearing weight is difficult or impossible
- Redness or warmth
Swelling that does not go away, also known as chronic swelling, can lead to joint damage, cartilage degradation, or bone softening.
Recommended Reading: Can You Rebuild Cartilage In Your Knee
How Do I Get Ready For A Joint Aspiration
-
Your healthcare provider will explain the procedure to you and offer you the chance to ask any questions that you might have about the procedure.
-
You will be asked to sign a consent form that gives your permission to do the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if something is not clear.
-
Tell your healthcare provider if you are sensitive to or are allergic to any medicines, latex, tape, and anesthetic agents .
-
Tell your healthcare provider of all medicines and herbal supplements that you are taking.
-
Tell your healthcare provider if you have a history of bleeding disorders or if you are taking any anticoagulant medicines, aspirin, or other medicines that affect blood clotting. It may be necessary for you to stop these medicines before the procedure.
-
If you are pregnant or suspect that you are pregnant, you should notify your healthcare provider.
-
Generally, no prior preparation, such as fasting or sedation is needed.
-
Based on your medical condition, your healthcare provider may request other specific preparation.
What Is Knee Fluid
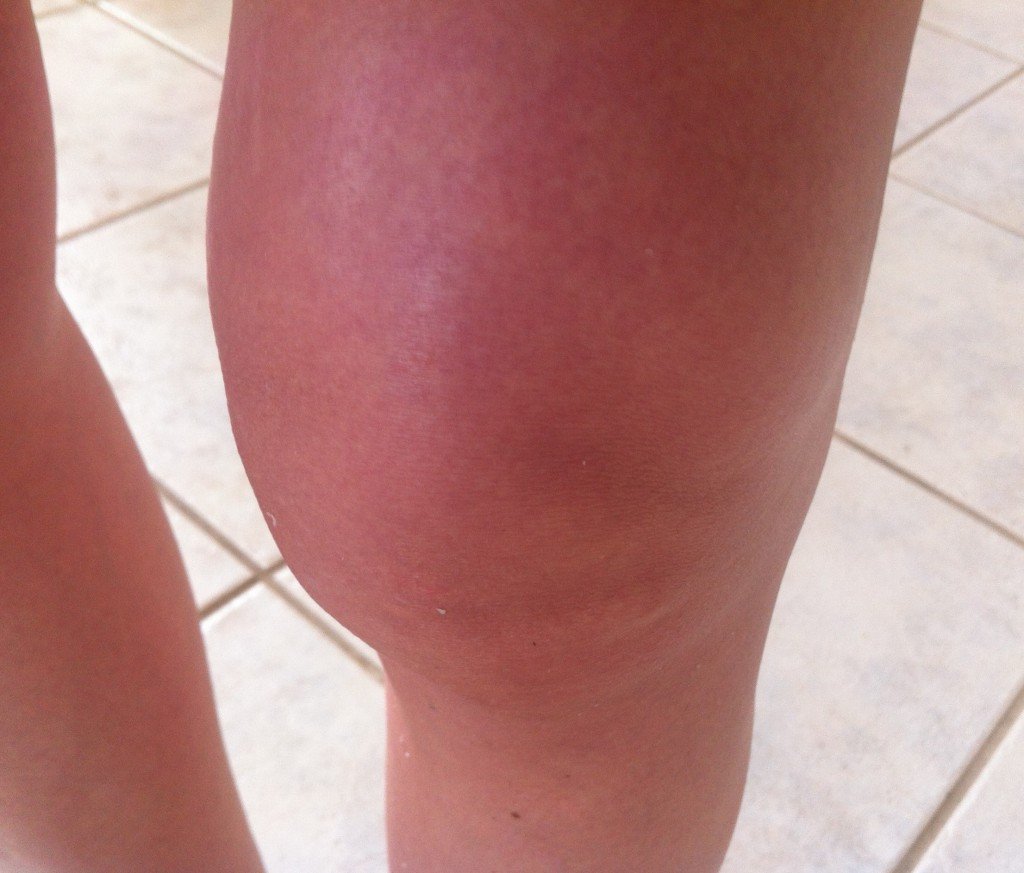
Knee fluid is a term that usually refers to the excess buildup of fluid in the knee joint that results from an injury or illness. Body joints contain small amounts of a thick, gel-like substance known as synovial fluid that helps to lubricate and protect joint tissue. In normal amounts, synovial fluid reduces friction between bones and helps to prevent erosion of joint cartilage. When a joint such as the knee is injured, the body tends to produce excessive synovial fluid in an effort to protect it. This often leads to additional problems, however, like swelling and a loss of mobility.
A buildup of knee fluid is often known as water on the knee, and can be caused by a direct injury, an infection, or an underlying disease. Trauma from a fall or a sports injury often results in intense pain, swelling, inflammation, and stiffness. In some cases, swelling and tenderness may be so severe that it is impossible to walk or even bend the knee. Conditions not related to injury, such as osteoarthritis, gout, and tumors, usually present very similar symptoms. A bacterial or viral infection can also lead to inflammation in the knee joint and prompt the body to produce excess knee fluid.
You May Like: Bioknee Cost