The Process Of Producing New Cartilage
The formation of cartilage starts even before a person is born. It starts as a primitive, loose and undifferentiated connective tissue that subsequently undergoes differentiation in a process called chondrogenesis.
The cells involved in cartilage formation are called chondrocytes.
To simplify the growth process of cartilage, there are two mechanisms involved:
1. Interstitial growth
- The chondrocytes undergo cell division and increase in number
- The matrix of the cartilage is synthesized
- The cartilage expands from within
2. Appositional growth
- Premature chondrocytes called chondroblasts differentiate
- The matrix of the cartilage is synthesized
- The girth of the cartilage expands
So, how is understanding this growth process important to you?
Previously, orthopedic specialist hypothesized that articular cartilage cannot regenerate because it has no blood supply.
When you recheck the processes outlined above, you can see how easy it is to manipulate the growth of cartilage.
For instance, you can:
Torn Knee Cartilage: Causes Treatment Recovery Period Symptoms
Knee cartilage is known to absorb shock, support the knee joint and prevent pain or injury to the knee joint. The knee cartilage is a C-shaped structure placed in between the knee joint. These shock absorber cartilage tissue are called menisci and the one covering at the ends of the bone is the articular cartilage.
Torn knee cartilage or damage to the knee cartilage is commonly seen in sports injuries. A tear in the knee cartilage can cause significant pain and discomfort in the knee joint.
When Will You Need Physiotherapy For A Meniscal Tear And Why
Small tears may heal by themselves in time, usually over about six weeks. You may be advised to see a physiotherapist or sports therapist to advise you on how to strengthen the supporting structures of your knee, such as the quadriceps and hamstring muscles. Some tears don’t heal but, even so, they may not cause long-term symptoms once the initial pain and swelling has settled, or cause only intermittent or mild symptoms. In these cases, no further treatment will be needed.
If you are having symptoms which interfere with your ability to work or which have been going on for more than 6-8 weeks, despite rehabilitation with a physiotherapist, a referral to an orthopaedic surgeon is advised. However, it is important to realise that if you have been diagnosed with a meniscal tear, even if it has shown up on an MRI scan, this doesn’t mean you will have to have surgery.
If you do need surgery to your knee, you will be advised to have physiotherapy afterwards. This is so as to keep the knee joint active and to strengthen the surrounding muscles to give support and strength to the knee.
Don’t Miss: What Procedures Require Antibiotics After Knee Replacement
What Causes A Meniscus Tear
Older people often get meniscus tears because their menisci become brittle and less flexible with age. But for teens, meniscus tears usually happen because of an injury often after twisting or turning the knee while it is bent and the foot is firmly planted. This might happen when:
- lifting heavy objects
- making sudden changes in direction or slowing or stopping quickly, as can happen in sports like soccer, baseball, basketball, tennis, and racquetball
- taking a direct hit to the knee while playing a contact sport, such as football, hockey, or rugby, where the knee may be forced to twist or turn awkwardly
- falling in a way that puts a lot of strain on the knee during a fall, as can happen in sports like skiing or snowboarding
Meniscus tears often happen along with other knee injuries such as ligament tears.
Varus Or Valgus Deformity
There are two disorders relating to an abnormal angle in the coronal plane at the level of the knee:
- Genu valgum is a valgus deformity in which the tibia is turned outward in relation to the femur, resulting in a knock-kneed appearance.
- Genu varum is a varus deformity in which the tibia is turned inward in relation to the femur, resulting in a bowlegged deformity.
The degree of varus or valgus deformity can be quantified by the hip-knee-ankle angle, which is an angle between the femoral mechanical axis and the center of the ankle joint. It is normally between 1.0° and 1.5° of varus in adults. Normal ranges are different in children.
| Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Before the advent of arthroscopy and arthroscopic surgery, patients having surgery for a torn ACL required at least nine months of rehabilitation, having initially spent several weeks in a full-length plaster cast. With current techniques, such patients may be walking without crutches in two weeks, and playing some sports in a few months.
In addition to developing new surgical procedures, ongoing research is looking into underlying problems which may increase the likelihood of an athlete suffering a severe knee injury. These findings may lead to effective preventive measures, especially in female athletes, who have been shown to be especially vulnerable to ACL tears from relatively minor trauma.
You May Like: How To Make Your Knees Stronger
Recovery From Cartilage Surgery
After most of these procedures you will need to be on crutches for a number of weeks. The amount of time on crutches will vary depending on this size of your cartilage defect, the location of the defect and the procedure you had. Physical therapy and range of motion activities are typically started soon after surgery. Cartilage nutrition and healing is actually improved by moving the knee.
Depending on the procedure you had it might take 8-12 months for a complete recovery. Cartilage transplants or allografts tend to heal faster. Many athletes and weekend warriors will be able to return to sports after a successful cartilage repair.
Traumatic cartilage defects are not very common injuries, but they can have significant consequences if they are untreated. Large defects can lead to osteoarthritis. Technology is improving in this area as our understanding of cartilage improves. Many cartilage defects are now amenable to one of the various techniques that we reviewed in this post.
Cartilage Injury And Cartilage Defects Of The Knee
The cartilage in your knee is a firm, rubbery, and very smooth surface. There is cartilage on the ends of the bones of your knee. Cartilage acts as a cushion to protect the bones from impact. Cartilage also allows your knee to glide and bend easily without pain. Injuries to the knee can cause also damage the cartilage. If the cartilage in your knee is severely damaged you can develop a hole or defect in the cartilage which could lead to a cartilage defect or hole in the cartilage. In active athletes of all ages, cartilage defects might require a repair to minimize the risk of developing arthritis. This post covers the most common procedures we used to replace or repair cartilage defects in the knee.
Have you been told that you are missing cartilage in your knee? The inner side of the knee or the medial femoral condyle is the most common area for a cartilage defect. Given its location, these are also the easiest cartilage defects to repair.
Read Also: How Do I Know When I Need Knee Replacement
How To Treat Loose Cartilage In Knee
The treatment of a piece of loose cartilage in the knee is dependent on how severe the tear is and how much pain and dysfunction it is causing you. Conservative treatment with physical therapy and NSAIDS is sometimes sufficient to alleviate the symptoms.
However, in many cases, more invasive procedures will be the answer. This may involve only a debridement of the knee, which is going inside the knee joint using an arthroscope and cleaning up any loose fragments.
MACI® Procedure and other available treatments at Dr. Burke Orthopedics
More severe cases of damaged or loose cartilage may require for that cartilage to be replaced. Dr. Burke performs a revolutionary new procedure called MACI . MACI is completed by harvesting of a collection of your own healthy cartilage taken from a non-weight bearing position. These cells are then placed onto a membrane of collagen which encourages expansion of these cells, and in turn, new healthy cartilage.
Dr. Burke will remove the area of damaged tissue on the affected knee. Next, the MACI implant will be surgically placed at the location of cartilage damage and absorbed back into your own tissue. MACI is a wonderful option that is not offered by all orthopedic surgeons.
Preventing Wear And Tear On The Knees
Knee wear and tear can be diagnosed by a medical examination. If you feel pain, discomfort or any other symptoms, donât hesitate to go to a professional who can carry out a thorough examination and give an accurate diagnosis. If the pain is unbearable or it is impossible to regenerate cartilage, you can always have a replacement prosthetic knee which can reduce your discomfort and improve your life.
Once youâve established a medical diagnosis, itâs time to launch a new lifestyle to help improve your kneeâs condition and prevent any further degeneration, whilst always following guidelines and treatment prescribed by your doctor. Try to avoid overexerting it which can accelerate the wear and tear of cartilage. For example, when it comes to walking, go on short walks and always take breaks.
Whatâs more, following a healthy and balanced diet to maintain an optimal weight is really important for protecting your knee. You should include foods rich in calcium, phosphorus and magnesium . Remember that your knees support your weight, so by avoiding being overweight, you can prevent progression of the disease. Additionally, you should increase the consumption of products such as cod, vegetables, eggs, gelatine or brewerâs yeast, as well as foods rich in vitamin C if you want to regenerate cartilage.
If you want to read similar articles to What are the Symptoms of a Worn Knee Cartilage, we recommend you visit our Diseases & secondary effects category.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Fluid On Your Knee
What Are The Types Of Knee Cartilage Damage
In general, there are two main types of knee cartilage damage involving the knee: the meniscus cartilage or the articular cartilage. There are different terms for these types of knee cartilage damage which include:
- Torn meniscus
- Chondral defect, lesion or damage
- OCD lesion
- Osteochondral defect, lesion or damage
- Cartilage loose body
Diagnosing Knee Cartilage Injuries
Three bones make up the knee joint:
- the bottom part of the thighbone, called the femur
- the top part of the shinbone, called the tibia
- the kneecap, called the patella.
The ends of these bones are lined with articular cartilage, a smooth protective material that absorbs weight and pressure placed on the joint and helps the bones to move easily while the body is in motion. Meniscus is another form of cartilage found in the knee. Two crescent-shaped discs, the menisci, provide cushioning between the bottom of the femur and the top of the tibia.
Cartilage does not have the capacity to heal without treatment. Unlike muscle and bone, the tissue has no direct blood supply to carry it oxygen and vital nutrients, which would help it recover from injury. Damage to the articular knee cartilage can cause pain, inflammation, a clicking noise and catching sensation, and reduced range of motion of the joint. Cartilage injuries that are wider than a centimeter have the potential to get bigger over time, which may lead to osteoarthritis, a degenerative condition of the joint.
Your doctor may refer to the injury as a full-thickness lesion, meaning a cartilage injury that reaches the underlying bone, or a partial-thickness lesion, which goes partway into the articular cartilage.
NYU Langone doctors conduct a comprehensive history and physical examination and use advanced imaging tests to diagnose knee cartilage injuries.
Don’t Miss: Will Losing Weight Help My Knee Pain
Benefits Of Knee Cartilage Replacement
Knee cartilage can cause daily pain and reduced mobility when it has been severely injured or worn down to the point where it no longer provides smooth bone movement within the joint or cushioning between the bones. It is not a condition that will improve on its own.
Repairing or replacing damaged knee cartilage can:
- provide pain relief
What Is A Knee Cartilage Loose Body
After a knee injury, or prolonged wear-and-tear, the knee cartilage can become frayed or damaged. On occasion, a fragment of the articular cartilage can break away. A knee cartilage loose body is a fragment of tissue or bone that freely floats inside the knee joint space. There can be one or several loose bodies within the joint, suspended in the fluid of the knee, called the synovial fluid. Loose bodies can impact the way the knee moves and can cause symptoms such as:
- Locking of the knee joint, making it difficult to bend or straighten the knee
- Knee catching
- Crepitus a crunching or popping sound within the knee
- Trouble walking
- Feeling that the knee will give way or is unable to support full weight
- Inability to participate in high impact activities and sports
Read Also: How To Exercise With Arthritic Knees
Overall Fitness And Knee Injury
Physical fitness is related integrally to the development of knee problems. The same activity such as climbing stairs may cause pain from patellofemoral compression for someone who is physically unfit, but not for someone else . Obesity is another major contributor to knee pain. For instance, a 30-year-old woman who weighed 120 lb at age 18 years, before her three pregnancies, and now weighs 285 lb, had added 660 lb of force across her patellofemoral joint with each step.
Can I Treat A Knee Cartilage Injury Myself
For the first 48-72 hours think of:
- Paying the PRICE – Protect, Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation and
- Do no HARM – no Heat, Alcohol, Running or Massage.
Paying the PRICE:
Avoid HARM for 72 hours after injury. That is, avoid:
- Heat – for example, hot baths, saunas, heat packs. Heat has the opposite effect to ice on the blood flow. That is, it encourages blood flow. So, heat should be avoided when inflammation is developing. However, after about 72 hours, no further inflammation is likely to develop and heat may then be soothing.
- Alcoholic drinks, which can increase bleeding and swelling and decrease healing.
- Running or any other form of exercise which may cause further damage.
- Massage, which may increase bleeding and swelling. However, as with heat, after about 72 hours, gentle massage may be soothing.
You May Like: How To Tell If Your Knee Is Sprained
Diagnosis Of Torn Knee Cartilage
Diagnosis of torn knee cartilage is based on the history of the person, background and the activities that were being performed in recent past. In case of injuries, X-rays may be taken to rule out any trauma to the bone or any other abnormality, but these do not help to identify a torn knee cartilage. MRI is required to detect bone and soft tissue injuries like cartilage or meniscal tears.
Book An Appointment With Capital Orthopaedics
If you are recently injured or concerned about ongoing pain, our team of specialists has the expertise to evaluate your discomfort and develop a plan to get you back to being active quickly and with the best long-term outcomes.
To book an appointment in one of our central London locations, contact us here.
Donât Miss: Bleach Dark Knees
Don’t Miss: How To Describe Knee Pain To Your Doctor
Symptoms Of Torn Knee Cartilage
How do you know if you’ve sustained a cartilage tear?
You may experience acute symptoms like pain and buckling of the knee right after an injury, but not necessarily sometimes, cartilage damage can happen gradually over time, resulting in intermittent symptoms. Some people with meniscus tears have no pain and don’t even realize they have an injury.
However, even if you’re pain-free, you will likely note one or more of the following symptoms:
- pain or tenderness in the knee
- buckling or locking of the knee joint
- crunching or popping noises when walking
- dull pain under the kneecap when exercising
- difficulty bearing weight
- inability to bend or straighten the knee
- swelling or “water on the knee,” a buildup of fluid inside the knee joint
- tightness of the knee joint
How Is A Meniscal Tear Diagnosed
- How you injured your knee and the symptoms you are getting may be enough to tell a doctor that you have a meniscal tear.
- A doctor or therapist will need to examine your knee. Certain features of the examination may point towards a meniscal tear. They will also want to examine the rest of your leg, including your hip, to check for other injuries or other causes of your symptoms.
- Cartilage doesn’t show up well on an X-ray so an X-ray of your knee is not usually necessary. The one time you might need to have an X-ray would be if your doctor is concerned that you might have damaged your bone when you injured your knee.
- The diagnosis of a meniscal tear can be confirmed by a magnetic resonance imaging scan.
- Computerised tomography scanning is not as good as an MRI for diagnosing a meniscal tear.
Read Also: How To Fix Knee Joint Pain
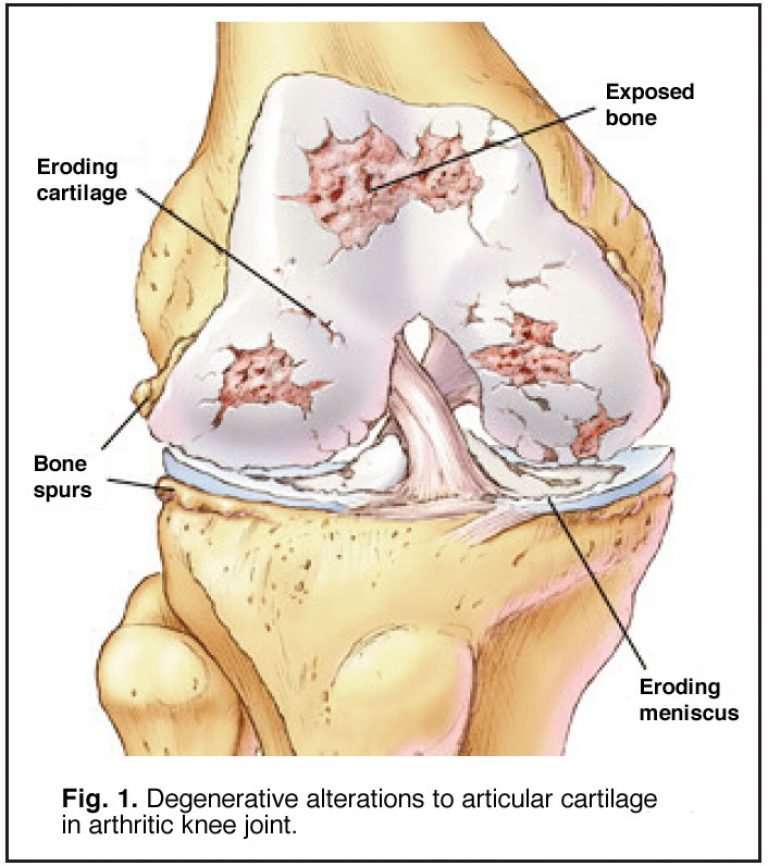
What Is Cartilage Damage
The slippery articular cartilage that coats your bones helps with smooth movement.
If its torn or worn, it can leave the rough bone surfaces exposed resulting in friction in the joint. Damaged cartilage can potentially lead to knee arthritis, with long-term effects on your knee function.
Damaged cartilage almost always has some sort of effect on your knees whether its pain, swelling or stiffness.
Initial Treatment And Self Care
If you’ve injured your joint and your symptoms are not too severe for example, you’re still able to put weight on and move the joint you can often look after yourself using PRICE therapy.
PRICE stands for:
- Protection protect the affected area from further injury by using a support, such as a knee brace
- Rest rest the affected joint as much as possible during the first 2 or 3 days , then try gradually returning to light activity over the next few days and weeks
- Ice apply an ice pack or a bag of frozen vegetables wrapped in a towel to the injured area for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours during the first 2 or 3 days
- Compression compress or bandage the injured area to limit any swelling and movement that could damage it further you can use a simple elastic bandage or an elasticated tubular bandage available from a pharmacy
- Elevation keep the injured area raised and supported on a pillow whenever you can to help reduce swelling
If your joint is painful, take ordinary painkillers such as paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen.
Visit your GP if your symptoms have not started to improve after a few days of PRICE therapy.
Read Also: Where Is The Acl In The Knee