How Is Osteoarthritis Of The Knee Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will do a physical examination and ask about your medical history. The physical examination might include checks to see:
- If your knee joint area is red or sore.
- If theres a sign you injured your knee.
- How much you can move your knee. This is called your range of motion.
- If your knee feels “loose,” which can mean your joint isnt stable.
- The way you walk, in case you have gait problems that affect your knee. A gait problem is when you dont walk as you would normally.
Special Devices And Footwear
Walking sticks can help to reduce the load on your knees and reduce pain when moving about. Other ways to improve symptoms of osteoarthritis include taping the joint, wearing braces, or using shoe insoles that improve your body alignment when standing and walking. Check with your physiotherapist for advice about using aids or supports.
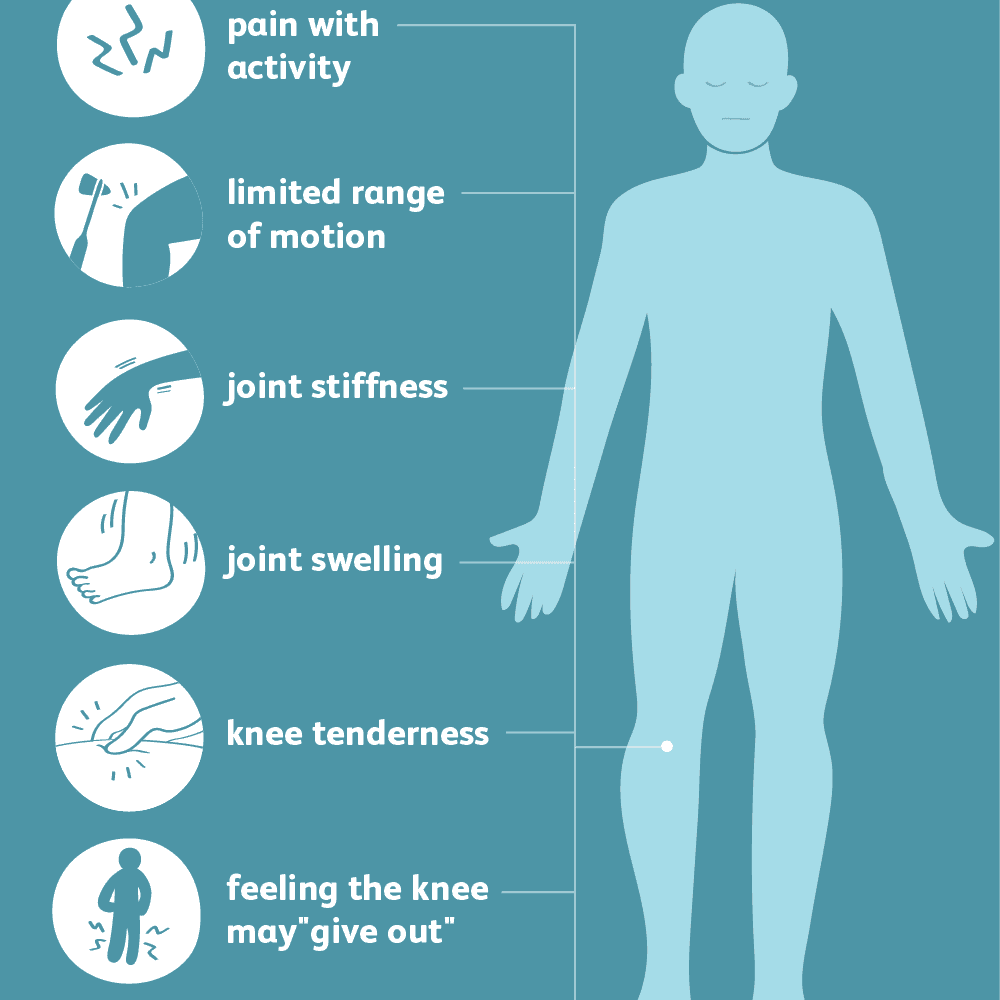
Limited Range Of Motion
People with knee osteoarthritis might not be able to bend or straighten their knees like they used to. This could be due to pain, stiffness, muscle weakness, and/or other factors.
This can look like not being able to squat anymore or sit on your heels while kneeling. And if this restriction is painless, you may be tempted to overlook it. But it will likely get worse with time.
If that sounds like you, please go to a physical therapist in your area. He/she will help you figure out whats going on and give you strategies to improve mobility.
Read Also: What Is Pvns In The Knee
Mild To Severe Knee Inflammation
The -itis in osteoarthritis means inflammation. However, some people have visible swelling around their knees, while others dont.
There are several ways to reduce swelling at home. Now, if you have inflammation on more than one joint at the same time, please visit your doctor to check if you have rheumatoid arthritis .
RA is one of the most common musculoskeletal and skin diseases in the world.
But while knee OA is caused by wear and tear, RA is a type of knee arthritis thats caused by problems with the immune system. This means their treatments are entirely different.
So, if you have a family history of RA or have other risk factors, pay a visit to your doctor. He/she will request blood tests and other exams to make an accurate diagnosis.
Related: What doctor is best for knee pain?
Can You Have Knee Osteoarthritis Without Symptoms
Yes!
In fact, research suggests that around 40-50% of people with knee osteoarthritis will have symptoms, while the other half wont. The percentage of symptomatic patients increases for people with a previous knee injury or a high BMI.
In a real-world scenario, this means that your X-rays or MRI might have shown damaged cartilage. But if you arent experiencing any of the symptoms, the only thing to do is manage any risk factors to delay its progression.
You May Like: My Knee Pops And Hurts
Diagnosing Osteoarthritis Of The Knee
Osteoarthritis of the knee is a progressive condition that causes aching pain, stiffness, and loss of mobility in the knee joint. The knee is the largest joint in the body, and is one of the strongest. Its composed of three bones: the bottom part of the thighbone, called the femur the top part of the shinbone, called the tibia and a large, round bone that covers and protects the joint, called the patella or kneecap. The ends of these bones are lined in a protective material called cartilage, a smooth material that acts like a shock absorber and helps the bones to move easily while the body is in motion.
The cause of knee pain and other osteoarthritis symptoms is often bone-on-bone friction, which happens when the cartilage has begun to erode. Over time, cartilage may wear away completely, leaving the joint vulnerable to permanent damage.
New research suggests that not everyone experiences osteoarthritis symptoms as a result of cartilage wear and tear. Knee pain results in many people from an inflammation in the membrane lining the knee joint, called the synovium. In a healthy knee, the synovium secretes a gel-like substance called synovial fluid that lubricates the joint and helps absorb stress during movement. Pain and stiffness related to osteoarthritis have been linked to a thinning of synovial fluid, which further contributes to joint degeneration.
How Common Is Osteoarthritis
Women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis than men. Australian studies show that about 1 in 10 women report having the condition, compared with about 1 in 16 men.
Osteoarthritis can develop at any age, but it is more common in people aged over 40 years or in those who have previously injured a joint. One in 5 Australians over the age of 45, and one in 3 over 75 years have osteoarthritis.
Also Check: How Do I Treat Knee Pain
Dont: Engage In Repetitive High
Joint-pounding exercises such as running and tennis can tax your already damaged knees, Dr. Pisetsky says. Its a vicious cycle because this type of exercise causes more pain. You stop using your muscle because it hurts, you lose strength, and then your alignment isnt good either, he says. This can also result in needing joint replacement surgery. Listen to your body, he says. If it is painful, dont do it.
Why Does It Become More Difficult To Perform Certain Movements
Osteoarthritis is disabling in the realization of some of our daily movements, sometimes the most basic ones. When pain and inflammation are too strong, the nervous system protects the body by slowing down certain joint movements. It is thanks to this brilliant unconscious reflex that our body is protected from intense pain and injury. But it also leads to the inhibition of certain movements.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis In Knees
Set Reasonable Expectations For Recovery
People often expect the total knee replacement to be a total cure which it is not. It takes work, time, and effort to make the knee feel good again, and even then, it wont be the same knee you had when you were 20 years old, Dr. Chen reminds her patients.
Full recovery can take as much as a year, but the knee will feel better as you begin to heal from surgery.
Patients often ask when they can return to driving. That depends on which knee received the operation. For the right knee, individuals can usually drive after three-to-four weeks for the left knee, you could drive as soon as two weeks. The important factor is the strength of the quadriceps, which affects your ability to move from brake to gas safely. I tell patients to go to an empty parking lot to practice, and when they feel comfortable enough to hit the brake if they needed to, theyre ready to drive, says Dr. Chen.
Another common question is when patients can return to work. Because it depends largely on the amount of physical labor in a persons job, at-home recovery can range from two weeks to three months.
Dr. Chen reminds patients that recovery takes time: The key is expectations. I always tell patients to remember their pain before surgery, because afterwards it normally feels a lot better than that.
Antonia F. Chen, MD, MBA, is an orthopaedic surgeon in the Department of Orthopaedics at Brigham and Womens Hospital.
Knee Osteoarthritis High Risk Groups
Generally, patients with knee osteoarthritis tend to be aged 50 and above, with females more prone to the condition than males due to hormonal as well as musculoskeletal factors. Additionally, there is currently an emerging trend of patients experiencing knee osteoarthritis at younger ages than ever, which places them at risk of developing early onset osteoarthritis. The following groups fall into this category: patients who have previously suffered a knee injury patients who have an unhealthy diet that has resulted in them becoming overweight or obese, thus placing greater strain on the knee joint or patients with underlying conditions that cause arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, as these disorders gradually wear away at the joint surface until the knee becomes severely swollen and eventually seizes up altogether.
Read Also: Which Knee Replacement Is Best
What Is Osteoarthritis Of The Knee
Osteoarthritis of the knee happens when the cartilage in your knee joint breaks down, enabling the bones to rub together. The friction makes your knees hurt, become stiff and sometimes swell. While osteoarthritis in the knee cant be cured, there are many treatments to slow its progress and ease your symptoms. Surgery is an option for more severe forms of osteoarthritis.
How Do I Determine If I Need A Knee Replacement
If youre considering knee replacement surgery, talk to an orthopedic surgeon. Orthopedic surgeons specialize in operations to fix joints and muscles.
Your orthopedic surgeon will:
- Ask about your symptoms, including how severe they are and how long youve had them. The surgeon may also ask whether anything makes symptoms better or worse, or whether symptoms interfere with your daily life.
- Take your medical history to learn about your overall health.
- Examine you to check knee motion, strength and stability.
- Order X-rays of your knee. The images can help the surgeon understand how much damage is in your knee. Advanced imaging is rarely helpful in the arthritic knee.
The orthopedic surgeon will then make a recommendation for surgery or another treatment option.
You May Like: How To Treat Bone Bruise Knee
How Does Osteoarthritis In The Knee Affect My Body
Knee pain is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis in the knee, making it painful for you to jog, run, climb stairs or kneel. It can also make your knees feel stiff or swollen. Over time, osteoarthritis of the knee can change the shape of your knee joint, making your joint feel unstable or wobbly.
Dont: Be Afraid To Use Assistive Devices If You Have Knee Osteoarthritis
Canes and knee braces can play a role in decreasing knee osteoarthritis pain and improving function, Pisetsky says. There can be a period of time when knee pain is disabling but its not the right time for surgery, so thats when assistive devices can make a difference, he explains. An occupational therapist can work with you to choose appropriate assistive devices.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Tall People’s Knees Hurt
Support & Protection For Knee Oa
- The latest DonJoy OA Knee Brace for patients with mild to moderate OA knee pain.Do I Order Left or Right?
Order according to the affected compartment of the knee. For example: If you have OA in the medial compartment of your left knee, order the Medial Left / Lateral Right option. If you have OA in the medial compartment of your right knee, order the Medial Right / Lateral Left option.
What Causes Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis does not have a specific, single cause. However, experts note that certain things put you more at risk of developing osteoarthritis in some joints, including:
- being overweight
- having a previous injury to the joint, such as a dislocation or a fracture
- frequent kneeling, climbing and squatting
- jobs that involve heavy lifting
- repetitive use of the hands
You may also be more likely to develop the condition if your family has a history of osteoarthritis.
You May Like: Which Knee Brace To Buy
Cracking Or Popping Sounds
When you bend or straighten your knee, you may feel a grinding sensation or hear cracking or popping sounds. Doctors call this crepitus.
These symptoms can occur when youve lost some of the cartilage that helps with smooth range of motion. Both OA and RA can result in cartilage damage.
When cartilage is damaged, rough surfaces and bone spurs develop. As you move your joints, these irregular areas rub against each other.
Read Also: How Do You Know If You Hurt Your Knee Badly
Who Is Most At Risk
Osteoarthritis of the knee is common in people over 50 years of age, in particular in women. It can affect either one knee or both knees .
Osteoarthritis occurs in the inside of the knee or the outside aspect of the knee. However, it occurs more commonly on the inner aspect of the knee.
Knee osteoarthritis is common in individuals who play intense physical sports, such as football. The previous injury to the knee is a strong indicator of the development of osteoarthritis in the future. Symptoms develop slowly over a number of years.
Recommended Reading: Is Heat Or Ice Better For Arthritis Knee Pain
Causes And Risk Factors
Primary osteoarthritis of the knee is mostly due to wear and tear of the cartilage in the knee joint due to age and stress. It is one of the most common types of arthrosis, since the knees carry the body weight every day and absorb the stress of walking upright .
Correspondingly, there are incorrect and excessive loads, for example through intensive sport, standing or heavy physical work, favorable risk factors and, in particular, overweight .
Congenital or acquired joint malpositions such as knock knees and bowlegs also promote gonarthrosis.
Inflammatory diseases or poorly healed injuries in the leg area are risk factors for secondary gonarthrosis.
You can find out more about the causes of arthrosis in the article Arthrosis .
What Are The Advantages Of Partial Knee Replacement Over Total Knee Replacement
Compared to total knee replacement, partial knee replacement better preserves range of motion and knee function because it preserves healthy tissue and bone in the knee. For these reasons, patients tend to be more satisfied with partial knee replacement compared with total knee replacement. They are still candidates for total knee replacement should they ever need it in the future.
There is also less blood loss during surgery, and knee motion recovers faster with partial knee replacement.
You May Like: Does Fluid On The Knee Cause Pain
What Is A Knee Osteotomy
A knee osteotomy is an operation that surgeons use to treat the pain and instability that can occur when there is damage or arthritis in part of the knee joint. Doctors may recommend an osteotomy instead of a knee replacement when only one area of the knee has damage.
During this knee surgery, a surgeon repositions the bones in the tibia or femur to realign the knee. This new positioning shifts your body weight from the damaged part of your knee to a healthy part.
A knee osteotomy can help slow deterioration of cartilage in the knee and may delay your need for knee replacement surgery for many years. Osteotomy of the knee has been used for decades to improve pain and function.
Is Surgery Used To Treat Knee Osteoarthritis
If your doctor wants to treat the osteoarthritis in the knee with surgery, the options are arthroscopy, osteotomy, and arthroplasty.
- Arthroscopy uses a small telescope and other small instruments. The surgery is performed through small incisions. The surgeon uses the arthroscope to see into the joint space. Once there, the surgeon can remove damaged cartilage or loose particles, clean the bone surface, and repair other types of tissue if those damages are discovered. The procedure is often used on younger patients in order to delay more serious surgery.
- An osteotomy is a procedure that aims to make the knee alignment better by changing the shape of the bones. This type of surgery may be recommended if you have damage primarily in one area of the knee. It might also be recommended if you have broken your knee and it has not healed well. An osteotomy is not permanent, and further surgery may be necessary later on.
- Joint replacement surgery, or arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which joints are replaced with artificial parts made from metals or plastic. The replacement could involve one side of the knee or the entire knee. Joint replacement surgery is usually reserved for people over age 50 with severe osteoarthritis. The surgery may need to be repeated later if the prosthetic joint wears out after several years. But with today’s modern advancements, most new joints will last over 20 years. The surgery has risks, but the results are generally very good.
Read Also: How To Get Your Knee To Stop Hurting
What Are The Risks
- An infection at the surgical site is possible. Blood clots are a risk as are injuries to a blood vessel or a nerve. These complications are quite rare.
- You may experience some knee joint stiffness.
- Late complications may include infection and a failure or loosening of the prosthesis, as well as continued pain.
Osteoarthritis Of The Knee: Pain Management And Treatment
The knee, the largest joint in the body, bears most of our weight. Due to the natural wear-and-tear that comes with constant lifting and moving, the knee is frequently affected by arthritis. Among the many forms of arthritis, osteoarthritis most commonly impacts the knee.
OA is a degenerative condition that involves the loss of the smooth cartilage surfaces on the end of bones. This can lead to bone-on-bone rubbing in the knee, which causes pain.
OA usually occurs with aging. For many years, knee replacement candidates were typically in their sixties or seventies, but increased sports participation at a younger age has contributed to rising numbers of knee problems earlier in life. As materials used in knee implants improve, knee replacement surgery is being used to treat OA in younger patients.
Read Also: Knee Pain On The Inside
Gradual Knee Joint Pain
The pain from knee osteoarthritis tends to have a gradual onset, rather than happening from one day to the next.
It often gets worse with movement like climbing stairs, squatting, or walking. Yet, it can also be present at rest, mostly while sitting or standing for long periods.
As the cartilage deterioration advances, you could have intense pain at night, too. However, the type of pain will vary from person to person.
It could feel like a dull, intermittent pain around your whole knee joint throughout the day. Or a sharp, severe pain that appears in specific movements.
Learn more:Reasons why knee osteoarthritis pain worsens at night.