Less Common Causes Of Knee Pain
Less-common causes of significant knee pain include conditions and injuries. Injuries include:
- Dislocated kneecap: Causes are sharp blows to the knee or twisting. Severe pain in the front of the knee plus buckling, slipping, or catching during movement.
- Kneecap fracture: Causes are a direct blow or falling onto the knee. Pain, difficulty straightening the leg, bruising, and swelling can occur. Sometimes there’s visible deformity.
Conditions include:
- Plica syndrome: Irritation of the synovium . Pain is in the middle and front of the knee. Worsens with inactivity or squatting, running, or kneeling. The knee may pop when bent.
- Osgood-Schlatter disease: Strikes after growth spurts in kids between 9 and 14. Pain is in the front of the knee. It improves with rest and worsens with activities like running and jumping.
- Osteochondritis dissecans: In children, lack of blood supply weakens the bone and cartilage. The knee may separate from the underlying bone. Causes pain with activity.
- Knee joint infection: Causes significant pain, swelling, warmth, painful movements, and fever. It may result from a bacterial infection in the bloodstream.
- Bone tumor: Very rarely the source of knee pain. Symptoms include fever, unintentional weight loss, and pain that’s worse at night.
Superior Tibiofibular Joint Sprain
The tibiofibular joint is the point in the knee where the tops of the shin bones join. Dislocation of this joint is likely to have been caused by an impact or fall onto the knee, particularly when it is in a fully bent position. Symptoms include:
- Pain and swelling on the outer surface of your shin.
- In addition, the top of the fibula bone may appear more prominent than normal on the outside of your knee.
- More on Tibiofibular joint sprain
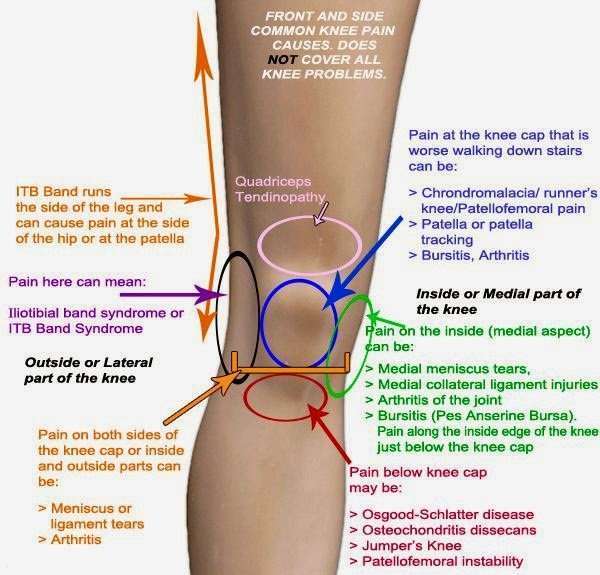
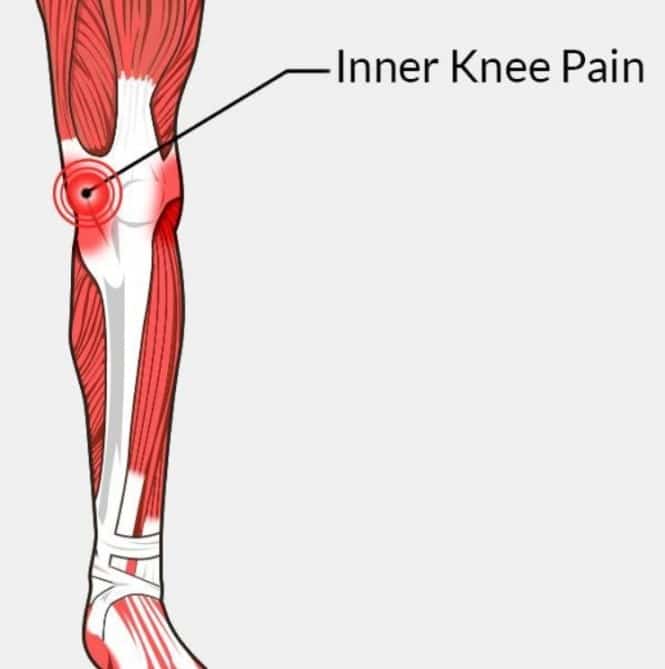
Pain On The Inner Side Of The Knee
The most common cause of medial knee pain or pain on the inside part of the knee is a medial meniscal tear. The tear can be acute or degenerative but either way can cause pain and limitation of activities. Occasionally a torn meniscus can flip in and out of the joint and cause pain as well as locking of the knee. The pain is typically worse with activity and fairly sharp in nature. Many patients complain that they cannot sleep with their knees together or find it uncomfortable to sit in a movie unless they can stretch their knee out in an aisle seat. The knee is often stiff after driving or sitting for long periods and particularly bad with twisting activities.
It is important to know whether the medial knee pain is dull or sharp, continuous or intermittent and its severity and location. Did it come on slowly over months or was it after and acute injury?
Medial compartment arthritis can cause pain on the inner side of the knee. This is usually more of an ache than a sharp catching pain and is present when you walk on the leg. As the arthritis worsens the pain can become continuous and interfere with sleep. Eventually even walking short distances becomes difficult.
Even significant tears rarely need a MCL repair and most can be adequately treated with crutches and a hinged knee brace.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Painful Knee Caps
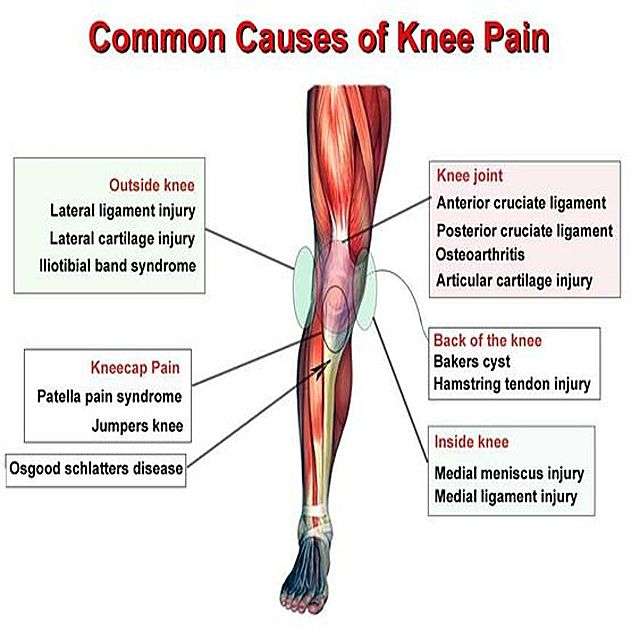
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries
The anterior cruciate ligament is a band of tissue that runs through the front of the knee joint, connecting the bones and helping keep the knee joint stable.
ACL strains often happen due to sudden stops or changes in direction. Similarly to meniscus tears, a strain in the ACL may cause a popping sound, followed by pain and swelling.
A torn ACL is a well-known, serious injury, often side-lining an athlete for a long time. Torn ACLs usually require reconstructive surgery.
How Can I Prevent Knee Pain
Although you canât prevent all injuries, you can take these steps to make them less likely.
- Stop exercising if you feel pain in your knee.
- If you want to make your workout more intense, always do it gradually.
- Stretch your legs before and after physical activity.
- Use kneepads to prevent bursitis, especially if you have to kneel a lot.
- Wear shoes that fit well and offer enough support.
- Keep your thigh muscles strong with regular stretching and strengthening.
- If youâre overweight, work to drop some pounds so thereâs less stress on all of your joints, including your knees.
Recommended Reading: How To Replace Cartilage In Knee
Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain Or Strain
Causes & Symptoms
The Lateral Collateral Ligament connects the outside of your thigh bone to your fibula, a narrow long bone outside of your lower leg. The injury occurs when a large force presses on the inside of the knee, pushing the joint laterally outwards . The LCL resists against this pressure, however, if it is significant enough the fibers of the ligament begin to tear away resulting in pain and instability.
Treatment
An LCL strain can be suspected given pain on the outside of the knee after receiving a traumatic contact force to the inside of the knee. Your physician may order diagnostic imaging to assess the full extent of the damage. In cases of a complete tear, surgery may be required. Generally, symptoms resolve with rest and activity modification. However, depending on the severity, recovery times may vary A grade 1 tear taking 2-3 weeks, and a grade 3 tear taking 3-6 months.
- Grade I: The LCL has been overstretched, while there is no major damage, its function will be compromised until it has healed.
- Grade II: The LCL has been partially torn and may require surgery to repair depending on the extent of the damage.
- Grade III: A complete tear of the LCL requiring surgery to reconstruct the ligament.
Osteoarthritis Of The Knee
The most common type of arthritis is osteoarthritis, which is a progressive wearing of the cartilage in the knee joint. It occurs more frequently in people age 50 and older.
After 50, the impact of osteoarthritis can worsen due to accumulated use and the wearing down of cartilage that occurs with age.
Osteoarthritis is often the result of bone rubbing on bone, and yes, thats as painful as it sounds. Osteoarthritis can also be caused by age, weight, genetics, previous injuries, infections, illness , and certain occupations, such as construction and manufacturing.
Don’t Miss: What To Do For Knee Swelling
Diagnosing Inner Knee Pain
If you experience consistent pain, speak to your doctor as soon as possible. Your doctor will ask questions about the pain and other symptoms and will perform a physical examination with special tests specifically for the knee.
He or she may also order a diagnostic test, such as an MRI or X-ray for more conclusive results or ruling out certain injuries. It is also important for your doctor to rule out other possible issues such as a low back injury-known as lumbar radiculopathy.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Of The Knee
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that causes the tissue around the joint to become inflamed and thickened. Chronic inflammation often leads to damage and loss of cartilage.
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs in about 0.6 percent of the U.S. population and is two to three times more common in women.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are similar to other types of arthritis in the knee:
Also Check: How Do They Do Knee Replacement Surgery
Who Is At Risk For Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Iliotibial band syndrome happens most commonly in distance runners. But it may also happen from other sports, like cycling, skiing, rowing, or soccer.
If you’re a runner, you might be more likely to develop iliotibial band syndrome if you:
- Run on uneven or downhill terrain
- Run in worn-out shoes
- Run many miles per day
- Have legs that slope a little inward from your knee to your ankle
- Run in cold weather
When Will My Kneecap Start To Feel Better
One broad caveat to keep in the back of your mind. Many of you are thinking that a few weeks are enough time to start to see improvements with treatments such as exercise or physical therapy. Sadly thats not going to happen. It is not unusual for it to take 3-4 months before you start to see significant improvement in your pain. Furthermore, it is not uncommon for it to take 8-12 months for a complete resolution of your symptoms. This is important I wouldnt want to seek a surgeons consultation because 4-6 weeks of therapy and exercise left you with persistent pain.
Down below.. under coping strategies, we list a few things to try that can calm down your pain while we give the exercise time to work.
Don’t Miss: Is Walking Good For Bone On Bone Knees
Causes Of Inner Knee Pain
The inside or medial part of the knee contains a wide variety of bones, ligaments, and soft tissue structures, all contained within a relatively small area. Because of this, pain in this area of the joint can be tough to diagnose.
Several of the most common conditions that cause medial knee symptoms are listed below.
What Is Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Iliotibial band syndrome is often called IT band syndrome. It’s a health problem that causes pain on the outside of the knee. It most commonly happens in athletes, especially distance runners, or those new to exercise.
The bones of your knee joint are your thighbone , your shinbone , and your kneecap . Your iliotibial band is a strong, thick band of tissue that runs down the outside of your thigh. It extends all the way from your hip bones to the top of your shinbone.
When you bend and extend your leg, this band moves over the outer lower edge of your thighbone. With repeated bending and extending of the knee, this movement of the iliotibial band may irritate nearby tissues, causing pain.
Anyone can develop iliotibial band syndrome. But it’s fairly common in distance runners.
Also Check: What To Wear To Hospital For Knee Surgery
What To Expect At Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam, and look at your knees, hips, legs, and other joints.
Your provider may do the following tests:
- MRI of the knee if a ligament or meniscus tear could be the cause
- CT scan of the knee
- Joint fluid culture
Your provider may inject a steroid into your knee to reduce pain and inflammation.
You may need to learn stretching and strengthening exercises. You also may need to see a podiatrist to be fitted for orthotics.
In some cases, you may need surgery.
Brief Anatomy Of The Knee
The knee is a vulnerable joint that bears a great deal of stress from everyday activities, such as lifting and kneeling, and from high-impact activities, such as jogging and aerobics.
The knee is formed by the following parts:
-
Tibia. This is the shin bone or larger bone of the lower leg.
-
Femur. This is the thighbone or upper leg bone.
-
Patella. This is the kneecap.
Each bone end is covered with a layer of cartilage that absorbs shock and protects the knee. Basically, the knee is 2 long leg bones held together by muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
There are 2 groups of muscles involved in the knee, including the quadriceps muscles , which straighten the legs, and the hamstring muscles , which bend the leg at the knee.
Tendons are tough cords of tissue that connect muscles to bones. Ligaments are elastic bands of tissue that connect bone to bone. Some ligaments on the knee provide stability and protection of the joints, while other ligaments limit forward and backward movement of the tibia .
Don’t Miss: Why Do I Have Knee Pain
How Do You Treat Anterior Knee Pain
Pain in the front of the knee is usually treated successfully without surgery. This may take some time. It is not unusual for the pain to last for many months. Many of you will respond to physical therapy, which should focus on your hips, yes, your hips and pelvic muscles as much as it focuses on your thigh muscles. Runners who focus on a strengthening program might repeat might have a lower incidence of anterior knee pain.
What Are The Possible Reasons Not To Take Nsaids And Coxibs
Various factors increase the risk of gastrointestinal problems. These problems are more common in people who
- are over 65 years old,
- have already had gastritis, an ulcer or stomach bleeding,
- have a bacterial infection with Helicobacter pylori,
- drink a lot of alcohol,
- take blood-thinning heart medicines, for example anticoagulants like warfarin or acetylsalicylic acid ,
- take corticosteroids ,
- take a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressant,
- take several anti-inflammatory painkillers at the same time, or
- have certain gastrointestinal conditions like or ulcerative colitis.
If your risk of stomach bleeding or other serious complications is very high, it can be a good idea to talk with your doctor about other treatments.
People who have cardiovascular disease or several risk factors for it should also carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of treatment with an NSAID or coxib. Treating pain with naproxen may be a good option for them since it doesn’t affect the heart or the circulatory system.
Recommended Reading: Can Knee Cartilage Repair Itself
How Are Knee Problems Diagnosed
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, other tests for knee problems may include:
-
X-ray. This test uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging . This test uses large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body can often determine damage or disease in a surrounding ligament or muscle.
-
Computed tomography scan . This test uses X-rays and computer technology to make horizontal, or axial, images of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
-
Arthroscopy. A minimally-invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used for conditions of a joint. This procedure uses a small, lighted, optic tube , which is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen used to evaluate any degenerative or arthritic changes in the joint to detect bone diseases and tumors to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation.
-
Radionuclide bone scan. A nuclear imaging technique that uses a very small amount of radioactive material, which is injected into the patient’s bloodstream to be detected by a scanner. This test shows blood flow to the bone and cell activity within the bone.
How Long Does Outer Knee Pain Take To Heal
There is no one answer to this question as the healing time for outer knee pain can vary depending on the cause and severity of the pain. However, in general, outer knee pain should start to improve within a few days to a week with rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medication. If the pain does not improve or worsens, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any serious underlying conditions.
The majority of knee injuries and discomfort do not develop into long-term chronic conditions. If swelling and pain persist after a few days, it could indicate a more serious injury to your knee. A moderate soft-tissue injury typically requires two weeks to heal. The return of a knee injury too soon after a knee injury can cause further pain and tissue damage.
Resting your sprained ankle as much as possible is the most effective way to heal it. In addition, the knee must be immobilized with a splints or support for the first four to six weeks. The swelling and pain will be reduced as a result of this. If the inflammation and pain have gone away, you will begin healing the tendon. The tendon can be stretched and strengthened, as well as ibuprofen, for pain relief and stretching. It is generally best to have healing completed in six to twelve weeks, but severe injuries can take up to three to four months. If you have any questions or concerns, you should consult with your doctor or physical therapist.
You May Like: What’s Good For Knees
How Is Iliotibial Band Syndrome Treated
Your healthcare provider might suggest several different treatment strategies to help ease your symptoms. These might include:
- Limiting activities that make your knee pain worse for a while , and returning to these activities slowly
- Icing the outside of your knee
- Taking over-the-counter pain medicines
- Getting corticosteroid shots to decrease inflammation
- Making changes to your activity, like lowering your bicycle seat for cycling or improving your running form
- Practicing special exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles around your hip and your knee
You may find it helpful to work with a physical therapist as well.
These changes help most people with iliotibial band syndrome. Your healthcare provider might advise surgery if you still have significant symptoms after 6 months of trying these other therapies. Several different surgical choices exist, including one that removes the part of the iliotibial band that moves over the femur. You can discuss all your surgical choices with your healthcare provider.
What You Need To Know
- The most common causes of knee pain are related to aging, injury or repeated stress on the knee.
- Common knee problems include sprained or strained ligaments, cartilage tears, tendonitis and arthritis.
- Diagnosing a knee injury or problem includes a medical examination and usually the use of a diagnostic procedure such as an x-ray, MRI, CT scan or arthroscopy.
- Both non-operative and surgical treatment options are available to treat knee pain and problems depending on the type and severity of the condition.
You May Like: Can You Run On Knee Replacements
Itb Syndrome Friction Syndrome
Iliotibial band syndrome or ITB syndrome usually occurs in runners. It is most common in long distance runners. ITB syndrome might also occur anyone who is training vigorously. On occasion we will see cyclists with ITB syndrome however, runners make up the majority of people we see who suffer from this. For the longest time referred to this as ITB friction syndrome. It was felt that the ilotibial band was rubbing against the bottom of the femur which led to a form of tendinitis. It is not actually of the tendon that is the issue in ITB syndrome. The pain in ITB syndrome is usually due to an inflamed bursa, or small fluid-filled sac, which sits just underneath or deep to the iliotibial band. This bursa becomes inflamed with repetitive activities. Many people also wrongly concluded ITB syndrome is common because the ITB is too tight. No research has actually found that the ITB is tight in patients who suffer from iliotibial band syndrome.
We are not quite certain why iliotibial band syndrome occurs. Many causes have been postulated. Some believe it may be due to improper shoe wear. It might be due to curvature of the road of the surface that you run on. One thing for sure, IT syndrome is more common in distance runners.