Additional Treatment For Iliotibial Band Syndrome
It may be a good idea to have an analysis of your running stance, technique and footwear at this point. Having an expert evaluate and tweak your technique can help tremendously.
A strengthening program, physical therapy and exercises, and manual therapy such as trigger point work can help, too.
Knee Pain When Bending Or Squatting
Wear and tear of your knee over time can cause pain when bending your knee due to damage to the bones, ligaments, muscles and/or tendons in and around your knee joint.
For roughly every 500g of body weight, about 3kg of pressure is applied to your knees when they are bearing weight eg when bending, running, squatting or walking.
What Else Can Help
These knee pain diagnosis charts are a great place to start when it comes to working out what is wrong with your knee, but what do you then do about it? You’ll find loads of great information about each of these knee problems, and more, using the links above.
Alternative, following multiple requests from our readers, we have recently published our second book, “Beat Knee Pain: Take Back Control”.
It tells you everything you need to know to help you work out what is wrong with your knee and gives you loads of great advice on how to get back to doing what you love. You’ll find all the information from this site and loads more. We know many people prefer having the information is book form so they can navigate through easily, so do check it out.
Beat Knee Pain: Take Back Control has an average rating of 4.8/5 and is ranked the #2 Best Seller in Orthopedics on *.
*Ranked #2 Best Seller in Orthopedics on Amazon.com in October 2021
Knee pain location charts are just the start. Now that you’ve got a good idea what is going on, it’s time to start fixing it so you can get back to the things you love.
Page Last Updated: 12/02/21
Read Also: How To Know When Knee Pain Is Serious
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Not all knee pain needs medical treatment, but delaying care when it’s needed can lead to more pain and disability. Symptoms to watch for are:
- Pain lasting more than 48 hours
- Inflammation lasting more than 48 hours
- Reduced range of motion
- Signs of infection
Your knee injury may need immediate care if:
- The joint looks deformed.
- You have sudden inflammation or swelling.
Cartilage Tears In The Knee
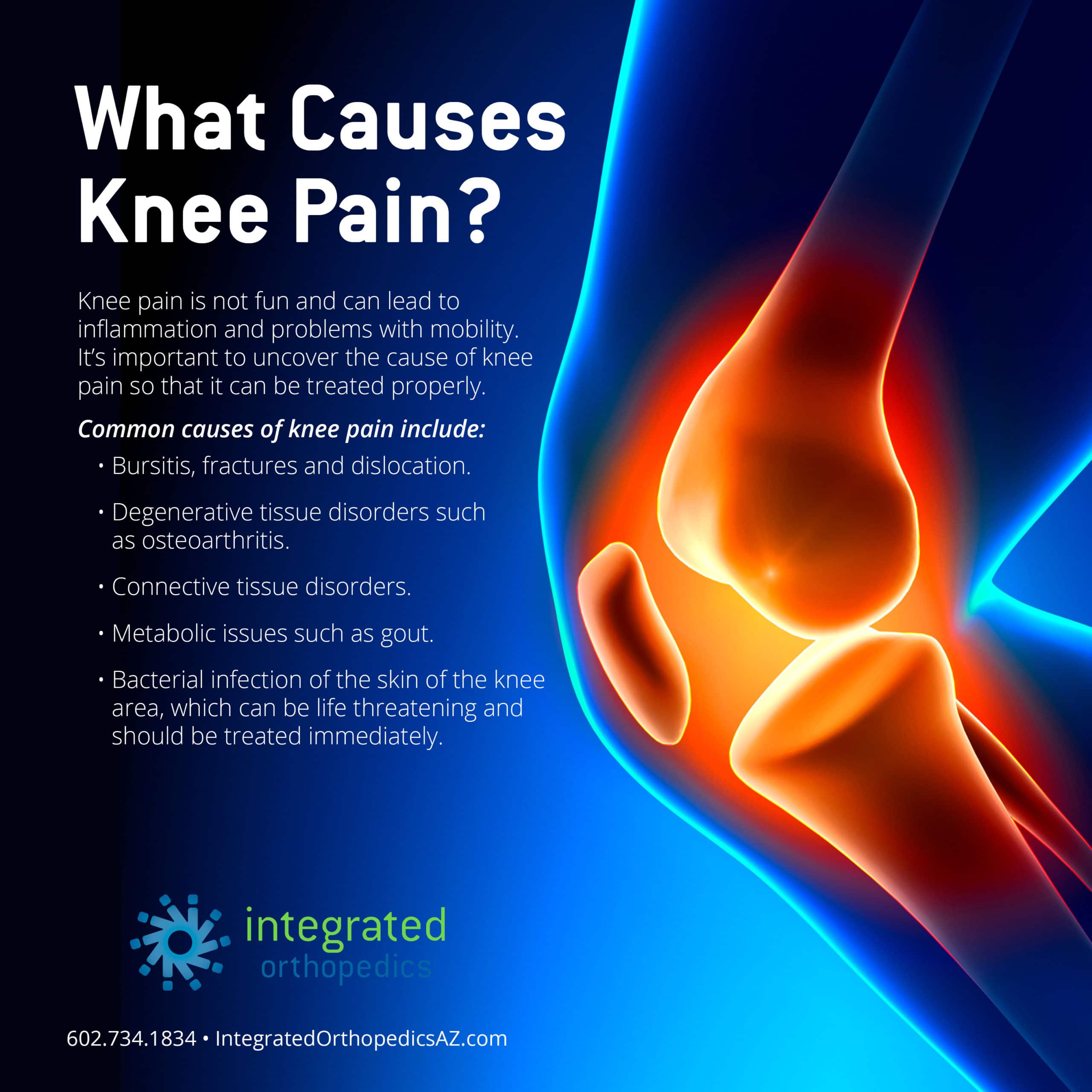
Knee discomfort can be caused by anything lodged in the joint. Each knee bone has a thick layer of cartilage covering it, which acts as a spacer between the joints, preventing friction while the knee flexes. This allows for pain-free movement.
During running and jumping, the knee cartilage acts as a shock absorber to lessen the impact on the knee joint itself. Small fragments of this knee cartilage can break off and become lodged in the joint.
Alternatively, this can occur in one of two ways:
- Cartilage Fragment: It is possible that a little fragment of cartilage has broken away from the central mass of the meniscus and is now floating in the knee joint.
- Bucket Handle Tear: A partial tear in the cartilage results in a loose flap that is partially linked to the meniscus, known as a “bucket handle tear.” Occasionally, this flap gets caught in the joint and can’t be moved.
Stabbing pain and locking of the knee joint can occur when loose cartilage gets lodged and cannot be removed. In most cases, the discomfort lessens after a few seconds of wriggling the knee about, but it can take a short while for this to happen.
You May Like: How Bad Is Knee Surgery
Understanding Knee Pain Diagnosis
Understanding what is causing your knee pain is the first, crucial step to overcoming knee pain. The knee pain diagnosis chart options here are very useful visual tools to help you work out what is wrong.
You can find out loads more about these conditions, the causes, symptoms and treatment options, by using the links above. Alternatively, if you want some more guidance, visit the knee pain diagnosis section.
Some useful articles that go alongside our knee pain diagnosis charts are:
- Calf Pain: lower leg
There are lots of other causes of knee pain that don’t appear on either of these knee pain diagnosis charts e.g. gout knee. They tend to cause more general, widespread knee pain, rather than pain in a specific locations so haven’t been included here on these knee pain diagnosis chart. You can find out more about them in the common knee conditions section.
Tips To Go Up And Down Stairs With Less Pain
Recommended Reading: What Running Shoes Are Best For Knee Pain
Stabbing Or Sharp Knee Pain That Comes And Goes
People are often stopped in their tracks by sharp knee pain. A knee bone or the surrounding nerve structures may be to blame for this symptom. Another cause of sharp knee pain is damage to the soft tissues around the joint itself.
Sharp knee pain is usually short-lived, occurring only when you do a certain movement and then subsiding as soon as you stop. It’s possible that the severe stabbing or sharp knee pain in or around the knee will continue, but it’s more likely that it will either entirely disappear or fade away, leaving behind some kind of residual soreness.
Knee problems, such as soft tissue damage or inflammation, can cause discomfort in the knee joint when localized. If it is accompanied by shooting pain down the leg, it usually signals a neurological problem in the lower back or the knee.
There are several causes of sharp knee pain, including:
- Torn Knee Cartilage
- Bursitis is caused at the knee joint by inflammation of the anti-friction sac
- Knee Arthritis: Worn-out Knees
- Loose Body: Bone Fragment Floating in Joint:
- Fracture: Brocken bone
- Nerve irritation
It is essential to understand the most prevalent reasons for intense knee pain, how they manifest, and what you can do to determine what’s wrong with your knee. These causes of severe stabbing pain in the knee are next examined.
Treatment For Top Of Knee Pain
Physical therapy, compression sleeves/wraps, and deep tissue massage can all be used in conjunction with one another to create an effective treatment plan that will promote healing and strengthen the injured area.
Anti-inflammatory medications will help to keep the swelling down. Walking or swimming will help keep the joint flexible without putting too much stress on the joint.
You May Like: How To Prevent Knee Pain
A Pain Behind The Knee
- Bakers Cyst: Most common cause of pain and swelling behind the knee. Inflammation of the popliteal bursa. LEARN MORE>
- Arthritis: Degeneration of the knee cartilage and bones causing pain and stiffness, especially in the morning. LEARN MORE>
- ACL Tear: Injury to the anterior cruciate ligament from twisting or force through the knee. Usually associated with knee instability. LEARN MORE>
- PCL Tear: Injury to the posterior cruciate ligament – less common than ACL Injury. Typically injured in RTA, fall or sports. LEARN MORE>
- Hyperextension Injury: Where the knee bends too far backwards causing pain, swelling and restricted movement. LEARN MORE>
When To Contact A Medical Professional
- You cannot bear weight on your knee.
- You have severe pain, even when not bearing weight.
- Your knee buckles, clicks, or locks.
- Your knee is deformed or misshapen.
- You cannot flex your knee or have trouble straightening it all the way out.
- You have a fever, redness or warmth around the knee, or a lot of swelling.
- You have pain, swelling, numbness, tingling, or bluish discoloration in the calf below the sore knee.
- You still have pain after 3 days of home treatment.
Read Also: Does Insurance Cover Knee Scooters
Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury
The posterior cruciate ligament is the ACLs partner. Its another band of tissue that connects your thighbone to your shinbone and supports your knee. However, the PCL isnt as likely to get injured as the ACL.
You can injure the PCL if you take a hard blow to the front of your knee, such as in a car accident. Sometimes injuries occur from twisting the knee or missing a step while walking.
Stretching the ligament too far causes a strain. With enough pressure, the ligament can tear into two parts.
Along with pain, a PCL injury causes:
- swelling of the knee
- trouble walking
- weakness of the knee
Rest, ice, and elevation can help a PCL injury heal faster. You might need surgery if youve injured more than one ligament in your knee, have symptoms of instability, or you also have cartilage damage.
What Is Knee Pain
Knee pain can occur for many reasons, most commonly because of overuse, injuries or arthritis. You can experience knee pain at any age, but older people are more likely to develop it due to degeneration of the joint, a condition known as osteoarthritis.
Depending on whats causing your pain, you may feel better with rest, anti-inflammatory medication and ice. If you have a more severe injury, you may need a procedure or a surgery.
Surgeons often use minimally invasive types of surgery to repair damage to the knee like torn tendons or ligaments. These types of injuries can cause knee instability and pain. In cases when the damage is severe, your healthcare provider may recommend knee replacement surgery.
Knee anatomy
The knee is made of
- Cartilage – protective lining and shock absorber for the bones.
- Meniscus – a type of cartilage to cushion deep in the joint.
- Tendons- fibers that connect muscles to bones.
- Ligaments- tissues that attach bones to other bones.
- Bursa- thin protective pads under the skin.
Also Check: What Gel Is Injected Into Knees
Urgent Advice: Get Advice From 111 Now If:
- your knee is very painful
- you cannot move your knee or put any weight on it
- your knee is badly swollen or has changed shape
- you have a very high temperature, feel hot and shivery, and have redness or heat around your knee this can be a sign of infection
111 will tell you what to do. They can tell you the right place to get help if you need to see someone.
Go to 111.nhs.uk or .
You can also go to an urgent treatment centre if you need to see someone now.
They’re also called walk-in centres or minor injuries units.
You may be seen quicker than you would at A& E.
Understanding What Knee Pain Is
Knee pain is described as extreme discomfort in the knee joint that is commonly the result of an injury or health condition that affects the joint. The knee consists of many moving parts.
Pain can be behind, in front, deep inside, or at the bottom or top of the knee. Pain and discomfort are accompanied by inflammation that causes stiffness and reduced flexibility or range of motion.
Don’t Miss: How To Protect Your Knees While Running
Can Someone With Pfp Syndrome Play Sports
Most people with PFP syndrome need to cut back or stop sports for some time. Follow the health care provider’s instructions on when it’s safe for you to go back to sports. This usually is when:
- Hip, leg, and core strength is near normal.
- Flexibility, especially in the hamstring muscle, has improved.
- There’s no pain with everyday activities, such as walking and going up/down stairs.
- Any pain with activity is very mild and goes away within a few minutes of starting the activity.
Medial Collateral Ligament Injury
The medial collateral ligament runs along the outside of your inner knee to stabilize the joint. If the ligament overstretches, you may have an MCL sprain.
The MCL can also tear partially or fully. An MCL injury most commonly occurs after force is applied to the outer knee, such as in contact sports.
Symptoms of an MCL injury include:
Recommended Reading: What Causes Knee Pain Years After Knee Replacement
Pain Located At The Bottom Of The Knee
Pain at the bottom part of the knee is commonly associated with four conditions:
- Osgood-Schlatter disease: This is a condition common in children in which the tendons of the knees pull on the knee’s growth plate during rapid growth spurts.
- Osteochondritis dissecans: This is an uncommon disorder that causes the knee meniscus starts to loosen and, in some cases, detach from the bone.
- Patellar tendonitis: This is the inflammation of the tendon of the kneecap, also known as “jumper’s knee,” that commonly occurs in athletes who jump or run
- Patellofemoral instability: This is a condition, once known as traumatic patellar dislocation, in which the patella gets moved out of the groove that connects it to the bottom of the femur.
Strenuous Activity & Sharp Knee Pain
Arthritis may be at blame if the discomfort in your knees is severe when you get out of bed and then eases when you get moving.
A neurological problem worsens the more you move. Spinal stenosis is likely if you find it simpler to walk uphill or bend slightly forward but more challenging to walk downhill or erect.
Also Check: Can You Have Arthritis In Your Knees
What To Expect At Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam, and look at your knees, hips, legs, and other joints.
Your provider may do the following tests:
- MRI of the knee if a ligament or meniscus tear could be the cause
- CT scan of the knee
- Joint fluid culture
Your provider may inject a steroid into your knee to reduce pain and inflammation.
You may need to learn stretching and strengthening exercises. You also may need to see a podiatrist to be fitted for orthotics.
In some cases, you may need surgery.
Is The Sound That My Knee Makes Bad
As we reviewed in a popular post about the sounds that our knees make, we discussed that the majority of these sounds are not mechanical or dangerous! That means that you are probably not bone on bone or grinding away the insides of your knee when you bend it. Yes, these sounds can be annoying or even embarrassing, but they are rarely dangerous. The most common cause of this grinding sensation or sound is actually due to inflammation of the tissues inside the knee. You do not need cortisone or lubricating injections to treat these sounds or sensations.
Don’t Miss: Rick Owens Knee High Sneaker
Common Causes Of Inner Knee Pain
There are a variety of causes of inner knee pain. Many of them can be linked to an injury. Some of the most common incidents that cause knee injury and pain include falls, sports injuries, or increased activity.
Adults particularly those older than 60 are most likely to experience knee pain. However, inner knee pain can also occur in children and adolescents.
According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, the most common causes of inner knee pain in children are:
- patellar subluxation
Less Common Causes Of Knee Pain
Less-common causes of significant knee pain include conditions and injuries. Injuries include:
- Dislocated kneecap: Causes are sharp blows to the knee or twisting. Severe pain in the front of the knee plus buckling, slipping, or catching during movement.
- Kneecap fracture: Causes are a direct blow or falling onto the knee. Pain, difficulty straightening the leg, bruising, and swelling can occur. Sometimes there’s visible deformity.
Conditions include:
- Plica syndrome: Irritation of the synovium . Pain is in the middle and front of the knee. Worsens with inactivity or squatting, running, or kneeling. The knee may pop when bent.
- Osgood-Schlatter disease: Strikes after growth spurts in kids between 9 and 14. Pain is in the front of the knee. It improves with rest and worsens with activities like running and jumping.
- Osteochondritis dissecans: In children, lack of blood supply weakens the bone and cartilage. The knee may separate from the underlying bone. Causes pain with activity.
- Knee joint infection: Causes significant pain, swelling, warmth, painful movements, and fever. It may result from a bacterial infection in the bloodstream.
- Bone tumor: Very rarely the source of knee pain. Symptoms include fever, unintentional weight loss, and pain that’s worse at night.
Don’t Miss: How To Avoid Knee Pain When Running
Superior Tibiofibular Joint Sprain
The tibiofibular joint is the point in the knee where the tops of the shin bones join. Dislocation of this joint is likely to have been caused by an impact or fall onto the knee, particularly when it is in a fully bent position. Symptoms include:
- Pain and swelling on the outer surface of your shin.
- In addition, the top of the fibula bone may appear more prominent than normal on the outside of your knee.
- More on Tibiofibular joint sprain
How Are Knee Problems Diagnosed
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, other tests for knee problems may include:
-
X-ray. This test uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging . This test uses large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body can often determine damage or disease in a surrounding ligament or muscle.
-
Computed tomography scan . This test uses X-rays and computer technology to make horizontal, or axial, images of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
-
Arthroscopy. A minimally-invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used for conditions of a joint. This procedure uses a small, lighted, optic tube , which is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen used to evaluate any degenerative or arthritic changes in the joint to detect bone diseases and tumors to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation.
-
Radionuclide bone scan. A nuclear imaging technique that uses a very small amount of radioactive material, which is injected into the patient’s bloodstream to be detected by a scanner. This test shows blood flow to the bone and cell activity within the bone.
Read Also: Do Doc Socks Help Knee Pain