Can A Bone Scan Tell The Difference Between Cancer And Arthritis
Changes in the bones seen during a bone scan are most likely not cancer. Radioactive material is usually present on the bone surfaces of joints when arthritis occurs, not in the bone itself. It can be difficult to tell the difference between cancer and arthritis, especially in the spine.
See Your Doctor Immediately If You Experience Any Unusual Symptoms
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of arthritis, such as pain, swelling, or redness, you should consult a doctor. A physical examination, as well as a blood test, can often be used to diagnose arthritis. If you have any unusual symptoms, such as a fever, chest pain, or shortness of breath, see a doctor as soon as possible. Although a bone scan is useful in some cases, it is not always necessary.
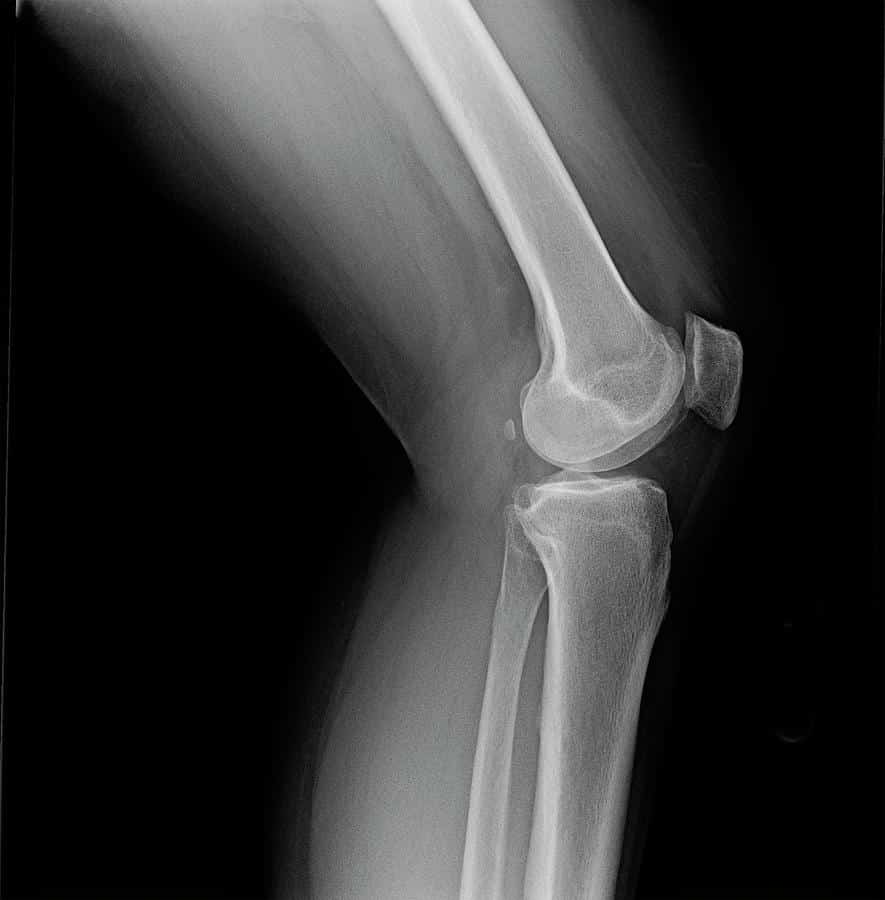
Normal Knee Anteroposterior View
The AP knee X-ray view shows the knee from directly in front.
This X-ray shows the four bones of the knee. The femur is the thigh bone. There are two bones below the joint line. The tibia is the larger bone we know as the shin. The smaller bone on the outside of the leg is the fibula, seen on the left in the above image.
The kneecap can be seen as a faint circular outline overlapping the thigh bone, centered at the widest part of the femur.
Knee joints are covered with smooth cartilage. This does not appear on X-rays, so although the bones are touching, they appear to have a gap between them. In a normal knee X-ray, the gap is easily seen and of an even height. The gap appears here as a black line through the middle of the knee.
How Ra Affects Your Knees
In RA, your immune system attacks and damages the synovial cell lining of your joint. The synovial cell is the connective tissue that lines your joints. RA causes your synovial cells to increase, which causes thickening and inflammation. Its the same with RA in your knees:
Over time, the inflammation can damage the cartilage and ligaments of your knee joints. Along with synovial fluid, these help your knees move and keep your bones from grinding against each other.
As they become damaged, your cartilage wears away and exposes your bone. Bone, unlike cartilage, has pain receptors. As your bone is exposed, your bones start to push and grind against each other. This results in pain and bone damage.
Tissue damage from RA can led to chronic, or lasting, pain, affect your balance and steadiness, and change the appearance of your joints.
A hallmark symptom of RA is tenderness, pain, or joint discomfort that worsens when you stand, walk, or exercise. This is known as a flare. It can range from a mild, throbbing pain to intense, sharp pain.
Also Check: Knees Hurt When Lying Down
Risk Factors For Knee Arthritis
- Age. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative, wear and tear condition. The older you are, the more likely you are to have worn-down knee joint cartilage.
- Heredity. Slight joint defects or double-jointedness and genetic defects may contribute to osteoarthritis in the knee.
- Excess weight. Being overweight or obese puts additional stress on the knees over time.
- Injury. Severe injury or repeated injury to the knee can lead to osteoarthritis years later.
- Overuse. Jobs and sports that require physically repetitive motions that place stress on the knee can increase risk for developing osteoarthritis.
- Gender. Postmenopausal women are more likely to have osteoarthritis than men.
- Autoimmune triggers. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis remains unknown, triggers of autoimmune diseases are still an area of active investigation.
- Developmental abnormalities. Deformities such as knock knee and bowleg place higher than normal stress on certain parts of the knee joint and can wear away cartilage in those areas.
- Other health conditions. People with diabetes, high cholesterol, hemochromatosis and vitamin D deficiency are more likely to have osteoarthritis.
Risks Of Radiofrequency Ablation For Knee Arthritis
As with any type of medical procedure, there is some risk, although with genicular radiofrequency ablation, the risks are rare. Some patients may experience an allergic reaction to anesthesia and there is some risk of infection and bleeding. Talk to your pain management doctor about any specific risks based on your age, health history, and current health condition.
Recommended Reading: Leg Compression Machine After Knee Surgery
What Are The Stages Of Arthritis Of The Knee
There are five stages of osteoarthritis, the most common type of arthritis that affects your knees:
- Stage 0 . If youre at stage 0, your knees are healthy. You dont have arthritis of the knee.
- Stage 1 . Stage 1 means that youve got some wear and tear in your knee joint. You probably wont notice pain.
- Stage 2 . The mild stage is when you might start to feel pain and stiffness, but theres still enough cartilage to keep the bones from actually touching.
- Stage 3 . If youre at the moderate stage, youll have more pain, especially when running, walking, squatting, and kneeling. Youll likely notice it after long periods of rest . You’re probably in a great deal of pain because the cartilage has narrowed even further and there are many bone spurs.
- Stage 4 . Severe osteoarthritis means that the cartilage is almost gone. Your knee is stiff, painful and possibly immobile. You might need surgery.
How Is Knee Arthritis Diagnosed
Your doctor may use some of the following diagnostic tests and procedures to determine if you have knee arthritis:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Blood tests for genetic markers or RA antibodies
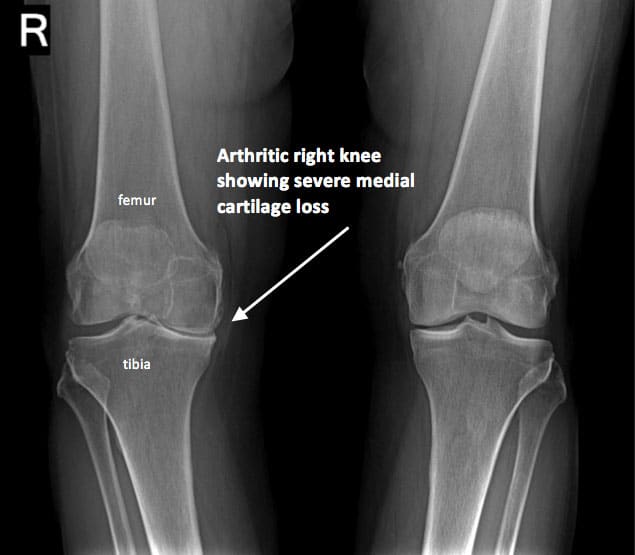
- X-rays to determine cartilage loss in the knee
- Joint aspiration: drawing out and testing the synovial fluid inside the knee joint
Cartilage cannot be seen on X-ray, but narrowing of the joint space between the bones indicates lost cartilage. X-rays show bone spurs and cysts, which can be caused by osteoarthritis. Other tests such as MRI or CT scans are rarely needed for diagnosis.
Read Also: How Does Tommie Copper Knee Sleeve Work
Deformities Of The Knee
The appearance of the knee can change during a flare and as damage progresses.
In RA, swelling and redness are common during a flare. In the long term, persistent inflammation can result in permanent damage to the cartilage and the tendons. This can affect the shape and appearance of the knee.
With OA, the muscles around the knee can weaken, resulting in a sunken appearance. The knees can start to point toward each other or bend outward.
Knee deformities range from barely noticeable to severe and debilitating.
Treatment will depend on the type of arthritis a person has.
Etiology And Risk Factors
Although osteoarthritis is especially common in older adults, its pathology of asymmetric joint cartilage loss, subchondral sclerosis , marginal osteophytes and subchondral cysts is the same in younger and older adults.1 Primary osteoarthritis is the most common form and is usually seen in weight-bearing joints that have undergone abnormal stresses .1316 The precise etiology of osteoarthritis is unknown, but biochemical and biomechanical factors are likely to be important in the etiology and pathogenesis.1 Biomechanical factors associated with osteoarthritis include obesity, muscle weakness and neurologic dysfunction. In primary osteoarthritis, the common sites of involvement include the hands, hips, knees and feet13,17. Secondary osteoarthritis is a complication of other arthropathies or secondary to trauma. Gout, rheumatoid arthritis and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease are correlated with the onset of secondary osteoarthritis.
Also Check: How Much Does It Cost For Knee Replacement Surgery
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
25 September 2020
Soon Bin Kwon, Yunseo Ku, Du Hyun Ro
15 May 2020
Jonas Bianchi, Antônio Carlos de Oliveira Ruellas, Lucia Helena Soares Cevidanes
volume 9, Article number: 5761
Which Body Parts Are X
RA begins as a peripheral disease that has a strong affinity for the hands. Plus, since there are more joints in the hands than any other region of the body, doctors often order x-ray images of the hands firstthen the feet.
There are more than 30 joints in the hands, so getting x-rays of the hands provides a very good diagnostic yield, says Dr. Magnati. If the x-rays show bone erosions and narrowing of the joints at the base of your fingers near the palm, the knuckles, and the uppermost joint of the thumb , thats classic RA.
RA tends to affect joints in pairs, so doctors typically order x-rays of both hands and both feet . The other area that can be involved in RA is the neck, where the spine connects to the skull, says Dr. Burk.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Fluid Off Knee
What Are The Risks Of A Knee X
X-rays are a quick, easy way for your healthcare provider to diagnose a medical condition in your knee or knees. Knee X-rays contain very low amounts of radiation that go directly through your body. Also, X-rays typically dont cause any side effects.
If youre pregnant, your growing baby could be exposed to the slight radiation. Tell your radiologic technologist if youre pregnant or thinking about getting pregnant. You may wear a lead apron to protect yourself and your baby from radiation exposure. Children have a slightly higher risk of issues with radiation exposure. Lower amounts may be used on children.
Extreme amounts of radiation exposure carry a small risk of cancer. However, the benefit of getting the correct diagnosis outweighs any risk of exposure. If youre concerned about the amount of radiation you may be exposed to during an X-ray, talk to your technologist or healthcare provider.
How Radiofrequency Ablation For Knee Arthritis Works
Genicular radiofrequency ablation treatments involve the use of precisely placed needles in the area where youre experiencing knee pain. Radio waves conducted through the needle essentially burn the nerve endings. This prevents the pain signals from those nerves from being sent back to your brain.
Radiofrequency ablation for knee arthritis is considered a nonsurgical, noninvasive treatment. This means your doctor makes no incisions and there is less recovery time and a very low complication rate. Many people who receive this treatment report long-lasting pain relief and greater functionality.
Recommended Reading: Knee Ripped Jeans Men’s
Section : The Prevalence Of Radiographic Osteoarthritis In People With Knee Pain
Table Table11 summarises the estimates of prevalence from the studies reviewed of persons with knee pain found to have x ray abnormalities consistent with radiographic knee OA. Knee pain was the most frequent marker symptom and has been used to construct this main table. However other symptoms were reported in the different studies, but definitions varied and could not be used to compare the study results. Pain, by contrast, featured in all the studies and therefore provided a common factor to which to relate estimates of the frequency of radiographic knee osteoarthritis. The figures are shown stratified by age, with the youngest group first and older age groups further down the table. The different radiographic views used are highlighted, as are the definitions used to classify an abnormal radiograph as showing osteoarthritis.
What Scan Is Best For Knee Pain
MRI combined with conventional x-rays is usually the best method of analyzing the major joints in the body, such as the knee. A knee evaluation usually includes the diagnosis or evaluation of knee pain, weakness, swelling, or bleeding within the joints tissues. There may be a cartilage, osteograf, ligaments, or tendons injury.
CT scans, in addition to creating more detailed images of the knee, can also provide faster results. A narrow table in the center of a CT scanner slides into the center of your body. In some cases, a dye called contrast will be injected into your body before the test. CT scans emit more radiation than x-rays. Over time, your chances of developing cancer may rise. If you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast dye injected, please notify your doctor. If the dye is used, it is extremely unlikely that it will cause a serious allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Disability For Two Knee Replacement
How Do I Get Ready For A Knee X
You dont have to do much to prepare for a knee X-ray. Make sure to wear comfortable clothing without any metal. Youll be asked to remove any clothing, jewelry, belts or other objects containing metal. These may show up on the X-rays, interfering with getting a fully detailed image.
Tell your radiologic technologist if youre pregnant or planning a pregnancy. Knee X-rays use a minimal amount of radiation, but theres a chance your growing baby could be exposed to it. Your healthcare provider will decide if you need the X-ray. If the X-ray is urgent, precautions will be taken to minimize radiation exposure to your baby.
Before your X-ray, your technologist will explain the X-ray process to you. If you have any questions about whats going to happen, theyll be happy to answer them for you.
What Causes Osteoarthritis
The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, is associated with injuries, wear-and-tear processes, and genetics. An arthritis joint will demonstrate the narrow bone spaces due to various reasons. The cartilage thins, the formation of cysts within bones, bones spurs seen on the edges, deformity of joints are some of the reasons, which leads to crooked joints.
You can get rid of joint pain instantly by browsing through the best joint supplement reviews on the market. Read them carefully to arrive at the decision of buying the best product on the market.
You May Like: What Anesthesia Is Used For Knee Replacement
Three Different Knee X
The three most common views used during a knee X-ray are:
- anteroposterior
The AP view is looking at the knee, held straight, from directly in front. This view is generally the easiest to understand as it looks like the skeleton we are familiar with. The kneecap is difficult to see in this view as it is overlapping the thigh bone. It can only be seen as a faint outline. The AP view is helpful in diagnosing arthritis in the knee joint between the thigh and shin bones. It can also show whether there is arthritis on the inside or outside of the knee.
The lateral view is taken perpendicular to the AP, showing the side of the knee. It clearly displays the kneecap and is most useful for diagnosing arthritis between the kneecap and the thigh bone.
The skyline view looks between the kneecap and the thigh bone. It is taken with the knee bent and is used to diagnose arthritis. It is much less common. Only about 30% of orthopedic surgeons use this view during a routine examination.
Is There A Special Preparation Needed For An X
There is no special preparation required for an arthritis X-Ray. The only people who should consider are the pregnant women. The pregnant women must inform the technician about their pregnancy because the exposure to radiation may cause harm to the fetus, so it must be minimized.
At the time of X-Ray, a person should take off their jewelry before taking a test. There could be a requirement to remove some clothes, depending on the body parts to be tested. The technician will provide some something to cover the body part.
*All individuals are unique. Your results can and will vary.
Recommended Reading: How Much Do Gel Shots In The Knee Cost
What Happens During A Knee X
A radiologic technologist will perform your knee X-ray in your healthcare providers office or a hospital radiology department. The procedure will take place in a room with a large X-ray machine hanging from the wall or ceiling. Once in the X-ray room, you may be given a lead apron to protect you from radiation exposure. The X-ray room is sometimes set at a cold temperature, but the process should only last about 10 minutes. An X-ray is like getting a picture of your knee taken you cant feel it, and it produces an image.
Your technologist will place an X-ray film holder or digital recording plate behind or under the X-ray machine. Theyll have you stand or sit in front of the X-ray machine or have you lie down on an X-ray table. Youll need to keep very still during the procedure. Any movement may cause the X-ray images to show up blurry. The technologist may ask you to hold your breath while theyre taking the images.
Your technologist will go into a small room or behind a wall to operate the X-ray machine. Theyll return to reposition you for additional images. Sometimes, they may have you bend your knee or knees in certain ways as well.
What Happens While Conducting An X

All the X-Ray tests are the part of a radiology department. The beam will be sent by an X-Ray machine for ionizing radiation via an X-Ray tube. The energy produced by the machine will pass through the body part that is being X-rayed.
After the energy is passed through the body part, the part of the body is captured on a digital camera or a film for the creation of a picture. The bones along with various other dense areas will be showed up as lighter shades of grey to white. There are some areas, which do not absorb the radiation. These areas will appear as dark grey to black color.
The X-Ray will not take much time. The entire test will be completed within 15 minutes, and there will be no discomfort during the test.
Don’t Miss: What Is Makoplasty Knee Replacement