Patients May Need Subsequent Surgeries To Maximize The Benefits Of Joint Replacement
Many patients with hip and knee arthritis have the condition in more than one of their hip or knee joints, said the studys lead author Dr. Gillian Hawker. So its not surprising that replacing a single joint doesnt alleviate all their pain and disability patients may need subsequent surgeries to maximize the benefits of joint replacement.
The study, published in the journal Arthritis & Rheumatism , followed a group of patients with osteoarthritis and inflammatory arthritis. Only half reported a meaningful improvement in their overall hip and knee pain and disability one to two years after surgery. Whats more, researchers found the patients who had the worse knee or hip pain to begin with but fewer general health problems and no arthritis outside of the replaced joint were more likely to report benefits.
According to the study authors, nearly 83 percent of study participants had at least two troublesome hips and or knees.
- In general, an estimated 25 percent of patients who undergo a single joint replacement will have another joint replacement usually the other hip or knee within two years.
How To Avoid Post
To reduce pain following knee replacement surgery, a few steps should be taken. If you have residual pain after the surgery, consult with a therapist to see if you can work it out. Maintaining good posture and keeping your weight off your knee is also a good way to keep it off your knee. Finally, if pain persists after surgery, you should consider revision surgery.
Problem: Fixing Pain After Total Knee Replacement May Include Amputation
Three in 1000 patients will need to have their leg amputated.
The causes of the amputation were:
- infection around the implant ,
- soft-tissue deficiency surrounding the implant ,
- severe bone loss ,
- fracture around the implant ,
- circulatory damage .
In 80% of the cases, there were more than 2 of these factors for amputation.
In research from April 2017, doctors writing in the European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology wrote:
Treatment for prosthetic knee replacement is becoming more common. Infection is an arthroplasty-related complication leading to prolonged hospitalization, multiple surgical procedures, permanent loss of the implant, impaired function, impaired quality of life, and even amputation of the limb.
The purpose of this study was to identify risk factors for amputation in the periprosthetic infected knee through a case-control study, analyzing patients treated from January 2012 to November 2016 in a hospital with a high incidence of this diagnosis. We included 183 patients with periprosthetic knee infection 23 required amputation as definitive management .
They found that patients with:
- Increased surgical time > 120 min,
- diabetes mellitus had an increased risk of amputation.
Read Also: Osteoarthritis Of Right Knee Icd 10
Lack Of Evidence About The Effectiveness Of Prediction And Management Strategies For Chronic Postsurgical Pain After Total Knee Replacement
The same doctors also wrote in the British Medical Journalthat the problem of post-surgical pain in knee replacement patients had reached a point of significance and that researchers should prioritize their studies to help people with pain. They wrote:
- Our highlights a lack of evidence about the effectiveness of prediction and management strategies for chronic postsurgical pain after total knee replacement. As a large number of people are affected by chronic pain after total knee replacement, development of an evidence base about care for these patients should be a research priority.We are going to return to this study below.
There is a significant problem. The main part of this problem is identifying what is causing people to have pain after knee replacement.
Read Also: Stiff Painful Knees After Sitting
Can You Still Have Arthritis After Knee Replacement
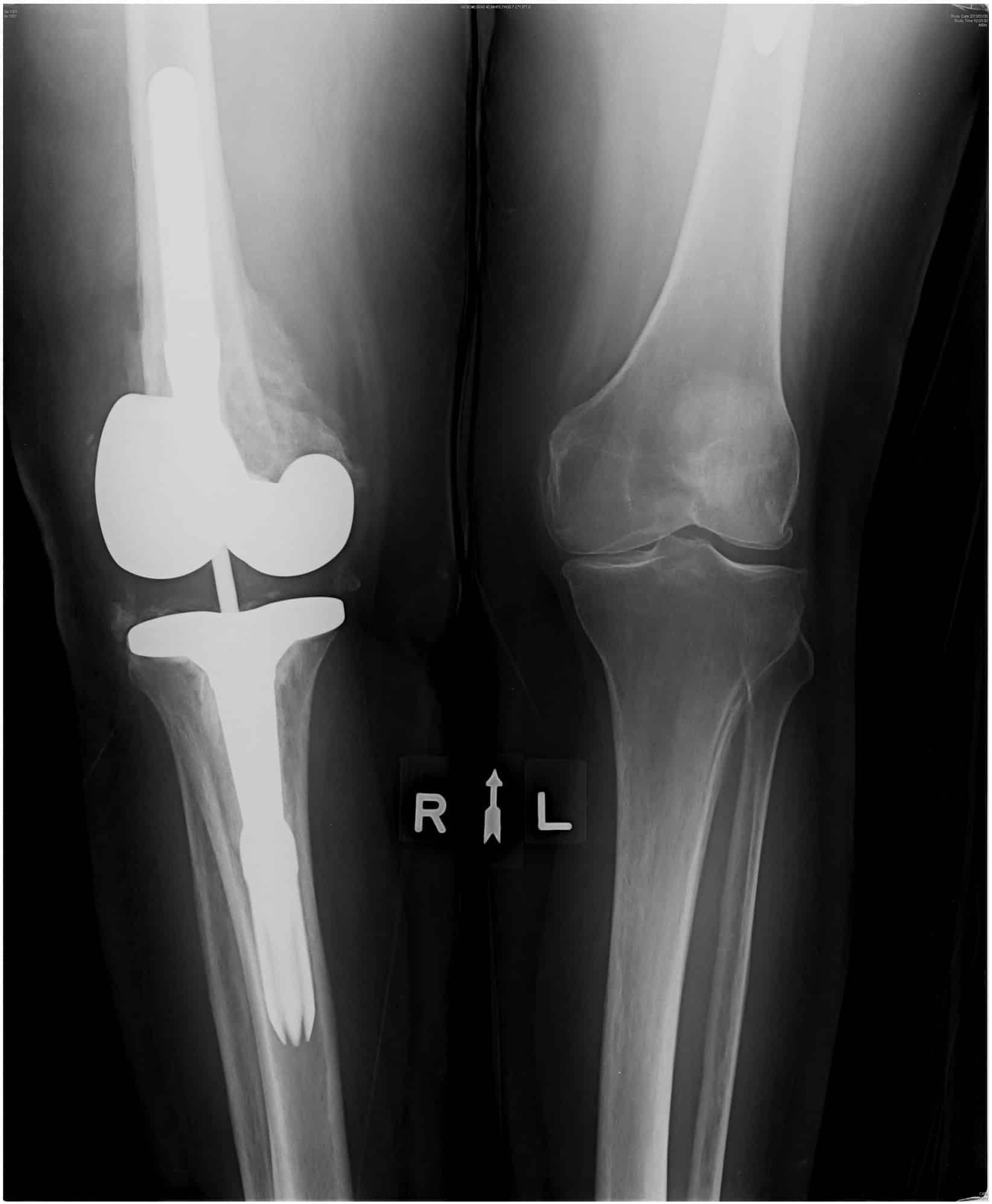
Arthritis can be treated with knee replacement surgery. It may be able to repair the damage caused by arthritis and alleviate pain caused by the condition, but it cannot cure it.
This common treatment has a 95% success rate, and it relieves pain and stiffness. The quality of life can be greatly improved in a person who requires knee replacement surgery. The term arthritis encompasses all joint pain or arthritis. The Centers for Disease Control estimates that 22.6% of adults in the United States have arthritis that has been diagnosed by a doctor. Surgery to replace knees does not cure arthritis. In addition to correcting the damage done to the body by arthritis, this treatment can also alleviate pain associated with the condition. Itâs critical to maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine after knee replacement surgery. It is critical to ensure a strong rehabilitation program following surgery in order to have a successful recovery.
Read Also: Who Is The Best Knee Surgeon In The World
After Knee Replacement Surgery
This might come as a surprise to you, but a negative attitude or negative mood after knee replacement surgery is associated with prolonged stiffness! This is because people with a negative attitude are less likely to adhere to a physical therapy protocol after knee replacement surgery. We are all humans, and we can experience negative emotions when we are in pain or anxious about our recovery, but it is important to remember that you should not let these emotions overwhelm you! Trusting your physical therapist and adhering to physical therapy is very important, and you should know that it will bring many positive outcomes, such as easing your stiffness. You should not force yourself into thinking that everything is okay but thinking that everything will be okay eventually with hard work actually helps your recovery.
What Are The Signs Of Knee Replacement Failure
The most common symptoms of a failed knee implant are pain, decrease in joint function, knee instability, and swelling or stiffness in the knee joint.
Persistent pain and swelling can indicate loosening, wear or infection, and the location of the pain can be all over the knee or in one particular area . A decline in knee function may result in a limp, stiffness or instability. Patients who demonstrate these symptoms and signs may require revision joint surgery.
You May Like: How Do I Stop My Knees From Popping
What Are The Alternatives To Revision Surgery
Alternatives to revision knee surgery are rarely used as they can sometimes be more complex and lead to worse results than revision surgery, but they include knee fusion or .
The following alternatives are employed depending on the seriousness of the problem affecting the knee:
- of the knee joint may relieve pain but at the expense of keeping the knee in a fixed, non-bending position.
- may be used in extreme cases in which the knee joint has a severe infection that cannot be eradicated
Research: Doctors Are Looking For The Causes Of Pain After Knee Replacement And It Is Hard To Find
The confusion as to what may be the cause of chronic knee pain after knee replacement is a cause of great concern not only among doctors but obviously among patients. We often find patients to be confused between what is normal and what is not normal after knee replacement.
- Is some pain normal?
- Are the clunking sounds normal?
- Is the instability normal?
Read Also: Why Does My Knee Swell
Frequent Or Recurring Hip Dislocations
Your hip joints are made of a stem, ball and socket. Hip dislocations occur when the ball of the joint comes out of the socket . Some hip dislocations are the result of trauma, such as an accident, but if you frequently have hip dislocations after a hip replacement surgery, you may need a revision to correct the position and size of your hip components.
Symptoms of a hip joint dislocation include:
- severe pain in and around the hip or groin area,
- inability to walk,
- weakness or inability to move your leg, and
- one leg that is noticeably shorter than the other.
The Second Knee Replacement Surgery
All of this also brings up a critical issue, when young people get a knee replacement, what happens when they need a second procedure? As a physician, I know that while the first surgery may take 60-90 minutes, the second knee replacement is a 2-4 hour affair. Why? Parts of your body have grown into the prosthesis and all of that has to be carefully dissected out so that complications like serious nerve or blood vessel injury dont happen.
We also know that the size of the bone tunnels must be expanded. Meaning that the new prosthesis needs fresh bone to latch onto, so the doctor has to ream out the existing tunnels and make them bigger.
Also Check: How Much Is Knee Replacement Surgery
Do Knee Replacements Work In Younger People
Back in 2017, researchers used the US governments Osteoarthritis Initiative dataset to look at the impact of age and activity on knee replacement outcomes . This was a critical study because it used data collected by disinterested researchers and not surgeons working on the behalf of knee replacement device companies. What did they find? Older and less functional patients did better with knee replacement, hence, in that age/activity group the procedure was cost-effective. The problem came when they looked at younger and more active patients, who were, in general, less likely to be satisfied and where it was more likely that the procedure wasnt cost-effective.
If youre interested in learning about knee replacement outcomes in general, heres a video reviewing research showing lackluster results from the first surgery:
Problem: Difficulty And Pain In Kneeling
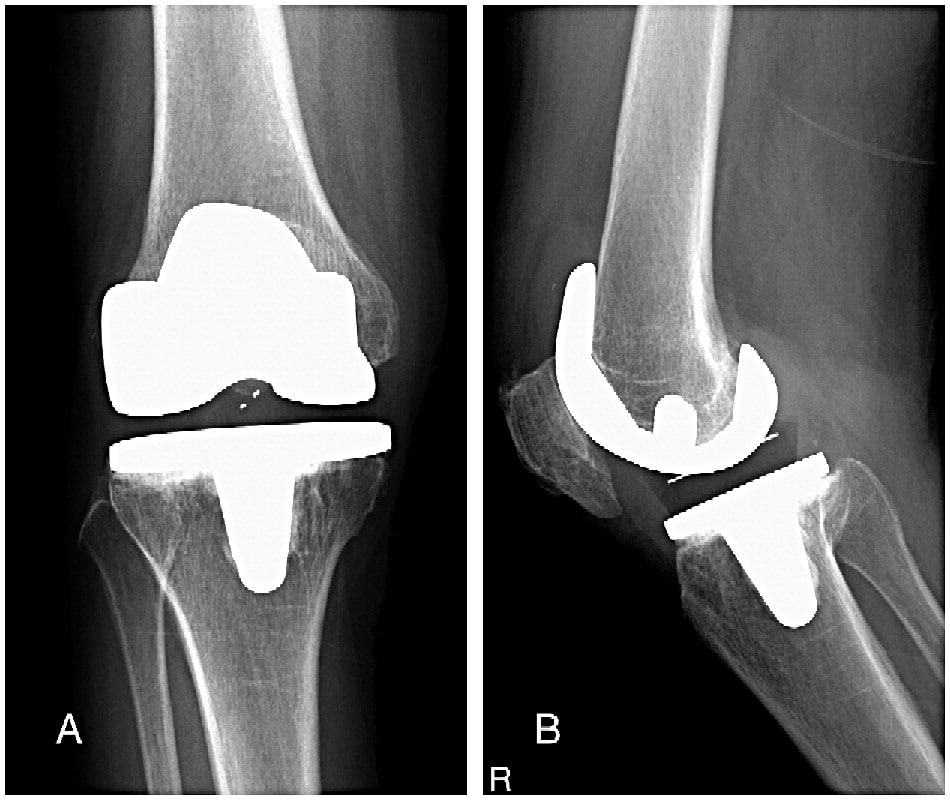
Most people had difficulty kneeling because of pain or discomfort in the replaced knee. Many patients described how this limitation affected their daily lives, including housework, gardening, religious practices, leisure activities, and getting up after a fall. Patients often adapted to these limitations by finding alternatives to kneeling, assistance from others, or home adaptations. Many patients had accepted that they could not kneel, however some still expressed frustration. Few patients had consulted with healthcare professionals about kneeling difficulties, and unmet needs included the provision of information about kneeling and post-operative physiotherapy.
You May Like: Why Do I Get Pain In My Knees
Medial Collateral Ligament Injury
During total knee replacement, medial collateral ligament is important for soft tissue stabilization and coronal plan stability. The incidence of iatrogenic MCL injury is 2.22.7% . In the case of surgical injuries, direct repair, constrained prosthesis use, and even revision at the same session are among the options . Unrecognized MCL injuries during surgery cause early instability. This leads to early implant wear and consequently the need for early revision. Therefore, it is important to diagnose and repair the injury during surgery . Sudden instability in the valgus stress test during knee stabilization indicates MCL injury. Injury may occur from femoral insertion, within the tendon or tibial insertion . Primary repair technique varies according to injury level. Fixation with screw is recommended if MCL injury occurs from its femoral insertion site. Otherwise, if it is through tendon, repairing with insoluble suture technique is recommended. Finally, if MCL injury occurs from its tibial insertion site, both insoluble suture anchor technique and fixation with staple technic are recommended . Factors that increase the risk of medial collateral ligament injury during surgery are as follows :
Using a larger saw blade than femoral condyle
Delayed excision of medial side osteophytes
Performing challenging manipulations of varus-valgus
Patients with flexion contractures
Patient-related risk factors include obesity and severe deformities .
Is It Normal To Have Knee Pain Years After Surgery
While it is extremely rare, a small percentage of patients who have had knee replacement continue to experience chronic pain after the procedure. Nonetheless, when this happens, you donât have to give up. If your situation is unsatisfactory, it is best to have it evaluated. Additional treatment options may be beneficial after knee replacement for patients who suffer from chronic knee pain.
Your pain level and recovery time will differ depending on whether or not you have a total or partial knee replacement. The average time required for total knee replacement after a walker or cane is one to three months. Patients who have a partial knee replacement have fewer invasive procedures, and they typically walk without assistance within two weeks. When you have a knee replacement, there are several different types of pain. It is expected as a result of the surgery itself, which entails swelling, bruising, and the use of prosthetics. There is also the possibility that you may experience pain in other parts of your body, such as your hips. Chronic pain is defined as pain that persists for three months or longer.
If you have knee pain or swelling, a Corticosteroid injection is a viable option. An anesthetic is injected into a genicular nerve block to interrupt pain signals being sent to the brain. There is a chance you will need to undergo revision surgery for your knee replacement.
Recommended Reading: What To Expect When Getting Gel Injections In Knee
Knee Replacement Pain: The Week Following Surgery
You should expect to stay in the hospital for several days following knee replacement surgery. This is often considered the most painful stage of the recovery process. Your doctor will prescribe medications to help you manage your pain level.
In addition to icing your knee, you may be encouraged to move your foot and ankle to increase blood flow and lower the risk of swelling and blood clots. Your doctor may also use blood thinners, support hose, and compression boots to prevent further complications.
Generally the day after surgery, a physical therapist will show you exercises that will help you recover your range of motion and continue to heal. You may even be asked to get up and take a few steps . Patients who get up and put a safe amount of weight on their new knee typically experience a quicker recovery.
After leaving the hospital, most patients continue to take some form of pain medication for two to six weeks. Your doctor will determine the best method of pain relief for your specific needs, whether it is over-the-counter medications or something stronger.
How Long Does Pain Last After Knee Replacement Surgery What To Expect
Knee pain can appear in many forms. Arthritis, an injury, and gradual wear and tear as you age can all have an effect on your activities and comfort level. If youre unable to walk or climb a stairs because of your pain , knee replacement surgery may be the best way to get your life back. While the benefits of the procedure may significantly outweigh temporary discomfort, its important to have realistic expectations regarding your recovery timeline and knee replacement pain after surgery.
Read Also: Can You Kneel After Knee Replacement
What Causes Pain After Knee Replacement Surgery
Researchers continue to study the many causes of pain after knee replacement surgery. Some are biological and due to conditions present before surgery, while others are due to complications that arise during surgery.
On the biological side, patients suffering from arthritis may experience increased sensitivity because of the ongoing pain that was present before surgery. As well explain below, inflammatory responses and allergy-related problems can also contribute to persistent pain. Another source of pain is referred pain originating from the hip due to a change in alignment.
If you are experiencing ongoing pain after knee replacement surgery, but do not have a medical history of arthritis or the previously mentioned issues, you may be dealing with surgical complications. While your doctor will take steps to prevent problems, its still possible for these to rare issues to occur:
Remember to stay open and honest with your doctors. This will help them properly diagnose and treat the problem to get you the pain relief youre looking for.
Risks Of Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery is a common operation and most people do not have complications. However, as with any operation, there are risks as well as benefits.
Complications are rare but can include:
- stiffness of the knee
- infection of the joint replacement, needing further surgery
- unexpected bleeding into the knee joint
- ligament, artery or nerve damage in the area around the knee joint
- persistent pain in the knee
- a break in the bone around the knee replacement during or after the operation
In some cases, the new knee joint may not be completely stable and further surgery may be needed to correct it.
Read Also: How Do I Get Rid Of Fat Around My Knees
How To Avoid An Early Knee Replacement
There are three randomized controlled trials showing how best to avoid an early knee replacement . One published by our group and two by Herigou in France. All three use the patients own bone marrow concentrate. Looking at this data, you have a 4 in 5 chance of not needing an early knee replacement at 15 years after the procedure if you pursue these much less invasive bone marrow concentrate injection that contains your own stem cells.
The upshot? Early knee replacement is a big problem. You want that procedure to be one and done. Hence, do your homework on non-surgical options to avoid needing a second knee replacement procedure,
____________________________
References:
Ferket BS, Feldman Z, Zhou J, Oei EH, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Mazumdar M. Impact of total knee replacement practice: cost effectiveness analysis of data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. BMJ. 2017 Mar 28 356:j1131. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1131. PMID: 28351833 PMCID: PMC6284324.
Singh JA, Lewallen DG. Time trends in the characteristics of patients undergoing primary total knee arthroplasty. Arthritis Care Res . 2014 66:897-906. doi:10.1002/acr.22233
Singh JA, Lewallen DG. Are outcomes after total knee arthroplasty worsening over time? A time-trends study of activity limitation and pain outcomes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014 Dec 17 15:440. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-440. PMID: 25519240 PMCID: PMC4301928.
Chris Centeno, MD
If you have questions or comments about this blog post, please email us at