Inner Knee Pain Chart
This chart helps understand the various concerns in the inner knee or the medical knee region.Ã
Medial Collateral Ligament Injury
This injury is similar to an ACL or a PCL, where the Medial Collateral Ligament tears due to extreme stress on the region. It is one of the important ligaments in the knee that aids stability. This can impact movement and cause severe pain and lack of mobility in the knees.
In this condition, the cartilages begin to degenerate, resulting in more friction, collection of synovial fluid in the joints, and reduced mobility and stiffness. It can be painful and take time to heal.
Pain Gradually Came On
A gradual onset of knee pain usually indicates an underlying problem that may have been there for a while without you realising. Sometimes, the knee will cope with a developing problem for so long, and then for no obvious reason will start being uncomfortable. It may be knee arthritis, tendonitis, bursitis or wear and tear
In theCommon Knee Conditionssection we look at common knee problems, what causes them, typical knee symptoms and how to treat them.
Knee injuries are often caused by:
- A Force Through The Knee e.g. from a fall or a tackle or
- Sudden Deceleration e.g. stopping suddenly causing the leg to bend too far backwards
- Twisting e.g. skiing
These most commonly result in knee injuries to theligaments and/or cartilage.Pain is usually instant, or certainly comes on within 24-48 hours and may be accompanied by swelling and bruising.
Visit theCommon Knee Injuriessection to find out more including symptoms and treatment options for different injuries to help you make an accurate knee pain diagnosis.
How Are Knee Problems Diagnosed
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, other tests for knee problems may include:
-
X-ray. This test uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging . This test uses large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body can often determine damage or disease in a surrounding ligament or muscle.
-
Computed tomography scan . This test uses X-rays and computer technology to make horizontal, or axial, images of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
-
Arthroscopy. A minimally-invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used for conditions of a joint. This procedure uses a small, lighted, optic tube , which is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen used to evaluate any degenerative or arthritic changes in the joint to detect bone diseases and tumors to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation.
-
Radionuclide bone scan. A nuclear imaging technique that uses a very small amount of radioactive material, which is injected into the patient’s bloodstream to be detected by a scanner. This test shows blood flow to the bone and cell activity within the bone.
Recommended Reading: Can I Run After Knee Replacement
Brief Anatomy Of The Knee
The knee is a vulnerable joint that bears a great deal of stress from everyday activities, such as lifting and kneeling, and from high-impact activities, such as jogging and aerobics.
The knee is formed by the following parts:
-
Tibia. This is the shin bone or larger bone of the lower leg.
-
Femur. This is the thighbone or upper leg bone.
-
Patella. This is the kneecap.
Each bone end is covered with a layer of cartilage that absorbs shock and protects the knee. Basically, the knee is 2 long leg bones held together by muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
There are 2 groups of muscles involved in the knee, including the quadriceps muscles , which straighten the legs, and the hamstring muscles , which bend the leg at the knee.
Tendons are tough cords of tissue that connect muscles to bones. Ligaments are elastic bands of tissue that connect bone to bone. Some ligaments on the knee provide stability and protection of the joints, while other ligaments limit forward and backward movement of the tibia .
Why Should I See A Pain Management Specialist
Pain management is an important part of any treatment plan, both for lessening discomfort and aiding in recovery. Pain management specialists understand the full range of pain relief options and how to use these options in combination. Treatments done as part of a comprehensive, multimodal plan may help even if each treatment does not seem to make a difference when used in isolation.
Pain management specialists work with patients to help diagnose pain and treat it safely and effectively with as few side effects as possible. These treatments do not have to involve medication. In fact, pain management is generally more successful when a comprehensive approach is used, with or without medications.
You May Like: How To Tell If You Tore Something In Your Knee
What Are The Complications Of Knee Pain
Frequently, knee pain will disappear without ever finding a specific cause. Depending on the underlying cause of the pain, the condition can progress and lead to more serious injuries or complications. Usually, these complications are long-term and result in worsening pain or an increasing difficulty to walk.
Understanding Knee Pain Diagnosis
Understanding what is causing your knee pain is the first, crucial step to overcoming knee pain. The knee pain diagnosis chart options here are very useful visual tools to help you work out what is wrong.
You can find out loads more about these conditions, the causes, symptoms and treatment options, by using the links above. Alternatively, if you want some more guidance, visit the knee pain diagnosis section.
Some useful articles that go alongside our knee pain diagnosis charts are:
- Calf Pain: lower leg
There are lots of other causes of knee pain that don’t appear on either of these knee pain diagnosis charts e.g. gout knee. They tend to cause more general, widespread knee pain, rather than pain in a specific locations so haven’t been included here on these knee pain diagnosis chart. You can find out more about them in the common knee conditions section.
Read Also: What Muscles Are Cut During Total Knee Replacement
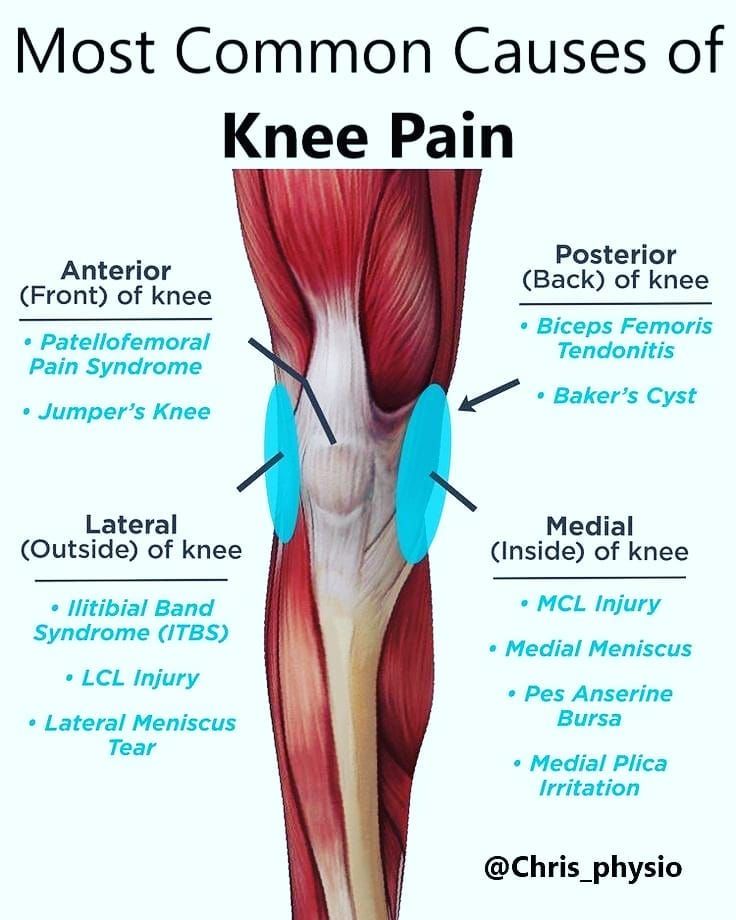
Lateral Knee Pain Location Chart
- Above the knee joint line: pain on the outside of the knee can be related to iliotibial band pain syndrome, and this is felt above the joint line into the outer side of the thigh, but can sometimes continue along the outside of the knee to just below the joint line.
- At the knee joint line: injury to the lateral meniscus or lateral collateral ligament will be felt along the joint line of the knee.
- Below the knee joint line: a calf injury can be felt on the outside of the knee, but located to the back and below the joint line.
- Quadriceps tendinopathy can sometimes be described as being on the outside of the knee but is usually more focused at the front of the knee at the superior pole of the patella.
A Pain Behind The Knee
- Bakers Cyst: Most common cause of pain and swelling behind the knee. Inflammation of the popliteal bursa. LEARN MORE>
- Arthritis: Degeneration of the knee cartilage and bones causing pain and stiffness, especially in the morning. LEARN MORE>
- ACL Tear: Injury to the anterior cruciate ligament from twisting or force through the knee. Usually associated with knee instability. LEARN MORE>
- PCL Tear: Injury to the posterior cruciate ligament – less common than ACL Injury. Typically injured in RTA, fall or sports. LEARN MORE>
- Hyperextension Injury: Where the knee bends too far backwards causing pain, swelling and restricted movement. LEARN MORE>
Also Check: Homemade Dog Knee Brace For Luxating Patella
What Are Knee Pain Symptoms And Signs
- Chronic use/overuse conditions: osteoarthritis, chondromalacia, IT band syndrome, patellar syndromes, tendinitis, and bursitis
Below is a list of some of the more common causes of knee pain. This is not an all-inclusive list but rather highlights a few common causes of knee pain in each of the above categories.
Acute knee injuries
Fractures: A direct blow to the bony structure can cause one of the bones in the knee to break. This is usually a very obvious and painful knee injury. Most knee fractures are not only painful but will also interfere with the proper functioning of the knee or make it very painful to bear weight . All fractures need immediate medical attention. Many fractures require significant force, and a thorough examination is performed to detect other injuries.
Ligament injuries: The most common injury is the ACL injury. An ACL injury is often a sports-related injury due to a sudden stop and change in directions. The remaining ligaments are injured less frequently.
Meniscus injuries: The menisci are made of cartilage and act as shock absorbers between bones in the knee. Twisting the knee can injure the meniscus.
Dislocation: The knee joint can be dislocated, which is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. Knee dislocation can compromise blood flow to the leg and have other related problems. This injury often occurs during a motor-vehicle accident when the knee hits the dashboard.
Medial Collateral Ligament Damage
One of the four ligaments that contribute to the stability of the knee joint is the medial collateral ligament. A knee ligament injury is one of the most common types of injuries to the knee. In most cases, ligament damage occurs as a result of an outward force acting on the joint in a lateral direction. The most common symptoms are pain, stiffness, and bruising.
Don’t Miss: How To Size Knee Sleeves
Possible Causes Of Pain
Quadriceps tendonitis this is caused by the irritation, strain or injury to the quadriceps tendon.
Patellofemoral Arthritis
This affects the underside of the kneecap and the trochlear groove in the femur in which it moves. When the articular cartilage covering the surfaces of the bone wears away and becomes inflamed the bones come into contact with each other resulting in pain.
Plica Syndrome
A plica is the fold in the thin synovial membrane that lines the knee joint. There were four of these folds in the knee joint originally, but they often become absorbed during foetal development. About 50% of the population is thought to have the remains of the embryonic plicae. When a plica becomes inflamed, perhaps because of repetitive knee movement, trauma or twisting, it causes pain and weakness in the knee.
Lateral patellar facet overload syndrome
This refers to dull aching pain underneath, around the sides or below kneecap. It is caused by increased pressure on the lateral facet of the patella. The reason for this is improper tracking, poor alignment or dislocation of the kneecap. The condition is often apparent during repetitive exercise such as climbing stairs.
Synovitis
Types Of Pain: How To Identify Pain And Take Action
According to the CDC, roughly 20.4% of adults in the US experience some form of chronic pain and an additional 8% suffer from high-impact chronic pain. Thats nearly 70 million people and this does not include other common types of pain like acute and neuropathic. Understanding and identifying your type of pain in order to communicate with your healthcare provider can be a difficult task for some, but is a vital step towards getting relief.
Dont Miss: Nano Knee Cost
Recommended Reading: How To Alleviate Knee Pain
Can Knee Pain Come Back After Treatment
Frequently, knee pain will occur for a short period of time and then resolve. Sometimes it can return a few weeks or months later. For chronic knee pain, it is important to get it evaluated to avoid further damage to cartilage, bones, or ligaments. Prognosis depends on the underlying causes of the pain.
With modern surgical techniques, its possible to relieve many of the knee pain syndromes and return to an active lifestyle.
Pain Located At The Top Of The Knee
Pain at the top of the knee, particularly pain felt when walking down a flight of stairs, is often the result of:
- Bursitis: This is the inflammation of the bursae commonly caused by an acute knee injury, a repetitive overuse injury, or a systemic inflammatory condition like rheumatoid arthritis or gout.
- Chondromalacia: This is the deterioration of the patella, also known as “runner’s knee,” most commonly caused by repetitive stress.
- Knee osteoarthritis: Thi is a non-inflammatory form of arthritis, also known as “wear-and-tear” arthritis. Arthritis in the patellofemoral compartment of the knee capsule, between the patella and femur, commonly causes upper knee pain.
- Patella tracking syndrome: This is a condition often due to a traumatic injury that causes the patella to shift out of place as the leg is bent or straightened.
Read Also: What Doctor To See For Knee Joint Pain
B Pain In The Back Of The Knee
The following are possible knee pain diagnoses that may cause pain in the back of the knee:
1. Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury
The posterior cruciate ligament is another major ligament inside the knee. Its situated behind the ACL. While injury to the PCL is not as common, it still can occur.
A PCL injury will more commonly occur with injury to another of the knee ligaments.
Athletes involved in contact sports are most susceptible to injuring the PCL, such as with soccer and football however, any type of trauma or stress to the ligament can potentially cause a PCL injury.
The PCL can experience a mild sprain, partial tear or complete tear.
Symptoms:
Depending on the cause of the PCL injury and severity of it, pain may come on immediately or gradually. If it is gradual, it will tend to worsen over time if not treated properly.
You may notice pain and stiffness in the back of the knee, reduced knee range of motion, feeling of instability in the knee, difficulty with weight bearing activities such as walking and climbing stairs, and swelling.
2. Hamstring Tear
Any hamstring muscle is susceptible to a tear: biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus. The hamstrings connect to the back of the knee and hip via their tendons.
A hamstring tear is very common in athletes but can also occur outside of a sports injury.
Repetitive stress over time, such as with runners or dancers, can cause a tear to occur.
Symptoms:
3. Hamstring Tendonitis
Symptoms:
4. Hamstring Tendon Strain
What Natural Home Remedies Relieve Knee Pain
Over-the-counter pain medications can frequently alleviate the pain. If someone is taking these medications on a regular basis, he or she should see a health care professional to evaluate the knee pain for proper diagnosis and to avoid the potential side effects of chronic medication use.
- The RICE mnemonic is often helpful, especially for minor injuries:
- Rest: Rest the joint, and take a break from your usual activities involving the knee joint.
- Ice: Applying ice can help with pain and inflammation.
- Compress: A compression bandage can help prevent swelling and help knee alignment. It should not be tight and should be removed at night.
- Elevate: Elevation can help with swelling and resting of the knee.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Extreme Pain Behind The Knee
Facts You Should Know About Knee Pain
- Knee pain is a common problem with many causes, from acute injuries to complications of medical conditions.
- Knee pain can be localized to a specific area of the knee or be diffuse throughout the knee.
- Knee pain is often accompanied by physical restriction.
- A thorough physical examination will usually establish the diagnosis of knee pain.
- The treatment of knee pain depends on the underlying cause.
- The prognosis of knee pain, even severe knee pain, is usually good although it might require surgery or other interventions.
Dont Miss: Best Knee Brace For Basketball Meniscus
What Is The Treatment For Knee Pain
Treatments for knee pain are as varied as the conditions that can cause the pain.
Medications
Medications might be prescribed to treat an underlying medical condition or for pain relief.
If you are taking over-the-counter anti-inflammatory pain medications regularly for your knee pain, you should see your doctor be evaluated.
Physical therapy
Sometimes physical therapy sessions to strengthen the muscles around the knee will make it more stable and help guarantee the best mechanical movements. Working with a physical therapist can help avoid injuries or further worsening of an injury.
Injections
Injecting medications directly into your knee might help in certain situations. The two most common injections are corticosteroids and lubricants. Corticosteroid injections can help arthritis and other inflammations of the knee. They usually need to be repeated every few months. Lubricants that are similar to the fluid already in your knee joint can help with movement and pain.
Also Check: What Causes Pain On The Inside Of The Knee
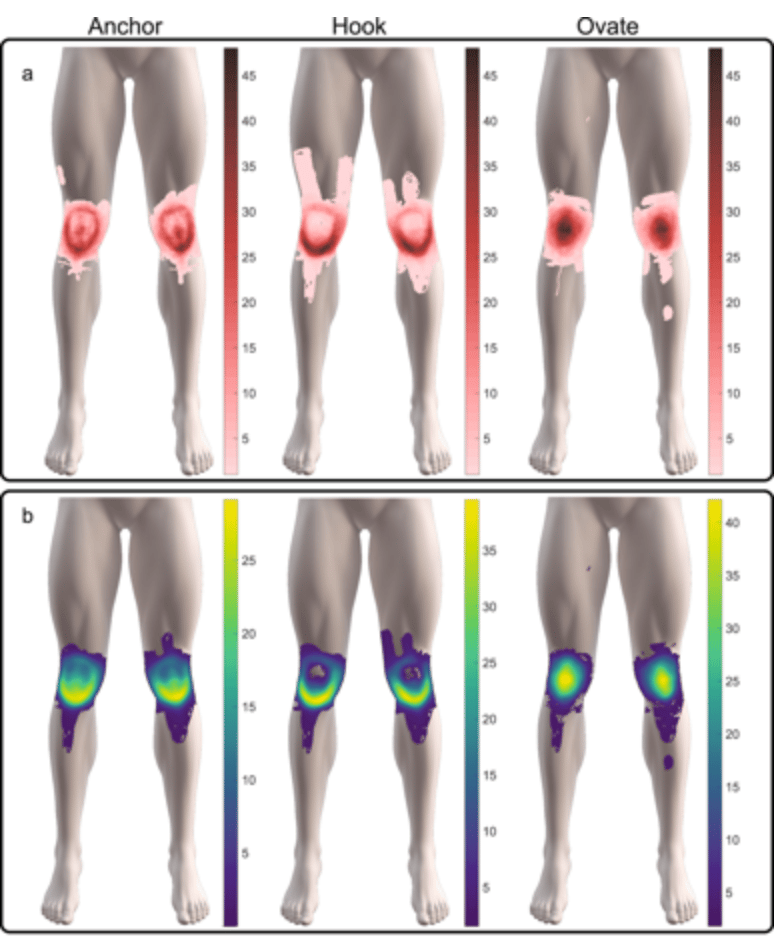
Mapping Knee Pain Is A Reliable Way To Identify Pain Location And Pattern
2019 – 201220192018201720162015201420132012201120102009200820072006200520042003200220011999
Being able to put a finger or two – or even the palm of your hand – on the source of your knee pain may one day be able to help your doctor identify its cause and determine appropriate treatment for it, says C. Kent Kwoh, MD, who led a study to better understand the localization and patterns of pain in knee osteoarthritis .
Supported in part by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases , the study involved 799 participants from the University of Pittsburgh Osteoarthritis Initiative Clinical Center who had experienced knee pain in the past 12 months. Participants were interviewed and assessed by trained interviewers who recorded their responses on the Knee Pain Map, a diagram consisting of an artist’s drawing of the seated participant’s knees from the examiner’s point of view.
The researchers found that participants with knee pain could identify pain locations and patterns and that trained examiners could reliably record the location of knee pain using the Knee Pain Map. “To our knowledge, this is the first study that allowed patients to either point to an area or cover a region that hurt, giving the patient the responsibility of identifying their pain as being in a specific location versus a more general region,” Dr. Kwoh and his colleagues wrote in the journal Arthritis & Rheumatism.
# # #