Personalized Exercise And Weight Loss
Although different types of exercise have similar pain-relieving effects,, exploratory analyses suggest potential benefits to targeting deficits in individual patients with specific exercises. A patient suffering from varus thrust during walking is likely to benefit from neuromuscular exercise, whereas an obese patient with muscle weakness is likely to benefit from strength training. Strategies for weight loss and exercise, as well as the use of appliances for biomechanical modification, should be tailored to the individual patient, rather than using a ‘one size fits all’ approach.
Joint Stiffness For Less Than 30 Minutes
This is a feeling of tightness on your knee that often limits your range of motion. Some people may have mild swelling as well.
For people with osteoarthritis of the knee, this stiffness tends to be present after periods of inactivity, like after sleeping. It goes away in half an hour or less, though.
However, if youve had +30 minutes of morning stiffness for a few days in a row, it might not be knee osteoarthritis. Please visit your doctor to find out whats going on.
How To Prevent Osteoarthritis In Knees
HelloI am a 29 yo male and I love to play basketaball. In 2008, I had an ACL reconstruction surgery of my left knee. A few months ago, i began to have swelling in my left knee. Doctor I went to recommended an MRI. The MRI revealed that I had a markedly diminutive medial meniscus and an oblique tear in the posterior horn of my lateral meniscus. It also showed that I had degenerative changes beginning in my knee. I love to play sports and lift weights. I am afraid that if I continue to play and compete the way i do I will end up with osteoarthritis which will limit my activities. Is there anything I can do to prevent osteoarthritis and still play and lift weights. I heard about the MACI cartilage repair procedure and Meniscus Transplant Are these probable options for me?
Interested in more discussions like this? Go to the Bones, Joints & Muscles group.
Hi and welcome to Connect. That must be frustrating to have those injuries affect your ability to live the active lifestyle you want to live.
I would like to introduce you to and may be able to offer you support as they have experience with osteoarthritis
Back to you , what has your doctor suggested you do to stave off the osteoarthritis?
These days I have read that meniscus surgery is not done as frequently, supposedly PT is just as effective!
I would like to introduce you to and may be able to offer you support as they have experience with osteoarthritis
Read Also: Does Aflac Pay For Sprains
Articles On Knee Pain
You can do many things to help knee pain, whether it’s due to a recent injury or arthritis you’ve had for years.
Follow these 11 dos and donâts to help your knees feel their best.
Donât rest too much. Too much rest can weaken your muscles, which can worsen joint pain. Find an exercise program that is safe for your knees and stick with it. If you’re not sure which motions are safe or how much you can do, talk with your doctor or a physical therapist.
Do exercise. Cardio exercises strengthen the muscles that support your knee and increase flexibility. Weight training and stretching do, too. For cardio, some good choices include walking, swimming, water aerobics, stationary cycling, and elliptical machines. Tai chi may also help ease stiffness and improve balance.
Donât risk a fall. A painful or unstable knee can make a fall more likely, which can cause more knee damage. Curb your risk of falling by making sure your home is well lit, using handrails on staircases, and using a sturdy ladder or foot stool if you need to reach something from a high shelf.
Do use “RICE.” Rest, ice, compression, and elevation is good for knee pain caused by a minor injury or an arthritis flare. Give your knee some rest, apply ice to reduce swelling, wear a compressive bandage, and keep your knee elevated.
Don’t overlook your weight. If you’re overweight, losing weight reduces the stress on your knee. You donât even need to get to your “ideal” weight. Smaller changes still make a difference.
How Will It Affect Me

If you have osteoarthritis of the knee, you will probably feel your knee is painful and stiff at times. It may only affect one knee, especially if youve injured it in the past, or you could have it in both. The pain may feel worse at the end of the day, or when you move your knee, and it may improve when you rest. You might have some stiffness in the morning, but this wont usually last more than half an hour.
The pain can be felt all around your knee, or just in a certain place such as the front and sides. It might feel worse after moving your knee in a particular way, such as going up or down stairs.
Sometimes, people have pain that wakes them up in the night. Youll probably find that the pain varies and that you have good and bad days.
You might find you cant move your knee as easily or as far as normal, or it might creak or crunch as you move it.
Sometimes your knee might look swollen. This can be caused by two things:
- Hard swelling: when the bone at the edge of the joint grows outwards, forming bony spurs, called osteophytes .
- Soft swelling: when your joint becomes inflamed and produces extra fluid, sometimes called an effusion or water on the knee.
Sometimes osteoarthritis of the knee can cause the muscles in the thighs to weaken, so your leg may look thinner. This weakness can make the joint feel unstable and could cause the knee to give way when you put weight on it.
Read Also: Bleach Dark Knees
Dont: Ignore New Or Worsening Knee Osteoarthritis Symptoms
Knee osteoarthritis is a chronic condition, which means that pain is always possible, Pisetsky says. However, if pain grows more severe and occurs at rest instead of after periods of activity, or if it awakens you from sleep, it could mean that your knee osteoarthritis is progressing, he says. Other symptoms such as swelling, a locked knee, or one that just gives way are concerning, too. Let your doctor know about new or worsening symptoms, as an adjustment to your treatment plan may be necessary.
Exercise And Sports In The Prevention Of Oa
In summary, investigations on the effectiveness of exercise in the prevention of OA have revealed some interesting facts. Animal studies and clinical trials clearly showed a protective effect of exercise on joint cartilage, thus perhaps reducing the likelihood for developing OA. Furthermore, an anti-inflammatory environment was found in OA knee joints upon exercise. Assuming that the same environment exists in a healthy joint under the same conditions exercise might be very effective in preventing the onset of disease. However, to fully understand the protective effects of exercise on the development of OA, further clinical and molecular studies are needed.
Also Check: Does Aflac Cover Hysterectomy
Knee Osteoarthritis: How To Avoid Knee Replacement
- New Regeneration Orthopedics
- May 19, 2021
By age 60, an estimated 10 percent of men and 13 percent of women have knee arthritis. This means you will have to curtail or avoid the activities you love . For many, it also means relying on over-the-counter pain medications, toxic steroid injections, dangerous narcotics, knee arthroscopy, or knee replacement surgery. But new advancements in regenerative procedures using your own bone marrow concentrate containing stem cells offer hope, healing, and pain relief for arthritis of the knee.
Osteoarthritis literally means inflammation of a joint. The problem is that it is really misnamed, unless we are discussing Rheumatoid Arthritis , which IS an inflammatory condition. The discomfort we feel is usually the result of the degeneration of the structures in the knee.
Common symptoms for knee arthritis include:
- Tenderness and swelling of your knee especially after activity.
- Instability. If untreated, knee arthritis can create weakness and instability in your knee. This can cause your knee to lock or buckle with weight-bearing.
- Reduced range of motion in your knee when doing everyday activities.
If you are diagnosed with knee arthritis, you will likely be recommended a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle modifications:
- Losing weight if youre overweight
- Acupuncture, topical creams, and ice packs
- Low-impact exercise/physical therapy
More aggressive treatments include:
What Are The Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis In The Knee
Pain is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis in the knee. Your knee might hurt when you move it, or even when you are just sitting still. Other symptoms are:
- Your knee feels stiff, particularly when you first get up or when youve been sitting for a long time.
- Your knee looks swollen or feels puffy.
- You hear a cracking or grinding noise when you move your knee.
- Your knee feels wobbly, as if it could buckle or give out.”
- Your knee might lock up, or feel as if it is stuck.
Recommended Reading: Roller Knee Walker
What The Studies Show
In a 2011 study published in the Journal of Biomechanics, Shull and his colleagues retrained nine healthy people without osteoarthritis to shift their gait.
They had the participants walk on a treadmill while wearing equipment that measured the forces on the knee and gave feedback on how they were walking. With the feedback, participants were able to learn how to shift weight to different parts of the knee. The pressure on the medial compartment was reduced by 20%. A knee brace can reduce pressure by 1015% and foot orthotics can reduce pressure by 510%.
Once Shull and his colleagues established that the technology could help healthy people learn new walking patterns, they decided to test it on people with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis.
The 2013 study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research, looked at 10 people with medial compartment knee OA and self-reported pain. They participated in weekly gait retraining sessions for six weeks. Their scores for pain and function improved by 29% and 32%, respectively.
Researchers at University of British Columbia and University of Melbourne have also been studying how changes in gait may lessen knee burden. In a 2012 study published in Arthritis Care and Research, they taught 22 participants with knee OA to shift their trunks toward their damaged knee. Although the greater the lean, the less pressure on the inner joint, participants had a tough time learning the new walk and initially at least, found no pain reduction.
How Does Osteoarthritis In The Knee Affect My Body
Knee pain is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis in the knee, making it painful for you to jog, run, climb stairs or kneel. It can also make your knees feel stiff or swollen. Over time, osteoarthritis of the knee can change the shape of your knee joint, making your joint feel unstable or wobbly.
Don’t Miss: How To Use Ginger For Knee Pain
Prevention Of Knee Oa May Start With The Young: The Role Of Physical Activity And Screening
There is circumstantial evidence that knee OA prevention might start in childhood. The benefits of physical activity in childhood on bone mass persist into adulthood , but the effect on joints and cartilage is less well known. An MRI study of children aged 9 to 18 years found younger children, males and those undertaking more vigorous sports have substantially higher articular cartilage accrual rates . While there are limitations to the available studies, the current evidence supports a prescription of vigorous physical activity for optimum joint development in children . Vigorous activity would also reduce childhood and possibly adult obesity – a leading risk factor for knee OA .
Citing the evidence that childhood and adolescent exercise and joint injury have long-term effects in adulthood, Nicholson and colleagues have recently proposed a screening program of adolescents covering sports and activities, joint injury, body mass index and family history. There is evidence that screening may identify athletes at future risk of ACL rupture through assessment of neuromuscular activation in the lower limb and core and trunk control , and standardized functional movement testing .
The identification of adolescents with early knee injury and those with potential neuromuscular and other risk factors might permit targeting of at-risk groups for exercise interventions, activity modification and education that may have an impact on prevention of knee OA, but this needs study.
Are There Complications Of Osteoarthritis
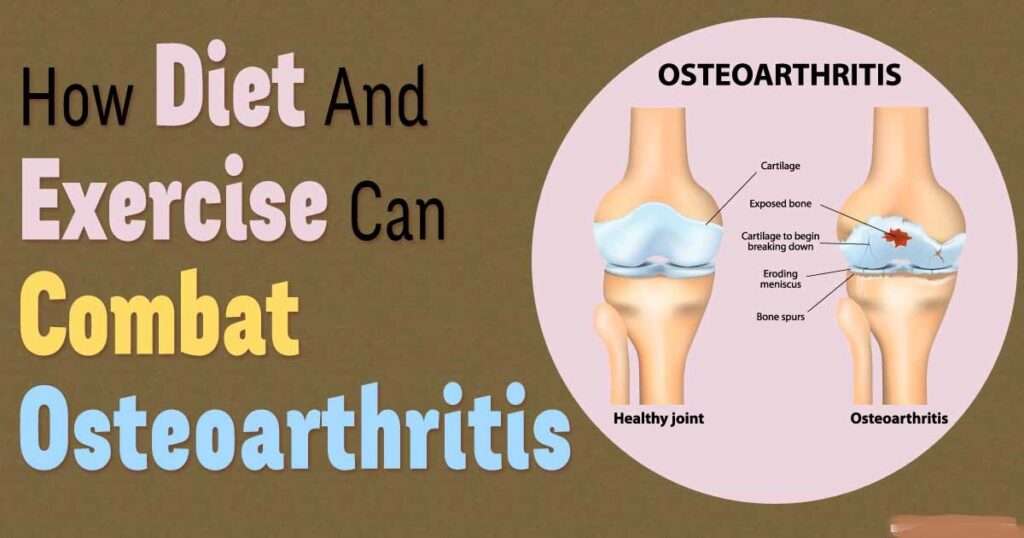
For many people, living with osteoarthritis will not cause major problems. However, complications that may arise from severe osteoarthritis include:
- deformity due to swelling of the joint
- poor sleep due to pain
- reduced ability to exercise
- restrictions performing daily tasks
As osteoarthritis is a long-term condition, you may feel anxious, frustrated or upset about how it is affecting your life. Talk with your doctor or a friend you trust if you need help and support.
Read Also: Whiten Knees Fast
Are There Any Complications
Osteoarthritis can develop over just a year or two, but more often its a slow process over many years that only causes fairly small changes in just part of the knee.
But in some cases, the cartilage can become so thin that it no longer covers the ends of the bones. This causes them to rub against each other and eventually wear away.
The loss of cartilage, the wearing of the bones, and the bony spurs can change the shape of the joint. This forces the bones out of their normal positions, making your knee feel unstable and painful.
Some people with osteoarthritis find a lump appears at the back of their knee. This is called a Bakers cyst or popliteal cyst.
A Bakers cyst is fluid-filled swelling at the back of the knee that happens when part of the joint lining bulges through a small tear in the joint capsule. This can then cause joint fluid to be trapped in the bulge.
It can happen on its own, but is more likely in a knee thats already affected by arthritis. A Bakers cyst doesnt always cause pain, but sometimes they can burst so the fluid leaks down into your calf, causing sharp pain, swelling and redness in the calf.
Osteoarthritis in the knee might change the way you walk or carry your weight, and this could cause you to develop the condition in other joints, such as your hips.
What Is Knee Arthritis
Knee arthritis is inflammation and deterioration of knee joint cartilage. Cartilage is the slippery coating on the ends of bones that serves as a cushion and allows the knee to smoothly bend and straighten. Knee cartilage coats the end of the thighbone , top of the shinbone and the backside of the kneecap . When cartilage wears away, the space between the bones narrows. In advanced arthritis, bone rubs on bone and bone spurs may form.
Damage to the joint cartilage over time may result in the development or worsening of deformities of the knee, including knock knees and bowleg.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Knee Surgery
Should You Avoid Certain Exercises With Oa
Nothing is off-limits until your body says so, advises Dr. Orlandi: Dont approach your fitness routine with the idea that you just cant do something, she says. Instead, look at moderation and modification.
So if youve been a runner for years, osteoarthritis doesnt mean you have to toss away your running shoes. Instead, consider scaling back mileage or intensity to ease strain on your knees. Try other activities, too, to work different muscles.
Just listen to your body and adjust accordingly, says Dr. Orlandi. And the most important thing? Dont use osteoarthritis as an excuse to stop exercising and working your knees and surrounding muscles.
If you have pain that lasts a few days after a workout, its certainly OK to back off a little. But dont take it as a message to stop.
Giving up and throwing your hands in the air isnt the answer for osteoarthritis, says Dr. Orlandi. Build exercise and movement into your lifestyle. Youll be better off for it.
Stretching Exercises For Knee Osteoarthritis
Stretching can help minimize the loss of flexibility in and around your knee. You want to make sure youre stretching your hamstrings, quads, calves and hip flexors to help address any stiffness you might feel, says Dr. Orlandi.
Examples include:
- Hamstring stretch. Stand in front of a chair or steps. Place your right foot on the chair or step, with your heel on the surface and toes pointed up. Slowly bend forward at the waist, keeping your back as straight as possible. You should feel the stretch in the back of your thigh. Hold for a few at least 10 seconds before returning to standing. Alternate feet and repeat 5-10 times.
- Quad stretch. While standing, bend your left leg back, bringing your heel toward your butt. Grab your foot with your left hand and hold. Try to bring your left thigh back until its even with your right thigh. Hold for at least 10 seconds. Alternate legs and repeat 5-10 times.
- Calf raises. Stand on a step with your heels hanging over the edge. Rise up on your toes and then slowly drop your heels down until theyre below the level of the step. Hold for at least 10 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Give yoga a try, too, to keep your joints and muscles in tip-top shape.
Read Also: How Do I Get Rid Of Fat Around My Knees
Exercise: Rx For Overcoming Osteoarthritis
Exercising may be the last thing you want to do when your joints are stiff and achy. But exercise is a crucial part of osteoarthritis treatment in order to ease pain and stay active.
Osteoarthritis is a chronic and progressive disease characterized by loss of the cartilage that covers and protects the ends of the bones where they meet at a joint. Without this protective coating, bone rubs against bone, causing irritation and inflammation. The result is pain and stiffness in the joint and often pain in the muscles and ligaments that surround it.
Osteoarthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. Nearly equal numbers of women and men have the condition, but women tend to develop symptoms after age 55, about 10 years later than men do. It most often affects the hips, knees, spine, and hands.
Because most people diagnosed with osteoarthritis are older about half of those over 65 have it to some degree it’s long been considered a normal part of aging that reflects a lifetime of wear and tear on cartilage. But experts now know that many factors besides age are involved. Osteoarthritis risk can be inherited. An injury or disease may also kick off the deterioration. The rate of progression depends on genetics, biomechanical forces, and biological and chemical processes, all of which vary from person to person.