How Gout Treatment Prevents Disease Progression
Fortunately, in part because of its long history, gout is one of the most well-understood and most medically treatable forms of arthritis. The progression of gout is preventable by starting appropriate treatment as soon as possible, Dr. Meysami says. Uric acid-lowering agents, such as allopurinol , can decrease uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks.
During flares, gout patients can take NSAIDs or corticosteroids to calm the attack. Local steroid injections may also be given. A medication called colchicine is also often used to stop acute attacks, but its given now at a much lower dose in order to avoid side effects, including stomach upset.
After a flare ends, long-term treatment can begin. Almost all people with gout will need medication to control their urate, Dr. Fields says. To get a good outcome, people with gout need to get their blood urate level below 6.0 mg/dl and keep it there. By doing that, the body will gradually pull the urate crystals out of their joints, and the flares can stop. Tophi will also gradually disappear.
Medications called xanthine oxidase inhibitors limit the amount of uric acid your body produces. These include allopurinol and febuxostat . Colchicine, which decreases the inflammatory response to gout, may also be given along with allopurinol at the start of long-term treatment after a flare subsides.
What Are The Risk Factors For Gout
Risk factors for gout include:
- being male
- taking medications that increase water excretion by the kidneys
- being overweight
- eating a diet with a lot of meat, offal and shellfish
- having kidney disease, high blood pressure, diabetes or abnormal levels of fat and cholesterol in the blood
- drinking a lot of alcohol, especially beer, port or spirits
- going on a crash diet or fasting
- being of Maori or Pacific Islander origin, which can predispose a person to high uric acid levels
Gout is more common in men than in women, and among women it’s more common after menopause. It’s more likely to occur in older people, but can affect anyone.
It can also affect people with certain types of blood disorder and people in treatment for cancer.
Pseudogout Symptoms & Signs
Pseudogout is a type of arthritis . Pseudogout has this name because its cause and symptoms resemble those of true gout, but gout is related to the presence or urate crystals. Pseudogout is related to aging and is linked to degenerative arthritis.
Signs and symptoms of pseudogout can include
- sudden, intense joint pain,
- red or purple skin around the affected joint, and
- severe joint tenderness .
Don’t Miss: Whiten Knees Fast
How Is Pseudogout Different Than Gout
Doctors sometimes refer to pseudogout and gout as crystal-induced arthropathies, which simply means they are joint diseases caused by microscopic crystals.
The primary difference between gout and pseudogout is the type of crystals that cause symptoms:
- Pseudogout is caused by calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals, often referred to as calcium pyrophosphate crystals or CPP crystals.
- Gout is caused by monosodium urate crystals, often referred to as uric acid crystals.
Unlike pseudogout, gout is often linked to alcohol consumption, diet, excess weight, and taking certain medications.
Researchers have known about calcium pyrophosphate crystals for decades but still do not fully understand why some people who have them experience pseudogout episodes and others do not.
When Gout Becomes A Long
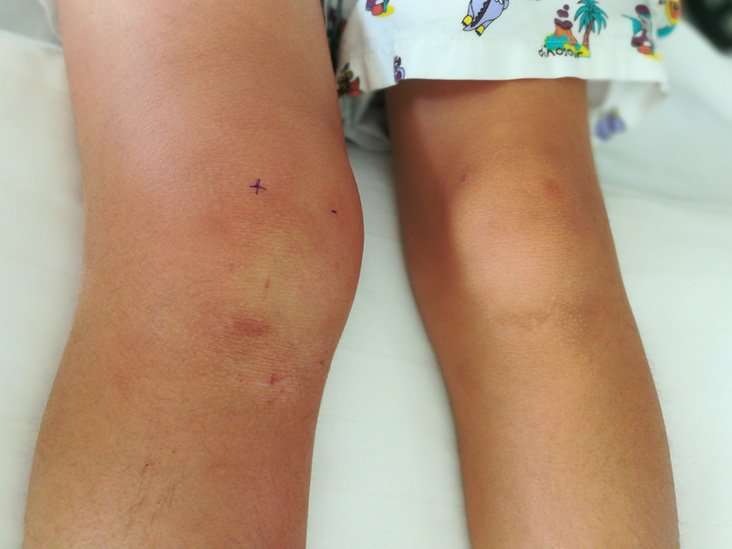
When uric acid levels in your blood stay too high, more and more crystals form around your joints. It can turn into a long-term condition, leading to painful and damaged joints.
Gout will happen differently for everyone. But signs that it may be getting worse include:
- Flares happen more often and last longer. Over time, the inflammation causes lasting damage to bone and cartilage.
- Flare-ups in other parts of your body. About half of people with gout have their first attack in the joint at the base of the big toe. When gout gets worse, it can affect other joints, including the ankle and knee.
- Bumps form under the skin. Uric acid crystals may start to collect in soft tissue, forming lumps called tophi. They often appear on the hands, fingers, elbows, and ears, but they can show up almost anywhere on the body.
- Kidney problems. Your kidneys normally get rid of uric acid in your body. But too much of it can also damage the organs. Kidney problems linked with gout — and signs that gout is getting worse — include gouty kidney, kidney stones, and kidney failure.
Read Also: Getting Rid Of Fat Around Knees
Can Pseudogout Be Prevented Or Avoided
Treatment can relieve the symptoms of pseudogout and slow or prevent damage to your joints. Unfortunately, no treatment can get rid of the crystal deposits that cause pseudogout. Taking low doses of colchicine may help to reduce your risk of future attacks. Your doctor can talk to you about the risks and benefits of taking this medicine.
If another condition, such as a thyroid problem, caused your pseudogout, treating that condition may help to make the symptoms of pseudogout less severe. It may also make flare-ups less frequent.
What Is The Prognosis Of Pseudogout
The outlook of pseudogout is generally very good. Aggressive treatment of the inflammation can lead to complete resolution of the inflammation, pain, tenderness, and loss of joint function. While this can last for weeks, the inflammation of resolves within days with proper treatment.
Recurrent attacks of pseudogout and chronic joint inflammation can lead to injury to the affected cartilage and bone.
Also Check: Can Knee Replacement Cause Neuropathy
What Are Causes Of Pseudogout
Pseudogout is primarily caused by the precipitation of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals developing within a joint space. Pseudogout has sometimes been referred to as calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease or CPPD.
Pseudogout is clearly related to aging as it is more common in the elderly and is associated with degenerative arthritis. Acute attacks of the arthritis of pseudogout can be caused by dehydration. This is particularly common in hospitalized patients and those recovering from operations, especially when associated with dehydration. Pseudogout can also be caused by the hormonal effects on calcium metabolism from hyperparathyroidism.
How Is Arthritis Of The Knee Treated
Healthcare providers can’t cure knee arthritis. But they have some tips that might reduce the severity of your symptoms and possibly stop the arthritis from getting worse, including:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise using low-impact activities instead of high-impact activities . Aim for about 150 minutes of exercise per week.
- Wear shock-absorbing inserts in your shoes.
- Apply heat or ice to the area.
- Wear a knee sleeve or brace.
- Physical therapy exercises that help with flexibility, strength and motion.
- Use a cane.
Most people have stage 4 arthritis when they get surgery.
You May Like: What Is Nano Knee Replacement
How Is Pseudogout Diagnosed
Your doctor may draw fluid from your joint to check for the crystals that cause pseudogout. X-rays might also show some buildup of crystals or signs of joint damage. Your doctor will probably want to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms, such as gout, osteoarthritis, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Acute Attack Pain Management
Home remedies. Reducing inflammation during an acute gout attack will provide pain relief.
- Ice. Apply ice to the affected area to reduce swelling. Do not apply ice directly to the skin. Use an ice pack or wrap a towel around the ice. Apply ice for about 20 minutes at a time.
- Elevate. Frequently raise and keep the affected area above the level of the heart.
- Rest. Move the affected area as little as possible while symptoms are present.
- Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines. If the gout attack is mild, anti-inflammatory drugs available without a prescription may relieve pain. Because there are serious side effect of using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs even the over-the-counter strength be sure to check with your doctor before taking them.
Prescription medications. Your doctor may recommend a prescription-strength non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine such as indomethacin.
Colchicine is also given to reduce inflammation during an acute gout attack. This drug has recently been approved by the Federal Drug Administration for treatment of gout. Like all medications, colchicine has side effects that you will need to discuss with your doctor.
Your doctor may also prescribe corticosteroids for acute gout attacks. These are strong anti-inflammatory medications that can be taken either in pill form, intravenously, or injected into the painful joint. Cortisone may improve the severe inflammation very quickly.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Knee Fat And Cellulite
What Else Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Gout
Consider asking your healthcare provider:
- What is causing the gout?
- Do I have any joint damage?
- What can I do to prevent future attacks?
- Can any gout medications help me?
- How long will I need to take gout medications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Gout is a painful form of arthritis. Extra uric acid in your body creates sharp crystals in the joints, leading to swelling and extreme tenderness. Gout usually starts in the big toe but can affect other joints. Gout is a treatable condition, and the uric acid level can be decreased by medication and lifestyle changes. Talk to your healthcare provider about medications that can reduce uric acid levels. They can also discuss changes you can make to your diet and lifestyle to prevent and reduce gout attacks.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/15/2020.
References
Symptoms And Signs Of Gout In Foot
An attack of gout is often sudden. Symptoms:
- It may present with excruciatingly painful swelling of joints in the big toe, it is known as Podagra. The joint may be stiff and appear red or purple, very swollen, and tender to even light touch. Other gout sites include the instep, wrist, ankle, fingers, and knee.
- Skin may peel and itch as healing begins.
- An attack often begins at night the acute phase lasts up to 12 hours. If untreated, the inflammation may last up to two weeks. In 10 percent of people, acute episodes present in more than one joint.
- Kidney stones precede the onset of gout in 14 percent of patients.
- Chronic gout may develop, and it may affect more than one joint, mimicking rheumatoid arthritis.
- Tophi are soft tissue swellings caused by urate buildup in chronic gout. They may be found in the ear, fingers, toes, kneecap, and elbow.
Some people have a single attack of gout, others are affected intermittently, often when they have overindulged or experienced dehydration.
COMPLICATIONS OF GOUT IN FOOT
Its rare for complications of gout to develop, but they do happen and can include severe degenerative arthritis, secondary infections, kidney stones and kidney damage, nerve or spinal cord impingement, and joint fractures.
Don’t Miss: Does Aflac Pay For Sprains
What Are The Stages Of Arthritis Of The Knee
There are five stages of osteoarthritis, the most common type of arthritis that affects your knees:
- Stage 0 . If youre at stage 0, your knees are healthy. You dont have arthritis of the knee.
- Stage 1 . Stage 1 means that youve got some wear and tear in your knee joint. You probably wont notice pain.
- Stage 2 . The mild stage is when you might start to feel pain and stiffness, but theres still enough cartilage to keep the bones from actually touching.
- Stage 3 . If youre at the moderate stage, youll have more pain, especially when running, walking, squatting, and kneeling. Youll likely notice it after long periods of rest . You’re probably in a great deal of pain because the cartilage has narrowed even further and there are many bone spurs.
- Stage 4 . Severe osteoarthritis means that the cartilage is almost gone. Your knee is stiff, painful and possibly immobile. You might need surgery.
Ways Gout And Pseudogout Are Different
Both gout and pseudogout cause sudden joint pain, swelling, and redness, making the two diseases difficult to tell apart. Understanding what makes each condition unique can help when diagnosing, treating, and preventing flare-ups, ultimately minimizing permanent joint damage.
Pseudogout is also known as acute calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis . This page describes four ways gout and pseudogout are different.
Half of all gout attacks affect the joint in the big toe. Learn more:Gout Symptoms
You May Like: What Is The Best Knee Walker
Whats The Outlook For People With Gout
Untreated gout can lead to permanent joint damage. The buildup of uric acid in the joints and soft tissue is called tophus. Some people with gout can also develop other health problems, such as severe arthritis, kidney stones and heart disease. Its important to discuss your symptoms with a healthcare provider.
Questions About Managing Gout
Treating gout includes both medication and lifestyle modifications. Knowing the right questions to ask your doctor can help you figure out the best treatment plan.
Thinkstock
Gout is a disease that can flare without warning. Asking your doctor these 10 questions can help you better manage the condition.
Why do I have gout?
Gout is caused by deposits of sharp, needle-like crystals of uric acid in the joints that create inflammation, redness, and heat around the joint, along with extreme pain. Uric acid comes from two main sources: internally from the destruction of old or damaged body cells and externally from foods, such as red meat and seafood, that contain a lot of a substance called purines.
A number of factors can increase your chances of getting gout, including genetics, gender, age, weight, and medical conditions, including hypertension. Some medications, like diuretics, can also cause gouts.
Your doctor may feel that some combination of these factors has put you at high risk, or that your diet has contributed to the problem.
What other medical conditions are linked to gout?
High uric acid levels are linked to hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol levels, and obesity. Treating these conditions may improve gout.
How long will a gout attack last and how often will I get one?
What are my gout medication options?
After the attack subsides, many people will need ongoing treatment designed to keep uric acid levels in a normal range to prevent further attacks.
You May Like: Does Copper Infused Fabric Really Work
Pain And Swelling Are Gouts Calling Cards
The most frequent signs of a gout attack are swelling, tenderness, redness, and a sharp pain in your big toe. These attacks are most common at night when you are sitting still and laying flat on your back. While gout usually manifests in the big toe, you may also experience gout attacks in your foot, ankle, or knees. The attacks can be short or long, anywhere from a few days to weeks and you may not have another attack may for months or years.
How Long Does Gout In The Knee Last
Gout flare-ups can last for several hours at a time, but you may feel pain in your knee for days or weeks. Some people only have one flare-up in their life, while others have them several times a year.
Keep in mind that gout is a chronic condition, meaning it lasts for a long time and requires ongoing management. Dietary changes and medications can make a big difference, but youll also be at risk of having a flare-up.
Keep in mind that it can also take some time to find the right combination of diet changes and medication that works for you. Dont be discouraged if things dont seem to be improving right away.
Don’t Miss: How To Whiten Your Knees Fast
How Can I Manage My Gout And Improve My Quality Of Life
Gout affects many aspects of daily living, including work and leisure activities. Fortunately, there are many low-cost self-management strategies that are proven to improve the quality of life of people with gout.
For gout in particular:
- Eat a healthy diet. Avoid foods that may trigger a gout flare, including foods high in purines , and limit alcohol intake .
CDCs Arthritis Program recommends five self-management strategies for managing arthritis and its symptoms. These can help with gout as well.
Build Muscle With Strength Exercises
Having strong muscles can protect your joint from wear and tear, especially for joints affected by gout. Beyond weight training, simple resistance exercises can be effective to build muscle. For example, try an elastic resistance band by holding each end and putting your foot in the middle, then repeat your flexibility exercises while pushing against the force of the band.
The key with any exercise after a gout flare is to go slow and listen to your body, Dr. Iversen stresses.
Also Check: Ginger Poultice For Knee Pain
How Long Does A Gout Attack Last
Gout attacks, also known as gout flares, are episodes of intense pain, similar to those described in the section about acute gout. Initially high levels of uric acid in the blood are asymptomatic as the uric acid crystals are accumulating in the joints. Acute attacks of gout appear suddenly and become worse within 5 to 8 hours. This attack is usually self-limiting, resolving in 3 to 14 days, depending on whether or not the patient receives treatment.
Thus, the natural course of a gout attack is as follows:
It usually starts late in the night or at early morning with severe joint pain
The pain increases and reaches its maximum between 5 and 8 hours after its onset
After its peak, the pain starts to alleviate in the following hours
The symptoms resolve in 3 days with treatment
In patients who do not receive treatment, gouty pain may last for up to 14 days
After the first attack, many patients may not experience a second attack for many years. But if they do, they can progress to chronic gout. Initially, there are only acute attacks until they transform into flares of gouty symptoms. As the disease progresses, the flares become longer than acute attacks, sometimes becoming a permanent flare which leads to chronicity.