What Are The Causes Of Knee Pain In Teenagers
Common knee pain problems in your teenager can be generally divided into three types:
- Anterior knee pain, also called patellofemoral pain.
- Injures to ligaments and tendons of the knee or to the kneecap itself.
- Medical conditions that affect the knee.
Anterior knee pain happens when your teens kneecap is pulled out of its groove from increased pressure. Increased pressure on the knee joint is caused by:
- Abnormal hip rotation due to imbalances in muscle strength and flexibility around the hips.
- Improper training methods or equipment.
- Poor flexibility of the thigh muscles, which support the knee joint. Thigh muscle weakness or tightness.
- Overuse of the knee from repetitive bending of the knee during running, jumping, and other activities.
- Problems with alignment, for example, the kneecap not being properly aligned within the knee or having flat feet, which changes the normal gait.
Knee pain resulting from sprains, strains and tears to ligaments and tendons or injuries to other soft tissues. These conditions include:
Medical conditions that can affect your teens knee include:
How Long Does Knee Pain In Teens Last
There is no specific duration for knee pain in teens. It may vary depending on the severity and type of underlying conditions. Knee pain due to overuse may relieve immediately with rest. Knee pain due to knee injuries, such as ligament tear, may even continue after treatment until the injury heals.
Growing pains in the knee are experienced during growth spurts in teenagers. This type of pain may resolve once the growth is completed.
Risk Factors For Knee Pain
The following factors may increase the risk for knee pain in teens .
- Overweight and obesity may increase strain on knee joints
- Lack of muscle strength and flexibility may make the knee joint unstable during motion
- Certain sports involving repeated jumps, such as alpine skiing and basketball, may increase chances of knee pain
- History of knee injury can increase the risk of knee pain and further knee injuries
Don’t Miss: What Is The Normal Range Of Motion After Knee Replacement
What Are The Symptoms Of Osgood
Symptoms are usually felt at the front of the knee and can include pain, swelling and tenderness below the kneecap at the top of the shin bone. The symptoms are aggravated by physical activity, especially when running, bending the knee, squatting, kicking and kneeling. Recent studies suggest Osgood-Schlatters affects boys and girls equally.
Prognosis Of The Growing Pains In The Knee

The prognosis of the growing pains is extremely good. With this kind of pain there is no physical harmso that the disease does not cause any consequential damage. As a rule, these are growing pains with the end of the growth phase, the end of puberty, completed.
In order to prevent the pain from becoming chronic, care should be taken to ensure adequate therapy and that the child’s symptoms are taken seriously during the pain phases. In this way you can ensure that the child processes the growing pains well psychologically and that no secondary symptoms develop.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Knee Pain When Bending
Sally S Harris Md Mph
Palo Alto Medical Foundation
Growing pains are just that pain children experience as they grow. They occur in children ages 3 to 12, are harmless and do not affect the growth of children who have them. About 10 to 20 percent of growing children get growing pains, and they are somewhat more common in girls.
Despite the name, growing pains do not occur during the time of most rapid growth, such as the adolescent growth spurt, or at specific sites of growth, says Sally S. Harris, M.D., a pediatric sports medicine specialist at the Palo Alto Medical Foundation.
About one-third of children with growing pains also experience other forms of recurring pain, such as headaches or stomach aches, she says.
Growing pains also have other characteristics:
If you want to relieve your childs pain, you can briefly rub the area, use a heating pad if needed, and be reassuring, Dr. Harris says. But, be sure to avoid giving medication or focusing undue attention on the issue that may promote attention-getting behaviors.
A child with growing pains will have normal physical exam results, as well as X-rays and lab tests. But, if any of the following are present, causes other than growing pains should be evaluated:
- Fever, weight loss and other symptoms of general illness
- Pain specific to a single joint
- Pain that worsens with time
- Pain that interferes with usual daytime activities
Knee Pain In Kids: The Ultimate Growing Pains
As a teenager, theres a lot of stress and pressure when it comes to school, sports, a social life, family life, etc. With all that going on, the last thing anybody wants to deal with is growing pains. The term growing pains is used a lot but there arent many painful conditions specifically caused by growth. What we are going to cover today is one of those conditions.
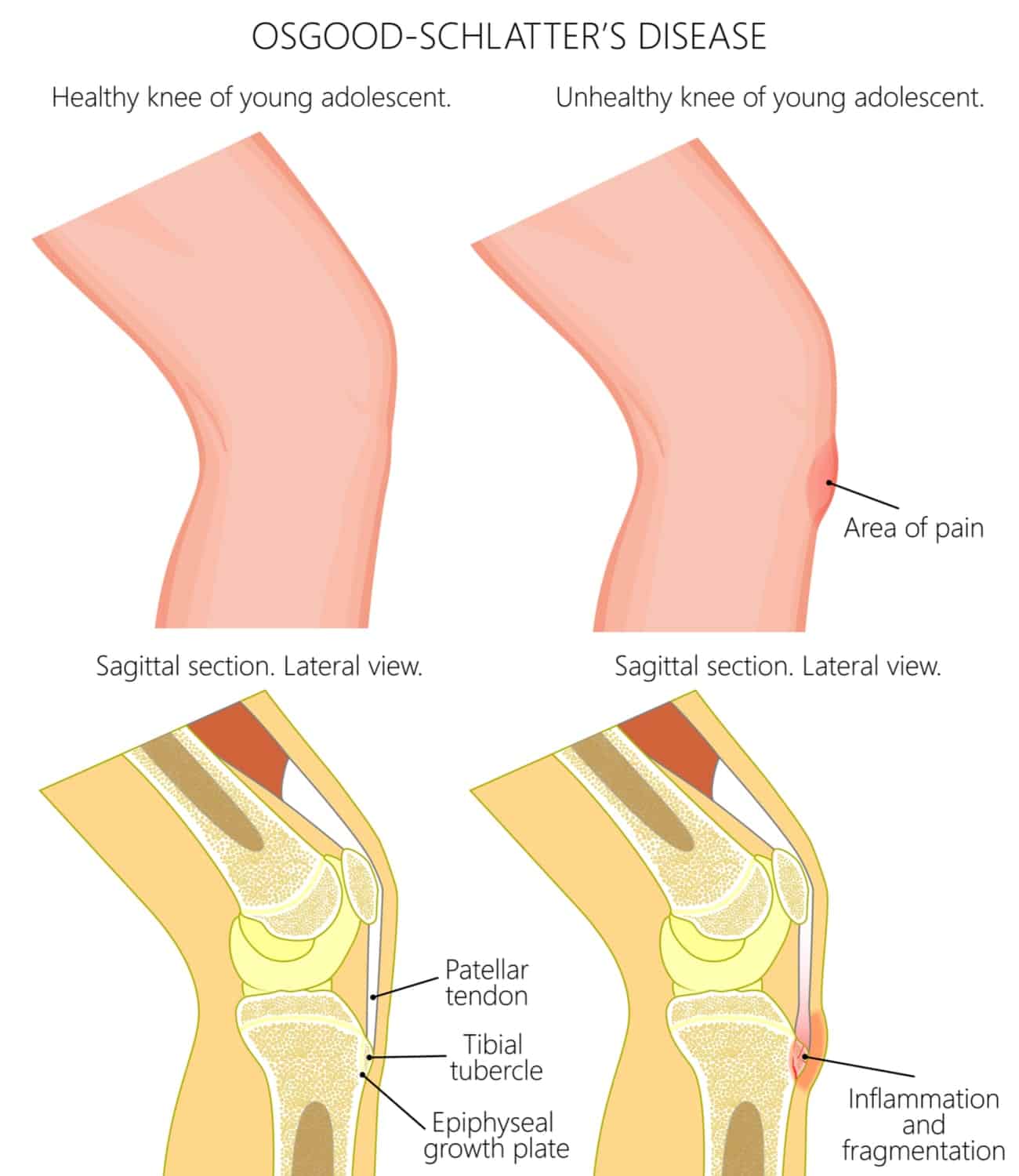
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a condition that effects one or both knees in growing childrenand young adults. There are more than 200,000 cases reported every year. The primary age group effected by this condition is 14-18 years old, followed up by ages 6-13. When present, the child will feel a lot of pain just under the kneecap and will have a lot of trouble with any jumping or running activities.
What exactly is Osgood-Schlatter disease? What causes it and what can we do about it?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is characterized by a painful lump present below the kneecap in children and adolescents. Below the kneecap there is a large bump on the front of your shin bone, known as the tibial tuberosity. This bump is where the tendons from your knee cap attach. During growth and development, this tendon can become irritated and painful. You may also notice redness and swelling just below the kneecap. This condition is most common when children experience a growth spurt and/or when they play sports that involves a lot of running or jumping.
How do we treat it?
Demonstration of a standing quad stretch
You May Like: Will Knee Pain Go Away
How Is Knee Pain In Teens Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will ask about your teens knee pain:
- Is there a known cause for the knee pain does it happen with certain movements or is there no specific known event?
- How long has the pain been present?
- Where on or around your knee do you feel pain?
- Does the pain wake you up at night?
Your provider will perform a physical exam, checking:
- Kneecap and knee stability.
- Alignment of lower leg, kneecap and thigh.
- Range of motion of hips and knees.
- Thigh muscle strength, flexibility, firmness.
Your provider may order imaging tests including X-rays or a CT scan or MRI .
Why Does My Knee Hurt
Anterior knee pain, or pain near the front of the knee, is one of the most common types of knee pain in teens and athletes of all ages. For young athletes this is no exception, and there are some unique causes to know about. One thing that all of these causes of anterior knee pain have in common is that they are usually OVERUSE INJURIES and can be treated and prevented without surgery.
You May Like: What Causes Your Knee To Swell
Diagnosis Of Growing Pains
- arthritis which damages joints
- infections and some virus infections
- problems that affect how the muscles work together such as knock knees and very flat feet.
- has severe pain or pain that only affects one leg , or if the pain is still there during the day
- is unwell or has a fever, loss of appetite or rashes
- has swelling, reddening or tenderness of the leg or arm
Could It Be Arthritis
Yes — it doesnât just affect older people. Itâs common for children to be told the pains in their legs are just growing pains, when they actually have juvenile idiopathic arthritis , says Richard Vehe, MD, director of the division of pediatric rheumatology at the University of Minnesota.
The symptoms can come and go, and itâs a hard disease to pin down, because itâs so unpredictable.
The biggest red flag: âGrowing pains do not involve swelling or pain in the joint,â Vehe says.
“Growing pains really shouldn’t leave lasting signs,â Homme says. They shouldnât affect your childâs movement or lower their strength.
If itâs JIA, he says, their knee will swell and stay that way for a while. The disease can also cause fevers and rashes.
The condition can have lasting effects if it goes untreated. The inflammation can cause changes in bone growth and lead to permanent problems. âMost of our current medicines can prevent or limit further damage, but they donât reverse the damage that has been done,â Lehman says.
Growing pains can also turn out to be bone tumors, both benign and malignant.
âSevere bone pain at night can be associated with a form of benign tumor called an osteoid osteoma, but can also occur with serious bone tumors. Thatâs why children with persistent or severe pain should see a knowledgeable physician and not simply be dismissed as growing pains,â Lehman says.
Show Sources
Also Check: How Do I Get My Knee To Stop Hurting
Growing Pains In Toddlers
Growing pains can start as early as 2 years old. They usually start between ages 3 and 5. Growing pains in toddlers are the same aching and throbbing as in older children.
Your child may wake up in the middle of the night because of the pain. You may notice them holding or rubbing their legs, or they may seem grumpier than normal. Gently massaging your childs leg can help ease their pain.
Treatment For Knee Pain
Treatment options may vary depending on the underlying cause of knee pain. The following treatments are usually prescribed for teens .
- Medications: Pain relievers are often prescribed for teens. Conditions such as gout and rheumatoid arthritis are also treated with medications.
- Physical therapy: This may help to strengthen the muscles by specific exercises. This may also improve flexibility and balance.
- Correction of sports techniques: If the knee pain is related to inappropriate sports techniques, your teen may feel better after correcting it.
- Arch supports: Wedges on one side of the heel may reduce pressure on the knee. This can be useful in the case of osteoarthritis.
- Knee braces: This may help support and protect the knee.
Some conditions may require direct injection of medication or other substances to the knee joint. Arthroscopic surgeries are often recommended for knee injuries.
Also Check: How Much Does Knee Surgery Cost Without Insurance
Are These Pains Associated With Growing
Because these pains most often occur during years when the childs growth is not at its fastest rate, the pains are NOT associated with growing. The name was given in the 1930s to 1940s when the pains were thought to be from faster growth of the bones when compared to the growth of the tendons. We know today that this is not true. The name has remained despite our new understanding of these pains.
Are Growing Pains Real
Growing pains isnt a good description for this condition because theyre not related to growing or a growth spurt. The name was given in the 1930s to 1940s when the pains were thought to be from faster growth of the bones than of the tendons. We know today thats not true. The name has remained despite our new understanding of these pains.
You May Like: How To Improve Knee Pain From Running
Growing Pains In Back
While back pain is a common ailment for both adults and active children, the available literature regarding growing pains does not include pain in the back. Therefore, back pain in children may be a sign of another issue.
It could be poor posture or muscle strain, but it may also be a sign of a more serious underlying disorder, especially if the pain lasts for more than a few days or gets progressively worse. See your doctor if that is the case.
When To Seek Medical Care
If the aforementioned therapies fail to provide relief, or if the pain is concerning in other ways, Dr. Kelly advises parents to enlist the help of the childs pediatricianand possibly an orthopedic specialist.
The concerning symptoms are if the pain only occurs in one leg, if its happening every single night, or if it develops at odd times in the day outside of the growing pain hours from about 8 p.m. to midnight, he explains. So, if the child is having pain in the mornings or throughout the school day, if theres any redness or swelling, or any types of deformities, then of course they should seek care sooner than later.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Arthritis In Your Knees
So What Can I Do About It
Stretch, stretch, stretch! Often times one of the major factors contributing to overuse injuries is inflexible muscles. Athletes need to pay particular attention to stretching the muscles surrounding the knees and hips specifically, hamstrings, quadriceps, hip flexors, piriformis, and calf muscles. Hold each stretch steadily for 30 seconds and repeat each 3 to 4 times.
There are also some basic strengthening exercises that can help decrease anterior knee pain:
How To Know If Your Child Has Growing Pains
Lab studies and x-rays wont help your doctor diagnose growing pains, although imaging can help rule out other, more serious conditions.
We help diagnose growing pains after an office visit and discussion with the child and parent, Dr. Weinberger explains.
The intensity and frequency of growing pains varies. They can range from feeling like a minor ache to an intense muscle cramp. But there are common factors you can expect to see:
- They occur at night or in the evening hours.
- Your child will probably feel pain in both legs or arms .
- Pain almost always includes the legs. If theres pain in the arms, it typically is in addition to pain in the legs.
- Theyre often intense enough to wake your child up.
They usually occur in the legs and last anywhere from five to 20 minutes, Dr. Weinberger says. There could be multiple nights between episodes or they could happen several nights in a row.
Also Check: How Do You Know You Have Arthritis In Your Knee
Care Advice For Leg Muscle Cramps Strains Growing Pains
Homeopathic Arnica Works Fast For Growing Pains
Lets take note before we move forward that I am not a doctor, nurse or practitioner of any kind, and Im just sharing the knowledge I have as a mom. Please take my advice as you would your neighbors or the crazy lady at your church! This post is not meant to be medical advice.
This is the little balls that my son was asking for. We have always used homeopathic arnica montana 30c as our magic growing pains balls. Arnica is said to be the first line of defense against any physical trauma. If you only have one homeopathic remedy on hand, this would be a good one.
Because this is a very quick remedy to administer, our little balls are the second option we always reach for.
To use a homeopathic remedy, you put the balls, usually 3, into the lid of the container. Try not to touch them with your fingers because the active remedy is on the outside of the ball and easily rubbed off.
Tip the contents of the lid into the childs mouth, and if they are old enough, instruct them to hold the balls under their tongue. Under the tongue is the fastest way to get the remedy into the bloodstream.
Its okay to use homeopathy even on children, and growing pains dont usually begin until at least age 2, so you dont have to worry about children younger . If the child does wake up again, you can give a second administration of the remedy as soon as 15 minutes later.
You May Like: How Can I Stop My Knee From Popping