Meniscal Cysts Vs Baker’s Cysts
Meniscal cysts are similar to popliteal or Baker’s cysts. Baker’s cysts, however, are located in the back of the knee joint.
Baker’s cysts are seen with many types of knee joint problems that lead to fluid accumulation. They can occur with meniscus tears, but also with arthritis, ligament injuries, and other problems that cause knee swelling.
My Grandfather Stated That Hitting The Ganglion With A Bible Would Make The Condition Go Away
To some extent your grandfather is correct, in that often the ganglion can be burst, resulting in the ganglion sac leaking into the soft tissue surrounding it and preventing a new ganglion forming. We would not recommend such a traumatic technique of treating a ganglion but certainly rupture of the ganglion can be successful. This is usually best done using ultrasound guidance for aspiration or surgically.
Citation Doi & Article Data
Citation:DOI:Dr Yuranga WeerakkodyRevisions:see full revision historySystem:
- Cystic lesions around the knee
- Differential diagnosis of cyst like lesions around the knee
- Cysts around the knee
- Cysts around the knee joint
There is broad differential for cyst-like lesions around the knee.
Differential diagnosis
- fibular collateral ligament-biceps femoris bursa/fibular collateral ligament)-biceps femoris bursitis
Don’t Miss: What’s Wrong With My Knee
How Is A Ganglion Cyst Diagnosed
Healthcare providers usually diagnose ganglia by physically examining you. A lumps appearance and location are telltale signs of ganglia. Your provider may press on the bump to see if it bothers you. Or they may shine a light on the lump to see if its translucent .
In some cases, your provider may remove a sample from inside the lump for further analysis. Ganglia usually contain a jellylike fluid, not solid tissue. In rare cases, your provider may recommend an X-ray to learn more about whats causing your symptoms.
Your provider may use ultrasound to tell the difference between a solid mass and a cyst. There is also a difference between a ganglion cyst and a synovial cell. The difference is in the make-up of the lining of the cyst.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have a ganglion cyst, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Do I need treatment right now?
- Which treatment options do you recommend I try first, and why?
- What are the chances a cyst will come back after treatment?
- When would you consider surgery to treat ganglion cysts?
- What are the risks and benefits of ganglionectomy surgery?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have a ganglion cyst, you may not need treatment right away. If the lump doesnt bother you, your provider may follow you over time to check for any concerning changes. Ganglion cysts are benign, which means these lumps arent cancer. They pose no long-term threat to your health. Many ganglion cysts go away on their own. If a ganglion cyst affects your quality of life in any way, ask your provider about treatment options. Splints, over-the-counter pain medication or surgery may provide relief.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/23/2020.
References
You May Like: Pain Behind And Side Of Knee
A Note About Sex And Gender
Sex and gender exist on spectrums. This article will use the terms male, female, or both to refer to sex assigned at birth. .
A ganglion cyst always forms near a joint, and a doctor can usually recognize one by examining it visually.
They may be soft or hard, and they should be able to move freely under the skin.
- Location: These cysts often occur on the top or back of the wrist. They may also appear on the palm side of the wrist, at the base of a finger, on top of a fingers end joint, or on the ankle or knee joints.
- Pain: Ganglion cysts may or may not be painful, depending on whether they press on a nerve.
- Size: This can range from the size of a pea to that of a golf ball.
The area around the cyst may feel numb. If a cyst forms on the hand or wrist, the person may lose grip strength.
Paramentic Cyst Of The Knee Joint
The paramental cyst of the knee joint is a meniscus cyst that has spread to the caapsular region and ligaments. Tumor formation reaches a large size and does not disappear when the knee is unbent. It is easy to palpate and diagnosis is not difficult. Paramentic knee cyst refers to the third degree of cystic degeneration of the meniscus and is a complex form, the treatment of which requires surgical intervention. In most cases, complex treatment, surgical intervention and subsequent physiotherapy gives a positive result and the functions of the knee joint in patients are almost completely restored, which helps a person return to a healthy and full life without restrictions. But do not forget that the paramenisk cyst of the knee joint is often a neglected form of the ordinary knee cyst, so a timely visit to the doctor, diagnosis and treatment of the disease at an early stage will avoid surgical intervention.
Don’t Miss: How To Relieve Knee Pain From Standing All Day
Who Gets Ganglion Cysts
From what the medical community understands about ganglion cysts, anyone can get them. Certain factors may increase your chances of having one of these cysts:
- Sex: Women develop ganglia three times more often than men.
- Age: For most people who develop a ganglion cyst, it appears in early to mid-adulthood, between 20 and 50.
- Previous injury: Some healthcare providers believe a joint injury could spur a ganglion cyst to develop in the future. Research hasnt proven this theory yet.
- Arthritis: Having arthritis in your hands makes it more likely youll get a ganglion cyst. People with arthritis often get a ganglion cyst near their fingertips . But having a ganglion cyst on your finger does not mean you have arthritis.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Ganglion Causing Flexion Restriction: A Case Report And Review Of Literature
Andrew Arjun Sayampanathan1, Thean Howe Bryan Koh1, Keng Thiam Lee2
1 Department of Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore
Correspondence to:
Keywords: Anterior cruciate ligament ganglion cyst flexion restriction
Submitted Apr 27, 2016. Accepted for publication May 06, 2016.
doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.05.46
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Need Knee Surgery
Symptoms Of A Ganglion Cyst
Ganglion cysts look and feel like a smooth lump under the skin.
They’re made up of a thick, jelly-like fluid called synovial fluid, which surrounds joints and tendons to lubricate and cushion them during movement.
Ganglions can occur alongside any joint in the body, but are most common on the wrists , hands and fingers.
Ganglions are harmless, but can sometimes be painful. If they do not cause any pain or discomfort, they can be left alone and may disappear without treatment, although this can take a number of years.
It’s not clear why ganglions form. They seem to happen when the synovial fluid that surrounds a joint or tendon leaks out and collects in a sac.
Joint Mobility After Treatment
Whether your ganglion cyst is aspirated or surgically removed, you will be fitted with a splint for around one week or so. Depending on the location of the excised ganglion cyst, full recovery can be anywhere from two to eight weeks. Be guided by your doctor or health care professional, but generally it is best to get the joint moving again as soon as possible. Using splints for extended periods of time can actually hamper joint mobility. Your doctor will give you specific exercises to perform.
Recommended Reading: Pain On The Left Side Of The Knee
Causes Of A Knee Cyst
With hyperproduction of the synovial fluid, it accumulates in the posterior part of the knee. The accumulation of synovial fluid in turn generates many diseases of the knee joint. The knee cyst usually appears due to these diseases. The most common cause may be rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis. Less commonly, the knee cyst arises from damage to cartilage tissue, excessive physical exertion, and traumatic injuries. The liquid that has accumulated, begins to press strongly on the nerve endings, which leads to painful sensations in the knee and restriction of movements. Sometimes the reasons for the appearance of the knee cyst remain unknown. In children, this disease is not observed often, mostly people of the older generation are exposed to it. To determine the exact cause of the knee cyst, the doctor prescribes an MRI or an ultrasound of the knee joint, and less often punctures the cyst to examine the contents. To date, the knee cyst occurs in 17% of all cases of knee disease.
Dual Acl Ganglion Cysts: Significance Of Detailed Arthroscopy
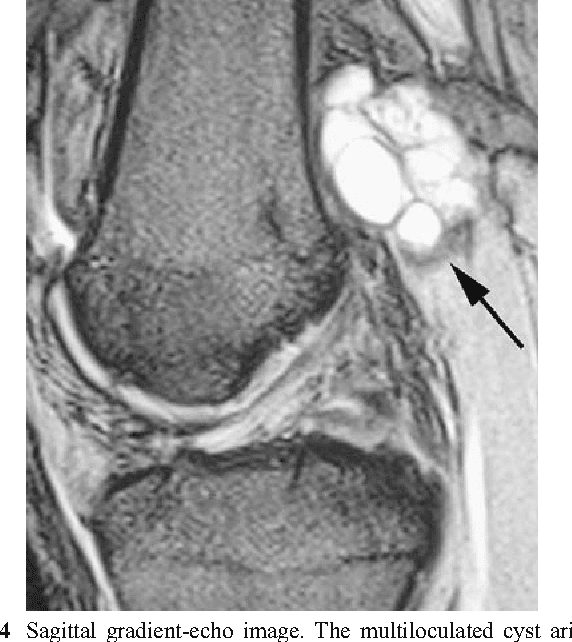
Samarth Mittal
Abstract
Intra-articular ganglion cysts of the knee joint are rare and most frequently are an incidental finding on MRI and arthroscopy. Most of the previous studies have reported a single ganglion cyst in the knee. There have been previous reports of more than one cyst in the same knee but not in the same structure within the knee. We are reporting a case of dual ACL ganglion cysts one of which was missed on radiological examination but later detected during arthroscopy. To the best of our knowledge, no such case has been reported in the indexed English literature till date.
1. Introduction
2. Case Report
A 28-year-old female presented with pain in her right knee joint for the past 18 months. She was a housewife and had a history of twisting injury to the right knee two years prior to presentation. At presentation, she had pain in the right knee, both beyond 120-degree flexion and in terminal extension. On clinical examination, there was mild wasting of the quadriceps muscle. Range of movement was full but both terminal knee flexion and extension were painful. Clinical tests for cruciate knee ligaments and meniscal injuries were negative.
Magnetic resonance imaging was reported as large lobulated multiloculated cystic lesion near the posterior aspect of the femoral attachment of ACL suggesting encysted synovial collection or cystic synovial neoplasm.
Also Check: Gucci Womens Knee High Boots
Treatment For Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts used to be treated by slamming them with a heavy book such as a Bible – which explains the term ‘Bible therapy’. This isn’t a good idea, as you could cause further injury. Medical treatment options include:
- Close monitoring – if the ganglion cyst isn’t causing pain or interfering with movement, some doctors prefer to wait and see. The cyst may simply disappear on its own.
- Needle aspiration – one of the tests to diagnose ganglion cysts involves drawing off the fluid with a fine needle. In many cases , this treatment empties the cyst and no further action is needed.
- Surgery – the cyst or cysts are surgically removed, usually by a specialist such as an orthopaedic surgeon. Ganglion cysts of the feet will usually require surgery.
Symptoms Of A Meniscal Cyst
Meniscal cysts do not always cause symptoms. When they do, the most common are:
- Pain in the knee when standing
- Tenderness directly along the joint
- A bump or lump at the cyst site, usually near the outside of the knee
- A bump that becomes more visible as the knee straightens, though the bump itself may be painless
- A bump that changes size
- Swelling or locking of the knee joint
Read Also: What’s Best For Aching Knees
Ganglion Cysts May Return
Ganglion cysts may grow back after treatment. This is less likely if your cysts were surgically removed rather than aspirated with a needle. Some estimates suggest that around half of patients who undergo needle aspiration can expect a recurrence. Since the cause of ganglion cysts is unknown, prevention is impossible. If you suspect your ganglion cyst is recurring, see your doctor for further treatment. A ganglion cyst that is aspirated three times has a better than 80 per cent chance of being cured.
How Are Ganglion Cysts Treated
Ganglia cyst treatments include:
- Anti-inflammatory medication may minimize swelling, easing mild levels of discomfort.
- Splints or braces offer support and stop you from moving the affected area, reducing swelling and pain.
- Aspiration is a procedure where your provider uses a needle to remove fluid from the cyst. Providers usually do aspiration in their office. You may feel better right away. Because this treatment only removes the fluid and not the entire cyst, your symptoms may return.
Don’t Miss: How To Sleep After Total Knee Replacement
Diagnosis Of The Knee Cyst
Diagnosis of the knee cyst is performed by a trauma doctor or orthopedist. The knee cyst is a secondary disease, therefore for the diagnosis it is taken into account the medical history, patient complaints, laboratory and instrumental methods of research. To date, the most popular and accurate methods of instrumental diagnosis are MRI and ultrasound of the knee joint, they can accurately determine the size and position of the cyst. Sometimes in very severe cases resort to the use of arthroscopic diagnosis – through a small incision with an optical tube examine the joint cavity. A popular laboratory method of diagnosis is a puncture of the knee cyst with subsequent examination of its contents. Due to accurate diagnosis and correctly diagnosed treatment of knee cyst will have a positive result.
Do All Ganglion Cysts Need To Be Treated
If a ganglion cyst doesnt bother you, it might not need treatment. Sometimes a ganglion cyst goes away on its own.
Your provider may recommend treatment if a ganglion cyst:
- Hurts, which may happen when a cyst presses against a nerve or joint tissues.
- Makes certain movements or tasks difficult, such as walking or gripping a pencil.
- Makes you self-conscious about your appearance.
Also Check: What Does Constant Knee Pain Mean
Ganglion Cysts Can Disappear
Around 30 to 50 per cent of ganglion cysts disappear by themselves without the need for medical treatment. However, it is always best to consult your doctor to make sure the lump isn’t a symptom of some other disease. If your ganglion cyst is painful, or if it interferes with your mobility or causes sensations of numbness or pins and needles, see your doctor.
Ganglion Cyst Causes And Risk Factors
The cause of ganglion cysts is not known. One theory suggests that trauma causes the tissue of the joint to break down, forming small cysts that then join into a larger, more obvious mass. The most likely theory involves a flaw in the joint capsule or tendon sheath that allows the joint tissue to bulge out.
Ganglion cysts are more common in women, and 70% occur in people between the ages of 20-40. Rarely, ganglion cysts can occur in children younger than 10 years.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Sudden Knee Pain
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Home Remedies And Tips
If a cyst causes discomfort, the following can help:
- Adapting footwear: If the cyst is on a foot or ankle, shoes should not rub or irritate it. It may help to wear soft or open shoes, insert padding, or lace the shoes in a different way.
- Immobilization: Moving the affected area may increase the cysts size. Wearing a splint or brace can help limit movement, and this may cause the cyst to shrink.
- Pain relief: If the cyst is painful, over-the-counter pain medication, such as ibuprofen, can help.
Also Check: What Causes Left Leg To Swell Below The Knee
Cyst Of Internal Knee Joint Meniscus
The cyst of the inner meniscus of the knee joint is less common than the cyst of the outer meniscus, for the reason that the lateral meniscus is more susceptible to strain. The meniscus cyst does not have the property to connect with the capsule of the joint and protrudes front or back relative to the inner lateral ligament, less often protrudes through the ligament thickness. The main and dominant symptom of the knee cyst of the inner meniscus is pain that appears when the joint is stressed and disappears at rest. When palpation is marked soreness, a dense swelling of a size of several mm to 3 or more cm. If for a long period of time there is no treatment for the knee cyst of the inner meniscus, this leads to bone tissue degeneration and, accordingly, to the development of deforming arthrosis. The most effective and popular method of treatment of the internal meniscus cyst is its removal by endoscopic arthroscopy, which is less traumatic for the joint and has a small risk of complications.
, , ,
Ganglion Cyst Of The Knee Joint
Ganglion cyst of the knee joint is not very common. This knee cyst is a benign formation that comes from the joint capsule and the tendon sheath. It is spherical or oval formations with a duct in the middle that connects the ganglion cyst with the joint capsule and the tendon sheath. These cysts are filled mainly with liquid transparent substance. When examined, the ganglion cyst is similar to a small water bag or similar to a tight and elastic tumor. The exact and unambiguous cause of the appearance of the ganglion cyst can not be named, but more often it appears in young women with hypermobility of the joint or due to traumatic joint injuries.
Don’t Miss: Can You Ski After Knee Replacement