What Are The Most Important Things A Person Can Do To Limit Chondral Or Cartilage Damage In The Knee
While there is not one specific thing that can prevent cartilage damage in the knee, there are a few measures that can be taken to delay the process.
- Since excess weight can cause damaged cartilage to wear down more quickly, losing extra pounds may be helpful.
- A person with cartilage damage should avoid high impact activities, such as prolonged running or jumping sports. These are very hard on the knee and can speed the progression of cartilage damage.
- Even those with significant joint damage will benefit from mild to moderate activities, such as walking, bicycling, or running in water.
How Are Articular Cartilage Injuries Diagnosed
Most orthopedic knee specialists, like Dr. Riley J. Williams will use an MRI Scan to diagnose an articular cartilage injury. An MRI will show him the articular cartilage surfaces and he can determine the size, shape and progression of the injury. For some patients, especially those who cannot undergo an MRI scan, a knee arthroscopy can be an excellent diagnostic tool for helping Dr. Williams visualize the articular cartilage. He can see through an arthroscope which displays images on a television-type screen and can determine the amount and type of damage.
Msc And Collagen Membrane Characterization
Bone marrow aspirates with a mean volume of 42 ± 5 mL were collected from each of 15 patients. BM-MSCs were isolated by plastic adherence and expanded in tissue-culture flasks under GMPc culture conditions. Following cell isolation, BM-MSCs exhibited spindle fibroblast-like morphology in culture , and they expressed classical MSCs surface markers, such as CD105, CD90, and CD73, in the absence of hematopoietic cell surface markers CD34 and CD45 . In each of 15 patients, the above phenotype was consistent, confirming the MSCs phenotype previously described.
Fig. 2
Representative images of cultured BM-MSCs in different states of confluence of two patients . On the left side, the confluence is about 3040%, while on the right confluence is about 80%, prior to trypsinization for use in subsequent experiments
Also Check: What Is Better For Knee Pain Heat Or Cold
What Is Cartilage Loss
Cartilage loss is defined by a decrease in cartilage volume and thickness. It occurs after cartilage wears away or deteriorates.
With the cartilage loss of severe osteoarthritis, the joint space narrows and bone rubs on bone after cartilage loss occurs . At that point, there is little or no cartilage left to do its job as a shock absorber. In the case of knees and hips, replacement surgery is the solution.
What Anchors Articular Cartilage To The Underlying Bone
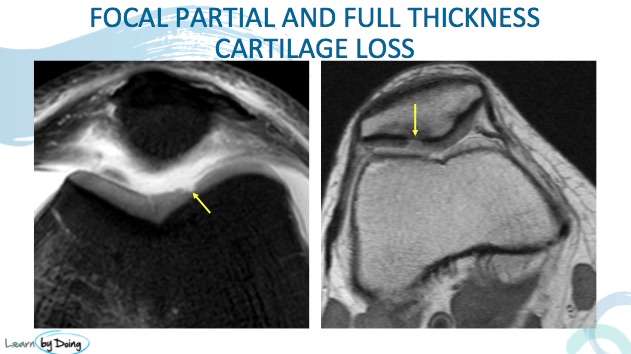
There is no true anchor of the cartilage to the underlying bone because the bone transitions ultimately into cartilage. Probably the most important layer to ensure that the cartilage does not fall off the bone is the calcified cartilage layer. This is a layer which is basically a transition zone between bone and the underlying cartilage. This layer is important to ensure that the cartilage does not shear off, or fissure, when one participates in twisting, turning, or pivoting type activities.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Inflammation In The Knee
Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Mr Manoj Sood Discusses The Options Available For Joint Preserving Knee Surgery
Every year, many people are diagnosed with cartilage damage, often as a result of injury. Articular cartilage is located at the ends of the bones that make joints in the body. When damaged, the cartilage does not heal and, in the knee, can progress to arthritis which can lead ultimately to the need for a knee replacement. More than 90,000 knee-replacement operations are performed every year in the UK.
As a result of this, there is a growing interest in joint-preserving options in a bid to repair damaged articular cartilage, relieve pain and delay the need for knee-replacement surgery.What causes damaged cartilage?
When healthy, articular cartilage allows smooth movement of the joint. When damaged through injury, a cartilage defect occurs which may involve either part or the whole thickness of the cartilage with the underlying bone becoming exposed. These cartilage defects cause the surface to become rough, damaging the joint further which may progress to painful arthritis. A number of techniques to repair cartilage are available, with this area of medicine developing rapidly as the focus shifts to prevent or delay the need for knee replacement.
If you suspect that you may have sustained cartilage damage or any problems with your joints, you should arrange an appointment with your GP or specialist, as soon as possible. Ignoring the problem could result in the injury becoming much worse and more difficult to treat.
What is joint preservation?
Chondroplasty
Microfracture
Femoral Condyle Cartilage Defect Treatment:
Treatment of cartilage defects of the femoral condyles requires a thorough workup and ensuring that the defects are truly symptomatic. An incidental finding on MRI scan may not need treatment, and close observation may be indicated in these cases. It is important that we treat the patient and not treat the MRI scan because some patients may have a cartilage defect and because they have normal strength and motion of their knee they may not have symptoms and may not have progression of the defect for a long time, if at all. Therefore, it is important to asses that these cartilage defects are causing symptoms to the patient before embarking on much bigger surgeries because the consequences of having a failed cartilage procedure are often worse than the symptoms that one has prior to having the cartilage surgery performed on a minimally or non-symptomatic knee.
For more information on femoral condyle conditions and the available treatment options for your knee pain, please contact the offices of Dr. Robert LaPrade, serving patients from the Twin Cities, Minneapolis-St. Paul, Edina and Eagan, MN.
You May Like: How Much Is Physical Therapy For Knee
What Is A Chondral Defect Or Cartilage Defect
A chondral defect refers to a specific, localized area of damage to the articular cartilage that lines the ends of the bones . Articular cartilage is the coating of the bones and allows for smooth motion between the ends of the bones. It is a common injury affecting 5-10% of people over age 40, but it can also affect young patients that experience traumatic injuries. Damage to knee cartilage can lead to osteoarthritis of the knee over time.
Focal chondral defects are graded by severity. Grade I is the mildest and grade IV is the most severe describing full thickness injury of the cartilage.
Why Do You Need Cartilage
Articular cartilage serves as the cushion within the joint and as a shock absorber. When cartilage is damaged or worn away, the affected joint becomes painful, stiff, and limited in its range of motion.
These are the symptoms that then lead you to see a healthcare provider to find out what can be done for your joints. That will often lead to further testing and a diagnosis of osteoarthritis.
Read Also: How To Stop Knees From Hurting
Full Thickness Cartilage Loss
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
What Is An Articular Cartilage Injury In The Knee
An articular cartilage injury I the knee occurs when damage occurs to the tough, thin cartilage that lines the ends of the bones. Articular cartilage injuries are often caused by trauma, knee instability, or by progressive degeneration from associated with long-term wear and tear. In sports activities, a direct blow to the knee in sports like hockey, football, soccer, or Lacrosse can cause articular cartilage damage. Cartilage injuries can also occur in association with instability events such as a dislocating patella or a dislocating knee that occurs with a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament . Dr. Riley J. Williams, orthopedic knee specialist, diagnoses and treats patients in Manhattan, Brooklyn, New York City, NY and surrounding areas who have an articular cartilage injury in the knee. Dr. Williams has extensive experience with these types of knee injuries and can offer the best orthopedic treatments available.
You May Like: How Long Is The Recovery From Knee Surgery
What Are The Types Of Knee Cartilage Damage
In general, there are two main types of knee cartilage damage involving the knee: the meniscus cartilage or the articular cartilage. There are different terms for these types of knee cartilage damage which include:
- Torn meniscus
- Chondral defect, lesion or damage
- OCD lesion
- Osteochondral defect, lesion or damage
- Cartilage loose body
How Does Articular Cartilage Heal
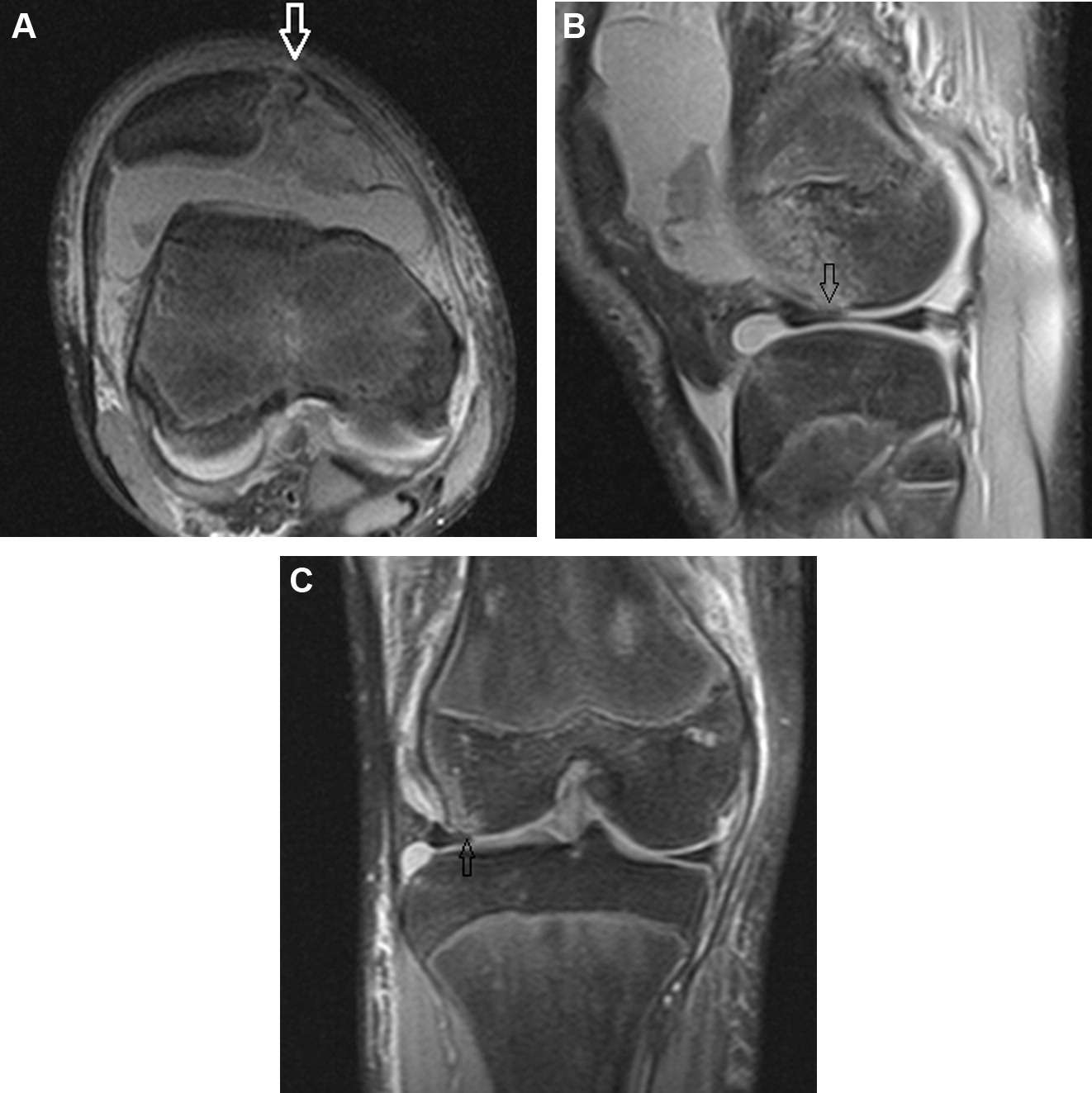
Unfortunately, articular cartilage does not heal with normal replacement cartilage tissue. When it does heal, it is usually a fibrocartilage tissue layer that heals, which may or may not be functional over the long term. A lot of this depends upon the size of the cartilage problem, and larger cartilage problems often have breakdown of the repair cartilage much quicker than those that are smaller and have good, normal cartilage edges .
You May Like: How To Repair Knee Cartilage Naturally
Receive Or Reset Password By Email
Contact UsPrivacy PolicyTerms of UseSitemapArticlesAsk an DermatologistAsk a GynecologistAsk a CardiologistAsk a PediatricianAsk an OncologistAsk a Sexologist Ask an Online PsychiatristAsk an Orthopedic surgeonAsk a STD Specialist Ask a Urologist Ask an Infertility Specialist Ask an EndocrinologistAsk an HIV AIDS Specialist
Consultations on DoctorSpring are not a substitute for physical consultation with a doctor or to hospital services. The service should not be used for medical emergencies. The service offers expert opinions of qualified doctors and medical advice on various medical conditions, medical diagnosis and treatment and it does not include a direct medical diagnosis, treatment or prescription.
Treatment Of Articular Cartilage Loss
Thousands of patients each year sustain articular cartilage injuries. These are not meniscal tears, but damage to the smooth cartilage that covers the ends of a bone and actually forms the joint itself. Although smaller lesions do not require any additional treatment besides removal of the loose pieces of cartilage, many of these injuries may ultimately progress to larger lesions with resultant pain, stiffness, and joint dysfunction. The loss of articular cartilage is often the first stage in the development of osteoarthritis. Young, active patients should be able to access effective treatment in the early stages of this process to hopefully prevent the loss of function and increasing pain that accompanies osteoarthritis.
There are many new biologic treatments for articular cartilage injuries with promising clinical results. Some have short-term follow up studies and have only been used in a limited number of patients. Other treatments have established treatment protocols and reliable results in many patients. Given the complexity of these injuries, it is important to have a variety of treatment options available. Many patients may also have alignment issues, meniscal problems, bone loss, and other factors that need to be addressed during joint preservation procedures.
Recommended Reading: Can Hip Problems Cause Knee Pain
What Causes Chondral Fissuring
Chondral fissuring, or a crack in the cartilage, can be due to many causes. Some of these may be genetic, whereby ones cartilage is not as strong as others and it is not able to be as durable with certain types of activities, or it could be due to an injury, where one falls on their knee and places a lot of stress on it and ultimately causes the cartilage to crack. Repetitive activities, such as squatting or lunging, may overload the cartilage and cause it to crack, ultimately leading to chondral fissuring.
S To Restore Articular Cartilage
Operative treatments to try to restore cartilage rather than replace the joint are most commonly done for younger patients.
- Arthroscopic procedures include microfracture, drilling and abrasion arthroplasty, all of which cause small areas of damage and encourage regrowth of cartilage.
- Grafting procedures implant new cartilage cells or whole sections of cartilage. These include autologous chondrocyte implantation, which harvests your own cartilage cells to implant where they are needed. Osteochondral transplantation takes plugs or blocks of tissues either from the patient or a cadaver donor and grafts them into the joint where they are needed.
- Research is ongoing into using stem cells, gene therapy, and tissue engineering to restore cartilage.
You May Like: Why Do I Have Joint Pain In My Knees
What Is The Treatment For Cartilage Loss In Knee Or No Cartilage In Knee
Treatment for knee cartilage damage is based on severity and the cause of cartilage loss in knee.
Medical management for cartilage loss in the knee or no cartilage in knee includes resting the knee joint and elevation to control swelling. In acute injuries, application of ice and compression with bandage may be advised. Medicines like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help to reduce pain and swelling associated with cartilage loss in the knee or no cartilage in knee. Certain nutritional supplements and steroid injection may be considered with advice of the physician.
Physiotherapy treatment that involves local application of heat and ice, ultrasound, etc. may be helpful for treating cartilage loss in the knee or no cartilage in knee. Therapeutic exercise to strengthen the muscles around knee joint, help to prevent further injuries and improves overall strength of the joint. Knee braces for cartilage loss in the knee or no cartilage in knee can be used to provide support to the knee joint. Weight control, regular exercise and modification of activities are an important conservative treatment approach for cartilage loss in the knee or no cartilage in knee.
Surgical treatment for cartilage loss in the knee involves use of various techniques like
- Arthroscopic lavage and debridement â The torn off cartilage is shaved off using an arthroscope.
- Small holes are made into the bone under the damaged cartilage, to stimulate the marrow, which can help to produce new cartilage.
Classification Of Articular Cartilage Lesions
For a good understanding of articular cartilage lesions and suitable treatment policies, there is a need for a simple classification and qualification of the lesion. The grading system devised by Outerbridge is simple and clinically useful in daily practice and is the most used system . Description of the lesion is based on accurate notation of the location , size , shape and description of the walls . The depth of the lesion is designated as mild , moderate or severe with extension into subchondral bone.
Table 1 : Classifications of chondral lesions
| Grade 0:normal articular cartilage |
|---|
Read Also: Can You Smoke After Knee Surgery
What Is An Articular Cartilage Fissure
A fissure in the cartilage is basically a crack. This crack can be just in the surface tissue, which is common in the kneecap cartilage because it is so thick, or it may extend down to bone. Therefore, the size, width and depth, of the cartilage fissure is an important thing to assess because it can ultimately determine the prognosis of being able to return back to normal activities or if one would need to adapt their activities going forward to avoid further progression of the cartilage damage.
Iculated Juvenile Cartilage Allograft

Juvenile articular cartilage has growth potential, which allows this implanted material to reproduce articular cartilage when implanted into cartilage defects. This cartilage graft is an allograft tissue, obtained from human donors and does not require tissue matching to avoid rejection. This is a single-stage procedure that can be done for a variety of articular cartilage defects. It is performed through an anterior knee incision and may be combined with other procedures. The rehabilitation program is determined by the location and size of the articular cartilage defect.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Pain On The Inside Of The Knee
What Are The Most Common Symptoms Of Cartilage Damage In The Knee
Cartilage damage can affect your knee in different ways.
Torn cartilage can get caught between the structures of your knee, resulting in pain, swelling and sometimes a locking or catching sensation.
You may also experience a feeling of instability and weakness.
Knee pain can cause you to alter your gait, which can, in turn, lead to misalignment and pain in your knees, ankles or hips.
What Is A Knee Cartilage Loose Body
After a knee injury, or prolonged wear-and-tear, the knee cartilage can become frayed or damaged. On occasion, a fragment of the articular cartilage can break away. A knee cartilage loose body is a fragment of tissue or bone that freely floats inside the knee joint space. There can be one or several loose bodies within the joint, suspended in the fluid of the knee, called the synovial fluid. Loose bodies can impact the way the knee moves and can cause symptoms such as:
- Locking of the knee joint, making it difficult to bend or straighten the knee
- Knee catching
- Crepitus a crunching or popping sound within the knee
- Trouble walking
- Feeling that the knee will give way or is unable to support full weight
- Inability to participate in high impact activities and sports
Don’t Miss: Can You Use An Inversion Table After Knee Replacement
What Is The Articular Cartilage Surgery Recovery Time
Because articular cartilage does not have a good blood supply, the recovery time is longer for most cartilage surgeries than it is for other types of surgeries around the knee. For microfracture surgeries, one has to limit weightbearing for six to eight weeks to allow the blood clot on the end of the bone to heal and not peel off. Then a slow progression of weightbearing is progressed and the return of activities is generally accepted to be able to be performed at seven to nine months after surgery.
For fresh osteoarticular allografts, a no or limited weightbearing program for six to eight weeks is followed and then a slow progression of full weightbearing is allowed at about the 3-month point. While most patients feel quite good and can do most low-impact activities, it is generally recommended to avoid impact activities until at least a year after surgery to allow the fresh graft to heal in sufficiently.