Do Symptoms Start In A Smaller Joint
Many autoimmune conditions, including rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis, cause initial symptoms in smaller joints before impacting the knee.
Lupus arthritis also does not typically start in the knee. Early symptoms can affect the fingers, wrists, elbows, ankles, and toes.
However, gout, infectious and reactive arthritis, post-traumatic injury, and lupus tend to impact the knee early on.
The following types of arthritis might affect the knee.
Osteoarthritis
is the most common type of arthritis and cause of knee arthritis. It is a degenerative disease that usually impacts people over 50 years old and is characterized by gradual loss of joint cartilage.
OA happens when joint cartilage degrades with age and wear and tear of joints, decreasing the cushioning space between the bones and producing painful growths called bone spurs.
Osteoarthritis can affect any joint in the body and more than one at a time.
Post-traumatic arthritis
Post-traumatic arthritis occurs after injury to the knee. Post-traumatic arthritis can affect the ligaments and cartilage that stabilize and support the joint.
Gout
Gout occurs when uric acid crystals deposit in joints, fluids, and tissues. Gout may also impact the ankles or feet.
- trying alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or magnetic pulse therapy
Osteoarthritis Of The Hand
Osteoarthritis often affects three main areas of your hand:
- the base of your thumb
- the joints closest to your fingertips
- the middle joints of your fingers
Your fingers may become stiff, painful and swollen and you may develop bumps on your finger joints. Over time, the pain may decrease and eventually disappear altogether, although the bumps and swelling can remain.
Your fingers may bend sideways slightly at your affected joints or you may develop painful cysts on the backs of your fingers.
In some cases, you may also develop a bump at the base of your thumb where it joins your wrist. This can be painful and you may find it difficult to perform some manual tasks, such as writing, opening jars or turning keys.
Page last reviewed: 19 August 2019 Next review due: 19 August 2022
Is Walking Bad For Knee Osteoarthritis
On the contrary, its excellent for this condition. Studies suggest that walking +6000 steps daily can ease symptoms and protect the knee from further deterioration.
But first, discuss it with your physio. You may need additional recommendations to get to those daily steps without making your symptoms worse.
Don’t Miss: Do Knee Compression Sleeves Work
What Medications/treatments Are Used
Over-the-counter NSAIDs like aspirin or ibuprofen can lead to bleeding and other complications after surgery. Your surgeon will talk to you about the medications you can take to reduce pain after your surgery.
Complications/side effects of the treatment
Side effects of NSAIDs include:
- Bowel complications.
What Is Arthritis Of The Knee
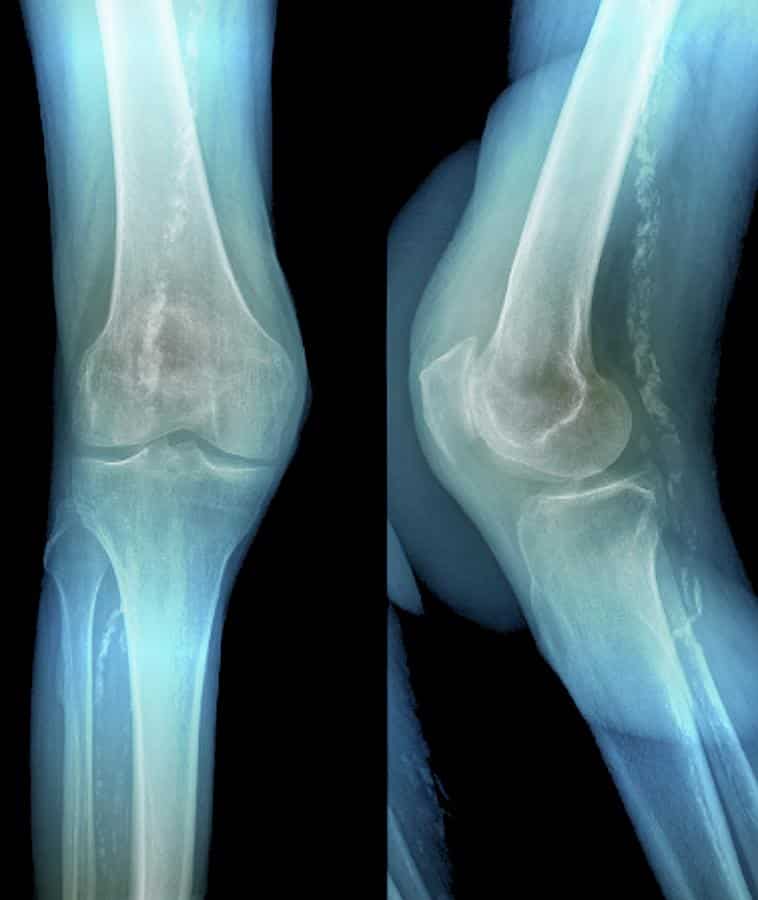
Arthritis is a disease that causes pain, swelling and stiffness in your joints. It can affect the largest and strongest joints in your body. Its common in knees. Arthritis of the knee can be a serious, debilitating disease.
Although there is no cure for knee arthritis, there are steps you can take that might ease your symptoms and potentially slow the progression of your disease.
Don’t Miss: Leg Workout Easy On Knees
The Anatomy Of The Knee
The patellofemoral joint is one of the two joints which make up the knee complex. The patella is located at the front of the knee and is responsible for increasing the strength and power of the quadriceps .
The patellofemoral joint is created by the patella and the femoral condyles of the femur . These two bony prominences create a central concave V shaped groove which perfectly fits the back of the patella, which has a reciprocally convex shape.
The trochlea and the back of the patella are both covered in a layer of articular cartilage. Articular cartilage provides a smooth, low friction surface for the bones to glide over one another during movement. Evidence has demonstrated that articular cartilage requires movement of the joint to maintain a healthy structure. However, research has also shown that abnormal loading of the joint causes the articular cartilage to negatively alter its composition. This negatively altered composition weakens its structure, causing the articular cartilage to become thinner . If this continues it can progress to what is known as osteoarthritis. Further research has suggested that maintaining good flexibility and strength around the joint will help to slow the disease progression associated with osteoarthritis .
Risk factors associated with patellofemoral osteoarthritis include:
Pseudogout: Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition
Pseudogout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that results from the buildup of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in the joints of the body. While less common than gout, pseudogout is more likely to affect the knee.
Like gout, pseudogout is caused by a build-up of microscopic crystals in a joint and can lead to sudden, severe knee pain, swelling, warmth, and redness. Pseudogout is less common than gout but more likely to affect the knee joint.
The microscopic crystals that cause pseudogout are called calcium pyrophosphate crystals. Doctors often refer to pseudogout as calcium pyrophosphate deposition .
Don’t Miss: Can Back Pain Cause Knee Pain
What Should I Expect From A Knee Osteotomy
Youll have knee osteotomy under anesthesia. Your doctor will recommend the best anesthesia option for you, including:
- General anesthesia: Your doctor gives you medicine that puts you to sleep during the surgery.
- Spinal anesthesia: You receive an injection in your back that numbs your body from the waist down.
Your doctor has several options to hold the osteotomy in place during healing. This includes metal screws and a plate or a biocomposite material to hold the realigned bone in place while it heals. Knee osteotomy surgery usually takes one to two hours.
After a knee osteotomy, your doctor will closely monitor you while you recover from the anesthesia. Most people who have a knee osteotomy leave the hospital one to two days after surgery. Some patients leave the same day of surgery. While healing from the surgery, you will likely need to use crutches or a walker for several weeks to avoid putting too much weight on the knee while it heals.
Is There A Cure For Patellofemoral Arthritis
There is no cure for arthritis in general, as no medications can reverse cartilage or bone loss. However, treatment usually eases pain and helps people move more easily in their daily lives.
Treatment outcomes may vary depending on the individuals health and the type of treatment. People should talk with their doctor about the results they can expect from treatment.
You May Like: Does Ice Help Knee Pain
Reducing The Strain On Your Knees
Apart from keeping an eye on your weight, there are a number of other ways you can reduce the strain on your knees.
- Pace your activities dont tackle all your physical jobs at once. Break the harder jobs up into chunks and do something gentler in between. Keep using your knee even if its slightly uncomfortable, but rest it before it becomes too painful.
- Wear shoes with thick soles and enough room for your toes. Wearing the right shoes can reduce the shock through your knees as you walk and prevent any changes to your feet.
- If you need extra support for your feet or knees when you walk, speak to your physiotherapist, occupational therapist or doctor about getting insoles made for your shoes.
- Use a walking stick if needed to reduce the weight and stress on a painful knee. An occupational therapist can advise on the correct length and the best way to use the stick.
- Use a handrail for support when going up or down stairs. Go upstairs one at a time with your good leg first.
- Think about making changes to your home, car or workplace to reduce unnecessary strain. An occupational therapist can advise you on special equipment that will make things you do every day easier.
Using a heat pack or something similar on a painful knee might help to relieve the pain and stiffness of osteoarthritis. An ice pack can also help but be careful not to put ice or heat packs or hot water bottles directly on your skin wrap them with a tea towel or cover.
What Happens Before Knee Arthroscopy
Before you have knee arthroscopy, tell your healthcare provider what medications youre taking. You may need to stop taking certain medications before surgery. Your healthcare provider will tell you what time to stop eating and drinking the night before your procedure, too.
You may have knee arthroscopy at a surgery clinic or in a hospital. Right before your procedure, your healthcare provider will give you anesthesia. Whether youre awake or asleep, you wont feel pain during knee surgery. Your healthcare provider may recommend:
- Local anesthetic, to numb the area.
- Regional anesthetic, to numb you from the waist down.
- General anesthetic, to put you to sleep for the procedure.
Also Check: Back Pain And Knee Pain
What Can I Expect If I Have Post
You should expect to feel some discomfort, but treatment should reduce your pain, stiffness and other symptoms. How long it takes to feel better depends on the original trauma that caused your arthritis. More serious injuries have longer recovery timelines and are more likely to experience complications. Talk to your provider about your specific injury and post-traumatic arthritis.
How long does post-traumatic arthritis last?
Most people have post-traumatic arthritis short-term, usually around a few months. Your symptoms might go away as your body recovers from your trauma. If you experience post-traumatic arthritis symptoms for longer than six months you could have chronic post-traumatic arthritis, which can last for the rest of your life.
Will I need to miss work or school?
If you can do your job or schoolwork without aggravating your arthritis symptoms, you shouldnt need to miss work or school.
Talk to your healthcare provider or surgeon before resuming any physical activities while youre recovering.
What is the outlook for post-traumatic arthritis?
Post-traumatic arthritis is something you might only have for a few months. But, if you have chronic post-traumatic arthritis, youll have to manage it as a long-term condition. Your provider will help you find the best ways to manage your specific symptoms while you heal.
What Causes Osteoarthritis Of The Knee
Osteoarthritis of the knee happens when your knee joint cartilage wears out or is damaged. Articular cartilage is tough, rubbery tissue on the ends of your bones that lets you bend and move. Meniscal cartilage absorbs shock from pressure on your knee.
Your cartilage is like your cars shock absorber, protecting your car from bumps and jolts. Drive on lots of rough roads, your shocks wear out fast. Drive on easy streets, your shocks last longer. You can wear out or damage your knee joint cartilage if:
- Youre overweight. If your body mass index is 30 or more, youre seven times more likely to develop osteoarthritis in your knee than someone with a lower BMI.
- You injure your knee or have an old knee injury.
- You frequently put stress on your knee at your job or playing sports.
- You inherited a tendency to develop osteoarthritis of the knee.
- You have crooked bones or joints, such as having knocked knees.
Don’t Miss: What Are Bone Spurs In Your Knee
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Arthritis Of The Knee
There are many signs and symptoms of arthritis of the knee:
- Creaking, clicking, grinding or snapping noises .
- Difficulty walking.
- Joint pain that changes depending on the weather.
- Joint stiffness.
- Knee joint pain that progresses slowly or pain that happens suddenly.
- Your knee locks or sticks when its trying to move.
Pain and swelling are the most common symptoms of arthritis of the knee. Some treatments might reduce the severity of your symptoms or even stall the progression. See your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of knee arthritis.
What Tests Are Done To Diagnose Post
After a physical exam, you might need at least one of a few imaging tests:
- X-rays: An X-ray will confirm show how damaged the bones in your joint are.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging : Your provider might use an MRI to get a complete picture of the damage to your joint and the area around it. This will show them your bones and the tissue around them.
- CT scan: If you need surgery, your provider or surgeon needs to know exactly how damaged your joint is. A CT scan will give them a more detailed picture of your bones and the surrounding tissue than an X-ray.
Don’t Miss: What To Do For Growing Pains In Your Knees
What Questions Might A Healthcare Provider Ask To Diagnose Arthritis Of The Knee
Your healthcare provider will interview you when you report your symptoms. Some questions might include:
- Does anyone in your family have arthritis of the knee?
- Does your knee swell up?
- Is your skin often red?
- Is your skin often warm?
- Do you have symptoms in one knee or both?
- How long have you had these symptoms?
- What medications do you take?
- How severe is your pain?
- Do you struggle to walk?
- Do the symptoms interfere with your daily activities?
Is Surgery Used To Treat Knee Osteoarthritis
If your doctor wants to treat the osteoarthritis in the knee with surgery, the options are arthroscopy, osteotomy, and arthroplasty.
- Arthroscopy uses a small telescope and other small instruments. The surgery is performed through small incisions. The surgeon uses the arthroscope to see into the joint space. Once there, the surgeon can remove damaged cartilage or loose particles, clean the bone surface, and repair other types of tissue if those damages are discovered. The procedure is often used on younger patients in order to delay more serious surgery.
- An osteotomy is a procedure that aims to make the knee alignment better by changing the shape of the bones. This type of surgery may be recommended if you have damage primarily in one area of the knee. It might also be recommended if you have broken your knee and it has not healed well. An osteotomy is not permanent, and further surgery may be necessary later on.
- Joint replacement surgery, or arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which joints are replaced with artificial parts made from metals or plastic. The replacement could involve one side of the knee or the entire knee. Joint replacement surgery is usually reserved for people over age 50 with severe osteoarthritis. The surgery may need to be repeated later if the prosthetic joint wears out after several years. But with today’s modern advancements, most new joints will last over 20 years. The surgery has risks, but the results are generally very good.
Recommended Reading: What Food Is Good For Knee Cartilage
Coping With Low Mood And Sleep Problems
You might find that osteoarthritis of the knee makes you feel depressed or anxious. Speak to your doctor if youre feeling low as they may be able to recommend psychological therapies to help you, such as cognitive behavioural therapy and stress-relieving techniques.
If your sleep is disturbed because of osteoarthritis of the knee, this could make your pain feel worse. However, there are things you can do for yourself that might help, such as:
- Keep a sleep diary to work out if there are any patterns to your sleep problems
- Sleep at regular times to get your body into a routine
- Avoid phones and other screens in the bedroom to help you wind down before bed.
If youre still having problems, speak to your doctor or an occupational therapist who can give you other tips and techniques to try, known as sleep hygiene.
What Causes Knee Osteoarthritis
The most common cause of osteoarthritis of the knee is age. Almost everyone will eventually develop some degree of osteoarthritis. However, several factors increase the risk of developing significant arthritis at an earlier age.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee may include:
- pain that increases when you are active, but gets a little better with rest
- feeling of warmth in the joint
- stiffness in the knee, especially in the morning or when you have been sitting for a while
- creaking, crackly sound that is heard when the knee moves
Also Check: How To Relieve Knee Pain While Sitting
Osteoarthritis Of The Knee
If you have osteoarthritis in your knees, both your knees will usually be affected over time, unless it occurred as the result of an injury or another condition affecting only 1 knee.
Your knees may be most painful when you walk, particularly when walking up or down hills or stairs.
Sometimes, your knees may “give way” beneath you or make it difficult to straighten your legs. You may also hear a soft, grating sound when you move the affected joint.
What Is Knee Arthroscopy
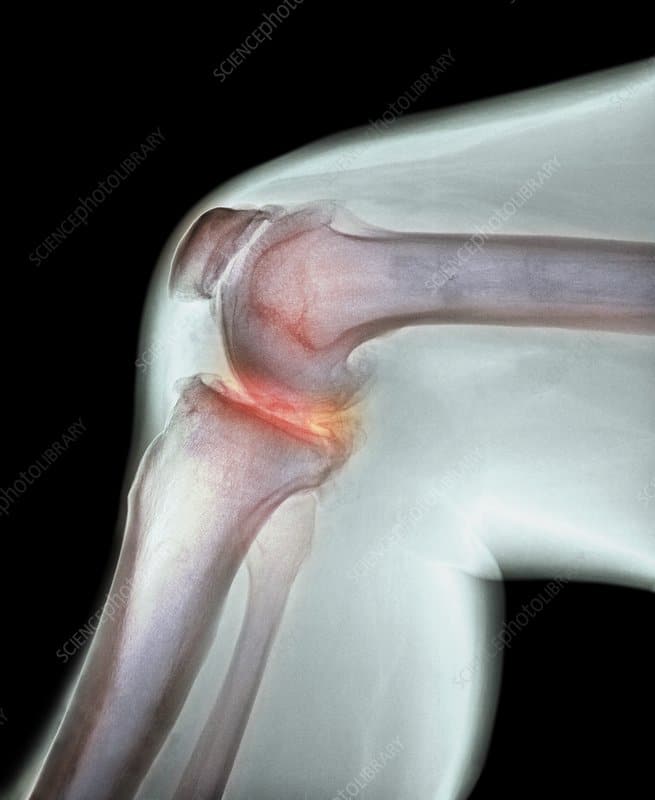
Healthcare providers use knee arthroscopy to diagnose and treat a wide range of knee injuries. During arthroscopic knee surgery, your healthcare provider inserts a tiny camera through an incision. The camera shows the inside of your knee. The images appear on a screen in the operating room. They help your healthcare provider diagnose problems inside of your knee.
Knee arthroscopy is a very common minimally invasive surgical procedure. Minimally invasive procedures require smaller incisions than traditional surgery. The incisions are about the size of a keyhole.
To treat injuries or structural problems, your healthcare provider inserts tiny tools through another incision. They use the tools to repair or remove damaged tissue.
Recommended Reading: Knee Pain On The Inside
Types Of Arthritis That Can Affect The Knee
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis of the knee. This particular type of arthritis occurs as a result of cartilage loss. This loss of cartilage may lead to the knee joints rubbing together.
During the early stages of osteoarthritis, you may experience knee pain only during specific activities. However, as it progresses, you may start feeling pain during normal daily activities.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. This arthritis of the knee causes inflammation of the knee joint. Inflammation may lead to the knee feeling stiff, swollen, or warm, as well as being painful.
With rheumatoid arthritis, once one knee is affected, it is highly likely that the other will also be affected too.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Just like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis is also an autoimmune disease. The symptoms of this are similar and include stiffness, tenderness, swelling, and pain.
Gout
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis. It can often cause acid crystals to build-up within the knee joint. Once crystals have been collected in the soft tissue, it can lead to excruciating pain. You may also experience some swelling, warmth, and redness around the joint.
Reactive Arthritis